Preparation and Characterization of Diblock Copolymer Micelles from Aqueous Solution
2011-06-04LIUXiaotianLIUChuanshengLIYongmeiWANGLishen
LIU Xiao-tian LIU Chuan-sheng LI Yong-meiWANG Li-shen
(College of Chemistry and Environmental Engineering,Dongguan University of Technology,Dongguan 523808,China)
Preparation and Characterization of Diblock Copolymer Micelles from Aqueous Solution
LIU Xiao-tian LIU Chuan-sheng LI Yong-meiWANG Li-shen
(College of Chemistry and Environmental Engineering,Dongguan University of Technology,Dongguan 523808,China)
Enzymatic polycondensation of benzyl-2,2-bis(methylol)propionate and sebacic acid has been performed by using lipase Novozyme-435 as a catalyst,subsequently enzymatic ring-opening polymerization is reacted by adding ε-caprolactone as the monomer in the same system.The reaction monitoring results indicates that two different modes of polymerization,as above mentioned,successively take place through enzyme catalysis in one-pot to produce the block copolymer successfully.The self-assembly of the copolymer into aggregation micelles in aqueous media is determined by dynamic light scattering(DLS)and the morphology of these solventless micelles is observed by atomic force microscopy(AFM).
enzymatic;self-assembly;diblock copolymer
Biography:LIU Xiao-tian(born in 1975),male,Changchun Jilin,Lecturer,Majored in Synthesis and Preparation of Biodegradable Medical Materials.
1 Introduction
Studies of enzymatic ring-opening polymerization(ROP)have been conducted for the polymerization of lactone monomers with ring size ranging from small(four-membered)to medium(six-and seven-membered)as well as macrolides(12-,13-and 16-membered).And researches on lipase-catalyzed polycondensation focused primarily on reactions between diols and diacids/activated diacids.Prominent examples of activated ester groups used include bis(2,2,2-trichloroethyl)and vinyl esters leaving groups to obtain polyesters[1-6].However,activation of diacids with such groups is expensive and limits the potential technological impact of these methods.Important progress has been made in lipase-catalyzed polycondensation of diols and diacids monomers using nonactivated free acids in the presence and absence of solvents[7].
A combination of different modes of polymerization is a promising way for preparation of polymers with novel structure.However,it is generally difficult that more than two modes of polymerization take place in one-pot to form copolymers since the reaction mechanism and conditions are normally different with each other.Fortunately,lipase-catalyzed polycondensation and ring-opening polymerization(ROP)proceed via the similar reaction intermediates(“acyl-enzyme intermediates”).
As it is mentioned above,activated ester groups are expensive and limited,we try to utilize diacids instead of activated diesters by using lipase catalyst to obtain ester copolymers.This paper reports on the Novozyme-435 catalyze copolymerization of diol with benzyl ester as a side chain,sebacic acid and ε-caprolactone(ε-CL)via combining polycondensation and ROP.Enzymatic polycondensation of the diol and sebacic acid reacts in vacuum to achieve the intermediate product,and its terminal hydroxyl group initiated ROP of ε-CL in succession.And self-assembly of the resulting copolymer into polymeric micelles in aqueous media was investigated with DLS in liquid media,and the solventless micelles on a solid substrate were observed by AFM in tapping mode.
2 Experimental Section
2.1 Materials
Novozyme-435(specific activity 7000 PLU/g)was purchased from Nordisk A/S and employed directly without further purification.ε-caprolactone(ε-CL ,AR grade)was provided from Aldrich Chemical Co.and distilled over CaH2at reduced pressure prior to use.Sebacic acid(AR grade)was obtained from Beijing Chemical Co.and recrystallized twice in ethanol before use.Tolune(Tianjin Chemical Co.)was freshly distilled from Sodium.Benzyl-2,2-bis(methyol)propionate was synthesized and characterized as described previously[8].All the reagents used in this study were of analytic grade.
2.2 Instruments
Molecular weights and molecular weight distributions of polyesters were determined by a Waters 410 Gel permeation chromography(GPC)apparatus equipped with a 10-μm Styregel HT6E Column(300 mm ×7.8 mm)using linear polystyrene standards.And THF was used as the eluent at a flow rate of 1 mL/min.Mean diameter and size distribution of prepared micelles were determined by the dynamic light scattering(DLS)method using a Brookheaven BI9000AT system(Brookheaven Instruments Corporation,USA).The measurement was averaged in five runs at 25℃ with a detector angle of 90°.The atomic force microscopy(AFM)observation of the surface was carried out with the commercial instrument(Digital Instrument,NanoscopeⅢa,Multimode).And the tapping mode images were taken at room temperature in air with the microfabricated rectangle crystal silicon cantilevers(Nanosensor).The topography images were obtained at a resonance frequency of approximate 365 kHz for the probe oscillation.
2.3 General Procedure for Diblock Copolymer Synthesis
Monomers benzyl-2,2 -bis(methyol)propionate and sebacic acid were added into a flask and stopped with a rubber septum,further sealed and heat to 70℃ in vacuum.After that,the flask was backfilled with argon,and ε-CL in tolune solvent was added under argon stirring at the same temperature of the polycondensation reaction.Then,the reaction was terminated by pouring the reactants into cold chloroform,and the enzyme was removed by filtration(glass-fritted filter,medium porosity).The filtrate was concentrated with rotary evaporation and precipitated in excess methanol to give the product copolymer.Polymeric micelles were formed from the resulting diblock copolymer in water.They were prepared by the dissolution of the copolymer in tetrahydrofuran,followed by the progressive addition(1 drop/5s)of deionized water under sonication at room temperature.Then the mixture was sonicated for 1 h continuously after completion of water addition.The mean diameter and the size distribution of the prepared micelles in the solution were determined by DLS.And one drop of the solution was cast on a silicon wafer surface through a burette,AFM was used to study the surface morphology of the micelles after complete evaporation of solvent at room temperature and ordinary pressure.
3 Results and Discussion
3.1 Synthesis of the Block Copolymer
Previous studies on the synthesis of polyesters using enzymes of different origin showed Novozyme-435 is the preferred lipase-catalyst for polymerization of(non)activated acids with alcohols and by ring-opening of lactones.Based on the above reasons,biocatalyst Novozyme-435 appeared the most promising to catalyze the cascade synthesis combining of polycondensation and ring-opening polymerization(ROP).
Early reports indicated that the best reaction conditions of Novozyme-435-catalyzed polycondensation between diacids and diols were carried out in bulk under vacuum.Since there’s little or no change for reaction temperatures varying from 65 to 90℃ in similar system,70℃ was used throughout these studies[8].In the present work,we found that benzyl-2,2-bis(methyol)propionate didn’t liquate like other studied aliphatic diols(e.g.1,3-propanediol,1,10-decanediol)at 70℃,so tolune was selected to be the solvent of diols/diacids polymerization reaction(70℃,16 h)at ordinary pressure to yield the corresponding oligomer firstly.The product oligomer was further polymerized in bulk by reducing the pressure to 0.5 mmHg at the same temperature,the degree of polymerization(DPavg)of condensation polyester was increased with reaction time by removing produced water of polycondensation.Until the predetermined reaction time(24 h in bulk),the reaction flask was filled with argon,and then a sample was taken for GPC.We found that the average degree of polymerization(DPavg)of the polycondensation product was ca.9.5,which was calculated from Mnof the GPC result utilizing the calculation method mentioned by Gross et al[9].Previous description of lipase-catalyzed condensation polyesters implicated their end-group structure comprising hydroxyl and carboxylic groups,and the hydroxyl group was capable of initiating lipase-catalyzed ring-opening polymerization of lactones.Therefore,the condensation product polyester as a macroinitiator could be used to initiate ε-caprolactone(ε-CL)with the catalyst Novozyme-435.Previous studies revealed that tolune was the most effective solvent at 70℃to result in relatively the highest percent monomer coversion and moderate molecular weights on Novozyme-435 catalyzed ε-CL polymerization,and the best ratio of tolune to ε-CL was considered about 2∶1(v/v)[10].The enzymatic ROP reaction was conduct consecutively in one pot without an intermediate workup step by addingε-CL to the same flask.Due to the removal of water caused by first step condensation reaction,the side reaction of initiating ROP by water could be minimized effectively.
3.2 DLS and Mophology Observation
Amphiphilic block copolymers could usually form core-shell type micelles in aqueous solution due to their amphiphilic characteristic.In this case,the polymeric micelles formed by the resulting copolymer in water were expected to be composed of the polyester with phenyl side groups block as the core and the PCL block as the surrounding shell,since the former block had relatively more hydrophobic capability than the latter.The particle size(mean diameter,202.5 nm)and the fairly low polydispersity(0.146)in aqueous solution were determined by DLS and illustrated in Figure 1.
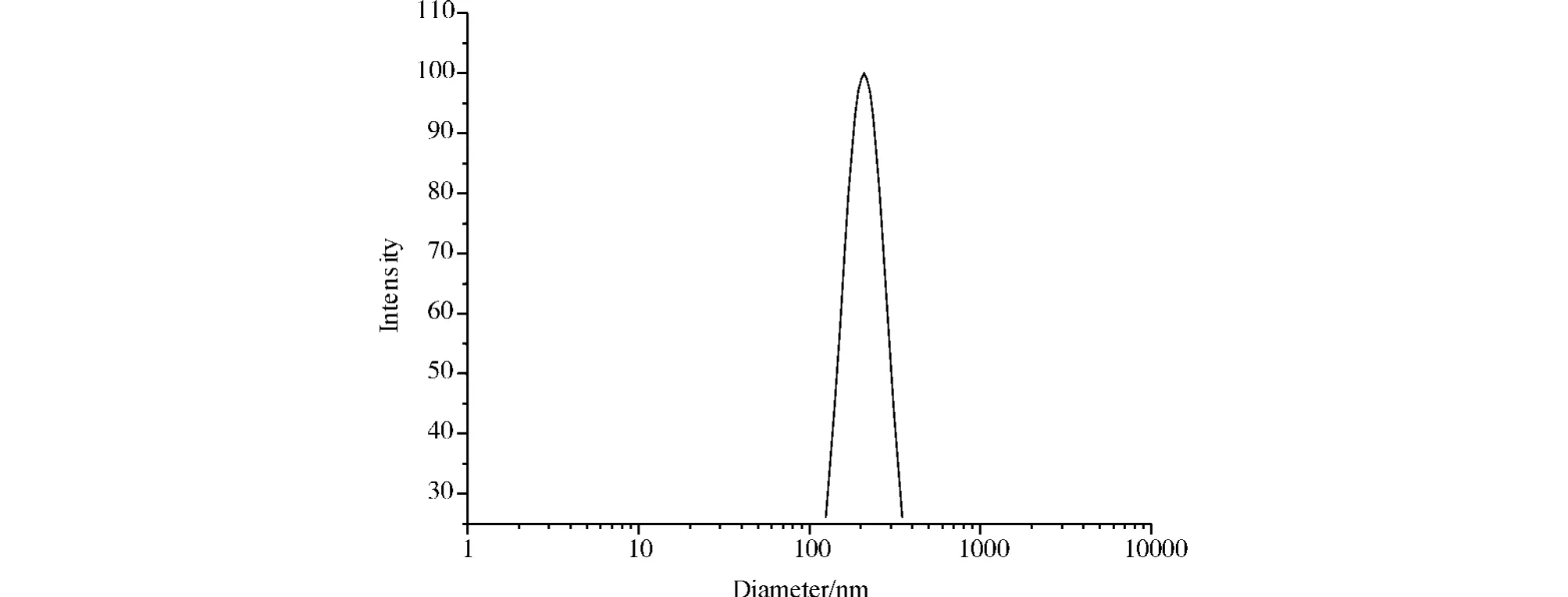
Figure 1 Size distribution of the resulting copolymer micelles measured by DLS
To have a more accurate description of the micellar size and its morphology directly,the thin films covered with solventless micelles were studied by AFM in tapping mode.Figure 2 showed the AFM image of the resulting polymeric micelles were spherical with a very narrow size dispersity,and they exhibited an average diameter equal to about 158 nm.The diameters of the micelles shown in the AFM image were slightly smaller than those obtained from DLS measurements,this difference was possible to originate from the absence of the solvent in AFM observation.
4 Conclusions
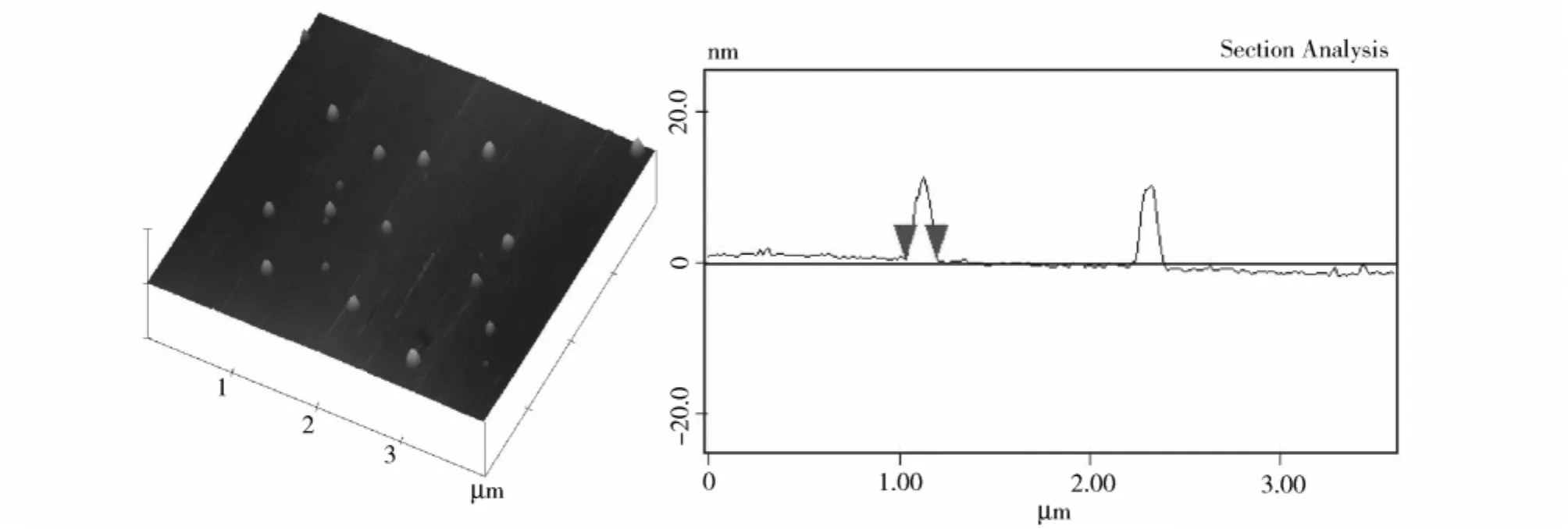
Figure 2 Three-dimension height images and the cross section of micelles formed by self-assembly of the resulting copolymer on the silicon sureface
This paper described how to combine two different types of polymerization,polycondensation and ring-opening polymerization,which successively occurred in one-pot by using lipase as the catalyst.The lipase-catalyzed polycondensation between the diol and diacid substrates produced the corresponding polyester which had chain ends of hydroxyl and carboxyl with the hydroxyl subsequently initiating lactone in-situ to yield the final copolymer product.And the self-assembly of the copolymer into aggregation micelles in aqueous media was determined by dynamic light scattering(DLS)and the morphology of these solventless micelles was observed by atomic force microscopy(AFM).
[1]Gross R A,Kumar A,Kalra B.Polymer Synthesis by In Vitro Enzyme Catalysis[J].Chem Rev,2001,101:2097 -2124.
[2]Kobayashi S,Uyama H,Kimura S.Enzymatic Polymerization[J].Chem Rev,2001,101:3793 -3818.
[3]Indra K Varma ,Ann-Christine Albertssonb,Ritimoni Rajkhowa,et al.Enzyme catalyzed synthesis of polyesters[J].Prog Polym Sci,2005,30:949-981.
[4]Ajay Kumar,Richard A Gross.Candida antartica Lipase B Catalyzed Polycaprolactone Synthesis:Effects of Organic Media and Temperature[J].Biomacromolecules,2000(1):133 -138.
[5]Wallace J S,Morrow C J.Biocatalytic synthesis of polymers:Synthesis of an optically active,epoxy-substituted polyester by lipase-catalyzed polymerization[J].Polym.Chem,1989,27:2553 -2567.
[6]Wang Y F,Lalonde J J,Momongan M,et al.Lipase-catalyzed irreversible transesterifications using enol esters as acylating reagents:preparative enantio-and regioselective syntheses of alcohols,glycerol derivatives,sugars and organometallics[J].J Am Chem Soc,1988,110:7200 -7205.
[7]Binns F,Harffey P,Roberts S M,et al.Studies of lipase-catalyzed polyesterification of an unactivated diacid/diol system[J].J Polym Sci Part A:Polym Chem,1998,36:2069-2079.
[8]Kobayashi S,Uyama H,Namekawa S.Enzymatic Synthesis of Polyesters from Lactones,Dicarboxylic Acid Divinyl Esters,and Glycols through Combination of Ring-Opening Polymerization and Polycondensation[J].Biomacromolecules,2000(1):335 -338.
[9]Ihre H,Hult A,Soderlind E.Synthesis,Characterization,and1H NMR Self-Diffusion Studies of Dendritic Aliphatic Polyesters Based on 2,2-Bis(hydroxymethyl)propionic Acid and 1,1,1-Tris(hydroxyphenyl)ethane[J].J Am Chem Soc,1996,118:6388 -6395.
[10]Rajiv K Srivastava.Ann-Christine Albertsson,Enzyme-Catalyzed Ring-Opening Polymerization of Seven-Membered Ring Lactones Leading to Terminal-Functionalized and Triblock Polyesters[J].Macromolecules,2006,39:46 -54.
水溶液中两嵌段共聚物胶束的制备与表征
刘啸天 刘传生 李永梅 王励申
(东莞理工学院 化学与环境工程学院,广东东莞 523808)
利用Novozyme-435酶催化2,2-双(羟甲基)丙酸苄基酯与癸二酸的缩聚反应,再在同一体系中加入己内酯进行酶催化开环反应。反应监测结果表明了,利用酶催化,两种不同的聚合反应在同一反应容器中成功进行并生成了嵌段聚合物。利用动态光散射仪测定了此嵌段聚合物在水溶液中的自组装形成胶束的行为,并利用原子力显微镜观察了固定化后的胶束的形貌。
酶催化;自组装;双嵌段共聚物
TQ460.34
A
1009-0312(2011)05-0035-05
2011-07-08
东莞市科技局高等院校科研机构项目提供资金支持 (项目编号:201010814007)。
刘啸天 (1975—),男,吉林省长春人,讲师,主要从事可降解医用材料的合成与制备研究。
date:2011-07-08
Supported by the Science Foundation of Dongguan(No.201010814007).
