Stackelberg微分博弈下的鲁棒最优投资-再保险问题
2024-05-15颜炳文陈密刘海燕
颜炳文 陈密 刘海燕

摘要: 考虑一个以模糊厌恶再保险公司为领导者, 模糊中立保险公司为追随者的Stackelberg随机微分博弈问题. 通过求解拓展的HJB(Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman)方程组, 给出时间一致性均值-方差准则下的鲁棒最优投资-再保险策略以及相应的值函数. 最后, 通过数值例子和敏感性分析说明最优策略与主要参数之间的关系.
关键词: 比例再保险; 常系数方差弹性模型; Stackelberg微分博弈; 时间一致性均值-方差框架; 模糊厌恶
中图分类号: O211.6文献标志码: A文章编号: 1671-5489(2024)02-0273-12
Robust Optimal Investment-Reinsurance Problemsunder Stackelberg Differential Game
YAN Bingwen1, CHEN Mi1,2, LIU Haiyan1,2
(1. School of Mathematics and Statistics, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou 350117, China;2. Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, Fuzhou 350117, China)
Abstract: We considered a Stackelberg stochastic differential game problem with an ambiguity-averse reinsurance company as the leader and an ambiguity-neutral insurance company as the follower. By solving the extended HJB (Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman) equation systems, we gave the robust optimal investment-reinsurance strategies and the corresponding value function under the time-consistent mean-variance criterion. Finally, we gave some numerical examples and sensitivity analyses to illustrate the relationship between the optimal strategies and the main parameters.
Keywords: proportion reinsurance; constant coefficient variance elasticity model; Stackelberg differential game; time-consistent mean-variance framework; ambiguity aversion
保險公司为获取更大的收益和转移部分风险, 通常选择将盈余投资金融市场和与再保险公司签订再保险合同使价值目标达到最大化. 通过随机控制理论研究保险公司的最优投资-再保险问题已成为精算领域的热门课题之一, 对不同目标下的投资和再保险优化问题研究目前已有很多成果[1-8].
现有保险精算研究大多数只基于保险公司的角度研究最优投资-再保险问题, 但再保险合同的拟定涉及保险公司和再保险公司双方的利益, 再保险公司对再保险合同的态度也有不可忽视的作用. 因此, 再保险公司的安全负荷不应只简单地设定为一个常数, 而应该是一个随机再保费策略η(t). 文献[9]在指数效用最大化准则下提出了Stackelberg微分再保险博弈模型, 即再保险公司作为博弈的领导者率先行动, 保险公司作为追随者做出反应. 文献[10]研究了时间一致性均值-方差框架下的最优再保险和保费策略, 采用在Stackelberg博弈中嵌入子Nash均衡博弈的思想处理时间不一致的最优再保险问题.
现实生活中, 保险公司可能比再保险公司有更多关于索赔过程的信息, 再保险公司无法判断保险索赔的真实性, 对再保险合同产生模糊厌恶的态度. 因此, 在设计再保险合同时应考虑信息不对称导致的模型不确定性影响. 目前, 模型不确定性已经得到了广泛的认可和应用[11-13], 其中文献[11]提出的鲁棒随机控制理论是解决模型不确定性问题的最常用方法.
本文在时间一致的均值-方差准则下, 构建以模糊厌恶再保险公司为领导者, 模糊中立保险公司为追随者的Stackelberg微分博弈框架, 同时考虑保险公司的竞争心理, 保险索赔过程采用扩散近似风险模型, 保费和再保费均使用期望值保费准则厘定. 与文献[9]不同, 本文中保险公司和再保险公司对索赔过程信息和各自的终端盈余持不同的态度. 不同于文献[14], 本文假设保险公司和再保险公司均可投资于风险资产和无风险资产, 风险资产价格由随机波动率常系数方差弹性(CEV)模型刻画, 通过求解拓展的HJB(Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman)方程组, 给出模糊中立保险公司和模糊厌恶再保险公司的鲁棒均衡最优投资-再保险策略和相应的均衡值函数.
1 模型构建
3 数值分析
下面用一些数值实例分析主要参数对定理2中推导出的均衡投资-再保险策略的影响, 并对结果进行说明. 除特别说明外, 假设各参数μ=5, σ=5, r0=0.1, r=0.2, s=2, σ1=0.6, β=1.1, θ=0.25, η1=0.2, η2=1.2, =0.5, m1=0.1, m2=0.2, k=0.4, T=8. 由于η*(t)在O1和O3中为常数, 所以本文只考虑最优策略在O2中对主要参数的敏感性结果.
3.1 最优再保险策略的敏感性分析
设m1,m2分别是保险公司和再保险公司的风险厌恶参数, 表示各自的风险偏好, 如图1和图2所示, 随着m1的增加, 保险公司愿意将更多的保险风险转移给再保险公司, 自留率q减小, 再保险公司作为Stcakelberg微分博弈的领导者, 拥有加价权, 当预期再保险业务增加时提高再保险价格; 当m2增大时, 再保险公司更倾向于增加再保险保费, 保险公司不得不承担更多的保险风险.
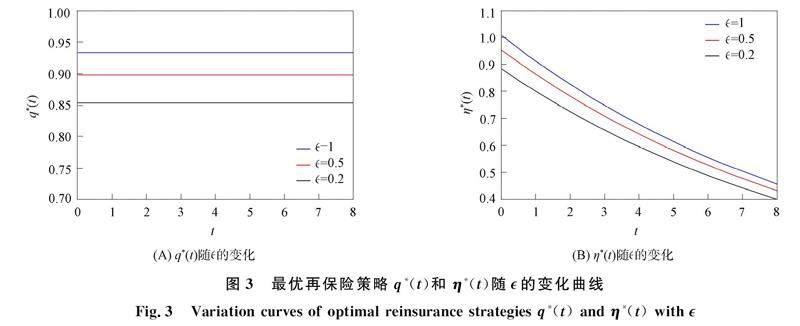
最优再保险策略q*(t)和η*(t)随的变化曲线如图3所示. 由图3可见, 随着再保险公司的模糊厌恶水平增加, 对保险公司提供的保险索赔信息越不信任, 越悲观, 更倾向于提高再保险保费以防范模型的不确定性, 保险公司减少购买再保险比例, 自留水平增加.
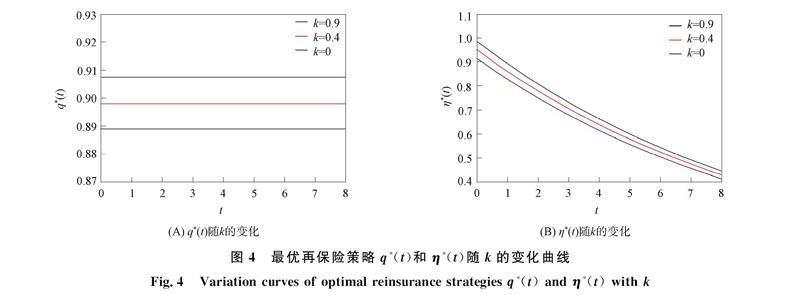
最优再保险策略q*(t)和η*(t)随k的变化曲线如图4所示. 由图4可见, 随着敏感性参数k的增加, 保险公司更关注再保险公司的财富盈余, 为缩小与再保险公司之间的盈余差距, 愿意冒更多的风险获取保险合同的价值, 保险自留比例增加, 再保险公司不得不降低再保险价格吸引保险公司购买再保险.
3.2 最优投资策略的敏感性分析
下面主要研究保险公司和再保险公司的最优投资策略a*1(t)和a*2(t)与风险规避参数、 风险资产的弹性参数和保险公司的敏感性参数之间的关系. 最优投资策略a*1(t)随m1和k的变化曲线如图5所示, 最优投资策略a*1(t)和a*2(t)随m2的变化曲线如图6所示.
由图5和图6可见, a*1(t)是关于m1和m2的递减函数, 并与k成正向关系, a*2(t)随着m2的增大而减小, 当保险公司和再保险公司各自的风险厌恶系数增大时, 更倾向于选择无风险的银行存款, 从而减少风险资产的投资来规避风险. 随着保险公司的敏感性参数k增大, 竞争心理更强烈的保险公司愿意将更多资金投资于风险资产, 为自身创造更多获取财富的机会.
参考文献
[1]BIAN B J, CHEN X F, XU Z Q. Utility Maximization under Trading Constraints with Discontinuous Utility [J]. SIAM Journal on Financial Mathematics, 2019, 10(1): 243-260.
[2]CHEN M, YUEN K C, WANG W Y. Optimal Reinsurance and Dividends with Transaction Costs and Taxes under Thinning Structure [J]. Scandinavian Actuarial Journal, 2021, 2021(3): 198-217.
[3]LIANG X Q, LIANG Z B, YOUNG V R. Optimal Reinsurance under the Mean-Variance Premium Principle to Minimize the Probability of Ruin [J]. Insurance: Mathematics and Economics, 2020, 92: 128-146.
[4]ZHANG C B, LIANG Z B. Optimal Time-Consistent Reinsurance and Investment Strategies for a Jump-Diffusion Financial Market without Cash [J]. The North American Journal of Economics and Finance, 2022, 59: 101578-1-101578-17.
[5]CHEN M, YUEN K C. Optimal Dividend and Reinsurance in the Presence of Two Reinsurers [J]. Journal of Applied Probability, 2016, 53(2): 554-571.
[6]JIANG X, YUEN K C, CHEN M. Optimal Investment and Reinsurance with Premium Control [J]. Journal of Industrial and Management Optimization, 2020, 16(6): 2781-2797.
[7]楊鹏, 刘琦. 均值方差准则下时间一致的再保险和投资策略选择 [J]. 东北师大学报(自然科学版), 2017, 49(4): 25-31. (YANG P, LIU Q. Time-Consistent Reinsurance and Investment Strategy Selection under Mean-Variance Criterion [J]. Journal of Northeast Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 49(4): 25-31.)
[8]杨鹏, 惠小健. Vasicek利率下基于随机微分博弈的最优再保险和投资 [J]. 东北师大学报(自然科学版), 2017, 49(2): 34-40. (YANG P, XI X J. Optimal Reinsurance and Investment Based on Stochastic Differential Games with Vasicek Interest Rate [J]. Journal of Northeast Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 49(2): 34-40.)
[9]CHEN L, SHEN Y. On a New Paradigm of Optimal Reinsurance: A Stochastic Stackelberg Differential Game between an Insurer and a Reinsurer [J]. ASTIN Bulletin: The Journal of the IAA, 2018, 48(2): 905-960.
[10]CHEN L, SHEN Y. Stochastic Stackelberg Differential Reinsurance Games under Time-Inconsistent Mean-Variance Framework [J]. Insurance: Mathematics and Economics, 2019, 88: 120-137.
[11]ANDERSON E W, HANSEN L P, SARGENT T J. A Quartet of Semigroups for Model Specification, Robustness, Prices of Risk, and Model Detection [J]. Journal of the European Economic Association, 2003, 1(1): 68-123.
[12]HUANG Y, OUYANG Y, TANG L X, et al. Robust Optimal Investment and Reinsurance Problem for the Product of the Insurers and the Reinsurers Utilities [J]. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2018, 344: 532-552.
[13]ZHANG W L, MENG H. Robust Optimal Investment-Reinsurance Strategies with the Preferred Reinsurance Level of Reinsurer [J]. AIMS Mathematics, 2022, 7(6): 10024-10051.
[14]YUAN Y, LIANG Z B, HAN X. Robust Reinsurance Contract with Asymmetric Information in a Stochastic Stackelberg Differential Game [J]. Scandinavian Actuarial Journal, 2022, 2022(4): 328-355.
[15]ZHAO H, WENG C G, SHEN Y, et al. Time-Consistent Investment-Reinsurance Strategies towards Joint Interests of the Insurer and the Reinsurer under CEV Models [J]. Science China: Mathematics, 2017, 60: 317-344.
[16]BAI Y F, ZHOU Z B, XIAO H L, et al. A Hybrid Stochastic Differential Reinsurance and Investment Game with Bounded Memory [J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2022, 296(2): 717-737.
[17]BJRK T, KHAPKO M, MURGOCI A. On Time-Inconsistent Stochastic Control in Continuous Time [J]. Finance and Stochastics, 2017, 21(2): 331-360.
(責任编辑: 赵立芹)
收稿日期: 2023-06-28. 网络首发日期: 2024-03-02.
第一作者简介: 颜炳文(1998—), 男, 汉族, 硕士研究生, 从事保险精算的研究, E-mail: ybw1112@163.com.
通信作者简介: 刘海燕(1986—), 女, 汉族, 博士, 副教授, 从事保险精算的研究, E-mail: rain6397@163.com.
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金(批准号: 11701087)和福建省自然科学基金(批准号: 2023J01537; 2023J01538).
网络首发地址: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/22.1340.o.20240228.1502.002.
