血栓弹力图对COPD患者下肢深静脉血栓形成的预测价值
2024-03-27谭华侨宾冬梅周杰良邵超华裴华黄伟华刘小娟
谭华侨?宾冬梅?周杰良?邵超华?裴华?黄伟华?刘小娟

【摘要】目的 分析血栓彈力图(TEG)参数对COPD患者下肢深静脉血栓形成的预测价值。方法 选择35例下肢深静脉血栓形成的COPD患者作为观察组,另选择同期的35例无下肢深静脉血栓形成的COPD患者作为对照组,收集患者入院后24 h内的TEG参数,包括凝血反应时间R值、血液凝固时间K值、凝固角α角及最大血块强度MA值、血常规、血气分析及基本资料,采用Logistic回归分析及受试者操作特征(ROC)曲线分析TEG各项参数对COPD患者下肢深静脉血栓形成的预测价值。结果 R值、K值、α角与COPD患者下肢深静脉血栓形成有关(P均< 0.05),R值的曲线下面积(AUC)为0.787(95%CI 0.679~0.895),K值的AUC为0.758(95%CI 0.646~0.870),α角的AUC为0.689(95%CI 0.565~0.812),MA值的AUC为0.660(95%CI 0.533~0.787);4组数值联合预测COPD患者下肢深静脉血栓形成灵敏度及特异度更高(AUC=0.882,95%CI 0.796~0.969,P < 0.001),截断值为0.436,灵敏度为94%,特异度为80%。结论 TEG中R值、K值及α角是COPD患者下肢深静脉形成的预测因素,R值、K值及α角均能良好预测COPD患者下肢深静脉血栓形成,且R值、K值、α角和MA四者联合预测灵敏度及特异度更高。
【关键词】慢性阻塞性肺疾病;下肢深静脉血栓;血栓弹力图;Logistic回归分析;受试者操作特征曲线
Predictive value of TEG for deep venous thrombosis of lower limbs in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseTan Huaqiao, Bin Dongmei, Zhou Jieliang, Shao Chaohua, Pei Hua, Huang Weihua, Liu Xiaojuan. Department of Intensive Care Unit, Dongguan Eastern Central Hospital, the Sixth Hospital of Jinan University, Dongguan 523573, China
Corresponding author, Tan Huaqiao, E-mail: tanhuaqiaodoctor@163.com
【Abstract】Objective To analyze the value of thromboelastogram (TEG) parameters in predicting deep venous thrombosis of the lower limbs in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD). Methods Thirty-five COPD patients complicated with deep venous thrombosis of the lower limbs were assigned into the observation group, and 35 COPD patients without deep venous thrombosis of the lower limbs of the same period were recruited in the control group. TEG parameters (R value of coagulation reaction time, K value of blood coagulation time, α angle of coagulation and MA value of maximum clot intensity), routine blood test, blood gas analysis and baseline data were collected within 24 hours after admission. Logistic regression analysis and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis were used to analyze the predictive value of all parameters of TEG for deep venous thrombosis of the lower limbs in patients with COPD. Results R value, K value and α angle were significantly correlated with deep venous thrombosis of the lower limbs in patients with COPD (all P < 0.05). The area under the ROC curve (AUC) of R value was 0.787 (95%CI: 0.679-0.895), 0.758 for K value (95%CI: 0.646-0.870), 0.689 for α angle (95%CI: 0.565-0.812), and 0.660 for MA value (95%CI: 0.533-0.787), respectively. The combination of four parameters yielded higher sensitivity and specificity for predicting deep venous thrombosis of the lower limbs (AUC:0.882, 95%CI:0.796-0.969, all P < 0.001), the cut-off value was 0.436, the sensitivity was 94.3% and the specificity was 80%, respectively. Conclusions R value, K value and α angle in TEG are the independent predictors of deep venous thrombosis of the lower limbs in patients with COPD. R value, K value and α angle can properly predict deep venous thrombosis of the lower limbs in patients with COPD, and the combination of R value, K value, α angle and MA value yields higher sensitivity and specificity.
讨论
在大多数国家,近6%成年人患有COPD,占所有慢性呼吸系统疾病约60%,社会经济负担巨大[4-5]。在中国40岁或以上的人群中,COPD患病率估计为13.7%[6]。COPD患者血栓栓塞风险增加的机制复杂,该类患者的缺氧可使血小板具有高反应性,增强组织因子的合成和纤溶酶原激活抑制剂-1(PAI-1)活化,也可减少FIB的清除,使促红细胞生成素的产生、血细胞比容以及血小板的量性均发生异常改变,诱导细胞间黏附分子-1(ICAM-1)的表达增加血液黏度,进一步增加血栓的形成率[7-10]。COPD急性加重(AECOPD)常发生在呼吸道感染后,多种炎症介质、细胞因子、炎性细胞和抗体增多,增加血液黏度,且CRP、IFN-γ、IL-1等炎症因子高表达,影响血液凝固[7]。
国内有研究者发现,COPD患者合并DVT的发生率较高,既往静脉血栓病史、卧床时间≥3 d、D-二聚体升高是COPD合并DVT的危险因素[11]。有研究表明,在印度北部,肺栓塞是部分患者(14%)发生AECOPD的原因,不明原因的AECOPD患者发生肺栓塞的风险增加[12]。与其他住院人群相比,PE的患病率为5.7%~6.0%,PE可能是患者发生AECOPD或症状加重的诱因[13]。同时AECOPD也可作为PE的危险因素存在[14]。国外有研究证实33%的COPD和PE患者检出DVT,对于呼吸道症状恶化的COPD,考虑PE的同时,也应考虑DVT[15]。与肺活量测定结果正常患者相比,COPD Ⅲ/Ⅳ期患者发生继发性静脉血栓栓塞(VTE)的风险是前者两倍(危险比2.05)[16]。肺栓塞栓子最常见的来源是下肢DVT,因而寻找能预测COPD患者群体下肢DVT形成的、易获取的临床指标显得极其重要。
TEG由德国的Harter于1948年发明,是一种通过高灵敏度悬挂线描述血液凝固过程的分析仪,可以获得血凝块形成及纤溶相关指数的图标,能够動态监测整个凝血及纤溶过程,临床上可运用于血栓性疾病。有研究证实,TEG血栓最大振幅值增大可能是老年急性脑梗死患者病死的影响因素(OR > 1,P < 0.05),各时点TEG血栓最大振幅预测病死的AUC均> 0.85,具有较高的预测价值,其中入院6 h的AUC最高,故TEG血栓最大振幅在预测急性脑梗死患者病死中具有较高的效能,可通过TEG动态监测并据此及时调整治疗方案,以改善患者预后、降低病死率[17]。另有研究者分析TEG对颅脑操作后创伤性凝血病的早期诊断与预后评价的临床效果,证实TEG可有效识别颅脑损伤后患者不同时间的凝血功能,指导临床采用针对性救治措施,具有较高的临床应用价值[18]。
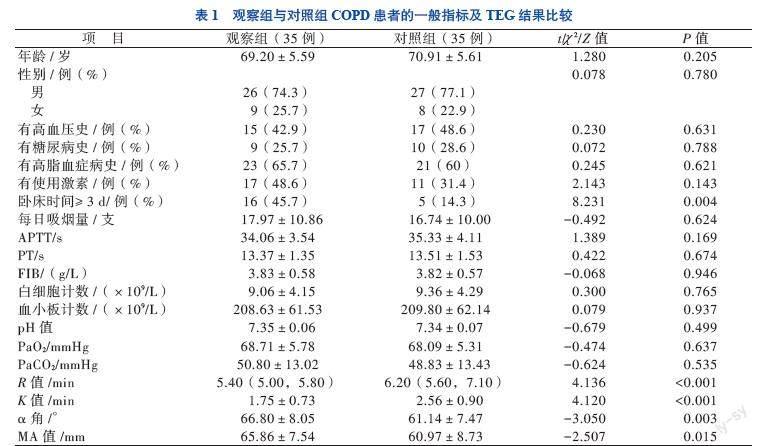
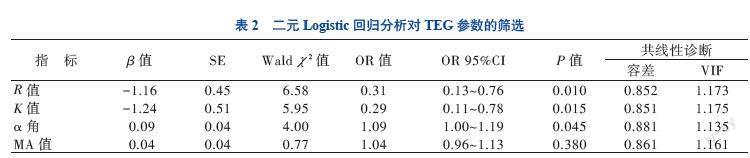
本研究根据COPD患者下肢静脉彩超的结果是否合并DVT形成分为观察组及对照组,分别对两组进行TEG检测,结果显示观察组的R值及K值短于对照组,观察组的α角及MA值大于对照组,这一结果表明COPD合并下肢DVT形成的患者凝血因子活性、纤维蛋白原功能及血小板功能增强。COPD患者慢性缺氧、炎症和二氧化碳潴留,引起继发性红细胞增多,血液黏度增加,且内皮细胞的破坏和功能紊乱,活化的炎症细胞释放出大量的炎症介质和炎症因子,不仅加重气道炎症,而且激活内源性和外源性凝血系统,增加凝血因子的活性及促进血小板功能、加快血小板的聚集,进而促进血栓的形成[19-21]。另本研究通过Logistic回归分析探讨TEG各参数与COPD患者下肢DVT形成的相关性,结果显示R值、K值、α角与COPD患者下肢DVT形成有关,而MA值与COPD患者下肢DVT形成无关,说明凝血因子的活性及纤维蛋白原功能的增强可作为COPD患者下肢DVT形成的预测因素。在稳定期COPD患者中,较高的D-二聚体水平被确定为较高病死率的预测因子,而抗凝血酶Ⅲ复合物水平较高与COPD患者加重风险增加相关[22]。故临床上可启用抗凝治疗来预防COPD患者下肢DVT形成。通过ROC曲线分析TEG参数,明确R值、K值及α角对COPD患者下肢DVT形成均有预测价值,且四者联合预测COPD患者下肢DVT形成的灵敏度及特异度更高,其AUC为0.882(95%CI 0.796~0.969),诊断阈值0.436,灵敏度为94.3%,特异度为80%,故建议在四者联合的预测概率>0.436时启用抗凝治疗。
COPD患者凝血因子活性、纤维蛋白原功能及血小板功能增强,但凝血因子活性、纤维蛋白功能是COPD患者下肢DVT形成的独立危险因素,故选择抗凝方式预防下肢DVT形成。综上所述,启动抗凝的时间为R值、K值、α角及MA值联合预测概率>0.436时可能为较好的时机,但本研究基于相对小样本量获得结论,存在一定局限性,尚需扩大样本量继续验证研究结论。
参 考 文 献
[1] Global initiative for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Global strategy for the diagnosis,management and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease 2022 report[EB/OL].(2021-11-15)[2022-08-03]. http://www.goldcopd.org.
[2] 庞景灼, 巫国勇, 叶敏, 等. 血栓弹力图在食管癌患者围手术期检测中的意义[J]. 中山大学学报(医学科学版), 2020, 41(6): 975-980.
Pang J Z, Wu G Y, Ye M, et al. Clinical significance of the application of thrombelastogram in perioperative detection of esophageal cancer patients[J]. J Sun Yat-Sen Univ(Med Sci), 2020, 41(6): 975-980.
[3] 巴志伟, 赵文, 刘传苗. eGFR-CysC联合血栓弹力图对慢加急性肝衰竭患者临床预后的预测价值[J]. 新医学, 2023, 54(3): 210-215.
Ba Z W, Zhao W, Liu C M. Predictive value of cystatin C-based estimated glomerular filtration rate combined with thromboelastogram for clinical prognosis of acute-on-chronic liver failure[J]. J New Med, 2023, 54(3): 210-215.
[4] Cao Y Q, Dong L X, Cao J. Pulmonary embolism in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Chin Med J, 2018, 131(14): 1732-1737.
[5] GBD Chronic Respiratory Disease Collaborators. Prevalence and attributable health burden of chronic respiratory diseases, 1990—2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. Lancet Respir Med, 2020, 8(6): 585-596.
[6] Wang C, Xu J, Yang L, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in China (the China Pulmonary Health[CPH]study): a national cross-sectional study[J]. Lancet, 2018, 391(10131): 1706-1717.
[7] Liu M, Hu R, Jiang X, et al. Coagulation dysfunction in patients with AECOPD and its relation to infection and hypercapnia[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2021, 35(4): e23733.
[8] Bikov A, Meszaros M, Schwarz E I. Coagulation and fibrinolysis in obstructive sleep apnoea[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(6): 2834.
[9] Fuqua J, Reece J, Sofka S. Successful use of phlebotomy to treat severe secondary polycythemia due to chronic lung disease[J]. Hematol Rep, 2021, 13(2): 8961.
[10] Obi A T, Andraska E, Kanthi Y, et al. Endotoxaemia-augmented murine venous thrombosis is dependent on TLR-4 and ICAM-1, and potentiated by neutropenia[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2017, 117(2): 339-348.
[11] 沈芳, 张景熙, 刘锦铭, 等. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病加重期合并靜脉血栓栓塞症的危险因素分析[J]. 中国呼吸与危重监护杂志, 2019, 18(5): 427-431.
Shen F, Zhang J X, Liu J M, et al. Risk factors of venous thromboembolism among patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Chin J Respir Crit Care Med, 2019, 18(5): 427-431.
[12] Chaudhary N, Khan U H, Shah T H, et al. Prevalence and predictors of pulmonary embolism in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[J]. Lung India, 2021, 38(6): 533-539.
[13] Aleva F E, Voets L W L M, Simons S O, et al. Prevalence and localization of pulmonary embolism in unexplained acute exacerbations of COPD: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Chest, 2017, 151(3): 544-554.
[14] 华晶, 韩蕙泽, 季颖群. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病合并肺栓塞的评估及处置[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2020, 40(10): 800-804.
Hua J, Han H Z, Ji Y Q. Evaluation and management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease complicated with pulmonary embolism[J]. Chin J Pract Intern Med, 2020, 40(10): 800-804.
[15] Castellana G, Intiglietta P, Dragonieri S, et al. Incidence of deep venous thrombosis in patients with both Pulmonary Embolism and COPD[J]. Acta Biomed, 2021, 92(3): e2021210.
[16] B?rvik T, Br?kkan S K, Enga K, et al. COPD and risk of venous thromboembolism and mortality in a general population[J]. Eur Respir J, 2016, 47(2): 473-481.
[17] 王麗红, 刘晓玲, 罗葆华. 血栓弹力图中血栓最大振幅对老年急性脑梗死患者病死的预测价值[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2020, 40(15): 3161-3164.
Wang L H, Liu X L, Luo B H. Predictive value of the maximum amplitude of thrombus in thromboelastography for the death of elderly patients with acute cerebral infarction[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2020, 40(15): 3161-3164.
[18] 张志华, 余国峰. 血栓弹力图用于诊断颅脑损伤后创伤性凝血病的临床研究[J]. 中华全科医学, 2021, 19(8): 1300-1302, 1329.
Zhang Z H, Yu G F. Clinical study of thromboelastography in the diagnosis of traumatic coagulopathy after craniocerebral injury[J]. Chin J Gen Pract, 2021, 19(8): 1300-1302, 1329.
[19] van der Vorm L N, Li L, Huskens D, et al. Acute exacerbations of COPD are associated with a prothrombotic state through platelet-monocyte complexes, endothelial activation and increased thrombin generation[J]. Respir Med, 2020, 171: 106094.
[20] Wang Y, Zheng Y, Zhai Y L, et al. Comparative analysis of MCP-1 and TF in elderly patients with acute exacerbations of COPD and its clinical significance[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2015, 19(2): 215-219.
[21] Zhou Y, Yu J, Zhou H. Changes in thrombelastography in patients with acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and the relationship with lung function[J]. Emerg Med Int, 2022, 2022: 4313394.
[22] Huseb? G R, Gabazza E C, DAlessandro Gabazza C, et al. Coagulation markers as predictors for clinical events in COPD [J]. Respirology, 2021, 26(4): 342-351.
(收稿日期:2023-10-31)
(本文编辑:林燕薇)
