急性尿潴留前列腺穿刺的意义
2010-03-08陶令之来永庆魏本林关志忱
陶令之 来永庆 魏本林 关志忱
急性尿潴留前列腺穿刺的意义
陶令之 来永庆 魏本林 关志忱
目的探讨是否应该对PSA升高的急性尿潴留患者先进行前列腺穿刺活检。方法回顾分析2003年1月~2009年4月我科收治的109例血清PSA浓度均大于4ng/mL的男性急性尿潴留患者(无尿道狭窄,神经原性膀胱等病因)。根据是否活检分为2组,20例为前列腺穿刺活检组,年龄54~85(68.907.64)岁,前列腺体积38~130(70.9427.97)ml,血清PSA4.30~487.46(48.12106)L。89例为未活检组,年龄54~97(71.788.64)岁,前列腺体积16~293(61.7943.77)ml,血清PSA4.06~411.2(24.9052.61)ng/mL,2组间年龄、前列腺体积和血清PSA比较无统计学差异(P>0.05);未活检组56例经尿道前列腺切除术(TURP),5例经开放手术。结果活检组20例,病理发现前列腺癌5例,阳性率25%;未活检组89例手术标本发现前列腺癌4例,均为经TURP者。阳性率4.49%。活检组和未活检组间比较有显著统计学差异(P<0.01)。结论经直肠前列腺穿刺活检发现PSA升高的急性尿潴留患者前列腺癌的发生率至少在25%以上,比未经穿刺而经手术发现的前列腺癌发生率高21%,有显著统计学差异,而手术发现的前列腺癌给再次根治性手术增加了难度。本研究证明PSA升高的急性尿潴留患者应该先进行前列腺穿刺活检。
急性尿潴留(AUR);前列腺特异性抗原(PSA);前列腺穿刺活检;经尿道前列腺切除术(TURP);前列腺癌
作为前列腺癌的筛选指标,血清前列腺特异性抗原PSA检测在临床中广泛应用。通常认为,PSA血清浓度大于10ng/mL是患者行前列腺穿刺活检的绝对指征。但血清 PSA水平受很多生理和病理因素的影响,传统认为前列腺增生急性尿潴留会导致血清PSA显著升高[1],尿潴留时PSA增高似乎不是前列腺癌的征象,治疗也曾多以解除梗阻为主,近年来随着对前列腺癌认识的提高,这一观点受到了挑战,对于PSA增高的尿潴留病人是否要先进行穿刺活检充满争议。出于这个目的,现将本院近6年收治的急性尿潴留患者的临床资料进行回顾性研究,探讨是否应该对PSA升高的急性尿潴留患者先进行前列腺穿刺活检。
1 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象 回顾分析2003年1月~2009年4月我科收治的109例血清PSA浓度均大于4ng/ml的男性急性尿潴留患者(无尿道狭窄,神经原性膀胱等病因)。根据是否活检分为2组,20例为前列腺穿刺活检组,89例为未活检组。
1.2 方法 血清PSA测定采用放射免疫法,经超声测量前列腺3径(前后、左右、上下),按公式计算前列腺体积:上下径×前后径×左右径×0.52。20例为前列腺穿刺活检组,年龄54~85(68.90±7.64)岁,前列腺体积38~130(70.94±27.97)ml,血清PSA4.30~487.46(48.12±106.92)ng/ml。89例为未活检组,年龄54~97(71.78±8.64)岁,前列腺体积16~293(61.79±43.77)ml,血清PSA4.06~411.2(24.90±52.61)ng/ml,未活检组56例经尿道前列腺切除术(TURP), 5例经开放手术。2组间年龄、前列腺体积和血清PSA比较无统计学差异 (P>0.05)。
2 结果
活检组20例,病理发现前列腺癌5例,阳性率25%;未活检组89例手术标本发现前列腺癌4例,均为经TURP者。阳性率4.49%。活检组和未活检组间比较有显著统计学差异(P<0.01)见表1。
3 讨论
自从1979年Wang等[2]首先用免疫沉淀法成功地从人前列腺组织中分离和提纯出PSA以来,PSA在临床上得到了广泛的研究和应用,成为前列腺癌诊断、治疗、随访中最重要的肿瘤标志物。PSA是前列腺组织特异性抗原而非前列腺癌特异性抗原,许多生理和病理因素如前列腺增生(BPH)、前列腺缺血、急性尿潴留(AUR)、细菌性前列腺炎、前列腺按摩等都可引起血清PSA的升高[3],其中以急性尿潴留作用甚为明显。Semjonow等[4]报道急性尿潴留时血清PSA水平较尿潴留缓解后高6倍。PSA为一种能催化肽类物质水解的蛋白酶,由前列腺上皮细胞分泌。正常情况下,前列腺腺泡内容物(富含PSA)与淋巴系统之间存在由内皮层,基底细胞层和基底膜构成的屏障,当癌肿或其它病变破坏这道屏障时,腺泡内容物即可漏入淋巴系统而进入血循环导致血清PSA升高[5]。急性尿潴留致血清PSA升高可能与AUR引起前列腺急性炎症或微灶性坏死病变破坏这道屏障有关。
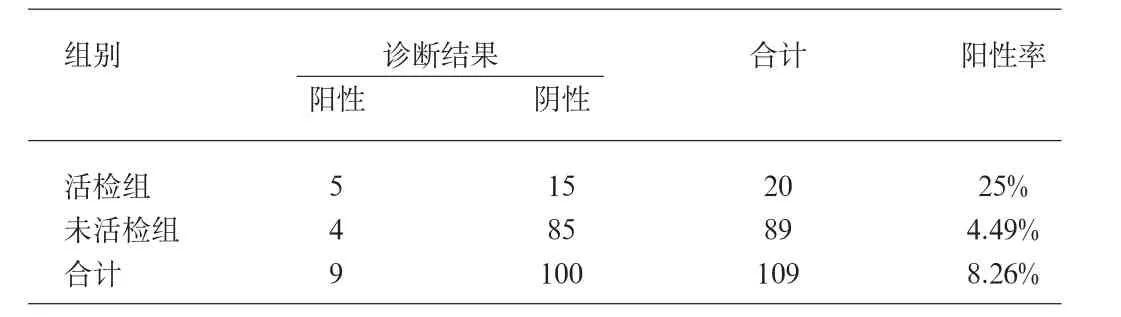
表1 2组前列腺癌阳性率的比较
由此对PSA升高的急性尿潴留患者如何进行诊治存在一定的争议。传统观点将患者血清PSA的升高归因于急性尿潴留的影响,认为对并发AUR的前列腺增生患者即使PSA>10ng/ml者,如术前肛门指诊(DRE)前列腺质地不硬且无结节,经直肠前列腺超声检查未见明显异常情况,则可无需行前列腺穿刺活检,而直接行前列腺增生手术解除梗阻[6],定期随访PSA的变化。
近年来随着对前列腺癌认识的提高,这一观点受到了挑战,在本研究中,经直肠前列腺穿刺活检发现PSA升高的急性尿潴留患者前列腺癌的发生率至少在25%以上,比未经穿刺而经手术发现的前列腺癌发生率高21%,有显著统计学差异,这说明如果PSA升高的急性尿潴留患者未经穿刺活检而直接手术或随访观察,就有至少21%~25%的前列腺癌患者失去最佳诊断治疗时机,这种传统的处置方式虽然在一定程度上减少了对部分患者进行不必要的前列腺穿刺活检,但是如此高的漏诊率是临床医师所不能接受的,同时手术发现的前列腺癌给再次进行根治性手术增加了难度。自1989年Hodge等[7]提出经直肠超声引导6点前列腺系统穿刺活检术,到1997年Eskew等[8]首先报道了经直肠超声引导13点前列腺系统穿刺活检术诊断前列腺癌的临床应用以来,采用经直肠超声引导下前列腺系统穿刺的方法使前列腺癌的临床检出率得到明显提高,并发症也随着技术的不断改进而减少。所以我们认为,对PSA升高的急性尿潴留患者无论DRE是否正常都应该先行TRUS引导下前列腺系统穿刺活检。
[1]Aliasgari M,Soleimani M,Hosseini Moghaddam S M.The effect of acute urinary retention on serum prostate-specific antigen level[J].J Urol,2005,2(2):89-92.
[2]Wang M C,Valenzuela L A,Murphy G P,et al.Purification of a human prostate specific antigen[J].Invest Urol,1979,17(2):159-163.
[3]Hammerer P G,Huland H.Systematic sextant biopsies in 651 patients referred for prostate evaluation[J].J Urol,1994,151(1):99-102.
[4]Semjonow A.De Angelis G.Oberpenning F,et a1.The clinical impact of different assays for prostate specific antigen[J].BJU Int,2000,86(5):590-597.
[5]Rifkin M D.Ultrasound of the prostate:imaging in the diagnosis and therapy of prestatic disease[M].(2nd ed).Philadelphia:LipincottRaven,1997.
[6]郭同本,许纯孝,陈炳刚,等.BPH并发与未并发急性尿潴留患者术前血清PSA对比观察[J].临床泌尿外科杂志,1998,l3(6):265-266.
[7]Hodge K K,McNeal J E,TerrisM K,et al.Random systematic versus directed ultrasound guided transreetal core biopsies of the prostate[J].J Urol,1989,142:71-74.
[8]Eskew L A,Bare R L,McCulloush D L.Systematic 5 region prostate biopsy is superior to sextant method for diagnosing carcinoma of the prostate[J].J Urol,1997,157:199-202.
Objective To explore whether a prostate biopsy should first conduct in patients with acute urinary retention combined with elevated serum PSA. Methods A total of 109 cases of men with acute urinary retention were retrospectively studied, and patients with urethral stricture and neurogenic bladder were excluded.Serum PSA concentration greater than 4ng/mL for selected.divided into two groups according to whether to biopsy or not.For 20 cases of prostate biopsy group, aged 54-85(68.90±7.64)years old, prostate volume of 38-130(70.94±27.97)ml, serum PSA 4.30-487.46(48.12±106.92)ng/mL. For 89 cases of non-biopsy group, aged 54-97(71.78±8.64)years old, prostate volume of 16-293(61.79±43.77)mL,serum PSA 4.06-411.2(24.90±52.61)ng/mL. In the non-biopsy group 56 cases conducted transurethral resection of prostate (TURP), 5 cases conducted open surgery. There were no statistically differences between the two groups in age, serum PSA and prostate volume(P>0.05). Results: For 20 cases of prostate biopsy group, 5 cases of prostate cancer, the positive rate was 25%; For 89 cases of non-biopsy group,4 cases of prostate cancer,all were diagnosed by TURP, the positive rate was 4.49%. There were statistically significant differences between the two groups(P<0.01). Conclusion The incidence of prostate cancer diagnosed by transrectal prostate biopsy in patients with acute urinary retention combined with elevated serum PSA was at least more than 25%, 21% higher than which diagnosed by surgery without biopsy, there were significant statistically differences, these operations without biopsy increased the difficulty of radical surgery. This study demonstrate that a prostate biopsy should first conduct in patients with acute urinary retention combined with elevated serum PSA.
acute urinary retention (AUR); prostate specific antigen(PSA); prostate needle biopsy; transurethral resection of prostate(TURP);prostate cancer
10.3969/j.issn.1009-4393.2010.14.009
518000 北京大学深圳医院泌尿外科 (陶令之 来永庆魏本林 关志忱)