植物钙依赖性蛋白激酶的进化和功能研究进展
2010-09-29耿帅锋赵永亮李爱丽王卫国
耿帅锋,赵永亮*,李爱丽,毛 龙,王卫国,李 磊
(1.河南工业大学生物工程学院,河南郑州 450001;2.中国农业科学院作物科学研究所,北京 100081)
植物钙依赖性蛋白激酶的进化和功能研究进展
耿帅锋1,赵永亮1*,李爱丽2,毛 龙2,王卫国1,李 磊1
(1.河南工业大学生物工程学院,河南郑州 450001;2.中国农业科学院作物科学研究所,北京 100081)
钙离子是植物细胞信号转导的第二信使,植物钙依赖性蛋白激酶 (CDPK)作为钙离子的感受器,在植物调控自身代谢及其对外界环境的适应性中具有重要作用.对植物中 CDPK的结构特性、进化特性、分布及表达特性,以及 CDPK在植物中的功能进行了概述,旨在为今后培育能抵御多种逆境胁迫,并兼具广谱抗病性的新品系提供参考依据.
钙依赖性蛋白激酶;结构;进化;功能
0 前言
所有生物体都依赖于复杂的信号传递网络来调控自身代谢及其对外界环境的适应性.在众多的信号传递路径中,钙离子作为一个普遍的二级信使发挥着重要作用[1-3].在植物中已经鉴定的Ca2+结合蛋白主要有 4种:钙依赖性蛋白激酶(calcium-dependent protein kinase,CDPK)、钙调素(calmodulins,CaM)、钙 /钙调素依赖性蛋白激酶(CCaMKs)以及钙调磷酸酯酶 B类蛋白 (calcineurin B-like proteins,CBL).其中 CDPK是植物和原生动物中所特有的 Ca2+离子结合蛋白,在钙离子介导的信号传递路径中扮演着关键角色[4].
1 植物钙依赖性蛋白激酶的结构特性
在植物中,CDPK具有明显的结构特征,从蛋白质的N端到 C端,存在 4个典型的结构域,即N末端可变区、蛋白激酶结构域、自抑区和类钙调蛋白结构域[5].
植物 CDPK的 N末端为可变区,通常由 20~200个氨基酸残基组成,且在氨基酸水平上的同源性很低,不同种属间该区域的氨基酸残基数量变化较大,保守性差.
与N末端可变区相连的蛋白激酶结构域通常由 300多个氨基酸残基组成,该区域中具有典型的 Ser/Thr蛋白激酶的催化保守序列,不同种属或不同成员之间具有较高的同源性.
自抑区紧连蛋白激酶结构域,由 20~30个氨基酸残基组成,在 CDPK中的各类功能区中最为保守,富含碱性氨基酸,具有以底物方式与蛋白激酶结构域结合进而表现自抑制特征的能力.当Ca2+低于某一浓度时,自抑区与蛋白激酶结构域结合,使其激酶活性受到抑制;当 Ca2+高于某一浓度时,自抑区对蛋白激酶结构域的抑制解除,使其具有激酶活性[6].
类钙调蛋白结构域是与 Ca2+结合的区域,含有一段结构和功能类似于 CaM的氨基酸序列,包括 4个与 Ca2+结合的 EF手型结构,通过该手型结构使 CDPK与 Ca2+高度亲和[5,7].类钙调蛋白结构域也是 CDPK有别于其他类型激酶的特有区域,但该区域保守性差[8].分子进化研究的结果显示,早期植物种属 CDPK基因可能来自于蛋白激酶和 CaM基因的融合[9].
此外,多数 CDPK在 N末端含有与蛋白质定位(膜定位)相关的豆蔻酰化位点 (MGXXXSK)[10].自抑区包含双元的保守区,与蛋白质核定位相关.类钙调蛋白结构域的 EF手环中关键氨基酸的偏离能够影响其与钙离子的结合能力,进而可能影响其功能.在花生中,有一个 CDPK基因的第二个 EF手结合位点发生偏离,从而引起其与钙离子的结合能力下降[11].
2 植物钙依赖性蛋白激酶的进化特性
对拟南芥和水稻的全基因组序列进行分析分别获得 34和 31个 CDPK基因[7,12,13].分属于 4个不同的 group(I-I V).在未全基因组测序的小麦中也鉴定出 20个 CDPK基因,分属于 4个不同的group(I-I V)[4].其他植物如大豆、番茄、玉米也含有 CDPK基因家族[10].对拟南芥、水稻和其他植物中 CDPK基因的系统发育进行分析表明基因家族的进化是多水平复制.在拟南芥中,4号染色体短臂上的一个基因簇包含 5个基因 (AtCPK21,22,23,27和 31),可能是通过基因末端复制产生的,在功能上可能相似或者互补.在水稻中,CDPK的氨基酸水平进化分析发现 11个基因对,其复制方式和拟南芥不同,有可能是通过片段复制而产生的.在小麦中,CDPK也是成对存在,而且 N端的 GC含量很高[4].总之,植物 CDPK在基因组进化过程中形成一个没有多大差别的多基因家族,表明该类基因的存在受自然界的正向选择,对植物适应环境有着重要的作用.
随着测序技术的发展和谷类作物几个主要物种 (水稻、高粱、玉米、短柄草)全基因组测序的完成,为基因组的进化分析奠定了基础.在不同物种的进化关系中,比较基因组学通过蛋白、RNA和不同生物调控区域的相似性和差异性推断这些因素在选择机制中的作用.就不同物种而言,生物体成功进化中重要的因素是保守的,不重要的因素是分化的.早期的禾本科家族基因结构比较研究显示从 50~80百万年前共同祖先分化的草类之间有共线性关系[13],如在短柄草、高粱、水稻和玉米之间有 59个共线基因区域包含 99.2%的短柄草基因[14].通过对不同物种同源基因对的同源替代率分析,可以估计出短柄草从小麦中分化是 32~39百万年前,水稻中是 40~53百万年前,高粱中是 45~60百万年前.另外,根据测序物种的基因组序列信息,可以利用比较基因组学研究未测序物种的进化和基因组信息.
3 植物钙依赖性蛋白激酶的分布及表达特性
由于 CDPK广泛参与植物生长发育和逆境的响应过程,因此,在长期演化过程中,形成了以众多成员组成的基因家族,各成员通过自身的结构特征分别介导不同的内部生育信号和外部逆境信号.在特定组织、生理条件或发育阶段下表达的不同 CDPK家族成员基因,分别执行特定的功能.在水稻中,OsCPK2和 OsCPK11在叶片对光的反应中具有不同的功能[15];在烟草中,N tCPK1在根、茎和花中都表达,而叶片中不表达[16];在马铃薯中,StCPK1的表达受发育调控,在开始形成块茎时被诱导表达[12].
CDPK在植物体内广泛分布,在器官水平上,CDPK分布于根、茎、叶、果实和种子中[17].在水稻中,OsCPK1、OsCPK6、OsCPK7、OsCPK8、Os-CPK13、OsCPK17、OsCPK23在根、茎、叶、穗中表达,OsCPK4、OsCPK14在根、茎、叶中表达,Os-CPK15、OsCPK16、OsCPK19在茎、叶、穗中表达 ,OsCPK9在茎、叶中表达,OsCPK12在叶、穗中表达,OsCPK24、OsCPK29只在根中表达[18].在小麦中,TaCPK1、TaCPK2、TaCPK5、TaCPK16在根、茎、叶、幼穗、未成熟种子中都表达,TaCPK3、TaCPK6、TaCPK9、TaCPK12、TaCPK14、TaCPK15在根、茎、叶、幼穗中表达;TaCPK10在根、叶、幼穗、未成熟种子中表达,TaCPK8在叶、未成熟种子中表达,TaCPK13只在幼穗中表达[4].
在亚细胞定位水平上,CDPK在细胞膜、细胞骨架、细胞质、叶绿体、线粒体、微粒体膜、细胞核和染色体等细胞器中均有表达.在拟南芥中,通过CDPK与绿色荧光蛋白融合的方法,对拟南芥 9个 CDPK成员 AtCPK2、A tCPK3、A tCPK4、A tCPK7、A tCPK8、AtCPK9、AtCPK16、AtCPK21和 A tCPK28的亚细胞定位进行研究,结果表明,A tCPK2定位在内质网膜 (ER),A tCPK1定位在过氧化物酶体,A tCPK7、A tCPK8、AtCPK9、AtCPK16、A tCPK21、A tCPK28定位在细胞膜,AtCPK3和 A tCPK4定位在细胞质,AtCPK3和 AtCPK4定位在细胞核、线粒体[19].另外,在亚细胞水平上部分 CDPK基因具有移动性,如冰草中,M cCPK1在低湿条件或者干旱胁迫下,亚细胞定位可以从质膜转移到核中,这可能和其功能相关[20].拟南芥中,A tCPK3和A tCPK4在感受逆境前分布于细胞质中,在感受逆境后分布于细胞核内,亚细胞定位的改变可能进一步激活位于细胞核内的转录因子,调控下游基因的表达[19].
4 植物钙依赖性蛋白激酶的功能研究
对于 CDPK的功能研究主要集中在两个方面,一是 CDPK对各种胁迫和刺激反应,二是通过基因转化研究对其功能进行验证.
CDPK的表达可受水分、盐分、低温、伤害等非生物因素和稻瘟病、真菌等生物因素以及赤霉素、生长素、细胞分裂素等激素的诱导,如表1所示.
从表1可以看出:冰草中M cCPK1受盐和水分胁迫诱导[20];葡萄中 ACPK1受 ABA(脱落酸)诱导,而其他植物激素如生长素、赤霉素以及细胞分裂素则对 ACPK1的表达没有影响,表明 ACPK1可能特异参与 ABA信号传递路径[21];水稻中有 4个 CDPK受低温、盐和脱水胁迫诱导[18],6个基因受稻瘟病诱导[18],4个基因受盐诱导[18],2个基因受低温诱导,而 OsCDPK13(OsCPK7)受低温和赤霉素诱导[22].烟草中 N tCPK2和 N tCPK3受真菌和渗透压诱导[23],N tCPK1受 I AA(生长素)、GA(赤霉素 )、盐、真菌、几丁质、细胞分裂素、伤害的诱导[16,23],N tCPK4受盐、赤霉素诱导[24].玉米中 ZmCPK7和 ZmCPK9受光诱导,ZmCPK1受低温诱导[25],ZmCPK11受伤害诱导.小麦中,目前只报道了 TaCDPK1参与了蔗糖诱导的信号传递路径[26].
目前有些 CDPK的功能则通过转基因得到了验证,如表2所示.
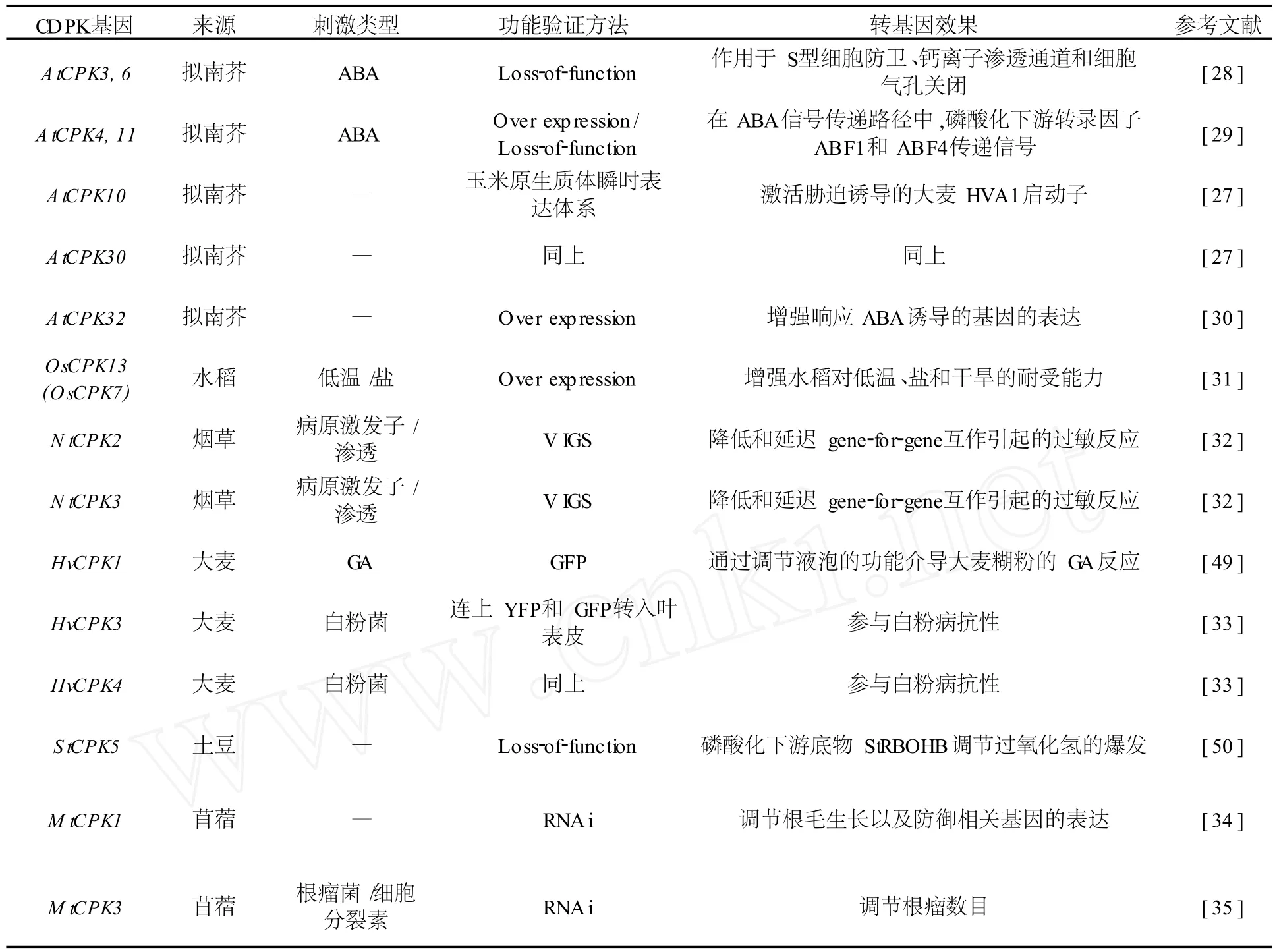
表2 已有文献报道的 CDPK功能验证
从表2可以看出:在逆境抵御方面,利用玉米原生质体瞬时表达体系证明了拟南芥 A tCPK10和AtCPK30可以激活胁迫和 ABA诱导的启动子[27];拟南芥中突变 AtCPK3和A tCPK6证明其作用于 S型细胞防卫、钙离子渗透通道和细胞气孔关闭[28];拟南芥中过表达和突变 A tCPK4和AtCPK11证明其在 ABA信号传递路径中磷酸化下游转录因子 ABF1和 ABF4[29].拟南芥A tCPK32的过量表达增强了响应 ABA的基因的表达[30].在水稻中过量表达水稻 OsCPK13(OsCDPK7)增强了水稻对低温、盐和干旱的耐受能力[31];在病原防卫方面,利用病毒诱导的基因沉默 (Virus-Induced Gene-Silencing,V IGS)体系的研究结果表明烟草N tCPK2的沉默降低和延迟了 gene-for-gene互作引起的过敏反应,从而证明 N tCPK2在烟草R基因介导的病原防卫中发挥着重要作用[32];大麦中应用瞬时表达体系证明大麦 HvCDPK3和HvCDPK4在白粉菌对寄主细胞早期侵染过程中至少存在着部分拮抗作用[33].在根发育方面,苜蓿M tCPK1能够调节根毛生长以及防御相关基因的表达[34],而 M tCPK3则在根与根瘤菌 Sinorhizobium m eliloti的共生互作中发挥关键作用[35].
5 植物钙依赖性蛋白激酶的展望
非生物胁迫和生物胁迫等刺激均可导致植物内源 Ca2+浓度发生变化[36-38],植物 Ca2+结合蛋白能够识别 Ca2+浓度变化,改变下游蛋白质 (如转录因子)磷酸化状态,从而影响基因表达模式[2].可见 Ca2+浓度变化可以被多种逆境胁迫以及病原所诱导,那么 Ca2+结合蛋白必然参与了多条抵御非生物胁迫及生物胁迫的防御路径.植物CDPK作为钙离子结合蛋白,在改善植物的抗逆和抗病方面一定有很大潜力.如在水稻中,过量表达OsCPK7的转基因水稻增强了胁迫信号在遗传作用区 (维管组织)的传导,改善了耐逆性,说明单一的 CDPK基因就有很重要的作用[31].
总之,环境胁迫 (如低温、盐和干旱)在世界范围内对作物产量造成巨大影响,而由各种作物病害所造成的减产也不容忽视.我国是一个农业大国,随着人口的增长和可利用耕地面积的日益减少,培育能抵御多种逆境胁迫,并兼具广谱抗病性的新品系显得越来越重要.
[1] TrewavasA,MalhóR.Ca2+signalling in plant cells:the big network[J].Curr Opin PlantBiol,1998,1(5):428-433.
[2] Sanders D,Brownlee C,Harper J.Communicatingwith calcium[J].Plant Cell,1999,11(4):691-706.
[3] BerridgeM,Lipp P,BootmanM.The versatility and universality of calcium signalling[J].NatRevMolCellBio,2000,1(1):11-21.
[4] LiA,Zhu Y,Tan X,et al.Evolutionary and functional study of the CDPK gene family in wheat(Triticum aestivumL.)[J].PlantMol Biol,2008,66(4):429-443.
[5] WeljieA,Clarke T,JufferA,et al.Comparative modeling studies of the ca lmodulin-like domain of calcium-dependent protein kinase from soybean[J].Proteins,2000,39(4):343-357.
[6] Cheng S,W il lmann M,Chen H,et al.Calcium signaling through protein kinases.The A rabidopsiscalcium-dependent protein kinase gene family[J].Plant Physiol,2002,129(2):469-485.
[7] Ha rmon A,GribskovM,Harper J.CDPKs-a kinase for every Ca2+signal?[J]. Trends Plant Sci,2000,5(4):154-159.
[8] Hrabak E,Dickmann L,Satterlee J,et al.Characterization of eight new members of the ca lmodulin-like domain protein kinase gene family fromArabidopsis thaliana[J]. Plant MolBiol,1996,31(2):405-412.
[9] Zhang X,Choi J.Molecular evolution of ca lmodulin-like domain protein kinases(CDPKs)in plants and protists[J].J Mol Evol,2001,53(3):214-224.
[10]Krupa A.Genome-wide comparative analyses of domain organisation of repertoiresof protein kinases ofA rabidopsis thalianaandO ryza sativa[J].Gene,2006,380(1):1-13.
[11]Christodoulou J,Malmendal A,Harper J,et al.Evidence for differing roles for each lobe of the calmodulin-like domain in a calciumdependent protein kinase[J].J Biol Chem,2004,279(28):29092-29100.
[12]Raíces M,Chico J,Téllez-Iñ ón M,et al.Molecular characterization ofStCDPK1,a calcium-dependent protein kinase fromSolanum tuberosumthat is induced at the onset of tuber development[J]. Plant Mol Biol,2001,46(5):591-601.
[13]Wolfe K,Gouy M,Yang Y,et al.Date of the monocot-dicot divergence est imated from chloroplast DNA sequence data[J].PTOC Natl Acad Sci USA,1989,86(6):6201-6205.
[14]W itte C,Keinath N,Dubiella U,et al.Tobacco calcium-dependent protein kinases are differentially phosphorylated invivoas part of a kinase cascade that regulates stress response[J].J Biol Chem,2010,285(13):9740-9748.
[15]FrattiniM,Morello L,Breviario D.Rice calcium-dependent protein kinase isofo rmsOs-CDPK2andOsCDPK11show different responses to light and different expression patterns during seed development[J].PlantMol Biol,1999,41(6):753-764.
[16]Mee Yoon G,Sun C H,Jung H H,et al.Characterization ofN tCDPK1,a calcium-dependent protein kinase gene inN icotiana tabacum,and the activity of its encoded protein[J].PlantMolBiol,1999,39(5):991-1001.
[17]Schenk P,Snaar-Jagalska B.Signal perception and transduction:the role of protein kinases[J].Bioch im Biophys Acta,1999,1449(1):1-24.
[18]Wan B,Lin Y,Mou T.Expression of rice Ca2+-dependent protein kinases(CDPKs)genes under different environmental stresses[J]. FEBS Lett,2007,581(6):1179-1189.
[19]Dammann C,Ichida A,HongB,et al.Subcellular targeting of nine calcium-dependent protein kinase isofo rms fromArabidopsis[J].Plant Physiol,2003,132(4):1840-1848.
[20]Chehab E,Patharkar O,Hegeman A,et al.Autophosphorylation and subcellular localization dynamics of a salt and water deficit-induced calcium-dependent protein kinase from ice plant[J].Plant Physiol,2004,135(3):1430-1446.
[21]Yu X,Zhu S,Gao G,et al.Expression of a grape calcium-dependent protein kinase ACPK1inA rabidopsis thalianapromotes plant growth and confers abscisic acid-hypersensitivity in ge rmination,postgermination growth,and stomatal movement[J].PlantMol Biol,2007,64(5):531-538.
[22]Abbasi F,Onodera H,Toki S,et al.OsCDPK13,a calcium-dependent protein kinase gene from rice,is induced by cold and gibberellin in rice leaf sheath[J].PlantMolBiol,2004,55(4):541-552.
[23]Klimecka M,Muszynska G.Structure and functions of plant calcium-dependent protein kinases[J].Acta Bicchim Pol,2007,54(2):219-233.
[24]ZhangM,Liang S,Lu Y.Cloning and functional characterization ofN tCPK4,a new tobacco calcium-dependent protein kinase[J].Biochim BiophysActa,2005,1729(3):174-185.
[25]Berberich T,Kusano T.Cycloheximide induces a subset of low temperature-inducible genes in maize[J].Mol Gene Genetics,1997,254(3):275-283.
[26]Martínez-Noёl G,Nagaraj V,CalóG,et al.Sucrose regulated expression of a Ca2+-dependent protein kinase(TaCDPK1)gene in excised leaves of wheat[J]. Plant Physiol Biochem,2007,45(6-7):410-419.
[27]Sheen J.Ca2+-dependent protein kinases and stress signal transduction in plants[J].Science,1996,274:1900-1902.
[28]Mori I,Murata Y,Yang Y,et al.CDPKs CPK6 and CPK3 function in ABA regulation of guard cell S-Type anion-and Ca2+-permeable channels and stomatal closure[J].PLoS Biol,2006,4(10):1749-1762.
[29]Zhu S,Yu X,Wang X,et al.Two calciumdependent protein kinases, CPK4 and CPK11,regulate abscisic acid signal transduction inA rabidopsis[J].Plant Cell,2007,19(10):3019-3036.
[30]Choi H,Park H,Park J,et al.Arabidopsis calcium-dependent protein kinaseA tCPK32 interacts withAB F4,a transcriptional regulator of abscisic acid-responsive gene expression,and modulates its activity[J]. Plant Physiol,2005,139(4):1750-1761.
[31]Saijo Y,Hata S,Kyozuka J,et al.Over-expression of a single Ca2+-dependent protein kinase confers both cold and salt/drought tolerance on rice plants[J].Plant J,2001,23(3):319-327.
[32]Romeis T,LudwigA,Martin R,et al.Calcium-dependent protein kinases play an essential role in a plant defence response[J].EMBO J,2001,20(20):5556-5567.
[33]Freymark G,Diehl T,MiklisM,et al.Antagonistic control ofpowdery m ildew host cell entry by barley calcium-dependent protein kinases(CDPKs)[J].Mol PlantMicrobe In,2007,20(10):1213-1221.
[34]Ivashuta S,Liu J,Lohar D,et al.RNA interference identifies a calcium-dependent protein kinase involved inM edicago truncatula root development[J].Plant Cell,2005,17(11):2911-2921.
[35]Gargantini P,Gonzalez-Rizzo S,Chinchilla D,et al.A CDPK isofo rm participates in the regulation of nodule number inM edicago truncatula[J]. Plant J,2006,48(6):843-856.
[36]Knight H,KnightM.Abiotic stress signalling pathways: specificity and cross-talk[J].Trends in Plant Sci,2001,6(6):262-267.
[37]Sanders D,Pelloux J,Brownlee C,et al.Calcium at the crossroads of signaling[J].Plant Cell,2002,S14:401-417.
[38] Iwata Y,Kuriyama M,Nakakita M,et al.Characterization of a calcium-dependent protein kinase of tobacco leaves that is associated with the pla smamembrane and is inducible by sucrose[J]. Plant Cell Physiol,1998,39(11):1176-1183.
[39]Liu G,Chen J,Wang X,et al.VfCPK1,a gene encoding calcium-dependent protein kinase fromV icia faba,is induced by drought and abscisic acid[J]. Plant Cell Environ,2006,29(11):2091-2099.
[40]LanteriML,Pagnussat GC,Lamattina L,et al.Calcium and calcium-dependent protein kinases are involved in nitric oxide-and auxininduced adventitious root formation in cucumber[J].J Exp Bot,2006,57(6):1341-1351.
[41]Ma S Y,WuW H.AtCPK23functions inA rabidopsisresponses to drought and salt stresses[J].PlantMolBiol,2007,65(4):511-518.
[42]Ye S,Wang L,Xie W,et al. Expression profile of calcium-dependent protein kinase(CDPKs)genes during the whole lifespan and under phytohormone treatment conditions in rice(Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica)[J].PlantMolBiol,2009,70(3):311-325.
[43]Breviario D,Morello L,Giani S.Molecular cloning of two novel rice cDNA sequences encoding putative calcium-dependent protein kinases[J].Plant Mol Biol,1995,27(5):953-967.
[44]Asano T,Tanaka N,Yang G,et al.Genome-wide identification of the rice calciumdependent protein kinase and its closely related kinase gene families:comprehensive analysis of the CDPKs gene family in rice[J].Plant Cell Physiol,2005,46(2):356-366.
[45]KhanM M,Jan A,Karibe H,et al.Identification of phosphoproteins regulated by gibberellin in rice leaf sheath[J].PlantMol Biol,2005,58(1):27-40.
[46]Saijo Y,Hata S,Sheen J,et al.cDNA cloning and prokaryotic expression of maize calcium-dependent protein kinases[J].Biochim BiophysActa,1997,1350(2):109-114.
[47]Murillo I,Jaeck E,Cordero M J,et al.Transcriptional activation of a maize calciumdependent protein kinase gene in response to fungal elicitors and infection[J].Plant Mol Biol,2001,45(2):145-158.
[48]Szczegielniak J,Klimecka M,L iwosz A,et al.A wound-responsive and phospholipid-regulated maize calcium-dependent protein kinase[J]. Plant physiol,2005,139(4):1970-1983.
[49]McCubbin A G,Ritchie SM,Swanson S J,et al.The calcium-dependent protein kinase HvCDPK1 mediates the gibberellic acid response of the barley aleurone through regulation of vacuolar function[J].Plant J,2004,39(2):206-218.
[50]KobayashiM,Ohura I,Kawakita K,et al.Calcium-dependent protein kinases regulate the production of reactive oxygen species by potato NADPH oxidase[J]. Plant Cell,2007,19(3):1065-1080.
RESEARCH PROGRESS OF EVOLUTI ON AND FUNCTI ON OF CALCI UM-DEPENDENT PROTEI N KI NASE I N PLANT
GENG Shuai-feng1,ZHAO Yong-liang1,L IAi-li2,MAO Long2,WANGWei-guo1,L ILei1
(1.School of B ioengineering,Henan University of Technology,Zhengzhou450001,China;2.Institute of Crop Sciences,Chinese Academ y of Agricultural Sciences,B eijing100081,China)
Calcium ions play the role of the second messenger in plant signal transduction.As the calcium ion sensor,the calcium-dependent protein kinase(CDPK)in plant has the important effect in regulating plant metabolism and the plant adaptability to the external environment.The paper summarized the structure characteristics,the evolutionary characteristics,distribution and expression characteristics,and the function of CDPK in plant to provide reference for the development of broad-spectrum disease-resistance varieties with resistance to different kinds of stresses.
calcium-dependent protein kinase;structure;evolution;function
TS201.2
A
1673-2383(2010)05-0086-07
2010-06-03
河南工业大学博士基金(150216)
耿帅锋 (1982-),男,河南汝州人,硕士研究生,研究方向为微生物与生化药学.
*通信作者
