基于双光子光折变效应的中心对称亮空间孤子的自偏转
2011-09-18杨联弟苏艳丽
杨联弟,苏艳丽
(山西运城学院物理与电子工程系,山西运城 044000)
基于双光子光折变效应的中心对称亮空间孤子的自偏转
杨联弟,苏艳丽
(山西运城学院物理与电子工程系,山西运城 044000)
基于外加电场的双光子中心对称光折变介质,数值研究了中心对称亮孤子的自偏转特性。结果表明:具有双光子效应的中心对称光折变介质中,亮孤子在扩散效应的作用下呈现出与光轴方向反向的自偏转特性;孤子中心偏转距离与外加电场和入射光强等参量相关。随着外加电场的增加,孤子的自偏转距离逐渐加大。亮孤子自偏转距离随着入射光强的增加表现出先增加后减小的非线性变化规律,在孤子半峰全宽最窄处,孤子的自偏转距离存在一最大值。
非线性光学;双光子光折变效应;自偏转
在光折变介质中,空间光孤子的形成源于光折变非线性效应与光束的衍射效应相平衡。光折变非线性效应即光致折射率变化主要有两种机制:一是非中心对称光折变晶体,折射率的非线性变化起因于线性电光效应。在此类光折变晶体中,根据不同的物理机制将孤子分为屏蔽孤子[1-2]、光伏孤子[3-4]和屏蔽光伏孤子[5-6]。二是中心对称光折变晶体,折射率的非线性变化是由二次电光效应支配的。与非中心对称光折变晶体相比,中心对称光折变晶体中的孤子一般需要外加电场,可称之为屏蔽孤子[7-8]。最近,展凯云等人基于Castro-Camus的双光子光折变模型[9],理论预言了中心对称光折变晶体中双光子亮、暗空间孤子[10]和双光子Manakov孤子[11]的存在。本文在忽略损耗的情况下,数值求解演化方程,研究了双光子亮空间孤子在中心对称光折变晶体中的自偏转特性,分析了外加电场和入射光强对自偏转的影响。
1 理论模型
一束只在x方向发生衍射的入射光I2,沿z方向在具有双光子效应的中心对称光折变材料中传播,材料上施加有沿x方向的外加电场。另有一束强度均匀的启动光I1照射晶体侧面,把入射光场I2表示为慢变振幅形式,即E=A(x,z)exp(ikz)。其中k=k0ne=(2π/λ0)ne,ne为材料未受扰动时的折射率,λ0为自由空间中的波长。在上述条件下光波满足如下的演化方程:
式中折射率的变化量Δn满足[7,8]:
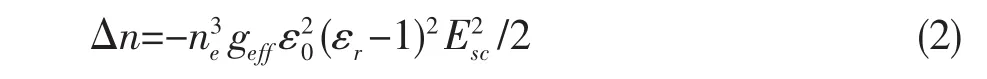
其中,geff为有效二次电光系数,ε0和εr分别为真空和相对介电常数,Esc为介质中的空间电荷场,它可从描述介质的光折变速率方程、电流方程及Poisson方程导出[10]
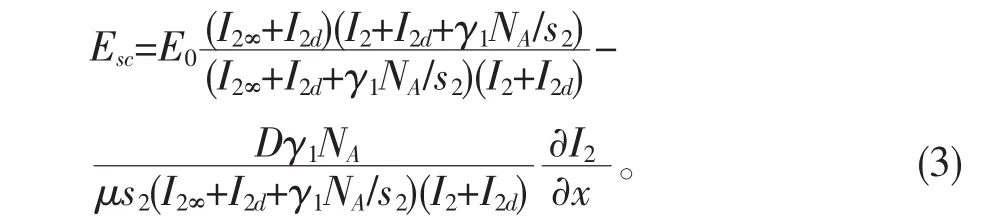
其中,I2d=β2/s2为所谓的暗辐射强度,I2∞代表远离光束横断面中心处的光强,E0为x→±∞处的空间电荷场。把(3)式和(2)式代入方程(1),并采用无量纲变量S=x/x0,及A=(2η0I2d/ne)1/2U,其中,x0为一任意空间宽度,可得光波演化方程
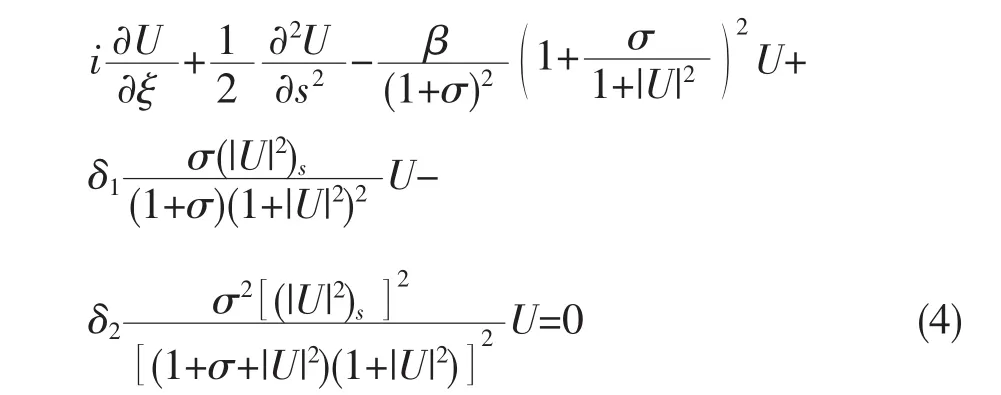
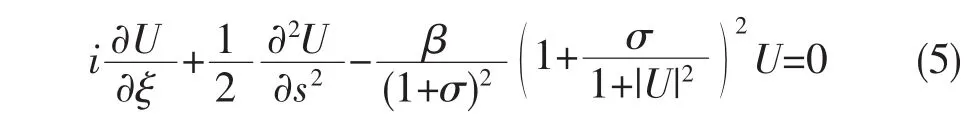
文献[10]给出了满足方程(5)的亮空间孤子解
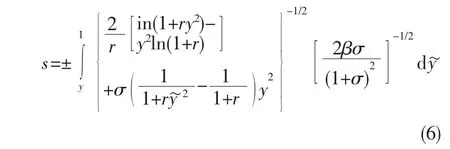
其中,r=I2(0)/I2d,I2(0)为光束的中心光强,y(s)是归一化的实函数(0≥y(s)≥1)。
2 亮空间孤子的自偏转特性
取晶体(KTN)参数[10]:T=295K,ne=2.29,geff=0.136m4C-2,εr=10 000,E0=2×105V/m,λ0=0.633μm,x0=30μm,由以上参数可计算出β=52,δ1=0.44,δ2=9.3×10-4。另取σ=104,r=5,数值求解方程(6)得到亮空间孤子的强度包络,将其作为入射光波,数值求解演化方程(4)得到相应的自偏转特性(图1)。

图1 亮空间孤子的自偏转当β=52,δ1=0.44,r=5
下面从方程(4)出发分析外加电场和入射光强对孤子自偏转的影响。分别取外加电场E0=2×105V/m(β=52),E0=2.5×105V/m(β=81),E0=3×105V/m(β=117)。数值求解演化方程(4)可以得到亮孤子中心自偏转距离随着传播距离的变化关系(图2)。从图2可以看出:随着外加电场的增加,孤子中心的自偏转距离逐渐加大。然后当外加电场取E0=2.5×105V/m时,取不同的入射光强得到图3。发现随着入射光强的增加,自偏转距离首先逐渐增加,并在r=1附近取得偏转的最大值,然后随着入射光强的加大,自偏转距离又逐渐减小。究其原因,我们认为主要是孤子的半峰全宽与入射光强呈现非线性关系,并在r=1附件取得最小值(图4),即在孤子最窄处其自偏转距离最大。
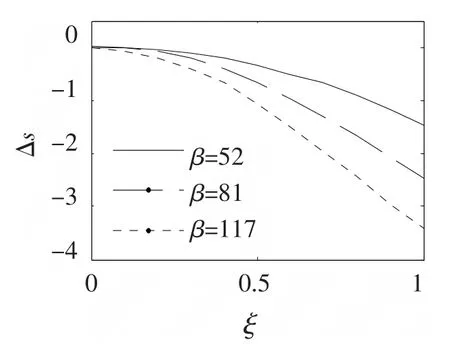
图2 当入射光强r=5,亮孤子中心自偏转距离与外加电场的关系

图3 当外加电场亮孤子中心自偏转距离与入射光强的关系

图4 当外加电场β=81,亮孤子半峰全宽随入射光强的变化曲线
3 结论
数值研究了具有双光子效应的中心对称光折变晶体中亮空间孤子的自偏转特性。结果表明,考虑扩散效应时,亮空间孤子在晶体中会发生自偏转现象,其自偏转距离与外加电场和入射光强有关。随着外加电场的增加,孤子的自偏转距离逐渐加大;随着入射光强的增加,孤子的自偏转距离呈现出先增加后减小的非线性关系。
[1]Segevm,Valley G C,Crosignani B,et al.Steady-state spatial screening solitons in photorefractive materials with external applied field[J].Phys Rev Lett,1994,73(24):3211-3214.
[2]Shih M F,Segevm,Valley G C,et al.Observation of two-dimensional steady-state photorefractive screening solitons[J].Electron Lett,1995,31(10):826-827.
[3]Valley G C,Segevm,Crosighani B,et al.Dark and right photovoltaic solitons[J].Phys Rev A,1994,50(14):R4457-R4460.
[4]Tayam,Bashaw M C,Fejermm,et al.Observation of dark photovoltaic spatial solitons[J].Phys Rev A,1995,52(4):3095-3100.
[5]Liu J S,Lu K Q.Screening-photovoltaic spatial solitons in biased photovoltaic photorefractive crystals and their self-deflection[J].J Opt Soc Am B,1999,16(4):550-555.
[6]Fazio E,Renzi F,Rinaldi R,et al.Screening-photovoltaic bright solitons in lithium niobate and associated single-mode waveguides [J].Appl Phys Lett,2004,85(12):2193-2195.
[7]Segevm,Agranat A J.Spatial solitons in centrosymmetric photorefractive media[J].Opt Lett,1997,22(17):1299-1301.
[8]Delre E,Crosignani B,Tamburrinim,et al.One-dimensional steady-state photorefractive spatial solitons in centrosymmetric paraelectric potassium lithium tantalite nilbate[J].Opt Lett,1998,23(6):421-423.
[9]Castro-Camus E,Magana L F.Prediction of the physical response for the two-photon photorefractive effect[J].Opt Lett,2003,28(13):1129-1131.
[10]Zhan K Y,Hou C F,Hao T,et al.Spatial solitons in centrosymmetric photorefractive crystals due to the two-photon photorefractive effect[J].J Opt,2010,12:015203.
[11]Zhan K Y,Hou C F,Hao T,et al.Manakov solitons in centrosymmetric photorefractive crystals due to two-photon photorefractive effect[J].Phys Lett A,2010,374:1242-1245.
〔编辑 李海〕
The Self-deflection of Centrosymmetric Bright Spatial Solitons based on the Two-photon Photorefractive Effect
YANG Lian-di,SU Yan-li
(Department of Physics and Electronics Engineering,Yuncheng University,Yuncheng Shanxi,044000)
The self-deflection characteristics of bright spatial solitons in biased two-photon centrosymmetric photorefractive crystals are studied numerically.The results show that the bright solitons possesses a self-deflection process in the direction opposite to the crystal's axis during propagation in two-photon centrosymmetric photorefractive crystals.The self-deflection distance of the bright solitons is relation to the external electric field and the input light intensity.The absolute value of the self-deflection increases as the external electric field increases.The relation of the self-deflection distance of bright solitons and the input light intensity is nonlinear.The absolute value of the self-deflection increases first,reaches its maximum value at aminimum value of the FWHM,then decreases as light intensity rises.
nonlinear optics;two-photon photorefractive effect;self-deflection
O437
A
1674-0874(2011)03-0027-03
2011-04-02
杨联弟(1964-),女,山西运城人,实验师,研究方向:物理实验及光学。
