中国各省市水资源供需平衡预测
2013-02-21陈超群迟晓妮刘志兵
邹 婷,陈超群,李 龙,迟晓妮,刘志兵
(黄冈师范学院 数学与计算机科学学院,湖北 黄州438000)
1 Introduction
In some sense,China is one of water shortage countries and its total water resources are only 2.812 4 trillion cubic meters,ranking the fourth in the world,per capita consumption being only 2 240 m3,which is about 1/4 of the world average value. Therefore,China has been classified by the United Nations as one of the world’s 13 water-poor countries[1]. That is why we should be concerned about the water resource in China.On that account,we here make a reasonable water planning for it in 2025.
In this paper,we establish the GM (1,1)model to forecast the water supply-demand of China’s provinces and municipalities except Taiwan,Hong Kong and Macao in 2025. In order to minimize the total cost,we propose a linear programming model to solve the problem of China’s water shortage in 2025. Our research can provide a feasible strategy for China’s sustainable development.
2 Forecast of water demand
2.1 The foundation of GM(1,1)model
By analyzing the reality of water demand of Chinese urban areas,we establish the GM (1,1)model[2]to predict the future water demand of China.
1)Series ratio testing
Set up a mathematical model for a regional total water demand over the years from 2003 to 2011:x(0)(1),x(0)(2),…,x(0)(n),Letx(0)=(x(0)(1),x(0)(2),…,x(0)(n)),x(0)(k),x(0)(k-1)∈x(0),and the series ratio σ(0)(k)is

2)Accumulating the initial data
Counting up a given sequencex(0)will yieldx(1)=(x(1)(1),x(1)(2),…,x(1)(n)),k=1,2,…,n,wherex(1)(k)
3)Establishing the GM(1,1)model as follows

The differential equation (1)is the Gray Prediction Model GM(1,1),whereais the development coefficient anduis the Gray action. Hereaanducan be obtained by the least-squares fitting:

The solution of the differential equation (1),also called the time response function,is given as

which is the formula of series. Since formula (2)is the predictive value of the one-accumulated generated sequence,we can obtain the restored predictive value of the original sequence through
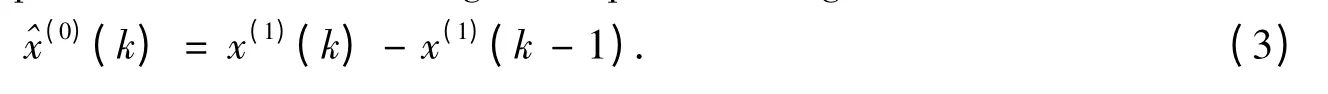
2.2 Model testing
The accuracy of the GM (1,1)model is generally checked by residuals,posterior testing,and series ratiodeviation testing.
1)Residuals testing
Residuals testing is a point-to-point checking method. The residualq(k)and relative error ε(k)are defined respectively by


Usually ε(k)should satisfy ε(k)<20% and it had better satisfy ε(k)<10%.
2)Posterior testing
Suppose thatx(0)is the original sequence,^x(0)is the model sequence,andq(0)is the residual sequence.Thus the mean value and variance ofx(0)are respectively

Similarly,the mean value and variance ofq(0)are respectively

Posterior difference ratioCand the small error frequencePare respectively

3)Series ratio deviation testing
For the given sequencex(0),its model sequence(0),sequence series ratio σ(0)(k)and model series ratio(0)(k),the series ratio deviation is

The GM (1,1)model passing the testing is used to predict and forecast the unknown data

2.3 Prediction of water demand
Based on the water demand of China from 2003 to 2011,firstly we set up a example of this model for the water demand of Beijing. We develop the GM(1,1)model to predict the water demand of Beijing in 2025.We can get au = [-0.005 8;33.986 3],which means

Whent=22,we havex(23)=39.763 5 ×108,the water demand of Beijing in 2025 is 39.763 5 ×108m3.
In the same way,we calculate the water demand in 2025 of China’s 27 provinces and all the other 3 municipalities. The results are plotted in the histogram form as in Figure1.

Figure 1 Annual water demand of all China in 2025
3 Usable fresh water
China is extremely a water-shortage country. According to the statistics from the China Statistical Yearbook[3],it is obvious that the main source of surface water strongly depends on rainfall. Thus it is not difficult to estimate the total freshwater resource of the every region by its annual precipitation. Specific modeling is set up as follows:

Herepis the average annual precipitation in the region (Unit:mm),Sis the geographical area of the region(unit:million square kilometers),andris the utilization rate of water resource in the region. The value ofrshould be related to the actual situation of the region. In order to simplify calculation,we assume that the average utilization rate of water resource is 20% for all regions.

Figure 2 Total usable water of all China in 2025
By using interpolation method and based on the data of usable freshwater from 2003 to 2011,we obtain that the annual precipitation of Beijing in 2025 is 622.15 mm and therefore the usable freshwater of Beijing is 20.904 24 ×108m3. In this way,we calculate the amount of the usable water of all 31 provinces and municipalities of China in 2025. The results are plotted in histogram as in Figure 2.
From Figure 2,we know that 4 provinces and 3 municipalities are lack of water:Beijing,Tianjin,Hebei,Shanghai,Jiangsu,Ningxia,and Shandong. Yet Shanghai and Jiangsu are the areas of water shortage due to water pollution. The results are coincident with the actual water resource in China.
4 Water movement and water desalinization
In order to avoid the water shortage in some areas of China in 2025,we adopt the strategy of water movement and desalination[4],which can minimize water supply cost and produce good economic benefits for the country.
To simplify the mathematical model,the total cost of water desalination in Tianjin,Shandong and Hebei is set to a fixed value M,which is coincident with the development trend of the desalination industry in China.
Let the unit price of water transfer be denoted asC,xijbe the amount of water transfer from thei-tharea to thej-thareabjbe the amount of water shortage in thej-tharea,and
aibe the amount of water abundance in thej-tharea.
Our model of water movement and desalinization is given as the following linear programming problem:


The linear programming problem above is solved with the software matlab. We obtain the following results:
(1)water diversion to Ningxia from shangxi is 4.868 billion cubic meters;
(2)water diversion to Beijing from Inner Mongolia is 1.886 billion cubic meters water;
(3)Water diversion from the Zhejiang and Anhui to Jiangsu is 348.521 billion cubic meters;and
(4)water diversion from Zhejiang to Shanghai is 11.371 billion cubic meters.
It is obvious that the total cost of water diversion and water desalination should be 1.035 ×105×C+M.
5 Conclusions
We have established the GM (1,1)model and the linear programming model to predict and improve the China’s water supply-demand relation in 2025. Our research result concludes that the Chinese government should choose scientific strategies to avoid water storage in the future,such as water diversion,desalinization,conservation and comprehensive use,and secure China’s water supply.
[1] 楚泽涵,封锡强,李艳丽.水资源问题应引起关注[J].古地理学报,2000,2(4):84 -85.
[2] 赵军凯,赵秉栋,李九发,等.城市水资源供需平衡及预测分析[J].水文,2009,29(6):52 -53.
[3] China Statistical Database[EB/OL]. http://219.235.129.58/reportYearQuery.do?id=0100&r=0.5950903581196367#.
[4] The Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China[EB/OL]. http://www.mwr.gov.cn/english.
