一维Z型链状配合物[Cd(BDC)(H2C2EIm)(H2O)]n的水热合成、晶体结构和荧光性质研究
2011-11-09冯国栋赵卫星李宗孝
冯国栋 姜 娈 赵卫星 王 艳 李宗孝
(宝鸡文理学院化学化工系功能配合物研究所,宝鸡 721013)
一维Z型链状配合物[Cd(BDC)(H2C2EIm)(H2O)]n的水热合成、晶体结构和荧光性质研究
冯国栋*姜 娈 赵卫星 王 艳 李宗孝
(宝鸡文理学院化学化工系功能配合物研究所,宝鸡 721013)
水热合成了1个新配合物[Cd(BDC)(H2C2EIm)(H2O)]n(BDC=对二苯甲酸;H2C2EIm=2,2′-乙基双苯丙咪唑)。通过元素分析、红外光谱、热重以及X-射线单晶洐射对其进行了表征。该晶体属三斜晶系,P1空间群。Cd(Ⅱ)原子通过BDC和H2C2EIm 2种配体连接成一维Z型带状结构,带与带之间通过N-H…O,O-H…O连接成三维超分子结构。室温下配合物具有较强的荧光发射光谱。
镉配合物;晶体结构;对苯二甲酸;双苯并咪唑;荧光
0 Introduction
Recently,owing to the variety of intriguing architectures and topologies and the potential applications in magnetism,electric conductivity, molecular adsorption,heterogeneous catalysis,and fluorescent materials[1-2],the construction of metalorganic framework(MOF)structures has been received increasing attention[3-5].However,the rational design and synthesis of MOFs with unique structure and function is still a challenge.Various factors such as the nature of metal ions,medium,pH value of solution,temperature,and numberofcoordination donors provided by organic ligands[6]are frequently influenced the resultant structural framework.The 1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid (BDC),an organic ligands with carboxylate groups,are especially interesting because of their various coordination modes to metal ions[7]and their abilities to act as H-bond acceptors and donors to assemble various supramolecular structures[8].Comparatively,bis(2-benzimidazoles)and some substituted bis (2-benzimidazolyl)alkanes containing N-donors are also particularly attractive as excellent building blocks with charge and multi-connecting ability.Very recently,a series of cadmium or zinc coordination polymers attract extensive interest for their non-linear optical and fluorescence properties[9-10].While compared with aforementioned cases,we report syntheses,crystal structure and luminescent properties of a coordination polymer [Cd(BDC)(H2C2EIm)(H2O)]nbased on the mixed ligands of aromatic carboxylates,1,4-benzenedicar-boxylic acid (BDC),and N-donor Ligands,2,2′-(ethanediyl)bis(1H-benzimidazole)(H2C2Eim).
1 Experimental
1.1 Materials and general methods
All chemicals for syntheses and analyses were commercially purchased and used without further purification.The H2C2EIm ligand was prepared according to the reported method[11].Elemental analyses (C,H and N)were performed on a Vario ELⅢelemental analyzer.FTIR spectra were recorded in the range of 400~4 000 cm-1on a Nicolet AVATAR-360 spectrophotometer with KBr pellets.The emission/ excitation spectra were recorded on a Varian Cary Eclipse spectrometer.All the measurements were carried out under the same experimental conditions.TG analyses were performed on a Perkin-Elmer TGA instrument in flowing N2with a heating rate of 10℃· min-1.
1.2 Synthesis of[Cd(BDC)(H2C2EIm)(H2O)]n(1)
The title complex was prepared by the mixture of Cd(NO3)2·4H2O(0.154 g,0.5 mmol),H2C2EIm(0.106 g,0.5 mmol),BDC (0.166 g 1 mmol),0.6 mmol of NaOH dissolved in 8 mL distilled water and H2O(16 mL).This mixture was heated in sealed Teflon-lined autoclave for three days at 150℃.After the reaction mixture was slowly cooled down to room temperature, colorless prism like crystals were produced with a yield of 75%.Anal.Calcd.for C24H20N4O5Cd(%):C,51.90;H, 3.26;N,10.09.Found(%):C,51.31;H,3.19;N,9.71.IR spectrum (cm-1):3420,3111,2881,1558,1506,1 455,1271,1209,1081,1002,952,854,745 and 551.
1.3 X-ray crystallography
A colorless block single crystal of 1 with 0.28 mm×0.23 mm×0.18 mm was carefully selected under a polarizing microscope and were mounted on a glass fiber and used for X-ray diffraction analyses.Single crystal structure determination by X-ray diffraction measurements were performed using a Bruker Smart ApexⅡ CCD diffractometer with graphite monochromated Mo Kα (λ=0.071073 nm)radiation.Absorption corrections were applied using the multi-scan technique[12].The structures were solved by the Direct Method and refined by full-matrix least-square techniques on F2using SHELXTL-97[13].All of the non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically[14].The H atoms attached to C atoms were positioned geometrically,with Uisovalues derived from Ueqvalues of the corresponding C atom.
CCDC:802048.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Description of crystal structure
Crystallographic and structural refinement data for the complex are given in Table 1.Selected bond distances and angles are shown in Table 2.
The single crystal X-ray analysis shows that the asymmetrical unit of title complex contains one Cd(Ⅱ)ion,one H2C2EIm ligand,one TPA molecules and one coordinated water molecule.As shown in Fig.1,the Cd site shows a distorted-octahedral geometry,being chelated by four O atoms from one BDC ligand and one O atom from one coordinated water.The remaining two coordination sites are chelated by two N atoms from one H2C2EIm ligand.The Cd-O bond lengths are in the range of 0.2254(2)~0.2617(2)nm and the Cd-N bond length is 0.2217(2)~0.2354(2)nm.The Cd(Ⅱ)atoms are bridged by BDC ligands with an intramolecular Cd…Cd distance of 1.1328 nm.Each BDC dianion acts as a μ2-bridge linking two Cd atoms into a zigzag chain with chelating coordination mode(Fig.2).Owing to the abundant nitrogen atoms in the H2C2EIm ligand, hydrogen-bonding interactions are formed.The complex are linked in to a three-dimensional supramolecular framework by the intermolecular hydrogen bonds N-H…O,O-H…O and π-π stacking interactions (d= 3.473).Hydrogen-bonding details for title complex are given in Table 3.
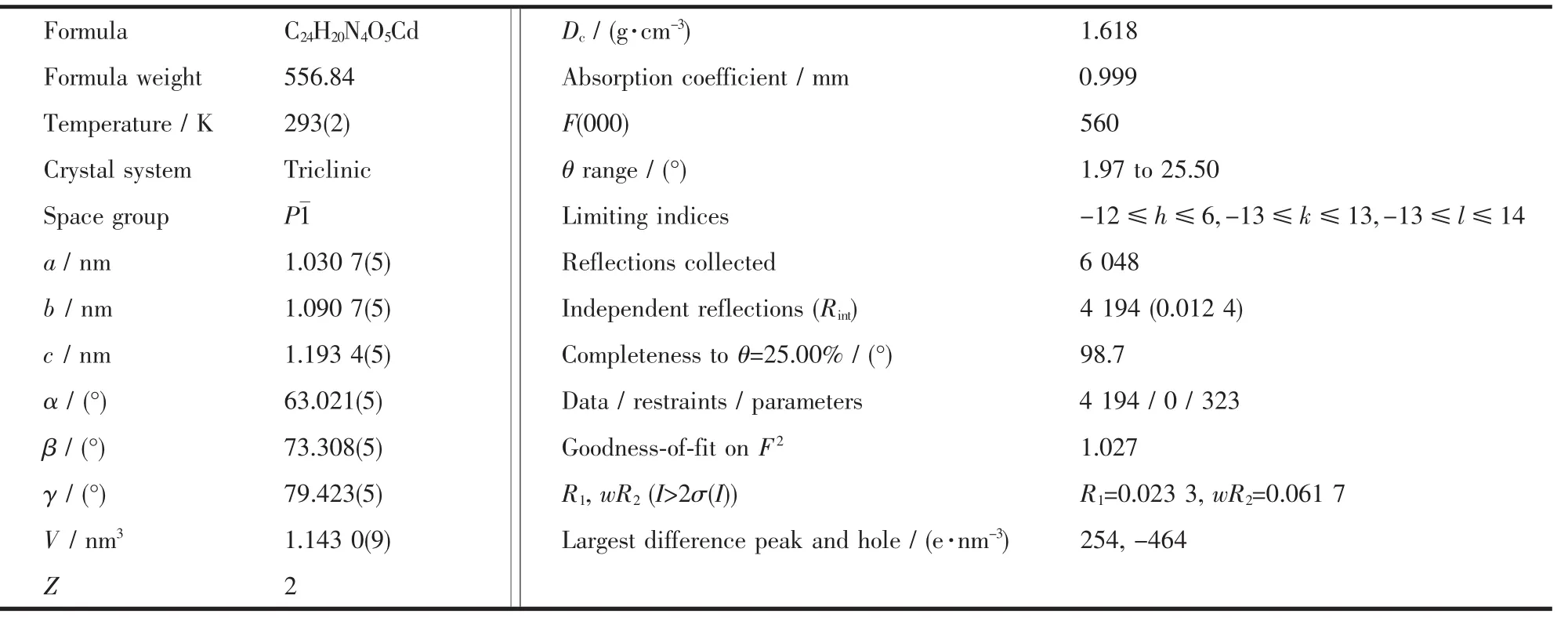
Table 1 Crystal data and structure refinement for title complex
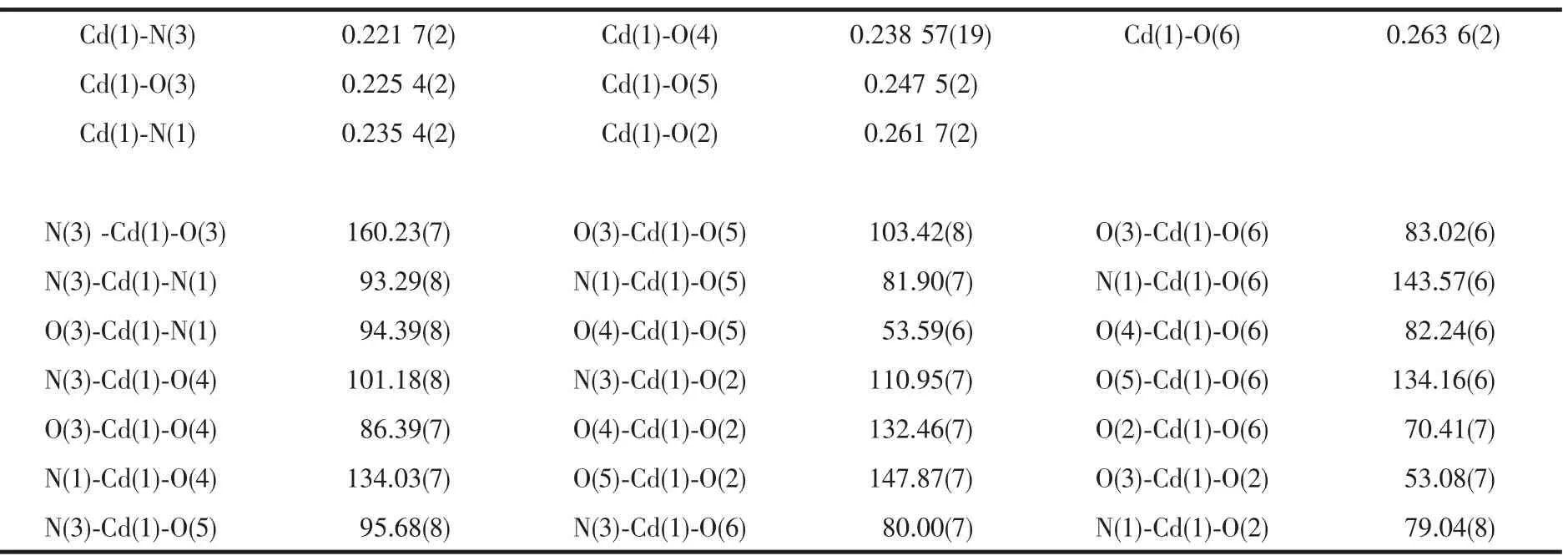
Table 2 Selected bond lengths(nm)and angles(°)



Table 3 Distance and angles of hydrogen-bonding for complex
2.2 IR spectra
The IR spectral data show features attributable to the carboxylate stretching vibrations of the complex (Fig.3).The broad bands centered at 3 420 cm-1due to the stretching vibrations of N-H bond and the peak on 3111 cm-1are ascribed to presence of water ligands[15-16].The strong peaks occurring at 1 558 and 1 506 cm-1demonstrating the antisymmetric and symmetric stretching vibrations of carboxylate with the vicinal values emphasize thatthe carboxylgroups are coordinated in chelating fashion,which is consistent with the results of the single-crystal X-ray analysis[17].The bands for the H2C2EIm ligand at 1 271 and 1 455 cm-1shows the C-N stretching vibration of arylamine group and the C=N stretching vibration of imidazole group[18],respectively.
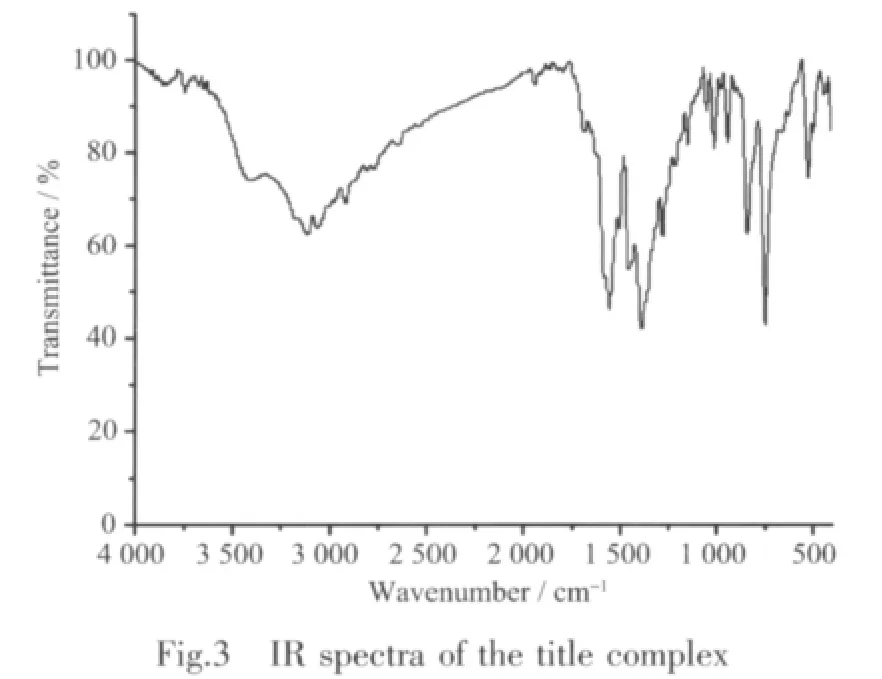
2.3 Thermogravimetric analyses
Thermal gravimetric analyses(TGA)were carried out to examine the thermal stability of the complex(Fig.4).The samples were heated up in N2at 101 kPa pressure with a heating rate of 10℃·min-1.The 4.1% weight loss below 150℃ for the two samples is attributed to a release of the physisorbed water[19].A weight loss of 2.0%occurred in the temperature range of 231~331℃ is attributed to the release of one coordinated water molecule per formula.Then a sharp weight-loss step is observed between 340 and 750℃attributed to the decomposition of organic ligands.
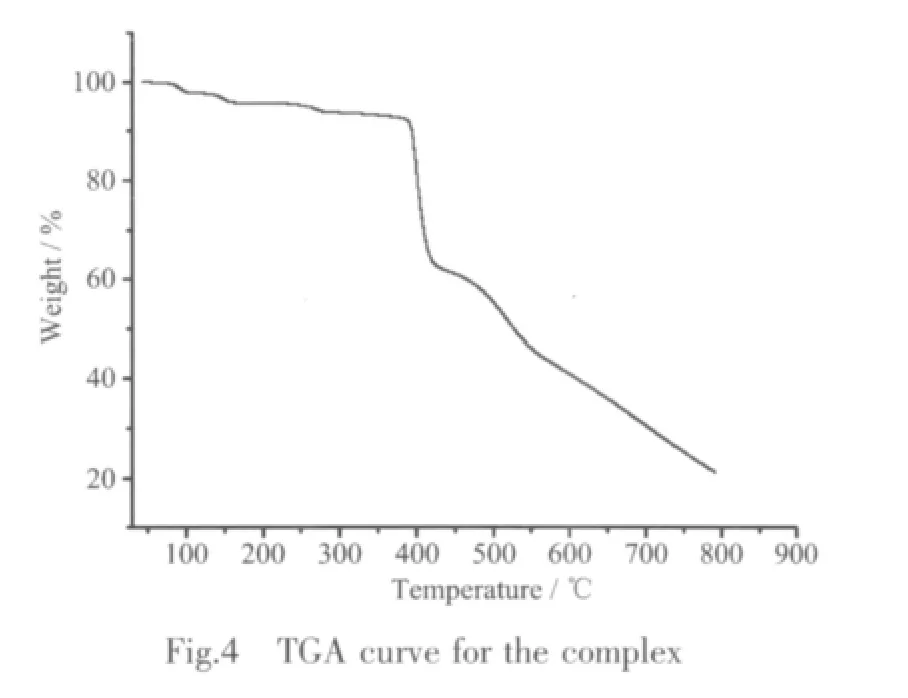
2.4 Luminescent properties

Luminescentcomplexesareofgreatcurrent interestbecauseoftheir various applications inchemical sensors, photochemistry, and electroluminescent display[20-21].As it is depicted in Fig.5,the complex in solid state at room temperature exhibits strong blue photoluminescence with an emission maximum at 468 nm,upon excitation at 332 nm.In addtion,it can be seen that the free H2C2EIm ligand shows a sharp peak with a maximum emission at 435 nm (under 291 nm excitation).The fluorescence emission of the complexes might be attributed to ligand-to-metal charge transfer (LMCT)[22-23].This observation indicates that the complex may be a good candidate for potential photoactive materials.
3 Conclusion
In summary,a novel one-dimensional (1D) cadmium(Ⅱ)coordination polymer with the features an uncommon zigzag chain structure based on ligand (H2C2EIm)and a chelate ligand (BDC)has been synthesized in hydrothermal reaction condition.The successful syntheses of the complex indicate that it is promisingto build up unusualarchitecturesvia transition metals and imidazole-carboxylate ligands. Moreover,the complex displaysblue fluorescent property indicating that the polymer may has potential applications in optical materials.
[1]Nouar F,Eubank J F,Bousquet T,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc., 2008,130:1833-1835
[2]Chun H P,Jung H J.Inorg.Chem.,2009,48:417-419
[3]Ye B H,Tong M L,Chen X M.Coord.Chem.Rev.,2005,249: 545-565
[4]Hill R J,Long D L,Champness N R,et al.Acc.Chem.Res., 2005,38:337-348
[5]Hong M C.Cryst.Growth Des.,2007,7:10-14
[6]Su C Y,Cai Y P,Chen C L,et al.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2003, 125:8595-8613
[7]Blatov V A,Carlucci L,Ciani G,et al.CrystEngComm,2004, 6:378-395
[8]Du M,Jiang X J,Zhao X J.Inorg.Chem.,2006,45:3998-4006
[9]Meng X R,Song Y L,Hou H W,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2003,42: 1306-
[10]He J H,Yu J H,Zhang Y T,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2005,44: 9279-
[11]Lilian L Y W,Madeleine M J.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,1957,79: 5706-5708
[12]Higashi T.Program for Absorption Correction.Rigaku Corporation,Tokyo,Japan,1995.
[13]SHELXTL,Version5.1,Siemens Industrial Automation,Inc., 1997.
[14]Sheldrick G M.SHELXL-97,Program for the Refinement of Crystal Structure,University of Göttingen,Germany,1997.
[15]Cordes M M,Walter J L.Spectrochim Acta A,1968,24(9): 1421-1435
[16]Bellam Y L J.The Infrared Spectra of Complex Molecules:Vol.I/II.London:Chapman and Hall,1980.
[17]Ashiry K O,Zhao Y H,Su Z M,et al.Solid State Sci.,2007,9: 1006-1011
[18]Zhou Z Y,Liu C B,Guo H X,et al.Chemical Journal on Internet,2006,8:65-69
[19]Staszczuk P,Jaroniec M,Gilpin R K.Anal.Chim.Acta,1992, 269:157-163
[20]McGarrah J E,Kim Y J,Hissler M,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2001, 40:4510-4511
[21]Wu Q G,Esteghamatian M,Hu N X,et al.Chem.Mater., 2000,12:79-83
[22]Tao J,Yin X,Jiang Y B,et al.Eur.J.Inorg.Chem.,2003.
[23]Yan Y,Wu C D,Lu C Z.Z.Anog.Allg.Chem.,2003,629: 1991-1996
Hydrothermal Synthesis,Crystal Structure and Photoluminescence of a One-Dimensional Zigzag Chain Cadmium(Ⅱ)Complex:[Cd(BDC)(H2C2EIm)(H2O)]n
FENG Guo-Dong*JIANG Luan ZHAO Wei-Xing WANG Yan LI Zong-Xiao
(Key Laboratory of Functional Coordination Compounds,Department of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Baoji University of Arts and Science,Baoji,Shaanxi 721013,China)
A one-dimensional cadmium(Ⅱ)complex[Cd(BDC)(H2C2EIm)(H2O)]nwith 1,4-benzenedicarbo-xylic acid (BDC)and 2,2′-(ethanediyl)bis(1H-benzimidazole)(H2C2EIm)has been synthesized by means of hydrothermal method and characterized by elemental analysis,thermal analysis,IR spectroscopy and X-ray single-crystal diffraction.The crystal is triclinic,space groupwith a=10.307(5)nm,b=10.907(5)nm,c=11.934(5)nm,α= 63.021(5)°,β=73.308(5)°,γ=79.423(5)°,V=1.143(9)nm3,Dc=1.618 g·cm-3,Z=2,F(000)=560,Goof=1.027,R1= 0.0233,wR2=0.0617.The complex shows a one-dimensional(1D)zigzag chain structure and further extends into a 3D supramolecular structure through N-H…O,O-H…O hydrogen bonding interactions.Luminescent studies show that the complex exhibits intense blue fluorescent emission.CCDC:802048.
cadmium(Ⅱ)complex;crystal structure;1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid;bis(1H-benzimidazole);luminescence
O614.24+2
A
1001-4861(2011)08-1664-05
2010-12-02。收修改稿日期:2011-03-31。
陕西省重点实验室项目(No.2010JS069),宝鸡文理学院重点学科项目(No.zk1020)资助。
*通讯联系人。E-mail:fengguodong00805@163.com
