柔性多羧酸配体锶配合物的合成、晶体结构及拓扑学分析
2011-09-16彦汪快兵陈友存刘光祥
王 彦汪快兵陈友存刘光祥
(1安庆师范学院化学化工学院,安徽省功能配合物重点实验室,安庆246011)(2南京大学配位化学国家重点实验室,南京210093)
柔性多羧酸配体锶配合物的合成、晶体结构及拓扑学分析
王 彦*,1,2汪快兵1陈友存1刘光祥1
(1安庆师范学院化学化工学院,安徽省功能配合物重点实验室,安庆246011)
(2南京大学配位化学国家重点实验室,南京210093)
利用水热合成制备了一个新颖的基于柔性多羧酸配体的碱土金属配合物Sr(BuTA)0.5(H2O)2(1)(H4BuTA=1,2,3,4-丁四酸)。利用元素分析及X-射线单晶衍射对其进行了表征。结构分析结果表明标题化合物1属于单斜晶系,P21/c空间群,晶胞参数为a=0.87003(5)nm,b=0.79303(5)nm,c=1.26807(5)nm,β=127.689(3)°,晶胞体积V=0.69236(7)nm3,Z=4,Dcalc=2.290 g·cm-3,F(000)= 468,μ=7.768 cm-1,R=0.0158,wR=0.0377。在化合物1中,每个Sr(Ⅱ)的配位环境为八配位的反四棱柱配位构型。在配合物中金属和配体互相连接形成一个三维的框架结构,其拓扑为(46)2(412.612.84)。在其结构中配体是少见的八连接点。对配合物1的热稳定性也做了测试。
晶体结构;锶配合物;拓扑;羧酸配体
Recently,one of the most-watched areas in coordination chemistry is the mimicking of topologies of natural minerals and the constructions of novel complexes with new topologies[1-6].Various MOFs with fascinating structural diversities as well as their interesting properties have been synthesized by theself-assembly of suitable metal salts with rigid or flexible ligands[7-9],among which the carboxylic ligands have been widely investigated,owing to the diversity of the binding modes of carboxylate group to metal atom[10-12].Meanwhile,the use of five-,seven-,or eightconnected blocks are quite rare with comparing to the connectivity of three-,four-,or six-connected blocks, probably due to the limitations in the symmetry or steric hindrance associated with connected nodes[13-15].
On the other side,the literature survey shows a certain number of GroupⅡcoordination architectures in the literature with a growing interest in the area of coordination polymers and host/guest chemistry[16]. With comparable oxidation states and atomic radii to divalent transition metals and rare earth metals,the alkaline earth metals could,in principle,lead to similar networks in the solid states.In this paper,we report a novel alkaline earth metal coordination complex with flexible multi-carboxylate ligand,namely Sr(BuTA)0.5(H2O)2(1)(H4BuTA=1,2,3,4-Butanetetracarboxylic acid),as well as its topological analysis.
1 Experimental
1.1 General
All commercially available chemicals are of reagent grade and used as received without further purification.Solvents were purified according to the standard methods.C,H and N analyses were made on Elementar Vario EL-Ⅲelemental analyzer.Thermogravimetric and differential thermal analyses were performed on a simultaneous NETZSCH STA 409 PC LUXX thermal analyzer.Powder samples were loaded into alumina pans and heated under N2at a heating rate of 20℃·min-1.
1.2 Structure determ inations
A suitable colorless single crystal of 1 with dimensions of 0.30 mm×0.10 mm×0.10 mm was selected for data collection at 293 K,using a Bruker Smart ApexⅡCCD equipped with a Mo Kα radiation (λ=0.071 073 nm).The structures were solved by direct methods using SHELXTL and refined by fullmatrix least-squares methods anisotropically for nonhydrogen atoms[17].The hydrogen atoms except for those of water molecules were generated geometrically. Calculations were performed on a personal computer with the SHELXTL program package[17].The details of the crystal parameters,data collection and refinement for the compounds are summarized in Table 1,and selected bond lengths and angels with their estimated standard deviations of 1 are listed in Table 2.
CCDC:825571.
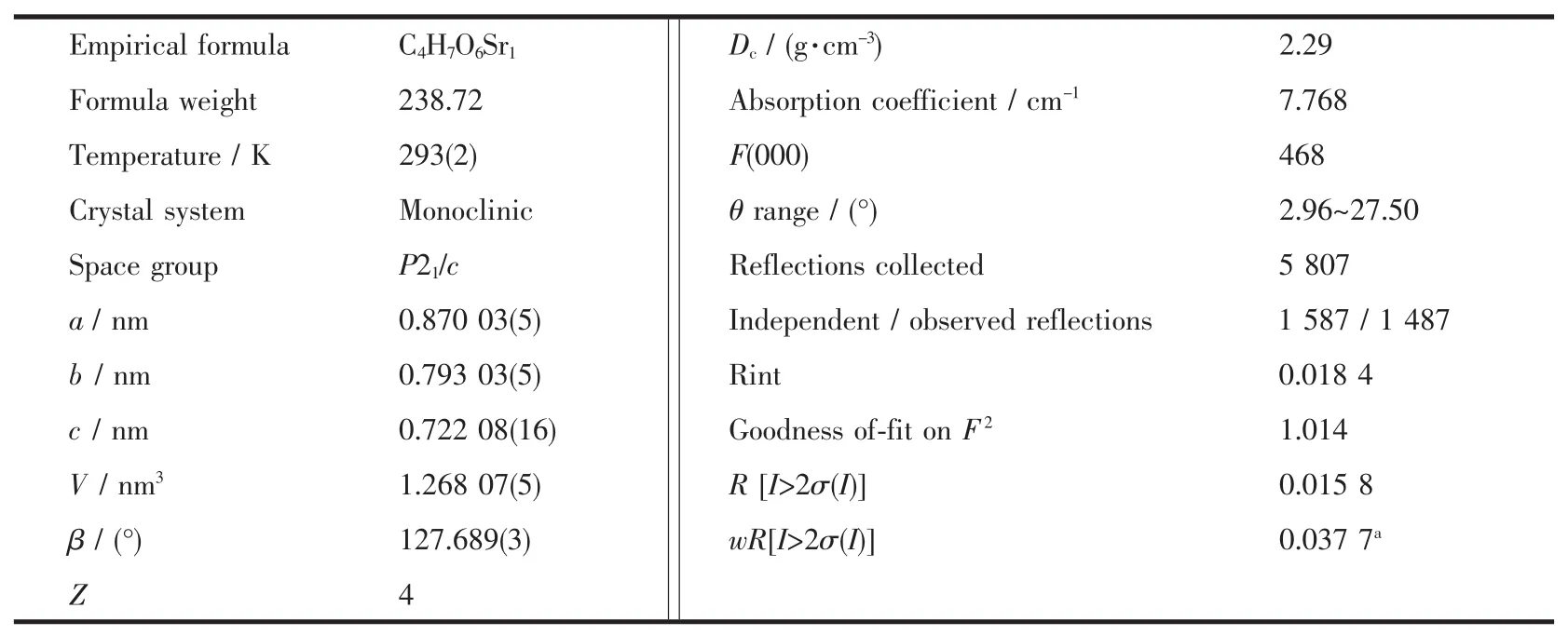
Table 1 Crystallographic data for com plex 1

Table 2 Selected bond lengths(nm)and bond angles(°)for comp lex 1

Symmetric code:#1:-x+2,-y+1,-z+1;#2:x-1,-y+1.5,z-0.5;#3:-x+2,y-0.5,-z+1.5.
1.3 Synthesis of Sr(BuTA)0.5(H2O)2(1)
Complex 1 was synthesized by hydrothermal method.A mixture of SrCl2(63.4 mg,0.4 mmol), H4BuTA(47.2 mg,0.2 mmol),KOH(44.9 mg,0.8 mmol)and H2O(10 mL)was placed in a 25 mL Teflon-lined stainless steel autoclave,and the autoclave was sealed,heated to 140℃for 48 h.After the mixture was cooled to room temperature,colorless column crystals of 1 were filtered and wash by H2O. Yield:56%.Anal.Calcd.for compound 1,C4H7O6Sr1: C,20.12;H,2.96.Found:C,20.86;H,4.65;H,2.77.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Structure description
Complex 1 was offered by treatment of SrCl2with the potassium salt of H4BuTA ligand in water by hydrothermal method and crystallized in monoclinic system,space group P21/c.As shown in Fig.1,there are one Sr(Ⅱ)ion,half BuTA2-anion and two coordination water molecules in the asymmetric unit of 1.The Sr(Ⅱ)center is eight-coordinated,where six of the eight sites are coordinated by six carboxylic oxygen atoms from four different BuTA2-ligands and two water molecules with Sr-O bond lengths varying from 0.25454(12)to 0.26853(12)nm,and the O-Sr-O bond angles around Sr(Ⅱ)ions are in the range of 48.82(3)° to 157.61(4)°,which is comparable to the reported ones in other strontium complexes[18-19].Thus,the coordina tion geometry of the Sr(Ⅱ)center can be regarded as a distorted square-antiprismatic geometry.In complex 1,each BuTA2-ligand coordinates to eight Sr(Ⅱ)ions, where there are two kinds of carboxylate group with different coordination modes(Fig.2).The first one coordinates to three Sr(Ⅱ)ions with μ3-η2∶η2mode(e.g. carboxylate group containing O3,O4),while the otherscoordinate to two Sr(Ⅱ)ions with μ2-η1∶η1mode(e.g. carboxylate group containing O1,O2).All these results above indicate that the carboxylate group have varied coordination modes.It is also notable that two Sr atoms are linked by μ-O atoms(O4),to give rise to a planar four-membered rings with Sr…Sr distance of 0.426 nm,indicating weak Sr…Sr interactions in 1[20].

Fig.1 Coordination environment around Sr(Ⅱ)center in complex 1 with atom numbering scheme where the hydrogen atoms were omitted for clarity

Fig.2 Coordination mode of BuTA2-ions in complex 1
In complex 1,with ignoring the coordination effect of carboxylate group containing O1 and O2,six Sr(Ⅱ)atoms were linked by carboxylate groups containing O3,O4 atoms to form a M6hexagon with Sr-Sr average distance of 0.47 nm.The hexagonal unit spread to form a 2D network,in which the ligands act as 6-connecting spots,and the metal centers are 3-connected(Fig.3).Thus,the network of 1 can be described as 2-nodal net of(43)2(46.66.83) topology,whose“long”Schlfli symbol is(4.4.4)2(4.4.4.4.4.4.62.62.62.62.62.62.88.88.88)(Fig.3).Furthermore,with the coordination of carboxylate groups containing O1 and O2,the 2D nets of 1 were expanded to a 3D framework.In the 3D framework of 1,each BuTA2-anion connects eight Sr(Ⅱ)atoms, which can be simplified as 8-connected spot.While each metal ion links four different BuTA2-ions,so it can be regarded as 4-connected spot.With this simplification of ligands and metal centers,the 3D framework of complex 1 can be topologically described as 2-nodal structure of(46)2(412.612.84)topology with“long”Schlfli symbol of(4.4.4.4.4.4)2(4.4.4.4. 4.4.4.4.4.4.4.4.64.64.64.64.64.64.64.64.64.64.64.64.824.824.824. 824)(Fig.4).

Fig.3(Left)2D net of complex 1,where the M6hexagonal unit was showed by blue lines;(Right)Simplified 2D topological net in complex 1,in which the BuTA2-were represented by smaller balls and the Sr(Ⅱ)atoms by bigger ones

Fig.4 Schematic drawing of 3D 2-nodal net of(46)2(412.612.84)topology in 1,in which the ligands and Sr髥atoms are represented by eight-and four-spokes radiation from a solid point, respectively
2.2 Thermogravimetric analysis
The Thermogravimetric analysis of complex 1 was carried out in the range 20~800℃under nitrogen atmosphere.The TGA data show that the initial weight loss of 15.4%(calcd.15.1%)occurred from 60 to 140℃corresponding to the loss of the coordinated water molecules.The second weight loss begins at 340℃.where the decomposition of the residue starts.
[1]Wang X W,Dong Y R,Zheng Y Q,et al.Cryst.Growth Des.,2007,7:613-615
[2]WANG Xiao(王潇),HOU Xian-Yang(侯向阳),FU Feng(付峰),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(Wuji Huaxue Xuebao),2010,27(1):174-178
[3]Wang Z,Zhang B,Otsuka T,et al.Dalton Trans.,2004:2209 -2216
[4]Abrahams B F,Haywood M G,Bobson R,et al.Angew.Chem. Int.Ed.,2003,42:1112-1115
[5]Mellot-Draznieks C,Dutour J,Ferey G.Angew.Chem.Int. Ed.,2004,43:6290-6296
[6]FU Hai-Ping(傅海萍),LIN Jin-Xiang(林景祥),HU Hai-Chun (胡海春),et al.Chinese J.Struct.Chem.(Jiegou Huaxue), 2010,29:686-689
[7]James S L.Chem.Soc.Rev.,2003,32:276-288
[8]Férey G,Mellot-Draznieks C,Serre C,et al.Acc.Chem.Res., 2005,38:217-225
[9]Constable E C.Coord.Chem.Rev.,2008,252:842-855
[10]Dalgarno S J,Power N P,Atwood J L.Coord.Chem.Rev., 2008,252:825-841
[11]LIN Zhen-Zhong(林郑忠),CHEN Lian(陈莲),YUE Chen-Yang(岳呈阳),et al.Chinese J.Struct.Chem.(Jiegou Huaxue),2010,29:142~145
[12]Athar M,Li G H,Shi Z,et al.Solid State Science,2008,10: 1853-1859
[13]Moulton B,Lu J,M.Zaworotko J.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2001, 123:9224-9225
[14]Chun H,Kim D,Dybtsev D N,et al.Angew.Chem.Int. Ed.,2004,43:971-974
[15]Luo T T,Tsai H L,Yang S L,et al.Angew.Chem.Int.Ed., 2005,44:6063-6067
[16]Starosta W,Leciejewicz J,Premkumar T,et al.J.Coord. Chem.,2007,60:313-318
[17]XSCANS,Version 2.1,Siemens Analytical X-ray Instruments, Madison,WI,1994.SHELXTL,Version 5.0,Siemens Industrial Automation,Analytical Instruments,Madison,WI, 1995.
[18]ZHENG Hong(郑红),ZHANG Tong-Lai(张同来),ZHANG Jian-Guo(张建国),et al.Chinese J.Inorg.Chem.(Wuji Huaxue Xuebao),2006,22(2):346-350
[19]Dan M,Cheetham A K,Rao C N R.Inorg.Chem.,2006,45: 8227-8238
[20]Zhu H F,Zhang Z H,Sun W Y,et al.Cryst.Growth Des., 2005,5:177-182
Syntheses,Characterization,and Topological Analysis of an Alkaline Earth M etal-Organic Frameworks w ith Flexible M ulti-Carboxylic ligand
WANG Yan*,1,2WANG Kuai-Bing1CHEN You-Cun1LIU Guang-Xiang1
(1School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering,Anhui Key Laboratory of Functional Coordination Compounds,
Anqing Teachers College,Anqing,Anhui 246011,China)
(2State Key Laboratory of Coordination Chemistry,Nanjing University,Nanjing 210093,China)
A alkaline earth metal-organic complex,namely,Sr(BuTA)0.5(H2O)2(1)(H4BuTA=1,2,3,4-Butanetetracarboxylic acid),was obtained in water system by hydrothermal method based on flexible multi-carboxylate ligand.The title complex was characterized by elemental analysis and X-ray crystallography.The result of structural analysis shows that the complex 1 crystallizes in monoclinic,space group P21/c with a=0.870 03(5)nm, b=0.79303(5)nm,c=1.26807(5)nm,β=127.689(3)°,V=0.69236(7)nm3,Z=4,Dc=2.290 g·cm-3,F(000)=468,μ= 7.768 cm-1,the final R=0.015 8,wR=0.037 7.In complex 1,the coordination environment of Sr(Ⅱ)is eightcoordinated with square antiprismatic geometry.The metal ions and ligands link each other to form a 3D framework of(46)2(412.612.84)topology,in which the BuTA2-anions act as rare 8-connected topological blocks.The thermal stability of complex 1 was also investigated.CCDC:825571.
crystal structure;Sr(Ⅱ)complex;topochemistry;carboxylate ligand
O614.23+2
A
1001-4861(2011)11-2303-05
2011-05-17。收修改稿日期:2011-07-05。国家自然科学基金(No.20901004)资助项目。
*通讯联系人。E-mail:njwangy@live.com
