Kodak Digital Camera and The Lost Business Opportunity①
2012-01-28HamsaThota
Hamsa Thota
(Innovation Business Development,Inc.,St.Simons Island,GA,USA)
Kodak’s business is pictures(Kodak 1997).Kodak was the world’s“story teller”(Collen,2012).It was one of the world’s dominant brands in the 20thcentury,and to be the dominant player in the picture business appeared to be smart at the turn of the 21stcentury(Kodak,2000).In 2002Kodak achieved 25%total return,including dividends.In 2002Kodak was the best-performing stock among companies that made up the Dow Jones Industrial Average(Kodak,2002).However,10years later,on January 19,2012the Eastman Kodak Company filed voluntary petition for Chapter 11business reorganization in the U.S Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of New York.On the same day New York Stock Exchange issued a news release:The“NYSE Regulation has determined that the Company is no longer suitable for listing”(NYSE,2012)and removed the Company’s registration.Prior to delisting,Kodak traded under the symbol EK on the NYSE.Its share was traded at a high of$63.25on the NYSE on December 31,1999.On March 27,2012,its share traded on the OTC Bulletin Board at a low of$0.32(under the symbol EKDKQ),a 99.5%decrease in value.
A systematic study of Kodak business strategies and operations during 2000-2012revealed that Kodak management mastered business model in the analog value chain and tweaked it to deliver profits consistently.However,it failed to anticipate the severity of disruption to its film business from digital evolution.Kodak management was slow to move into the consumer dedicated capture device business with low margins.It fell behind the power curve in the digital camera business that eventually led to its bankruptcy in 2012.The analogy of falling behind the power curve comes from the aviation industry.For example,when an aircraft loses air speed to maintain altitude,the captain increases engine power to pitch the aircraft up to regain the altitude.However increased pitch of the aircraft causes increased air drag,i.e.,additional power from the engine is mostly nullified by additional air friction from increased pitch.In such a situation,the aircraft continues to lose speed below the minimum speed required to keep it in the air and it crashes to the ground.One solution to this problem is to lose some altitude,willingly,to regain speed.The Kodak management had a choice to decrease altitude,i.e.,accept lower profit margin for digital camera business willingly and regain speed,i.e.increase speed of introduction of compelling new product and services into the digital camera market.Targeting the digital image capture ecosystem for leadership rather than focusing on expanding uses for film would have given Kodak’s R&D and new business development teams a mission to increase breadth of compelling digital camera products and services offered.During 2000-2012Kodak management was aware of the headwinds facing its film business,i.e.,consumer demand shifting from analog film products to digital products and services.Recognizing headwinds in 2000,the Kodak management began increasing throttle of its operations engine,i.e.increased efficiencies in operations and cut costs,eliminated losses by exiting unprofitable businesses,and reformulated business strategies such as the infoimaging strategy.Similar to an aircraft that falls from the sky when airspeed drops below a minimum threshold,Kodak became a nonviable business in digital cameras,pocket video cameras and digital picture frames market,exited them,and went into bankruptcy protection in 2012.Kodak management underestimated the power of the digital evolution storm,i.e.,consumers’ability to find new and better ways to create,deliver and experience the“Kodak moments”without purchasing the Kodak film or needed Kodak’s new technologies to extend uses for film to share memories.Kodak’s 2003turnaround strategy to helping people better use meaningful images and information in their life worked well for a short period of time.However,when consumers changed their behavior and switched to the new digital platform in large numbers demand for Kodak’s traditional pictures was decimated.In retrospect,Kodak fell behind the power curve beginning in 2000when it embraced the infoimaging strategy to extend benefits of film.The infoimaging strategy delivered short-term profits at the expense of long-term viability of the business.Kodak’s 2003digital business model and other strategies that followed it did not allow it to become a strong competitor in the digital world.Kodak digital camera business became a lost business opportunity for a company that invented the digital camera with a groundbreaking invention disclosed in US patent no.4,131,919in 1978(Daneman,2012).
1 Evolution of digital camera business at Kodak
Kodak invented the digital technology in the 1970s.Kodak made pioneering investments in the digital and materials deposition technologies.However,for the next 20years,the digital business remained in the shadows of its analog film business.Kodak was an entrenched player in the analog value chain.Benign negligence of emerging demand for digital products and services in the US consumer markets during 1975-1995allowed space for new entrants such as the Canon,Nikon,Panasonic,Sony and Casio in the digital Point-and-Shoot camera segment to establish a beachhead.In 1995Kodak CEO George Fisher announced Kodak’s digital strategies and plans for digital imaging included a digital camera priced less than$1,000and alliances with industry leaders such as Adobe,IBM,and Microsoft.
2 Kodak 2000infoimaging strategy:Reap profits from pixels
In 2000,Kodak embraced the“infoimaging strategy.Infoimaging”is the convergence of information technology(IT)and imaging science,and Kodak(2000)identified it as a$225billion dollar growth business.Kodak identified three new infoimaging sectors.They were:1)Imaging devices,2)New imaging services and media,and 3)Construction of digital infrastructure.The“Reap profits from pixels”strategy provided dual mission to Kodak’s Consumer Imaging business:better pictures and better sharing.To execute the infoimaging strategy,Kodak invested in infoimaging science and patented 1,000inventions in imaging technology ayear.Kodak achieved leadership in film-to-digital image scanning capability and capacity,and online image distribution.
The portfolio of products and services Kodak introduced in two of three infoimaging sectors are shown in Table 1.In 2000,the sale of Kodak digital cameras jumped 80%.The inkjet paper and media business achieved 31%growth in revenues.In 2000,Kodak’s digital offerings contributed 21%or about$3billion out of total year revenues of$13.9billion(Kodak,2000).All Academy Award nominated films were produced on Kodak film.The national Air &Space Museum recognized Kodak for outstanding scientific achievement.In 2000,Kodak was a catalyst for value creation by companies producing infoimaging products and services.For Daniel Karp,president and CEO of Kodak(2000),the imaging technologies drove value from online commerce to interstellar exploration and Kodak was driving the images.

Table 1:Kodak product introductions in 2000in support of the Infoimaging Strategy
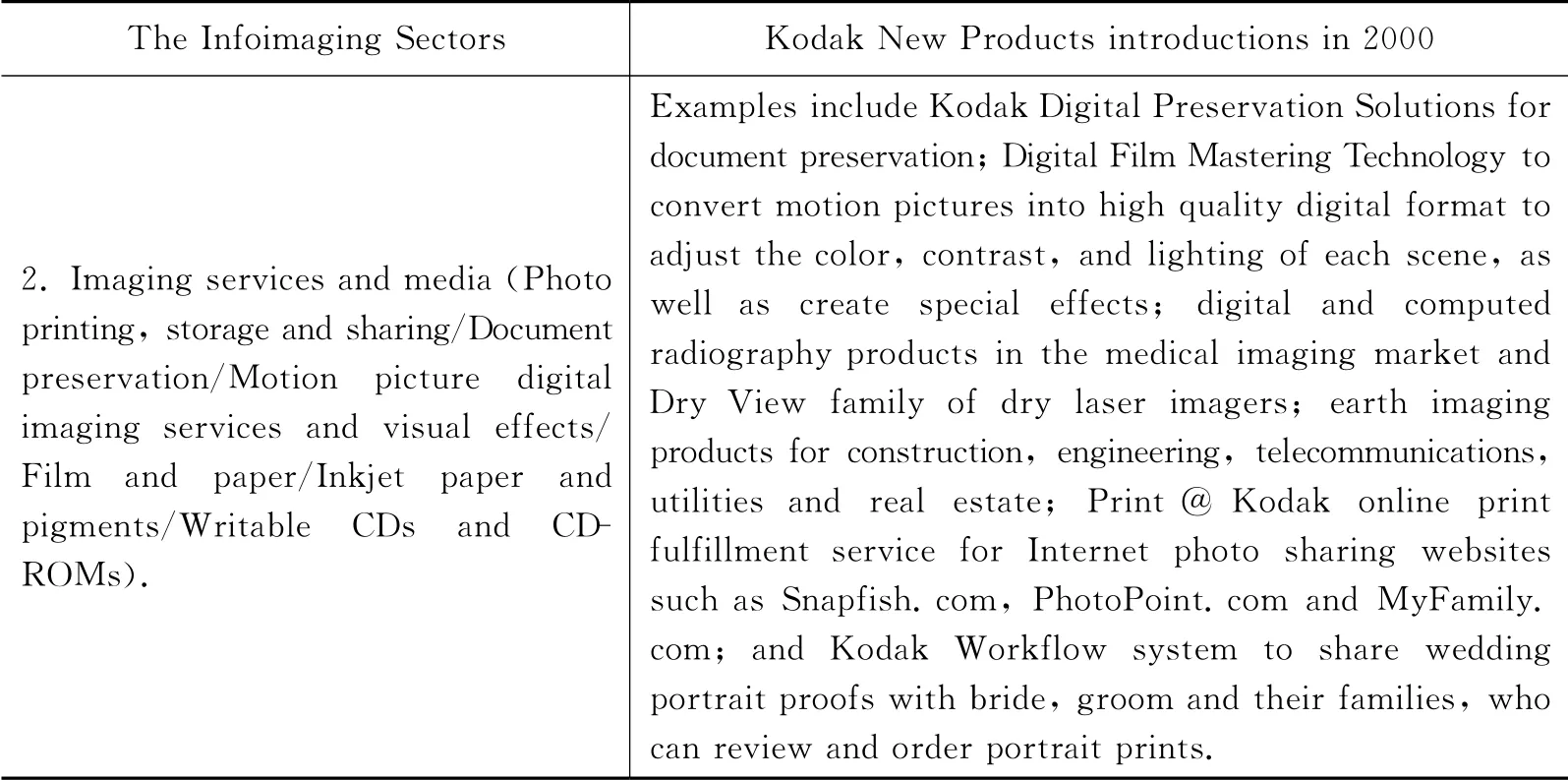
续表
3 Snap shot of Kodak operations in 2000
In 2000Kodak film business model depended on selling inexpensive cameras and reliance on frequent purchases of expensive film by new,and repeat customers.Kodak’s core competencies were in processing“film to negatives,negatives to pictures,and pictures to mantelpieces and memories”(Passikoff,2012).In 2000,amateur photographers ordered 100billion Kodak prints.Healthcare professionals ordered 1.5billion Kodak radiological images.With the infoimaging strategy Kodak redefined its business“to help people with new and better ways to use their pictures”(Kodak 2000).The 2000annual operating results proved that Kodak’s“fit and leverage”strategy(Allen Adamson,2012)was effective and that Kodak’s value proposition remained strong.Kodak enabled consumers to capture the“Kodak moments”and to“creating memories.”The strategic arenas,in which it competed,i.e.cameras,film,and printing,supported its strong value proposition.Kodak was executing on its mission to“help consumers,businesses,and creative professionals unleash the power of pictures and printing to enrich their lives”well(Kodak,2011).In 2000,Kodak was a profitable“well oiled business machine”.
4 Kodak growth strategy in 2001:Expanding the benefits of film
In 2001Kodak saw the film business as a growth business and focused on expanding the benefits of film through the application of digital technology in wholesale and retail photofinishing,and by expanding into emerging film markets.Its traditional film business was healthy,and it was developing in new markets around the world.It experienced some expected digital substitution in the professional markets.Kodak’s 2001growth strategy consisted of four paths:1)Expand the benefits of film,2)Drive image output in all forms,3)Facilitate ease of use in digital imaging,and 4)Develop new business in new markets(Table 2).

Table 2:Kodak growth strategies in 2001
4A Snapshot of Kodak operations in 2001
In 2001Kodak management was confident that it grasped the digital problem and found the right solution.Kodak management applied time-tested management methods to reduce costs in the traditional business,managed cash and maintained market share.It improved manufacturing operations by 34%reduction in inventories and increased inventory turns by 17%.It dramatically shrank the number of stockkeeping units offered by focusing on the best sellers,and eliminated those that were redundant or no longer in demand(Kodak,2001).Kodak management strengthened Kodak online photo services with acquisition of popular Ofoto online services,and customized and cobranded online services with key retailers such as Kmart,CVS,Costco and Rite-Aid.In the digital arena,Kodak remained one of the top three marketers of digital cameras in the U.S.,and the largest supplier of digital photo kiosks in the world.Kodak Qualex wholesale labs scanned more consumer snapshots than any other company.And Kodak was the market leader in online photo services and other forms of digital output like the picture CD.It appeared that Kodak was developing not only smarter products,but also smarter ways to create,deliver and use those products.
4B Strategic product groups at Kodak in 2001
To achieve profitable growth,Kodak created new operating business units in 2001to leverage its historical strengths in image and material science.The new units shared common technology and product platforms and customer sets to enable sharper focus on diversification into high-growth product areas(Kodak 2001).The new business units were:the photography group,health imaging,commercial imaging,and the components group(Table 3).
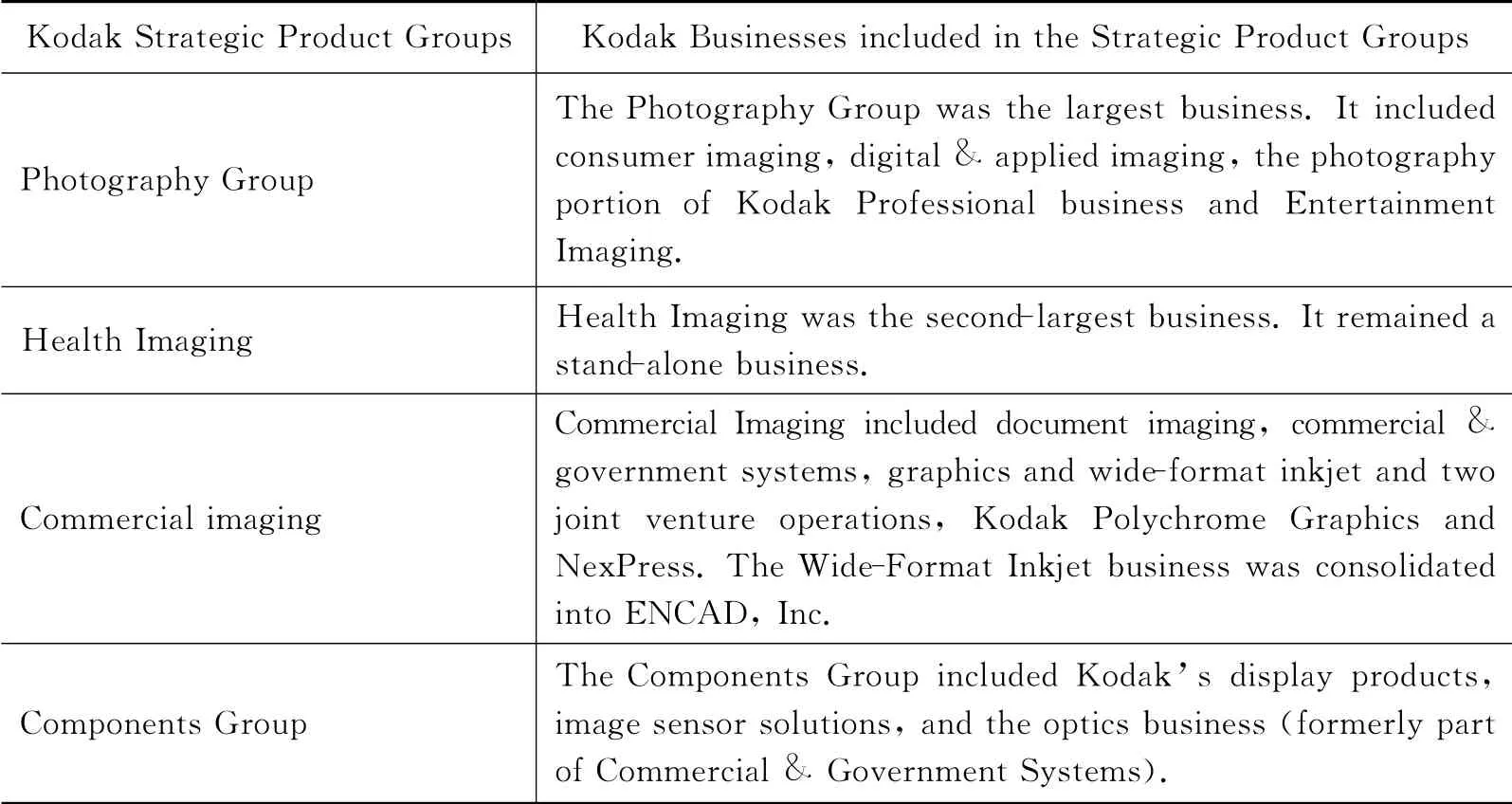
Table 3:Strategic product groups at Kodak in 2001
5 Snapshot of Kodak operations in 2002
In 2002Kodak delivered strong performance.The continuing economic slump led to worldwide decline in sales by 3%.However,Kodak operations achieved a 16%year-over-year increase in operational earnings.Kodak saw strong growth in the emerging markets of China(+25%),Russia(+20%)and India(+8%).In the U.S.,it held market share in consumer film steady for the fifth straight year(Kodak,2002).
6 Kodak’s digitally oriented strategy &Four-year transformation in 2003
In 2003Kodak digital business grew to$4billion.The 2003sales volume increased 2.4%over 2002and increased sales volumes came primarily from consumer digital cameras,printer dock products,inkjet media and motion picture print films in the Photography segment,digital products in Health Imaging and imaging services and document scanners in the Commercial Imaging segment(Kodak,2003).Forrester Technology Brand Scorecard ranked Kodak number two in trust among 58 major technology brands.Kodak management acknowledged that the digital evolution impacted traditional imaging industry-wide(Kodak,2003).Management envisioned a new digital business model that will allow“Kodak to become a strong competitor in the digital world,with the brand,intellectual property,products,and people to achieve sustainable,profitable growth and high return on invested capital for our shareholders”(Kodak,2006).This was a four-year turnaround effort announced in September 2003.Focus of the digitally oriented strategy was“on helping people better use meaningful images and information in their life and work”(Kodak,2006).It reorganized business into commercial,consumer and health market sectors.Kodak management was confident that the company has the market knowledge,the technical assets and the global brand strength to succeed(Kodak,2003).A four-year Kodak transformation process has begun.Transformative actions Kodak took in 2003are listed in Table 4.
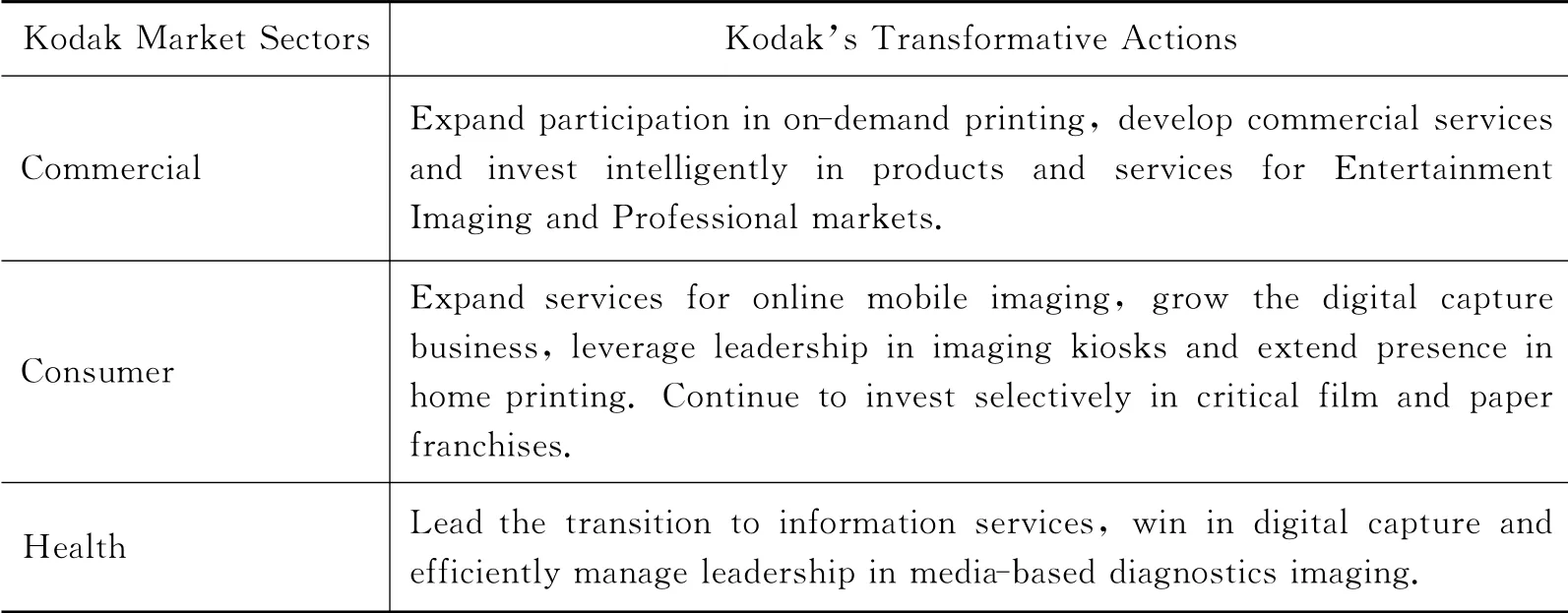
Table 4:Kodak digitally oriented strategy in 2003
6A Kodak operating results in 2003
In 2003Kodak reported a decrease of 9%in net worldwide sales of consumer film products,including 35mm film,Advantix film and one-time-use cameras and a decrease of 18%in sale of consumer film products within the US.However,emerging markets like Russia,India and China experienced increased sales growth of 26%,17%and 12%respectively due to expanded distribution channels for Kodak products and services through independently owned Kodak Express stores in Russia and Photoshop stores in India,and increased levels of camera ownership in India.Kodak attributed lower film product sales to a declining industry demand driven primarily by the impact of digital substitution in advanced markets and retailer inventory reductions(Kodak,2003).Its 2003net earnings decreased 66%as compared to 2002.However,Kodak maintained the gross profit margin at a healthy 35.9%level as compared with 34.5%in 2002.Kodak attributed increase of 1.4 percentage points in gross profits to reduced manufacturing cost,i.e.,reduced labor expense,favorable materials pricing and improved product yields(Kodak,2003).
7 Snapshot of Kodak Digital and Film Imaging Systems in 2005
2005was a successful year for Kodak’s digital products and services.Kodak retained its#1U.S.market position in digital still cameras in 2005,and ascended to the#2position worldwide.Kodak was also:#1worldwide in snapshot printers,#1in retail photo kiosks,with nearly 75,000installed worldwide and#1in online services with the Kodak EasyShare Gallery,with more than 30million registered members(Kodak 2005).Kodak captured the highest rankings in two of four price segments($200-$399and$199or less),which account for more than 85%of the U.S.digital camera market in the J.D.Power and Associates Digital Camera Satisfaction Study.Kodak launched EasyShare-One digital camera,the world’s first consumer camera offering wireless transmission of pictures.It was also featured on the cover of Business Week as one of that magazine’s Best Products of 2005.Also new Kodak photo kiosk G4became an attractive alternative to minilabs for digital printing for retailers with wireless input of images from digital cameras and camera phones,four-second printing and is 30%lighter and smaller than previous models.To meet growing demand for thermal prints,Kodak added manufacturing capacity for thermal paper and media.Kodak negotiated a 10-year global product,crosslicensing and marketing alliance with Motorola to sell image sensors to Motorola,and to link Motorola phone users with the Kodak Gallery and other Kodak services for storing and printing pictures(Kodak,2005).
7A Future Outlook for Kodak in 2005
Kodak effectively managed the overall decline in sales from traditional products and services as“cash cows”with inventory reductions and cost controls to generate substantial cash to fund the four-year transformation.In the motion picture industry,every movie nominated for the Oscar for“Best Picture”of 2005was recorded on Kodak film,as was the case since 1928.Kodak Vision2film platform dramatically improved the quality of motion picture film and Kodak began development into hybrid technologies and digital services,to make film perform even better with digital postproduction work(Kodak,2005).
Kodak’s future looked bright in 2005.Continued restructuring of traditional business and administrative functions that began in 2003remained a painful and anxious time for many of its employees and yet people at Kodak remained focused on innovation.A confident Chairman and CEO Antonio M.Perez pronounced,“Staying true to our strategy,by 2008we expect all of Kodak’s businesses to be leaders in their industry segments—achieving attractive margins and generating substantial cash”.
8 Kodak R&D investments during transformation in 2005-2007
Kodak Research and development groups worked in close cooperation with manufacturing units and marketing organizations to develop new products and applications to serve both existing and new markets.Kodak continued funding of R&D during 2003-2007transformation.For example,during 2005-2007,Kodak continued protection of R&D investments as shown in Table 5.By investing in R&D,Kodak preserved its freedom to use its own-patented inventions and create new revenue streams from licensing.The Kodak Easyshare printers introduced in 2007were derived from groundbreaking research work on MEMS(Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems)in Kodak research centers,which enabled Kodak to offer,“consumers replacement ink cartridges with a breakthrough value proposition that saved consumers 50%on everything they printed”(Kodak,2006).Another product of Kodak research was the advanced nanoparticle pigment ink,which yields images that will hold their color for more than a century(Kodak,2006).Kodak development centers in the U.S.,China and Europe collaborated on award winning products such as the Kodak picture kiosk,Kodak Professional digital printing software(DP1),Document Imaging’s Smart Touch,and Entertainment Imaging’s Kodak look management system(KLMS)(Kodak,2006).
Kodak held a broad portfolio of patents including digital cameras and image sensors;network photo sharing and fulfillment;flexographic and lithographic printing plates and systems;digital printing workflow and color management proofing systems;color and black and white electrophotographic printing systems;wide-format,continuous,and consumer inkjet printers;inkjet inks and media;thermal dye transfer and dye sublimation printing systems;digital cinema;color negative films,processing and papers;and organic light-emitting diodes.
Kodak completed its four-year restructuring program in 2007.
8A Snapshot of Kodak Consumer Digital Imaging Group in 2005-2007
During 2005-2007Kodak Consumer Digital Imaging Group(CDG)strategy was to extend picture taking,picture search/organizing,creativity,sharing and printing to bring innovative new experiences to consumers(Kodak,2007).In 2007Kodak held Kodak holds top three market shares in digital still cameras,retail printing,and digital picture frames.In January 2007Kodak introduced a new line of Digital Picture Frames.They played customizable slideshows of pictures and videos that customers could set to music of their choice.Kodak’s full line of camera products and accessories were relevant to consumers to personalize their digital cameras and photographic experiences.In the Online Imaging Services category,Kodak Gallery remained leading online merchandise and sharing services with more than 50million members.Kodak Gallery sold branded Martha Stewart photoproducts.The Kodakgallery.com site provided consumers with a secure and easy way to view,store and share their photos with friends and family.Also consumers could receive Kodak prints from their pictures,such as photo books,frames,calendars etc.Major retailers such as Adobe,Apple,Microsoft,and Amazon partnered with Kodakgallery.com.Kodak distributed Kodak EasyShare desktop software free to consumers to unify their experiences between digital cameras,home printers,and the Kodak Gallery services.
In February 2007,Kodak launched a major initiative to drive future revenue growth and earnings with introduction of Kodak All-in-One Inkjet Printing System.Kodak targeted the high-volume document and photo printer market with a lower cost per printed page as compared with competitive products(Kodak,2007).For Kodak,the All-in-One Inkjet Printing system with a permanent print head delivered unmatched value proposition to the marketplace.
In 2007CDG’s marketing strategy emphasized ease of use,quality and the complete solution offered by Kodak products and services.However,Kodak faced hyper competition from other online service companies,consumer electronics and printer companies which competed on price and technological advances.New products experienced rapid price declines shortly after product introduction because competitors continually introduced new models with enhanced capabilities,such as improved resolution and/or optical systems in cameras(Kodak,2007).In January 2007,Kodak redefined the Retail Printing Group to manage Kodak’s digital printing hardware,media and infrastructure offerings to retailers to stabilize CDG’s ongoing revenue,cash flows and earnings.Sales from the CDG segment for 2007,2006and 2005were(in millions)$4,631,$4,711,and$5,646,respectively(Kodak,2007).
8B Snapshot of Kodak Film Products Group(FPG)in 2005-2007
Sales in the Kodak Film Products Group(FPG)continued to decline during 2005-2007due to increasing levels of digital substitution of consumer and professional films and industrial and aerial films.The demand for motion picture films remained relatively stable.However,Kodak management anticipated significant declines in demand for motion picture film but could not predict the future impact of digital substitution on its motion picture film business.It is very difficult to predict the pace of digital technology adoption in major world markets(Kodak,2007).
9 From market leadership to bankruptcy in 2008-2012
Global recession hit Kodak business hard beginning with second half of 2008.Kodak management made pragmatic decisions and rationalized its product portfolio.It decided to invest in Consumer Inkjet,Commercial Inkjet(including stream technology)and Enterprise workflow businesses and reposition other digital businesses,including Kodak Gallery,OLED,Imaging Sensors and Electrophotographic Printing to generate maximum value(Kodak,2008).Kodak’s key priorities for 2009were to align the cost structure with external economic realities,fund core investments,transform portions of its product portfolio and drive positive cash flow before dividends and restructuring.In our“behind the power curve”analogy,the Kodak management realized that“Kodak,the aircraft”was losing altitude and focused all its resources to keep the aircraft in the air.
The CDG introduced the KODAK Zi6Pocket Video Camera in 2008allowing stunning HD videos,which can be easily uploaded to YouTube via a built-in USB connector(Kodak 2008).The Company also introduced a variety of stylish and compact digital still cameras as well as high performance long zoom cameras with image stabilization like the Z1015IS in 2008(Kodak,2008).In the digital picture frame category,Kodak introduced the world’s first OLED wireless picture frame,featuring a vivid display based on Kodak’s invention(Kodak,2008).The Retail Systems Solutions,formerly known as the Retail Printing Group,introduced its Adaptive Picture Exchange(“APEX”)drylab system as an alternative lower total cost ownership system to traditional photofinishing processing at retailer locations(Kodak,2008).It also launched the DL2100printer to enable retailers to connect directly to a kiosk or APEX,and enable customers to make double-sided photobooks,calendars and greeting cards,almost instantly in-store Kodak,2008).The consumer’s could combine own pictures with original artist music with the Kodak Picture-Movie DVD and create a powerful multimedia show playable on any DVD player,posters,collages etc.(Kodak,2008).By the end of 2008,KODAK Gallery had more than 70million members and more than one million EASYSHARE All-in-One line of consumer inkjet printers were installed(Kodak,2008).In 2008 Kodak remained as the most recognized and respected brands in the world but it played in the hyper competitive markets in which price and technological advances drove the market.Kodak could not harvest premium prices using its fabled Kodak brand in such hyper competitive markets.
In 2008,the Kodak continued aggressive management cost structures in the traditional,“Film,Photofinishing and Entertainment Group(FPEG)”,with a focus on sustaining cash flow and earnings performance while revenues declined continuously(Kodak,2008).In its 2008Annul Report,Kodak management acknowledged that if the“Company is unable to anticipate and develop improvements to its current technology,to adapt its products to changing customer preferences or requirements or to continue to produce high quality products in a timely and costeffective manner in order to compete with products offered by its competitors,this could adversely affect the revenues of the Company”(Kodak,2008).Also,Kodak management stated that lax enforcement of proprietary rights and third parties’legal claims that Kodak violated their intellectual property rights,might adversely impact Kodak’s future revenue,earnings and expenses.Kodak relied upon enforcement of patent,copyright,trademark and trade secret laws in the United States and similar laws in other countries(Kodak,2008).Many of Kodak products relied on key technologies developed or licensed by third parties.Kodak’s profits depended on its ability to obtain licenses and technologies from them at reasonable terms(Kodak,2008).
2009was a tough year for Kodak.The demand for Kodak’s end markets continued to decline and adversely affected sales of both commercial and consumer products and their profitability.In its 2009Annual Report,Kodak management warned that its financial performance and liquidity is at risk if demand continues to be weak,economic conditions worsen,or if strategic investments in consumer inkjet,commercial inkjet,enterprise workflow,and digital packaging printing solutions do not deliver strong growth(Kodak,2009).In addition,the competitive pressures could harm Kodak’s future revenue,gross margins and market share.Product quality issues may increase expenses,decrease liquidity and Kodak may reputation may be harmed.In our falling behind the power curve analogy,the Kodak management is no longer in charge of its destiny.The“Kodak”aircraft is unable to maintain altitude,the Kodak“operations engine”is delivering the maximum thrust and yet the aircraft is descending.The“Kodak”aircraft is in trouble and faced the potential reality of crashing to the ground(i.e.faced the prospect of Kodak Company’s inability to sustain ongoing operations and go into bankruptcy for protection from creditors).
In 2010,competitive pricing and rising commodity costs continued to negatively impact results in more mature product lines,including Prepress Solutions,Digital Capture and Devices,and Entertainment Imaging.Kodak“continued investment in its four growth initiatives”(Kodak,2010).Kodak’s revenues from consumer inkjet,commercial inkjet,workflow software and services product lines,and packaging solutions grew 18%for the full year in 2010(Kodak,2010).Also,on a positive note,Kodak Company executed its intellectual property strategy,entered into three significant intellectual property arrangements in 2010,and recognized$838million in revenues(Kodak,2010).
Kodak net sales from continuing operations decreased year-over-the-year during 2008-2010.Net sales decrease from continuing operations in 2010,2009,and 2008 were-6%,-19%,and-2%respectively and losses from continuing operations were-571million,-117million and-874million dollars respectively.Kodak operations lost a total of$1.562billion dollars during 2008-2010.The Kodak“aircraft”crashed to the ground.
Reaction to Kodak’s failure to sustain profitable operations was quick and harsh in Blog posts and in the popular press.McCue(2012)attributed Kodak’s struggles for many years to achieve profitability in the hyper competitive,dedicated capture devices business-comprising digital cameras,pocket video cameras and digital picture frames to Kodak management failure.In the minds of consumers,Kodak created digital camera products and services that were not meaningfully differentiated from their competition.Adamson(2012)claimed that Kodak lost its competitive edge in the digital age because it“no longer had a product that solved a problem for consumers,or meets a consumer need,in a way that’s relevantly better or different than other brands in its field,be it imaging and printing,cameras,celluloid film,or basic photography.”A Wall Street Journal reporter Beth Carter painted a poor picture about the financial health of Kodak in November 2011.In the face of“sweeping collapse of the market for analog film”,Beth Carter concluded that Kodak’s efforts to“cut costs and recalibrate operations around the printing business were fruitless”(Carter,2011).
By 2012Kodak exited unprofitable capture device business to achieve annual operating savings of more than$100million in line with Kodak’s strategy“to improve margins in the capture device business by narrowing participation in terms of product portfolio,geographies and retail outlets”(Kodak,2012).Kodak’s narrowed focus included profitable retail print solutions,destination photo solutions such as picture kiosks and home printing products such as the inkjet printers with high-quality,affordable ink(Kodak 2012b).
10 Summary
A systematic study of Kodak’s annual operations and business strategies during 2000-2010revealed that Kodak management faltered in transitioning the Kodak Company from an analog business model to a digital business model.In 2000Kodak delivered strong performance and it appeared to be smart to be in the picture business.It implemented the infoimaging strategy in 2000,which identified infoimaging as a$225billion dollar growth business.The“Reap profits from pixels”strategy worked for short time.In 2002Kodak was recognized as the bestperforming stock among companies that made up the Dow Jones Industrial Average.In 2003Kodak management implemented a digitally oriented growth strategy to“helping people better use meaningful images and information in their life and work,”and a four-year transformation plan to position Kodak competitively during the digital revolution and to sustain leadership in global imaging,in a digital world.In 2005Kodak future looked bright.A confident Chairman and CEO Antonio M.Perez pronounced that by 2008he expected all of Kodak’s businesses to be leaders in their industry segments.In 2007Kodak Consumer Digital Imaging Group(CDG)’s marketing strategy emphasized ease of use,quality and the complete solution offered by Kodak products and services.Also In 2007,Kodak launched a major initiative to drive future revenue growth and earnings with introduction of Kodak All-in-One Inkjet Printing System.In 2008Kodak remained as the most recognized and respected brands in the world but it played in the hyper competitive markets in which price and technological advances drove the market.So Kodak was unable to reap premium prices from its famous brand and became a nonviable business due to sustained losses from continuing operations.
During 2008-2012Kodak fell from being a market leader to becoming a bankrupt Company.Using the analogy of“behind the power curve”,this article shines light on Kodak’s crash to the ground,i.e.bankruptcy filing in 2012and asserts that Kodak management triggered the process of falling behind the power curve in 2000 when it embraced the infoimaging strategy to extend the benefits of film.Kodak’s 2003digital business model and other strategies that followed it did not allow Kodak to become a strong competitor in the digital world.Kodak digital camera business became a lost business opportunity.
[1]Adamson A.How Barnes &Noble Can Save Itself From Becoming A Kodak Moment[EB/OL].[2012-03-28].http://www.forbes.com/sites/allenadamson/2012/02/02/how-barnesnoble-can-save-itself-from-becoming-a-kodak-moment.
[2]Carter B.Kodak’s Financial Picture:Poorly Composed[EB/OL].[2012-03-29].http://www.wired.com/epicenter/2011/11/kodaks-poor-financial-picture.
[3]Collen J.Happy Birthday to the KODAK Trademark[EB/OL].[2012-02-10].http://www.forbes.com/sites/jesscollen/2012/02/22/happy-birthday-to-the-kodak-trademark.
[4]Daneman M.End of an era at Kodak.Rochester Democrat and Chronicle[M].Rochester,NY,2012.
[5]Kodak.Form 10-K for the year ended Dec.31,1998.Securities and exchange Commission,Washington D.C[EB/OL].http://www.getfilings.com/o0000031235-99-000001.html.
[6]Kodak.Kodak 2000Annual Report and 2001Proxy Statement[EB/OL].[2012-03-29].http://investor.kodak.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=115911&p=irol-reportsannual.
[7]Kodak.Kodak 2001Annual Report and 2002Proxy Statement[EB/OL].[2012-03-29].http://investor.kodak.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=115911&p=irol-reportsannual.
[8]Kodak.Kodak 2002Annual Report and 2003Proxy Statement[EB/OL].[2012-03-29].http://investor.kodak.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=115911&p=irol-reportsannual.
[9]Kodak.Kodak 2003Annual Report and 2004Proxy Statement[EB/OL].[2012-03-29].http://investor.kodak.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=115911&p=irol-reportsannual.
[10]Kodak.Kodak 2005Annual Report and 2006Proxy Statement[EB/OL].[2012-03-29].http://investor.kodak.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=115911&p=irol-reportsannual.
[11]Kodak.Kodak 2006Annual Report and 2007Proxy Statement[EB/OL].[2012-03-29].http://investor.kodak.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=115911&p=irol-reportsannual.
[12]Kodak.Kodak 2007Annual Report and 2008Proxy Statement[EB/OL].[2012-03-29].http://investor.kodak.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=115911&p=irol-reportsannual.
[13]Kodak.Kodak 2008Annual Report and 2009Proxy Statement[EB/OL].[2012-03-29].http://investor.kodak.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=115911&p=irol-reportsannual.
[14]Kodak.Kodak 2009Annual Report and 2010Proxy Statement[EB/OL].[2012-03-29].http://investor.kodak.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=115911&p=irol-reportsannual.
[15]Kodak.Kodak 2010Annual Report and 2011Proxy Statement[EB/OL].[2012-03-29].http://investor.kodak.com/phoenix.zhtml?c=115911&p=irol-reportsannual.
[16]Kodak.Kodak news release,August 1,2011(Rochester,NY):Kodak Adopts Plan to Preserve Valuable Net Operating Losses[EB/OL].[2012-03-29].http://www.kodak.com/ek/US/en/Kodak_Adopts_Plan_to_Preserve_Valuable_Net_Operating_Losses.htm.
[17]Kodak.Kodak Focuses Consumer Business On More Profitable Growth Opportunities[EB/OL].[2012-02-09].http://www.kodak.com/ek/US/en/Kodak_Focuses_Consumer_Business_On_More_Profitable_Growth_Opportunities.htm.
[18]Kodak.Kodak Enters into Agreement for Proposed Sale of Gallery Photo Services Site to Shutterfly[EB/OL].[2012-03-01].http://www.kodak.com/ek/US/en/Kodak_Enters_into_Agreement_for_Proposed_Sale_of_Gallery_Photo_Services_Site_to_Shutterfly.htm.
[19]McCue T J.Kodak closes camera business[EB/OL].[2012-03-28].http://www.forbes.com/sites/tjmccue/2012/02/09/kodak-closes-camera-business.
[20]NYSE.[EB/OL].[2012-03-28].http://www.nyse.com/press/1326970332818.html.
[21]Passikoff R.Customer Loyalty Engagement Index 2012Commandment:Delight Thy Customer.CMONetwork[EB/OL].[2012-03-29].http://www.forbes.com/sites/marketshare/2012/02/07/customer-loyalty-engagement-index-2012-commandment-delightthy-customer.
[22]Passikoff R,Shea A.No more Kodak moments[EB/OL].[2012-03-28].http://brandkeys.blogspot.com/2012/02/no-more-kodak-moments.html.
[23]Rich’s Management Blog.A case in poor management:Kodak[EB/OL].http://www.richsmanagementblog.com/a-case-in-poor-management-kodak/management-principles.
