尿肌氨酸水平对前列腺癌诊断及预后判断的应用价值
2013-04-23张晓毅刘德忠赵国华孙家各
张晓毅, 邹 练, 刘德忠, 高 翔, 孙 博, 赵国华, 孙家各
尿肌氨酸水平对前列腺癌诊断及预后判断的应用价值
张晓毅*, 邹 练, 刘德忠, 高 翔, 孙 博, 赵国华, 孙家各
(中国人民解放军第二炮兵总医院泌尿外科, 北京 100088)
探讨尿肌氨酸水平对前列腺癌(PCa)的诊断和病情判断方面的应用价值。选取我院泌尿外科住院的经前列腺穿刺活检确诊的PCa患者16例,年龄65~89(68.4±10.2)岁。采集PCa患者的血标本和尿标本,然后用同位素稀释液相色谱质谱法检测其血、尿肌氨酸水平,电化学发光法检测血清前列腺特异抗原(PSA)水平,并根据其Gleason评分及是否骨转移进行统计学分析。PCa伴有骨转移患者(=9)与无转移患者(=7)血清总前列腺持异抗原(TPSA)水平含量差异具有统计学意义[(203.95±169.68)(35.53±35.77)µg/L,<0.05],而游离前列腺持异抗原(fPSA)水平在两组间差异无统计学意义[(14.41±11.84)(3.92±4.15)µg/L]。PCa伴有骨转移患者的尿液中肌氨酸含量明显高于不伴发骨转移患者[(1277.67±432.78)(494.71±211.35)µg/L,=0.018]。按照PCa病理结果分级,血肌氨酸水平在各个Gleason评分组中差异无统计学意义;而尿肌氨酸含量差异具有统计学意义(<0.015),且Gleason评分越高,尿液中肌氨酸含量也越高。PCa患者的尿肌氨酸水平与Gleason评分及是否骨转移具有相关性,且组间差异具有统计学意义(<0.05)。尿肌氨酸有可能成为用于诊断PCa的肿瘤标志物,并具有一定的判断病情的应用价值。
前列腺癌; 尿肌氨酸; 质谱分析法
在前列腺癌(prostate cancer,PCa)的早期筛查与诊断中,前列腺特异抗原(prostate specific antigen,PSA)是近年来应用最为广泛的肿瘤标志物,但其检测结果有假阳性及假阴性可能。为了提高PCa的诊断水平,人们一直在寻找一种灵敏度和特异度高、安全便捷的标志物。肌氨酸为人体内一种微量的非必需氨基酸,有文献报道其广泛存在于PCa组织细胞及尿液中,本研究拟论证尿肌氨酸与PCa的关系。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
选取2009年5月至2011年5月在中国人民解放军第二炮兵总医院泌尿外科住院的经前列腺穿刺活检确诊的PCa患者16例,年龄65~89(68.4±10.25)岁。取患者血标本、尿标本(晨尿、中段尿),血样经分离血浆后-40℃冰冻保存,尿液直接-40℃冰冻保存待检。所有标本均在穿刺前收集完成,并且满足试剂盒样本数后立即进行检测。
1.2 仪器及试剂
3200QTRAP型液相色谱-串联质谱仪,配有电喷雾离子化源(ESI)以及Analyst 1.4.2数据处理软件,美国Applied Biosystem公司;UltiMate 3000标准型液相色谱仪,美国戴安公司;氮吹浓缩仪,日本东京理化器械株式会社;iTRAQ试剂盒(200人份),批号:0709002,美国Applied Biosystem公司,包括400μmol/L正异亮氨酸的10%磺基水杨酸溶液、标记缓冲液(0.45mol/L硼酸盐缓冲液,pH8.5含有20μmol/L正缬氨酸)、115-iTRAQ衍生化试剂(15人份/瓶,每瓶用70μl异丙醇稀释后使用)、1.2%羟胺水溶液、iTRAQ-114同位素标记的44种氨基酸内标。
1.3 研究方法
由我院检验科常规检测所有患者总前列腺特异抗原(total prostate specific antigen,TPSA)及游离PSA(free prostate specific antigen,fPSA),按Cavaliere等[1]介绍的方法检测所有患者尿标本的肌氨酸含量。
1.4 统计学处理
采用SPSS17.0软件对所获得的数据进行统计分析,用及one-way ANOVA检验进行各组之间均数比较。以<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结 果
2.1 PCa骨转移与PSA水平相关性分析
按照PCa是否伴有骨转移进行分组,有转移组(=9)与无转移组(=7)血清TPSA水平差异具有统计学意义[(203.95±169.68)(35.53±35.77)µg/L,<0.05],而fPSA水平差异无统计学意义[(14.41±11.84)(3.92±4.15)µg/L]。PCa分期越晚,TPSA水平越高,而fPSA水平差异不大。
2.2 PCa患者病理Gleason评分与血、尿肌氨酸水平相关性分析
如表1所示,按照PCa病理结果分级,各个Gleason评分/分化程度中,血肌氨酸水平在各个Gleason评分组中差异均无统计学意义;尿肌氨酸含量差异具有统计学意义(<0.05),且Gleason评分越高(分化程度越低、恶性程度越高),尿液中肌氨酸含量也越高。
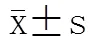
表1 前列腺癌患者肌氨酸水平与PCa临床病理Gleason评分的关系
Compared mutually between groups,*<0.05
2.3 PCa患者尿肌氨酸水平与骨转移相关性分析
PCa伴有骨转移患者(=9)的尿液中肌氨酸含量明显高于不伴发骨转移患者[=7,(1277.67±432.78)(494.71±211.35)µg/L,=0.018]。PCa患者的尿肌氨酸水平与骨转移具有明确的相关性。
3 讨 论
血清PSA是前列腺上皮分泌的一种蛋白酶,以两种形式存在:结合形式和非结合形式(即fPSA,占TPSA的10%~30%),其水平受多种因素的影响[2]。有资料显示血清PSA检测对PCa的检测具有明显的局限性,PSA在4µg/L时,其假阳性率为25%[3],假阴性率可高达38%~48%[4]。最新的临床多中心研究表明,在PSA<4.0µg/L的PCa患者中10%~21%能通过直肠指诊发现[5],而在血清PSA>4.0µg/L的人群中,彩超引导下经直肠前列腺穿刺活检阳性患者只有25%~30%,这意味着接受超声引导下前列腺穿刺活检的患者,>70%不能诊断出PCa[6]。
PSA水平与PCa细胞生长有关,当肿瘤细胞生长迅速、破坏前列腺腺泡和导管腔与血液循环系统之间的屏障,PSA直接泌入细胞间与血液中,从而使血清PSA升高[7]。当肿瘤具有骨转移时,TPSA差异具有统计学意义,可能与肿瘤的体积有关,可以分泌较多的PSA蛋白,而fPSA含量本身较低,所以差异没有统计学意义。
Sreekumar等[8]的研究提示,人体内存在的一种微量非必需氨基酸——肌氨酸,在PCa患者的组织细胞中浓度显著升高,并证实肌氨酸参与了前列腺的癌变过程,是其进展并发生转移时显著增高的一种肿瘤代谢产物,而且易在尿液中被检测出来。我们研究证实尿肌氨酸在伴发骨转移的PCa患者中明显增高,且与Gleason评分密切相关,这也与他们的结果一致。这说明尿液中肌氨酸含量可以在PCa的筛检和早期鉴别诊断中发挥作用,可能是由于尿液中的肌氨酸由肾脏排泄,并不能完全代表血液中的水平。当然,Bohm等[9]研究表明肌氨酸水平并不能用来鉴别PCa的分期,如果利用肌胺酸/丙氨酸比值进行鉴别,意义可能更大。
本研究在进行肌氨酸检测前饮食未加控制,且受样本量的限制,可能具有一定的局限性,尚需要进一步深入探讨肌氨酸在PCa的发生及发展过程中的作用机制,有望成为临床较为有效的评价指标。
[1] Cavaliere B, Macchione B, Monteleone M,. Sarcosine as a marker in prostate cancer progression: a rapid and simple method for its quantification in human urine by solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry[J]. Anal Bioanal Chem, 2011, 400(9): 2903−2912.
[2] Cilja H, Chritensson A, Dahlen U,. Prostate specific antigen in serum occurs predominantly in complex with alpha 1 antichymotrypsin[J]. Clin Chem, 1991, 37(9): 1618−1625.
[3] Rifkin MD. Ultrasound of the prostate: imaging in the diagnosis and therapy of prostate disease[M]. 2nd Edition. Philadelphia. New York: Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1997: 48−50.
[4] Kalish J, Conner WH, Graham SD. Serum PSA adjusted for volume of transition zone (PSAT) is more accurate than PSA adjusted for total gland volume(PSAD) in detecting adenocarcinoma of the prostate[J]. Urology, 1994, 43(5): 601−606.
[5] Catalona WJ, Partin AW, Slawin KM. Use of the percentage of free prostatic specific antigen to enhance differentiation of prostate cancer from benign prostatic disease: a prospective multi-center clinical trial[J]. JAMA, 1998, 279(34): 1542−1547.
[6] Kamoi K, Babaian RJ. Advances in the application of prostate specific antigen in the detection of early stage prostate cancer[J]. Sem Oncol, 1999, 26(3): 140−149.
[7] Thompson IM, Ankerst DP. Prostate specific antigen in the early detection of prostate cancer[J]. CMAJ, 2007, 176(13): 1853−1858.
[8] Sreekumar A, Poisson LM, Rajendiran TM,. Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression[J]. Nature, 2009, 457(7231): 910−914.
[9] Bohm L, Serafin AM, Fernandez P,. Plasma sarcosine does not distinguish early and advanced stages of prostate cancer[J]. Resarch, 2012, 102(8): 677−679.
(编辑: 金美娜, 王雪萍)
Diagnostic and prognostic value of urinary sarcosine for prostatic cancer
ZHANG Xiao-Yi*, ZOU Lian, LIU De-Zhong, GAO Xiang, SUN Bo, ZHAO Guo-Hua, SUN Jia-Ge
(Department of Urology, General Hospital of the Second Artillery, Beijing 100088, China)
To investigate the value of the urinary sarcosine in the diagnosis and prognosis of prostate cancer(PCa).A total of 16 PCa patients, with age ranging from 65 to 89(68.4±10.2)years, diagnosed by prostate biopsy in our department from May 2009 to May 2011, were enrolled in this study. Their blood and urinary samples were collected for detection of sarcosine level by isotope dilution-liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC/MS). Electrochemiluminescence assay was used for the detection of serum level of prostate specific antigen (PSA). The results were statistically analyzed with their Gleason scores and with bone metastasis.There was significant difference in the total PSA(TPSA) level between the PCa patients with bone metastases [=9, (203.95±169.68)µg/L] and without [=7, (35.53±35.77)µg/L,<0.05], while no difference was found in free PSA (fPSA) level between them [(14.41±11.84)(3.92±4.15)µg/L,>0.05]. The urinary sarcosine level was significantly higher in the PCa patients with bone metastasis than those without [(1277.67±432.78)(494.71±211.35) µg/L,=0.018]. There was no significant difference in the serum sarcosine level between different pathological Gleason scores, but urinary sarcosine level was significantly elevated with the increase of Gleason score(>0.05). Urinary sarcosin level was correlated with Gleason score and bone metastasis(<0.05).Urinary sarcosine might be used as a useful tumor marker for the diagnosis and prognosis of PCa.
prostate cancer; urinary sarcosine; mass spectrometry
R737. 25
A
10.3724/SP.J.1264.2013.00209
2013−06−21;
2013−08−16
张晓毅, E-mail: doctorzhxy@163.com
