Prostaglandin D2 regulation of autophagy affects stemness of gastric cancer stem cells
2024-05-09TIANHengjinWANGFeifanGAOPeiyaoCHENAminWANGNaZHANGQiang
TIAN Heng-jin, WANG Fei-fan, GAO Peiyao, CHEN Amin, WANG Na, ZHANG Qiang✉
1. Department of Clinical Laboratory, the First Affiliated Hospital of Bengbu Medical University, Bengbu 233004, China
2. Department of Blood Transfusion, the First Affiliated Hospital of Naval Medical University, Bengbu 233004, China
3. Key Laboratory of Cancer Research and Clinical Laboratory Diagnosis, Bengbu Medical University, Bengbu 233004, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To explore the effect and mechanism of prostaglandins D2 (PGD2) on the stemness of gastric cancer stem cells (GCSCs).Methods: 7901-GCSCs were enriched by serum-free culture method; then the positivity rate of CD44, a stemness marker, was detected by flow cytometry in serum-free cultured 7901-GCSCs; the sphere-forming ability was detected by the sphere-forming assay after stimulation with different concentrations of PGD2 (2.5, 5,10) μg/mL, and the expression of stemness-related indicators (OCT4, CD44) and autophagyrelated proteins (LC3, Beclin-1) after PGD2 stimulation was detected by the western blot assay in different concentrations.The expression of stemness-related indexes (OCT4, CD44)and autophagy-related proteins (LC3, Beclin-1) were detected by Western blot assay after stimulation with different concentrations of PGD2.The expression of autophagy-related proteins after stimulation with different concentrations of CQ (2.5, 5, 10) μM was detected by Western blot experiment.The protein expression of autophagy-related proteins (LC3, Beclin-1)and stemness-related indexes (OCT4, CD44) was detected by Western blot experiment after PGD2 as well as PGD2+CQ treatment.Results: Flow cytometry results showed that the expression of CD44 positivity was increased in serum-free cultured 7901-GCSCs compared with gastric cancer cells SGC-7901 (P<0.05), which fulfilled the needs of subsequent experiments.The results of stem cell spheroid formation assay showed that the spheroid formation ability of 7901-GCSCs in the PGD2 group was significantly weakened compared with that of the DMSO group (P<0.05).Western blot results showed that the protein expression of stemness-related indexes (OCT4, CD44) was down-regulated in the 7901-GCSCs in the PGD2 group compared with that of the DMSO group (P<0.05), and the expression of autophagy-related proteins (LC3, Beclin-1) expression increased (P<0.05).Compared with the DMSO group, the expression of autophagy-related proteins (LC3, Beclin-1) was decreased in the CQ group (P<0.05).Western blot results also showed that the expression of cellular autophagy-related proteins and stemness-related indexes in the PGD2+CQ group was not significantly changed compared with that of the DMSO group (ns: the difference was not significant),suggesting that the CQ could block the effect of PGD2 on the expression of stemness markers in 7901-GCSCs.7901-GCSCs stemness inhibition.Conclusion: PGD2 may affect the stemness of 7901-GCSCs by regulating autophagy.
1.Introduction
Gastric cancer (GC) is a malignant tumour that poses a serious threat to human health, and the incidence and mortality rates of gastric cancer rank fifth and fourth among malignant tumours in the world[1].Currently, gastric cancer is still the third leading cause of cancer death in China[2].With the rapid development of the theory of cancer stem cells (CSCs), it has been gradually recognised that CSCs with high tumorigenicity are the source of development,recurrence, metastasis and drug resistance of tumours, including GC.CSCs have the ability of unlimited proliferation and self-renewal,which can promote the rapid growth of tumours[3].Some researchers have suggested that GCSCs are transformed from normal stem or progenitor cells in gastric tissues[4,5].In addition, some researchers have also cultured a spherical cell by serum-free culture, which has the ability of self-renewal and multidirectional differentiation, and was identified and presumed to be a possible tumour stem cell[6].In our group, GCSCs and AGS-GCSCs were isolated and identified by serum-free culture technique in the previous stage[5,7], and the serum-free suspension culture technique is considered to be the most convenient way to obtain GCSCs and can be used for the subsequent experiments[8].PGD2 is a lipohormone-like signalling ligand derived from arachidonic acid with physiological activity[6], and PGD2 synthase (L-PTGDS) is a key enzyme for PGD2 synthesis.The expression of L-PTGDS can indirectly reflect the secretion of PGD2,while it is capable of limiting PGD2 synthesis to a certain extent[9].Some studies have reported that PGD2 can inhibit the growth and migration ability of gastric cancer cells[9,10], but there is no report on the specific mechanism by which PGD2 inhibits the stemness of GCSCs.Autophagy can maintain the stability of the intracellular environment by removing damaged or aged organelles, as well as restoring misfolded and damaged proteins, and it is a highly conserved self-defence mechanism in mammals[11-13].In addition,autophagy plays an important role in tumours as it is an important mechanism to maintain cellular integrity during metabolic stress,drug treatment or radiation damage in tumour cells[14].Beclin-1 plays a key role in the autophagy pathway, and by degrading the autophagy-related protein Beclin-1, autophagy can be inhibited,promoting tumourigenesis and proliferation in vitro and in vivo [15].In this study, PGD2 was found to promote the upregulation of Beclin-1 protein and activate autophagy in gastric cancer cells.Therefore, in this study, we investigated the activation of autophagy by PGD2,which affects the stemness of GCSCs, with a view to providing a theoretical basis for the clinical treatment of gastric cancer.
2.Materials and methods
2.1 Cell lines and primary reagents
Human gastric cancer cell line SGC-7901 was supplied by Shanghai CAS Cell Bank, Prostaglandin D2 (PGD2 Batch No.23Z293-D1, Shanghai Zhenzhun), Chloroquine (CQ, Batch No.159402).Shanghai Haoyuan Biomedical Technology Co., Ltd.),penicillin and streptomycin double antibody (100×) (China Biosharp Company), primary antibody OCT4, CD44, Beclin-1, GAPDH,LC3, secondary antibody (Wuhan Three Eagles Bio-Technology Co.,Ltd.).: 8122453), B27 (Gibco, USA), CD44 flow-through antibody(BD Biosciences, USA), RIPA lysate, PMSF (100 mM), foetal bovine serum (Hangzhou Tianhang Bio-technology Co., Ltd.), BCA Protein Quantification Kit (Batch No.: 020123230413, Shanghai Biyuntian Bio-technology Co., Ltd.), basic fibrolast growth factor(bFGF) and epidermal growth factor (EGF), Pepro Tech, USA),ultra-low adsorption 6-well plate (Corning, USA).
2.2 Culture of gastric cancer cells and GCSCs
Gastric cancer cells SGC-7901 were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum and 1% penicillinstreptomycin double antibody and incubated at 37 ℃ and 5% CO2incubator.The culture was incubated for 2-3 d for passaging or for subsequent experiments.SGC-7901 cells in logarithmic growth phase were digested with trypsin, collected into centrifuge tubes and added with serum-free medium, and then inoculated into ultra-low adsorbent 6-well plates at a count of 1 × 104cells per well, in which the serum-free medium contained 10 μL/mL B27, 10 ng/mL bFGF,and 20 ng/mL EGF, and the culture system was 2 mL/well.The plates were cultured for 7-10 d and enriched with 7901-GCSCs for subsequent experiments.
2.3 Positivity of stem cell marker CD44 by flow cytometry
Flow cytometry was used to detect the positivity of CD44, a stemness marker for serum-free suspension culture of 7901-GCSCs stem cells.Gastric cancer cells SGC-7901 in adherent culture and 7901-GCSCs in serum-free culture were collected respectively, and 20 × 104cells were counted respectively, which were then transferred to flow tubes and then added with 1.5 μL of flow antibody against CD44, and incubated on ice for 15-30 min, and then finally 500 μL of PBS was added to each tube for mixing, and then detected on the machine.
2.4 Stem Cell Ball Formation Experiment
The cells of DMSO and PGD2 groups were digested with trypsin and counted, and cultured in ultra-low adsorption 6-well plates at a density of 200 cells per well, with 2 ml of medium added to each well, and the size and number of 7901-GCSCs in each group were observed and counted (cell spheres with a diameter of >40 μm) after 7 d.The cells of the DMSO and PGD2 groups were counted by trypsin digestion.
2.5 Experimental grouping
SGC-7901 was subjected to serum-free suspension culture, and the enriched 7901-GCSCs were first divided into: the DMSO group,the PGD2 group (2.5, 5, 10 ) μg/mL.and then the enriched 7901-GCSCs were divided into: (1) the DMSO group, the PGD2 group(2.5, 5, 10 ) μg/ml; (2) the DMSO group, the CQ group (2.5, 5 ,10) μM; (3) DMSO group, PGD2 group, and PGD2+CQ group,the concentration of PGD2 in the PGD2 group was 5 μg/m, and the concentrations of PGD2 and CQ in the PGD2+CQ group were 5 μg/mL and 5 μM, respectively.
2.6 Western blot detection of OCT4, CD44, LC3, Beclin-1 and other related protein expression
Western blot technique was used to detect the expression of OCT4,CD44 stemness marker and LC3, Beclin-1 related autophagy proteins in DMSO group and PGD2 group.The expression of OCT4, CD44 stemness marker and LC3, Beclin-1-related autophagy proteins were detected in DMSO group, PGD2 group and PGD2+CQ group.Total proteins of each group were lysed and extracted with lysis solution (RIPA : PMSF = 100 : 1) for BCA protein quantification, and electrophoresis was carried out using SDS-PAGE gels, followed by transferring the protein bands onto PVDF membranes.The membranes were closed with skimmed milk for 1-2 h.Primary antibody ratio Beclin-1, LC3, OCT4, CD44 (1 :2 000), GAPDH (1 : 3 000).The membrane was shaken overnight at 4 ℃.The membrane was washed three times with TBST for 10 min each time, followed by the addition of secondary antibody (1 : 5 000) and incubation at room temperature for 2 h.The membrane was washed three times with TBST, and then developed by ECL to detect the protein bands.
2.7 Statistical methods
Graphpad prism 8 was used for statistical analyses and graphing,and each experiment was repeated more than three times.Comparisons between two groups were made using independent samples t-test, and comparisons between multiple groups were made using one-way ANOVA.Differences were expressed as statistically significant at P<0.05.
3.Results
3.1 Culture and identification of 7901-GCSCs
The growth morphology of normal cultured gastric cancer cells SGC-7901 and serum-free suspension cultured 7901-GCSCs were shown in Figure 1A-B.Flow cytometry was used to detect the positivity rate of CD44 in SGC-7901 and 7901-GCSCs, and the results showed that the positivity rate of CD44, a stemness marker,was significantly increased in 7901-GCSCs compared with that in normal SGC-7901 (P<0.05) as shown in Fig.2A-C.It indicated that 7901-GCSCs with stemness characteristics were successfully enriched.
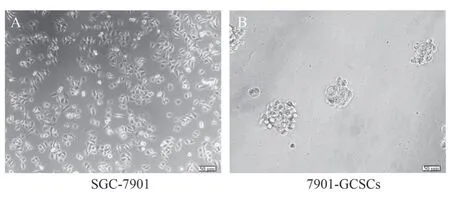
Fig 1 SGC-7901 and 7901-GCSCs growth forms

Fig 2 Positive rate of CD44 in SGC-7901 and 7901-GCSCs detected by flow cytometry
3.2 PGD2 inhibits the stemness of 7901-GCSCs
Inverted microscope was used to observe the sphere-forming morphology of 7901-GCSCs cells stimulated by the addition of different concentrations of PGD2 (2.5, 5, 10) μg/mL.The experimental results showed that compared with the DMSO group,the number of cytospheres in 7901-GCSCS cells stimulated with 5 μg/mL and 10 μg/mL concentrations of PGD2 was significantly reduced (P<0.05) and showed a concentration-dependent pattern, as shown in Fig.3 A-B.In addition, the Western blot results showed that, compared with the DMSO group, the stemness markers in the PGD2 group (CD44 , OCT4) proteins were also down-regulated(P<0.05) in concentration-dependent expression, as shown in Figure 4 A-C.The above experimental results indicated that PGD2 inhibited the stemness of 7901-GCSCs.

Fig 3 Ball-forming ability of 7901-GCSCs is diminished after PGD2 stimulation

Fig 4 Decreased expression of CD44, OCT4 in 7901-GCSCs after PGD2 stimulation
3.3 PGD2 promotes the activation of autophagy in 7901-GCSCs
The protein expression of 7901-GCSCs cells stimulated by the addition of different concentrations of PGD2 (2.5, 5, 10) μg/mL was examined by Western blot, and the results showed that the protein expression of autophagy-related markers (LC3, Beclin-1) was upregulated in the PGD2 group compared with the DMSO group(P<0.05) in a concentration-dependent manner.PGD2 was able to activate autophagy, as shown in Figure 5A-C.

Fig 5 Increased protein expression of LC3 and Beclin-1 in 7901-GCSCs after PGD2stimulation
3.4 CQ inhibits the activation of autophagy in 7901-GCSCs
The protein expression of 7901-GCSCs cells stimulated by the addition of different concentrations of CQ (2.5, 5, 10) μM was examined by Western blot, and the results showed that the protein expression of autophagy-related markers (LC3, Beclin-1) was downregulated in the CQ group compared with that in the DMSO group(P<0.05), and the results indicated that CQ was able to inhibit autophagy as shown in Figure 6A-C.
3.5 The effect of PGD2 on autophagy levels and stemness of 7901-GCSCs can be inhibited by CQ

Fig 6 Reduced protein expression of LC3, Beclin-1 in 7901-GCSCs after CQ stimulation
The protein expression of 7901-GCSCs cells was stimulated by the addition of 5 μg/mL PGD2 and 5 μM CQ using Western blot,and the results showed that the protein expression of stemness markers (CD44, OCT4) was significantly down-regulated, and the protein expression of autophagy-associated proteins (LC3, Beclin-1)was up-regulated in the PGD2 group, as compared with that in the DMSO group (P<0.05).as shown in Figure 7A-B.While there was no significant change in the expression of cellular autophagyrelated proteins as well as stemness markers in the PGD2+CQ group compared with the DMSO group.(ns: the difference was not significant) As shown in Figure 7A-B, the above experimental results indicated that CQ could block the stemness inhibitory effect of PGD2 on 7901-GCSCs.

Fig 7 CQ blocks the stemness inhibition of 7901-GCSCs by PGD2
4.Discussion
Gastric cancer remains one of the most common tumours in the world, with more than 1 million new cases and nearly 800,000 deaths reported in 2020[1].CSCs are also known as the “initiating cells” of tumours, and a very small number of CSCs can induce tumourigenesis[16].Tumour stem cells are closely related to tumour angiogenesis, drug resistance and invasiveness[17].Also the presence of CSCs is an important mechanism for tumour resistance to radiotherapy[18].Some researchers have suggested that GCSCs are mutations in gastric stem cells (GSCs) that cause normal gastric cancer tissues to develop from atrophic gastritis, intestinal metaplasia,atypical hyperplasia, and finally gastric cancer[19].It has also been shown that the process of GCSCs formation is often accompanied by epithelial-mesenchymal transformation of cellsontogenesis and high expression of stem cell-specific genes[20,21].Therefore, isolation and identification of stem cell-specific genes is crucial for targeting GCSCs.Currently, the regulatory mechanism of targeted drugs against GCSCs is unclear and requires further investigation.PGD2 is produced from arachidonic acid through a series of enzymatic reactions, and subsequently decomposed into the intermediate product prostaglandin H2 under the action of cyclooxygenase(COX), which is finally converted to PGD2 under the action of L-PTGDS[22].Currently, domestic and international research on PGD2 has focused on immune system diseases such as inflammation and asthma, while less research has been conducted on tumours.Kim J et al.found that tumour mesenchymal stromal cell-derived PGD2 inhibited the growth of prostate cancer cells[23].Mast cellderived PGD2 inhibits lung cancer tissue angiogenesis and enteritisinduced tumourigenesis[22,24].A previous study by the group found that PGD2 affected the biological functions of GCSCs[6].Therefore,the present study further investigated the molecular mechanisms by which PGD2 affects the stemness of GCSCs, with the aim of providing new ideas and targets for the diagnosis and treatment of clinical gastric cancer.
Autophagy is generally regarded as a process of cellular selffeeding, which involves the passage of cytoplasmic components through segregation and confinement in vesicles (autophagosomes),which subsequently bind to lysosomes to become autophagylysosomes and degrade the material contained therein[25].During tumour development, autophagy has a dual role: on the one hand,it achieves tumour suppression by inducing autophagic death of tumour cells, and on the other hand, it can contribute to tumour transformation and enhance its chemoresistance[26].Recent studies have shown that stem cell self-renewal and differentiation depend on the activation of autophagy[27,28].And activation of autophagy can promote the proliferation and drug resistance of CSCs, which is essential for the malignant biological functions of CSCs[29].However, after stimulation by PGD2 in this study, Western blot results showed that the protein expression of autophagy-related proteins LC3 and Beclin-1 increased in a concentration-dependent manner compared with the DMSO group, while the protein expression of stemness indicators OCT4 and CD44 also decreased in a concentration-dependent manner, indicating that PGD2 can activate autophagy while inhibiting the stemness of GCSCs.
Some studies have reported that PGD2 and L-PTGDS may inhibit gastric carcinogenesis, metastasis, invasion and proliferation through PPARγsignalling pathway[30].In this experiment, the results of stem cell spheroids and Western blot experiments showed that the inhibitory effect of PGD2 on the ability of stem cell spheroids became concentration-dependent, with the higher concentration of PGD2, the weaker the spheroids, and PGD2 inhibited the expression of stemness-related proteins.CQ is an autophagy inhibitor, which inhibits the fusion of autophagosome and lysosome[31].Zhao et al.blocked the activating effect of AQP5 on autophagy by using CQ, thus further suggesting that AQP5 may regulate the biological function of GCSCs through autophagy[32].And in this study by whether CQ could block the activation of autophagy by PGD2, we explored that PGD2 might affect the stemness of gastric cancer stem cells through autophagy.Therefore, while PGD2 was found to promote the expression of autophagy-related proteins in 7901-GCSCs in this study, the inhibitory effect of PGD2 on the stemness of 7901-GCSCs could be blocked by the autophagy inhibitor CQ.It suggests that PGD2 may affect the stemness of GCSCs by regulating autophagy.However, in this experiment it was only illustrated that PGD2 might be affecting the stemness of GCSCs through autophagy,but the specific molecular mechanisms regulating autophagy need to be further explored.Briefly, exogenous PGD2 was able to inhibit the sphere-forming ability of 7901-GCSCs, and the inhibitory effect of PGD2 on the stemness of 7901-GCSCs could be blocked by the autophagy inhibitor CQ, suggesting that PGD2 may inhibit the stemness of GCSCs through autophagy.
Authors’ contribution description:
Qiang Zhang: research supervision and article review; Feifan Wang:responsible for related experiments, analysing data and revising the paper; Peiyao Gao: experimental supervision and revising the paper;Hengjin Tian: writing the paper; Amin Chen and Na Wang: literature collection and analysis;
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Effects of Yigan Capsule on the expression of HMGB1, RAGE and NFκB protein in rats with drug-induced liver injury
- Analysis of clinical characteristics of leptomeningeal metastasis with band-like high signal in the brainstem
- Sequential experimental observation on the curative effect of Yingbupu decoction of Zhuang medicine on stage I and II acute kidney injury
- To explore the mechanism of Fuyang Jiebiao granules against viral pneumonia based on network pharmacology and pharmacodynamics
- Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of Bushen Huoxue decoction in the treatment of Osteoporosis
- Recent research progress from biological perspective on the mechanism of formation of osteoarthritis after anterior cruciate ligament injury
