褪黑素对胰腺癌细胞株SW1990体外增殖及凋亡的影响
2009-11-28朱华许春芳叶建新
朱华 许春芳 叶建新
褪黑素对胰腺癌细胞株SW1990体外增殖及凋亡的影响
朱华 许春芳 叶建新
目的探讨褪黑素(MT)体外抑制胰腺癌细胞株SW1990增殖及诱导其凋亡的作用。方法以不同浓度的MT(0.1、0.5、1.0、2.5及5.0 mmol/L)处理体外培养的胰腺癌细胞株SW1990细胞24、48、72 h。用MTT法测定细胞增殖,以AnnexinⅤ/PI检测细胞凋亡,流式细胞仪分析细胞周期及Western blotting检测细胞Bcl-2、Bax蛋白表达。结果MT呈浓度和时间依赖性抑制SW1990细胞的增殖。0.1~5.0 mmol/L MT作用48 h后,细胞的增殖抑制率为7.4%~85.8%。1.0~5.0 mmol/L MT作用48 h后,G0/G1期比例为72.6%~85.3%,细胞凋亡率为21.5%~41.7%,同时Bcl-2蛋白表达下调,Bcl-2/Bax比值下降。结论MT可以抑制SW1990细胞增殖,其机制可能与上调Bax表达,下调Bcl-2表达,促进细胞凋亡,将细胞周期阻止于G0/G1期有关。
胰腺肿瘤; 细胞增殖; 细胞凋亡; 褪黑素
胰腺癌是一种预后极差的恶性肿瘤,70%~80%的患者诊断时已属晚期失去手术时机,而化疗药物疗效却不尽人意,因此,寻找一种高效低毒的化疗药物仍是众多学者研究的热点之一。褪黑素(melatonin,MT)是松果腺分泌的一种吲哚类激素,其作为一种天然的抗肿瘤药物,已被众多研究者关注。本研究探讨褪黑素在体外对人胰腺癌细胞株SW1990细胞增殖及凋亡的影响,探讨其抗肿瘤的可能机制。
材料和方法
一、细胞株、药物及主要试剂
人胰腺癌细胞株SW1990购自苏州大学附属第一人民医院血液研究所,常规培养及传代;MT及噻唑盐(MTT)购自美国Sigma公司;RPMI1640培养基购自GIBCO公司;抗bcl-2和bax一抗购自SantaCruz公司,二抗购自中杉金桥。
二、细胞增殖检测
采用MTT法。将SW1990细胞按每孔4×103个接种于96孔板,常规培养24 h后,分别加入终浓度为0.1、0.5、1.0、2.5及5.0 mmol/L的MT继续培养24、48、72 h后,分别加入5 mg/ml的MTT 20 μl轻轻晃匀,37℃温育4 h,去除培养液后,每孔加入DMSO 100 μl,振荡混匀10 min,应用BIOLISA酶标仪测各孔A492值。每一浓度设5复孔,实验重复3次。
三、细胞周期及凋亡检测
用1.0、2.5及5.0 mmol/L的MT作用SW1990细胞48 h,EDTA消化收获细胞后70%乙醇固定过夜,相应处理后加入PI 500 μl,上BIOLISA流式细胞仪分析细胞周期;另收集细胞,2 000 g离心5 min,PBS洗涤2次后加入Binding Buffer 500 μl、AnnexinV(FITC)5 μl,混匀后加入PI 5 μl,室温避光反应5~15 min,于流式细胞仪检测细胞凋亡率。实验重复3次。
四、Bcl-2及Bax蛋白检测
取上述各组5×105个细胞,加入5倍体积的细胞裂解液孵育20 min。测蛋白浓度,取40 μg常规行Western blotting,最后ECL发光,X线曝光、显影和定影。条带进行吸光度扫描分析,并与对照组结果进行对比。
五、统计学分析
结 果
一、胰腺癌细胞增殖的变化
MT以浓度依赖性地抑制胰腺癌细胞株SW1990细胞的生长,且随浓度的增加抑制作用增强。MT 0.1、0.5 mmol/L各时间点组及MT 1.0 mmol/L、24 h组与对照组比较差异均无统计学意义,1.0 mmol/L 48、72 h组及2.5、5.0 mmol/L各时间点组与对照组比较,差异均有显著性(P﹤0.05或0.01,图1)。
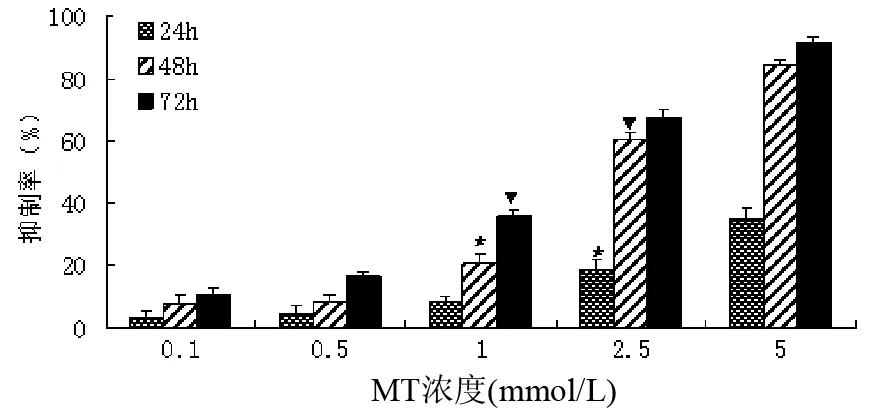
与对照组比较,★Plt;0.05,▼Plt;0.01
二、细胞周期改变
经MT处理后,SW1990细胞G0/G1期增多,S期和G2/M期减少(表1)。
表1 不同浓度MT对SW1990细胞周期的影响
注:与对照组比较,*Plt;0.05
三、细胞凋亡率改变
MT 1.0、2.5、5.0 mmol/L处理SW1990细胞48 h后,细胞的凋亡率分别为21.5%、34.3%和41.7%(图2)。

图2 各组SW1990细胞的流式细胞仪检测图
四、Bcl-2和Bax蛋白表达的变化
MT处理SW1990细胞48 h后,Bax表达增强,而Bcl-2表达降低,差异有显著性(Plt;0.05,图3)。

图3 各组SW1990 细胞的Bcl-2和Bax蛋白表达
讨 论
大量体外实验显示,MT对多种良恶性肿瘤细胞,如乳腺癌MCF-7细胞株、恶性黑色素瘤B7、S9细胞株等均有显著的生长抑制作用,并具有浓度依赖性。但MT的作用可表现为双向性,在微摩尔浓度时可刺激细胞增殖,在毫摩尔浓度时则表现为抑制作用,即抑制细胞增殖、增加凋亡细胞数及阻碍细胞周期的正常运行[1]。本实验结果显示,MT呈浓度、时间依赖性抑制SW1990细胞的增殖,瘤细胞周期明显地被阻止于G1期,并使S期细胞比例减少,这与Shiu等[2]的结果相吻合。
在细胞凋亡早期,往往是在细胞膜上发生变化[3-4]。其中胞膜的一个改变是磷脂酰丝氨酸(phosphatidylserine,PS)从胞膜内易位到胞膜外,暴露在细胞表面。AnnexinV是Ca2+依赖性脂结合蛋白,与PS具高度亲和性。虽然坏死细胞亦可出现此类表现,但由于同时结合PI染色,因此可以排除坏死细胞。本结果显示,MT处理SW1990细胞后,细胞早期凋亡率增加,提示MT抑制细胞增殖的机制可能与诱导细胞凋亡有关。
肿瘤细胞凋亡是一个涉及多基因参与的过程,包括p53 、c-myc 、Fas、bcl-2、bax 等基因[5],其中,bcl-2是最主要的细胞凋亡抑制基因[6],bax是最主要的细胞凋亡促进基因[7],bcl-2/bax的比率影响细胞凋亡的发生,是肿瘤发生的决定因素[8-9]。本实验结果显示,MT处理SW1990细胞后其Bcl-2蛋白表达下调,Bax蛋白表达上调,Bcl-2/Bax的比值降低,进一步证实MT促进肿瘤细胞凋亡的作用,为MT治疗胰腺癌的进一步研究提供实验基础。
[1] Vijayalaxmi,Thomas CR Jr,Reiter RJ,et al.Melatonin:from basic research to cancer treatment clinics.J Clin Oncol,2002,20:2575-2601.
[2] Shiu SY, Li L,Xu JN,et al.Melatonin-induced inhibition of proliferation and G1/S cell cycle transition delay of human choriocarcinoma JAr cells:possible involvement of MT2(MEL1B)receptor.J Pineal Res,1999,27:183-192.
[3] Andree HA,Reutelingsperger CP,Hauptmann R,et al.Binding of vascular anticoagulant alpha(VAC alpha) to planar phospholipid bilayers.J Biol chem,1990,265:4923-4928.
[4] Creutz CE.The annexins and exocytosis.science,1992,258:924-931.
[5] Porebska I,Wyrodek E,Kosacka M,et al.Apoptotic markers p53,Bcl-2 and Bax in pring lung cancer.In Vivo,2006,20:599-604.
[6] Hengartner MO,Horvitz HR.Celegans cell survival gene ced-9 encodes a functional homolog of the mammalian proto-oncogene Bcl-2.Cell,1994,76:665-676.
[7] Bannova AV,Men′shanov PN,Il′inykh FA,et al.Bax and Bcl-XL apoptosis protein mRNA in rat brain stem and cortex during ontogeny.Bull Exp Biol Med,2005,139:700-702.
[8] Jo EH,Hong HD,Ahn NC,et al.Modulations of the Bcl-2/Bax family were involved in the chemopreventive effects of licorice root(Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch)in MCF-7 human breast cancer cell.J Agric Food Chem,2004,52:1715-1719.
[9] Cory S,Adams JM.Killing cancer cells by flipping the Bcl-2/Bax switch.Cancer Cell,2005,8:5-6.
2008-12-10)
(本文编辑:吕芳萍)
EffectsofmelatoninonproliferationandapoptosisinhumanpancreaticcancercelllineSW1990
ZHUHua,XUChun-fang,YEJiang-xin.
DepartmentOfGastroenterology,FirstPeople′sHospitalofSuzhou,SuzhouUniversity,Suzhou215006,China
XUChun-fang,Email:xcf601@163.com
ObjectiveTo investigate the effect of melatonin (MT) on the proliferation and apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cell SW1990 in vitro.MethodsSW1990 cell line were treated with MT at different concentrations (0.1, 0.5, 1.0, 2.5 and 5.0 mmol/L) and at different time points (24 h, 48 h and 72 h). Cell proliferation was evaluated by MTT and apoptosis was determined by AnnexinV/PI, cell cycle was determined by flow cytometry, and Western Blot was used to detect the expression of Bcl-2 and Bax.ResultsMT could inhibit the proliferation of SW1990 cell in a time and dose dependent manner. 48 h after 0.1~5.0 mmol/L MT treatment, the proliferation inhibitory rate was 7.4%~85.8%, the proportion of SW1990 cell in phase G0/G1was 72.6%~85.33%. 48 h after 1~5.0 mmol/L MT treatment, the apoptosis rate was 21.5%~41.7%, and the expression of Bcl-2 was down-regulated and the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax decreased.ConclusionsMT could inhibit the proliferation of SW1990 pancreatic cancer cells by up-regulating the expression of Bax and down-regulating the expression of Bcl-2, as well as enhancing apoptosis and blocking SW1990 cell in phase G0/G1.
Pancreatic neoplasms; Cell proliferation; Apoptosis; Melatonin
10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-1935.2009.02.013
215006 苏州,苏州大学附属第一人民医院消化科
许春芳,Email:xcf601@163.com
