Genetic Polymorphisms of 15 STR Loci in Gansu Hui Population
2013-03-11孙红兵,杨鑫,哈飞等
·研究简报·
Genetic Polymorphisms of 15 STR Loci in Gansu Hui Population
SUN Hong-bing1,2,YANG Xin2,HA Fei2,LUO Ji-huai2,ZHANG Zi-long1
(1.Key Laboratory of Evidence of Science and Technology Research and Application of Gansu Province,730070 Lanzhou,China;2.Forensic Science Institute of Lanzhou Public Security,730070 Lanzhou,China)
forensic genetics;polymorphism,genetic;short tandem repeats;Hui nationality
Article IC:1004-5619(2013)06-0464-02
The short tandem repeat(STR)markers are widely used in human identification and paternity testing in the field of forensic genetics[1].Recent researches on polymorphic STRs have led to their applications to population genetics,forensic DNA database,human individual identification,paternity testing,genetic mapping,disease linkage analysis, archaeology and potential inference of the ethnic origin of an individual[2].
Hui nationality,one of the largest and most widespread ethnic minorities in China,has a population of approximately 9.8 million,who are culturally distinguished from other Chinese for their practice of Islam[3].Most of Hui residents inhabit Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region,Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region,Gansu,Qinghai,Henan,Hebei,Shandong and Yunnan Province.
Gansu,located in northwestern China,is inhabited by 54 ethnic groups,including Tibetan,Hui, Tu,Salar,Baoan,Yugur,Dongxiang and Mongol, who account for 9.43%of its total population.Hui ethnic group accounts for 4.81%of Gansu’s total population,comprising 58.9%of the totalethnic population.As such,Hui nationality has held an important economic and political position in Gansu. Much research has been done on the history and culture of Hui,but their genetic information remains unknown.
The current study investigated the allelic frequencies and forensic statistical parameters for 15 STR loci of Hui population in Gansu.The data can be a crucial first step towards understanding the genetic history and diversity of the important ethnic minority in China.
Materials and methods
Materials
Five hundred unrelated healthy individuals of Lanzhou Hui origin were randomly selected from2008—2011.The families of all participants had lived in the region for at least three generations.
DNA extraction
Genomic DNA was extracted using the Chelex-100 protocol as described by reference[4].
PCR
Fifteen autosomal STR loci,D8S1179,D21S11, D7S820,CSF1PO,D3S1358,TH01,D13S317, D16S539,D2S1338,D19S433,vWA,TPOX,D18S51, D5S818 and FGA,were co-amplified in fluorescencebased multiplex reaction using the IdentifilerTMkit (Applied Biosystems,USA).The amplification reactions of 25μL contained 5μL of genomic DNA. Based on the manufacturer’s protocols,thermal cycling conditions were done by GeneAmp PCR System 9700(Applied Biosystems,USA).
Typing
The amplified products were separated by capillary electrophoresis on PRISM 3130 Genetic Analyzer(Applied Biosystems,USA)according to the manufacturer’s instructions.The sample run data were analyzed together with an allelic ladder and positive and negative controls using GeneMapper ID v3.2. The allele designation was established following the recommendations of the DNAcommission of the International Society for Forensic Genetics(ISFG).
Quality control
The laboratory internal control standards and kit controls were employed.
Data analysis
The allele,genotype frequencies,Hardy-Weinberg expectations,polymorphism information content (PIC)and forensically significant parameters,discrimination power(DP),probability of matching (Pm),probability of paternity exclusion(PE),expected heterozygosity(He),cumulative discrimination power(CDP)and cumulative probability of exclusion(CPE)were computed using the Power-State v1.2 spreadsheet(Promega Corporation,USA)as described by reference[5].Microsoft Excel and SPSS 17.0 were used for data analysis.
Results and discussion
No deviation from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium was observed(P>0.05).A total of 143 alleles were observed and allelic frequencies ranged from 0.0025 to 0.500 0(Table 1).DP varied between 0.807 1 (TPOX)and 0.964 2(D2S1338),and CDP was 0.999999999999999986.PE was 0.3220(TH01) to 0.717 4(D2S1338),and CPE for 15 loci was 0.999 995 813.PIC varied from 0.577 4(TPOX)to 0.8488(D2S1338).The other statistical parameters of 15 STR loci showed in Table 2.All loci were highly polymorphic.
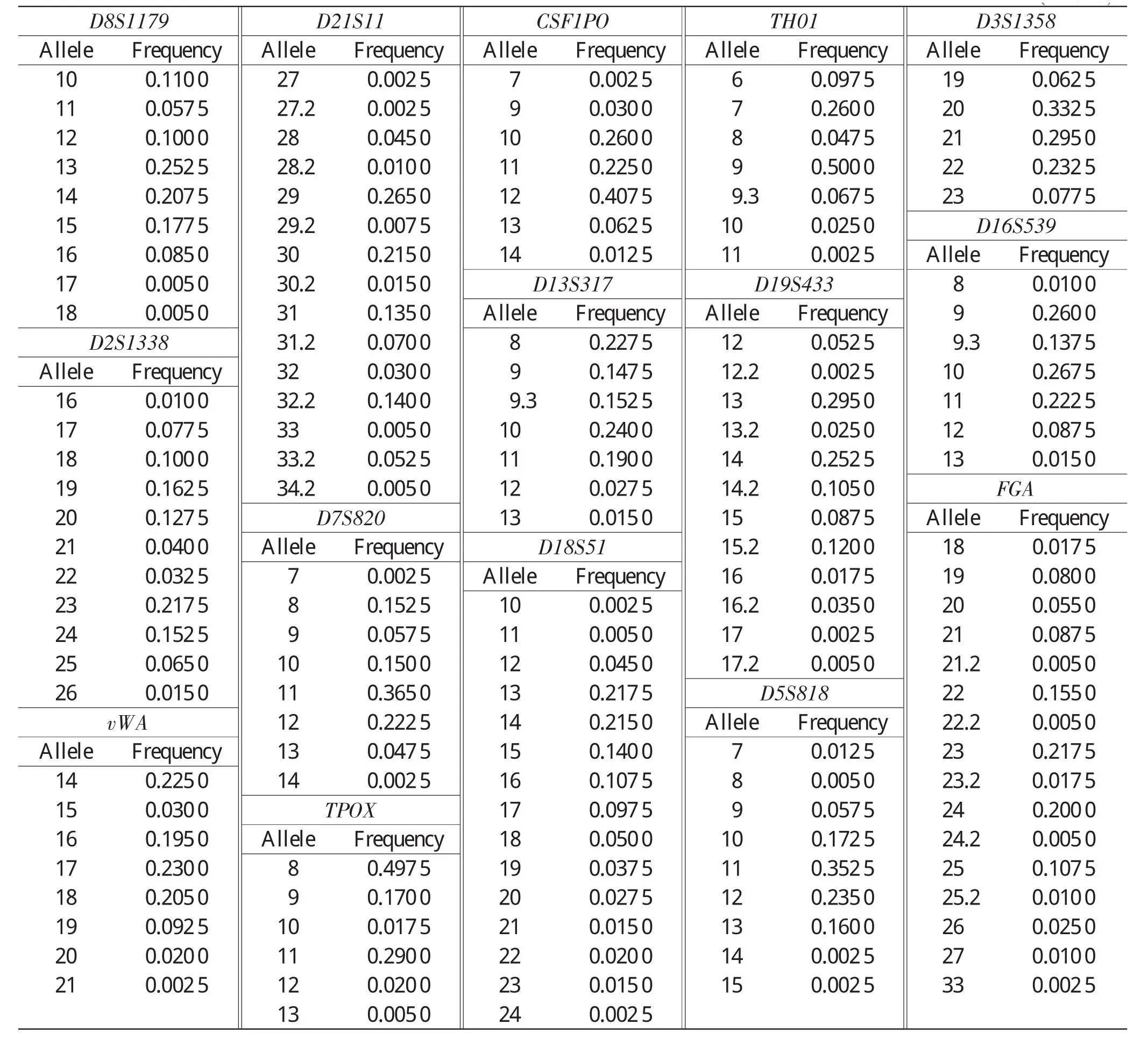
Table 1The allelic frequencies regarding the 15 STR loci in Gansu Hui population(n=500)

Table 2The statistical parameters regarding the 15 STR loci in Gansu Hui population(n=500)
The currentstudyindicated thatTH01and TPOX had lower PIC than any other loci in Hui nationality.Over the past fewyears,SinoFilerTMPCR Amplification kit(Applied Biosystems,USA)has been used in paternity testing and individual identification in which TH01 and TPOX were substituted by D6S1043 and D12S391.
The value of He,DP,PE and PIC calculated among these fifteen autosomal STRs loci showed the same tendency as Han Chinese in Gansu[6], making it impossible to identify people among different ethnic groups.Some studies have begun to focus on the application of molecular biology and special genetic markers to distinguishing nationality, skin pigmentation,eye pigmentation or hair color. Most of the investigations have been concentrated in the SNP field,and few reports have applied STR loci.The current study showed that the application of these fifteen STR loci could quickly achieve individual identification,but could not determine such situations as ancestor information,geographical origin of biological individuals or individual organism signs.
Acknowledgments
The current research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81302622),the Science Technology Foundation of Lanzhou(2012-1-22),and Youth Science and Technology Foundation of Gansu(1208RJYA073).
References:
[1]Fan H,Chu JY.A brief review of short tandem repeat mutation[J].Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics, 2007,5(1):7-14.
[2]Xie ZH.Advances of study on human STR[J].Journal of Dezhou University,2005,21(6):40-44.
[3]李生信.回族语言的民族属性[J].固原师专学报(社会科学版),2001,22(5):61-64.
[4]Walsh PS,Metzger DA,Higuchi R.Chelex 100 as a medium for simple extraction of DNA for PCR-based typing from forensic material[J].Biotechniques,1991, 10(4):506-513.
[5]Tereba A.Tools for analysis of population statistics[J]. Profiles in DNA,1999,2(3):14-16.
[6]孙红兵,杨鑫,张子龙,等.兰州地区汉族人群15个STR基因座多态性[J].法医学杂志,2011,27(3):224-225.
DF795.2
B
10.3969/j.issn.1004-5619.2013.06.017
Author:SUN Hong-bing(1966—),professor,major in forensic science;E-mail:sunhb.good@163.com
YANG Xin,research fellow,major in forensic science;E-mail:lz.yangxin@gmail.com
(Received date:2013-09-03)
(Editor:LI Cheng-tao)
