四种寄生性天敌昆虫对山杨楔天牛的室内寄生效果
2013-02-28哈米提杨忠岐白兰兰木拉提
哈米提, 唐 桦, 杨忠岐*, 白兰兰·木拉提
(1.新疆维吾尔自治区额敏县林业局,塔城 834600;2.中国林业科学研究院森林生态环境与保护研究所/国家林业局森林保护学重点实验室,北京 100091)
山杨楔天牛[Saper da carcharias (L.)](鞘翅目:天牛科Cerambycidae)在我国分布于黑龙江、吉林、辽宁,为害不重[1-2],但近年来在新疆维吾尔自治区塔城市额敏县暴发成灾,造成大量杨树受害致死,成为该县杨树生产上为害严重、防治困难的重大害虫[3]。新疆维吾尔自治区降雨量少,植被单一。杨树是该地区的主要树种,在防风固沙、涵养水源、保护生态环境上起着极其重要的作用。该害虫2年1代,主要以幼虫在树干基部内蛀食为害,对当地防护林建设、农林业生产造成了严重威胁。根据从国内外几大数据库所查文献资料来看,有关山杨楔天牛的研究,国内报道较少(分布,形态特征,生物学特性,以化学防治为主的综合防治技术)[1-5],国外报道较多(包括树种抗虫性,人工防治,化学防治,利用线虫、真菌、啄木鸟进行的生物防治)[6-32]。报道中的方法虽有一定效果,但费工耗时,难以大面积推广;而便于大面积推广的利用天敌昆虫控制山杨楔天牛的研究尚未见报道。为筛选出生物防治可利用的有效天敌,选择4种寄生性天敌昆虫对山杨楔天牛幼虫进行了室内防治试验。
1 材料与方法
1.1 试验用虫及材料
4种天敌昆虫的成虫——花绒寄甲[Dastarcus helophoroides(Fair maire)]光肩星天牛生物型(鞘翅目:寄甲科 Bothrideridae)、白蜡吉丁肿腿蜂(Scleroder mus pupariae Yang et Yao)(膜翅目:肿腿蜂科Bethylidae)、苹小吉丁肿腿蜂(Scleroder mus sp.1)和落叶松吉丁肿腿蜂 (Scleroder mus sp.2),均由中国林业科学研究院森林生态环境与保护研究所生物防治研究室提供。试验用杨树木段(长30 c m左右,直径约6 c m,内有天牛幼虫,各木段所含天牛幼虫的数量为1~5头不等,多为2或3头,因不同部位木段所含天牛幼虫的数量是随机的)采自新疆塔城地区额敏县萨尔也牧勒前进乡、上户乡和十月乡5~13年生被害的山杨(Populus davidiana Dode)植株(树高3~15 m)。
1.2 研究方法
试验于2012年8月上旬-10月下旬进行。根据“山杨楔天牛在新疆额敏县2年发生1代”,世代重叠现象明显的特点[4],通过观察树干上山杨楔天牛幼虫排粪孔大小来初步判断所采杨树木段内的幼虫大小(据笔者多年研究经验发现:排粪孔极细小是初龄小幼虫,排粪孔较大为中老龄幼虫);由于花绒寄甲只寄生天牛中老龄幼虫和蛹,而肿腿蜂只寄生天牛初龄小幼虫,因而选择中老龄幼虫较多的木段56个作为花绒寄甲的试验木,选择初龄小幼虫较多的木段140个作为3种肿腿蜂的试验木。
1.2.1 试验设计
采用单因素随机区组设计法,以4种天敌昆虫为因素,每种天敌随机分为3个试验区组和1个不放天敌的对照区组,每试验区组各释放40头天敌,每试验区组和对照区组各有14个木段(每试验区组14个木段中含有的天牛幼虫总数平均为24.00~28.67头,对照区组14个木段中含有的天牛幼虫总数平均为36.50头)。分别放入用尼龙纱网(网眼极细,直径约0.1 mm,以阻止释放的天敌逃逸)制作的1 m×1 m×0.3 m养虫笼内。
1.2.2 试验方法
试验前先将木段的两头用石蜡封好,以减少水分的散失。将封好蜡的木段放入养虫笼内,同时释放天敌成虫并关闭养虫笼后,将养虫笼放置于室内并拉上窗帘遮光,然后每天观察天敌在笼内的活动情况;同时注意观察和调整室内的温湿度,确保温度和相对湿度分别保持在25℃和RH50%左右,两个月后检查寄生效果。
1.3 效果检查
取出养虫笼内的木段,用斧头小心地劈开,仔细检查天牛幼虫被4种天敌昆虫(或自然界中其他天敌)所寄生的情况,同时记录数据并拍摄照片。统计各区组的寄生率,对所获数据进行方差分析和多重比较。
1.4 统计方法
对试验数据进行单因素随机区组设计方差分析,并采用Duncan新复极差检验法进行多重比较。
2 结果与分析
将各区组中4种天敌昆虫寄生山杨楔天牛幼虫的寄生率汇总填于表1。由表1可看出,4种天敌昆虫在3个试验区组中对山杨楔天牛均有一定的寄生效果,而在未释放天敌的对照区组中未见寄生现象。同时发现林间一种姬蜂对山杨楔天牛幼虫的寄生现象,但寄生率很低,仅为1.24%;所以,在比较这4种天敌寄生效果的强弱时,姬蜂对试验效果的影响可忽略不计。由于对照的寄生率均为零,因而这4种天敌的寄生率无需校正,可直接进行统计分析。对这4种天敌3个试验区组的寄生率进行方差分析和多重比较,所得结果见表1中的“平均寄生率”一栏(可靠性95%)。
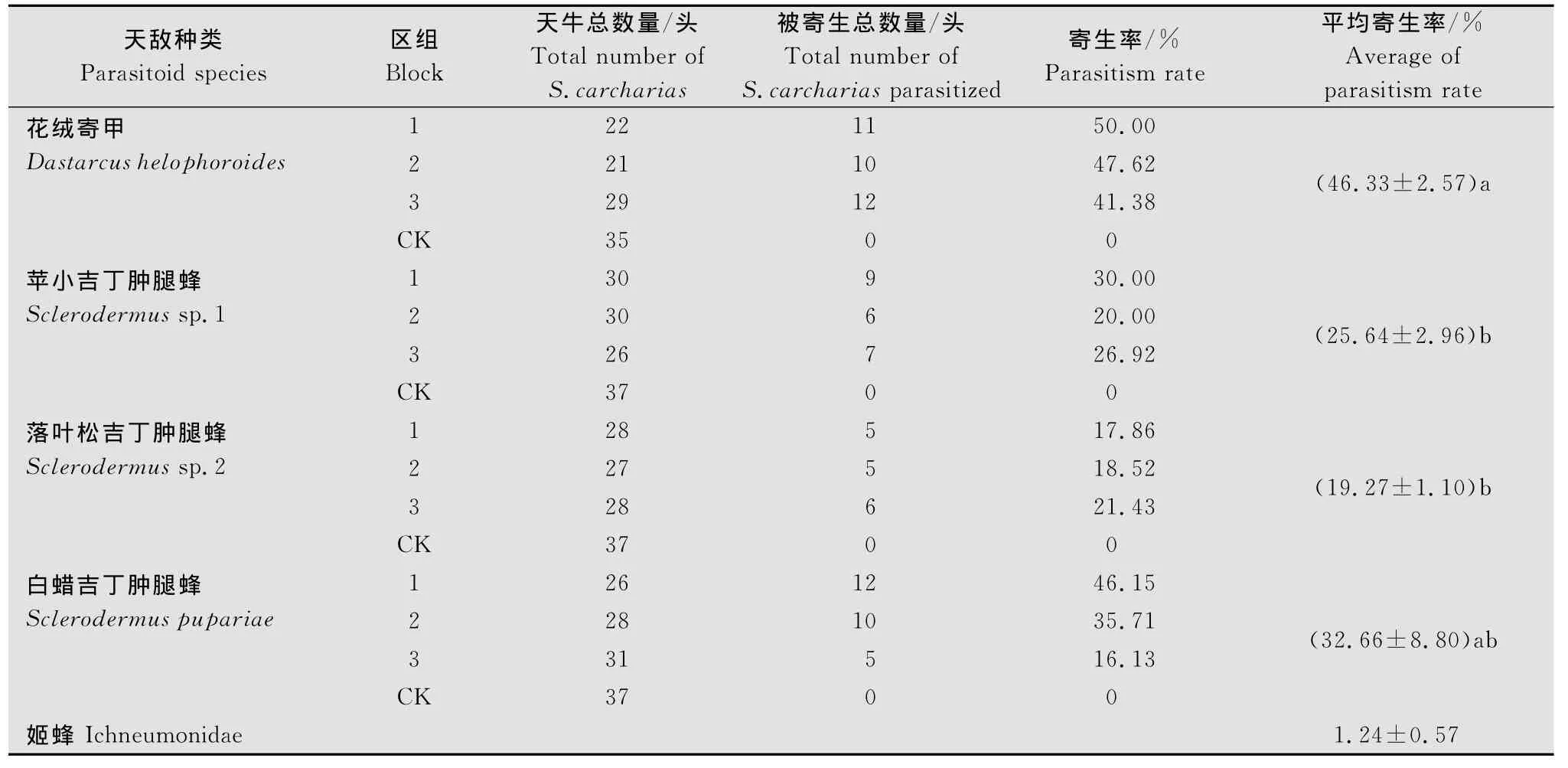
表1 三个试验区组4种天敌的寄生率Table 1 Parasitism rates of 4 parasitoid species in 3 wood blocks on larvae of Saper da carcharias
从表1可以看出,这4种天敌的寄生效果存在显著差异,它们的寄生效果按从大到小的顺序排列如下:花绒寄甲(光肩星天牛生物型)>白蜡吉丁肿腿蜂>苹小吉丁肿腿蜂=落叶松吉丁肿腿蜂。由于花绒寄甲只寄生天牛中老龄幼虫和蛹,而肿腿蜂只寄生天牛初龄小幼虫,因此,在生产防治中,可在山杨楔天牛中老龄幼虫期和蛹期利用花绒寄甲、在初龄小幼虫期利用白蜡吉丁肿腿蜂进行防治;由于山杨楔天牛的世代重叠现象明显,不同龄期幼虫同时发生,因而建议在实际应用中同时释放这两种天敌昆虫,以提高防治效果。
3 讨论
试验结果表明,花绒寄甲(光肩星天牛生物型)和白蜡吉丁肿腿蜂对山杨楔天牛均具有较好的控制作用(寄生率分别为46.33%和32.66%),但仍然不够理想,还需在如何提高寄生率方面进行深入研究。花绒寄甲有多种生物型,今后可选择几种花绒寄甲其他生物型对山杨楔天牛进行寄生性强弱室内筛选试验,有望筛选出防治效果更好的花绒寄甲生物型;同理,还可进行其他多种肿腿蜂寄生效果的室内筛选研究。
[1] 萧刚柔.中国森林昆虫[M].第2版.北京:中国林业出版社,1992:498-498.
[2] 任炳忠,李玉.东北地区危害农业、林业的鞘翅目昆虫多样性的研究(Ⅲ)[J].吉林农业大学学报,2001,23(2):26-30.
[3] 宿秀凤,汪红梅.山杨楔天牛综合防治技术[J].新疆林业,2005(3):26-26.
[4] 哈米提,巴海提·居马汗,魏建荣.新疆额敏县山杨楔天牛发生与为害调查[J].植物保护,2012,38(6):151-153.
[5] 黄竞芳.杨树虫害动态与防治对策[J].世界林业研究,1989(2):34-38.
[6] Allegro G.Defence against insect pests of poplar:a revised technique[J].L’Infor matore Agrario,1989,45(16):93-96.
[7] Allegro G.Mechanical control of the principal xylophagous insects of poplar using trunk barriers[J].L’Infor matore Agrario,1990,46(11):91-95.
[8] Allegro G.Bionomics and control of the large poplar borer(Saper da carcharias)[J].Sher wood-Foreste ed Alberi Oggi,1998,4(5):35-40.
[9] Arr u G M,Lapietra G.Suscettibilitàde i cloni di pioppo‘I-214’e‘I-488’agli attacchi di Saper da carcharias L.(Coleoptera Cerambycidae)[J].Cellulosa e Carta,1976,27(3):1-7.
[10]Barani A,Vezzadini S,Ferrari M,et al.La difesa da Saper da carcharias,xilofago del pioppo[J].L’Infor matore Agrario,2000,56(20):69-73.
[11]Cavalcaselle B,Bellis E de.Experi ment with new insecticides at low toxicity against the subcortical larvae of Cr yptorhynchus l apathi L.and Saper da carcharias L.[J].Cellulosa e Carta 1983,34(5):29-34.
[12]De Bellis E.Contributo alla conoscenza della biologia e della etologia della Saper da carcharias L.(Coleoptera Cera mbycidae)[J].Pubbl Centro Sper agr for Roma,1969,10:249-303.
[13]Giorcelli A,Allegro G.Suggested treat ments for the pr oper pr otection of poplar plantations[J].Sher wood-Foreste ed Alberi Oggi,1999,5(5):39-44.
[14]Kr ol A.Occurrence of Saper da carcharias (L.),Saper da popul nea (L.)(Cerambycidae:Coleoptera),and Par anthrene tabanifor mis Rott.(Aegeriidae:Lepidoptera),on a fertilized plantation of Popul us"r obusta"in a filling sand pit at Sczakowa Poland.1[J].Zeszyty Naukowe Lesnict wo,1981,13(164):93-103.
[15]Lapietra G.Trials of localized treat ments against larvae of Saper da carcharias L.by insecticides in aerosol for mulations[J].Cellulosa e Carta,1980,31(5):3-9.
[16]Lapietra G,Allegro G.Insects damaging poplars in Italy during 1987-89,control strategies and f ut ure perspectives[C]∥Proceedings-Wor king Party on Insects and Other Ani mal Pests,FAO Inter national Poplar Co mmission,1990(35):31-36.
[17]Monter mini A,Barani A,Oliva G,et al.Assessmentof an infor mation model for the reasoned phytosanitary pr otection of the poplar[J].Atti delle Giornate Fitopatologiche,1998:709-714.
[18]Nuorteva M,Pato maki J,Saari L.Large poplar longhor n,Saper da carcharias (L.)as food for white-backed woodpecker,Dendrocopos leucotos (Bechst.)[J].Silva Fennica,1981,15(2):208-221.
[19]Pollini A.The enemies of cultivated poplar[J].Vita in Ca mpagna,1990,8(5):49-51.
[20]Rouard M.Contribution to the Belgiu m fauna:interesting catches of the coleopteran Cerambycidae[J].Bulletin & Annales de la Societe Royale Belge d’Entomologie,1995,131(2):159-160.
[21]Schnaider owa J,Instyt ut B L.Zaklad Ochr ony Lasu,Przyc-zyny masowego wystepo wania rzemlikow(Saper da carcharias L.and Saper da populnea L.)na ziemiach polskich[M].Warsaw,Poland:Warazawa,Instyt ut Badawczy Lesnict wa,Zaklad Ochreny Lasu,1964.
[22]Srot M.Factors reducing the population density of the lar ge poplar borer (Saper da carcharias)[J].Lesnict vi UVTIZ,1983,29(9):785-804.
[23]Strojny W.Damages on the leaves of Popul us tremul a caused by the adults of Saper da carcharias (Coleoptera,Cerambycidae)[M].Polskie pis mo ento mologiczne.Poland:Bulletin ento mologique de la Pologne,1974:231-234.
[24]Strojny W.Feeding of the i mago of Saper da carcharias (L.)(Coleoptera:Cerambycidae)on bar k of Popul us tremul a L.spr outs[M].Polskie pis mo ento mologiczne.Poland:Bulletin ento mologique de la Pologne,1975:625-632.
[25]Taris B.Ani mal pests of poplars(Aegeria apifor mis,Capnodis miliaris,Melolontha melolontha,Phloeomyzus passerinii,Cossus cossus,Pher ocomma populeu m,Zeuzer a pirina,Saper da carcharias,Saper da popul nea,Cr yptor r hynchus lapathi,Sciapter on tabanifor mis,Mel aso ma populi,Phyllodecta spp.,Leucoma salicis,Gypsonoma aceriana,Trichioca mpus vi minalis)[J].Phytoma,1986(376):51-55.
[26]Thomas H.Zur bekampf ung des grossen pappelbockes,Saper da carcharias L.[J].Soz Forst wirtsch,1975,25(5):154-156.
[27]Tozlu G.Deter mination of the har mf ul insects on trembling aspen(Popul us tremul a L.)and st udies on the biology of so me i mportant species in Sarkams(Kars)district[J].Turkiye Ento moloji Der gisi,2001,25(2):133-146.
[28]Vali maki S,Heliovaara K.Hybrid aspen is not preferred by the large poplar borer(Saper da carcharias)[J].Arthropod-Plant Interactions,2007,1(4):205-211.
[29]Varga L.The possibilities of the application of deep planting technology on the all uvia of rivers[J].Lesnicky Casopis,1995,41(5):339-351.
[30]Verenini M.How to protect itself against some enemies of poplar Cr yptorr hynchus l apathi L.,Saper da carcharias L[J].Monti e Boschi,1984,35(6):56-58.
[31]Verenini M.Poplar enemies,Cr yptor r hynchus lapat hi L.,Saper da carcharias L.(Coleopteran)[J].Infor matore Fitopatologico,1984,34(6):31-34.
[32]Walerys G,Sadej W.Longhor n beetles(Cera mbycidae)as a potential pest insecton plantations of shrubby willow?[J].Pr ogress in Plant Pr otection,2009,49(4):1734-1737.
