Speed limit effect during lane change in a two-lane lattice model under V2X environment
2024-03-25CanJin金灿GuangHanPeng彭光含andFangYanNie聂方彦
Can Jin(金灿), Guang-Han Peng(彭光含), and Fang-Yan Nie(聂方彦)
1College of Physical Science and Technology,Guangxi Normal University,Guilin 541004,China
2Guangxi Key Laboratory of Nuclear Physics and Technology,Guangxi Normal University,Guilin 541004,China
3Information and Modern Education Technology Center,Hunan University of Arts and Science,Changde 415000,China
4Computer and Information Engineering College,Guizhou University of Commerce,Guiyang 550014,China
Keywords: traffic flow,lattice model,speed limit
1.Introduction
With the increase of traffic flux, traffic problems are becoming more and more severe.Therefore, many scholars actively have engaged in traffic flow modeling research to investigate the underlying causes of traffic congestion.Currently, traffic micro models[1-13]and macro models[14-20]are advantageous in investigating traffic phenomena.Especially,Natagani[21-23]provided original lattice models to reproduce complex traffic phenomena on a single lane and two lanes,which can demonstrate the evolution process of traffic flux,density and speed.In recent years, many derivative models have successfully emerged since various traffic information factors were mined.These traffic factors are mainly connected with the differences of flux and density.[24-32]Also, the impact of traffic information in lattice models has been attracted by scholars, which covered the time delay,[33-38]the interruption probability,[39,40]the driver’s anticipation[41-45]and others.[46-66]Moreover, the lane-changing phenomenon also attracts the interest of some scholars.[67-78]Recently, vehicle to everything(V2X)technology helps to enable the real-time transmission of traffic information.In an actual transportation environment, the slope, curve, narrow road and tunnel inevitably exist on the road, which require adopting a speed limit method to ensure traffic safety especially in lane changing situations.In addition, in the information coverage area,the speed limit requirements of roads can be shared as traffic information.And connected vehicles can use V2X communication technology to obtain the speed limit information,which contributes adopting corresponding reaction behaviors.But the speed limit effect(SLE)has not been surveyed under lane change.Subsequently,the SLE will be employed to fabricate a novel two-lane lattice model under V2X environment.Also,the effectiveness of the SLE will be proven through theoretical analysis and numerical simulation concerning density and hysteresis loop.
2.Construction of two-lane model integrating the speed limit effect
Figure 1 presents the lane change in the Nagatani’s twolane lattice model, integrating double continuity equations as follows:[3]


Hereais the sensitivity coefficient.Nagatani’s two-lane lattice model includes Eqs.(3) and (5).Subsequently, a number of extended two-lane lattice models[67-78]are concerned with different traffic factors.In modern transportation environments,transportation infrastructure is complex and dangerous roads often appear.Therefore, the speed limit method is an important measure to ensure safety, which will occur in the SLE.However, previous two-lane lattice models have not thought about the SLE during the evolution process.Accordingly, a new evolution equation is put forward by integrating the SLE under the V2X environment

whereτ=1/aexpresses the delay time.
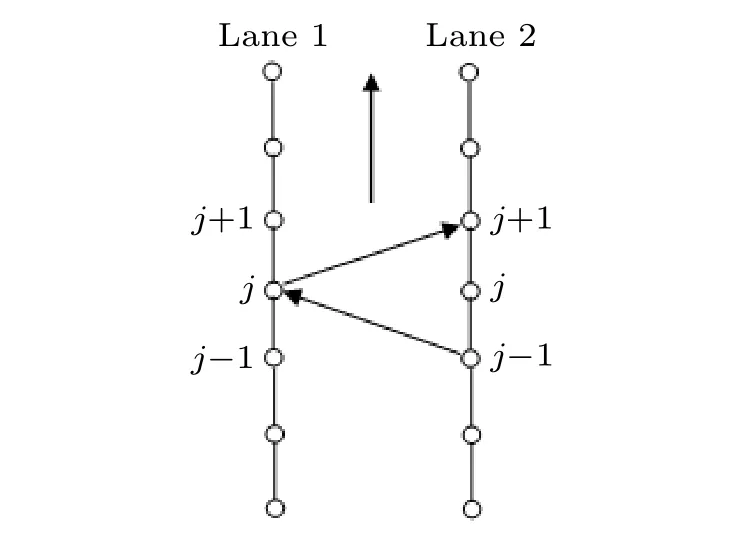
Fig.1.The schematic model of traffic flow on two lanes.
3.Linear stability analysis
Firstly,yj(t)is defined as a small deviation as follows:

Accordingly, we fulfil the neutral stability curve as shown in Fig.2 (the solid line).Herevmax=2,γ=0.05 andvlim=0.8vmax.Obviously,the stable range gradually magnifies with the reaction coefficient of SLE amplifying.

Fig.2.The phase diagram in parameter space(ρ,a).
4.Nonlinear analysis
To begin with,we define a small variableεfor the following variablesXandTwith a constantb:

HereR(X,T) implies a function involvingXandT.Consequently,we can expand Eq.(7)to quintic power by variableεas follows:

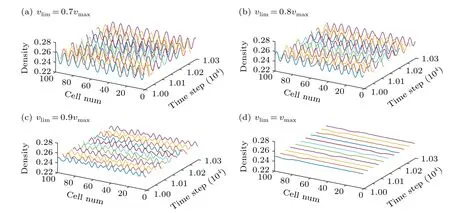
Fig.3.The spatiotemporal evolution of density waves for different vlim.
Consequently, the kink-antikink soliton solution is described by

Thereupon, the coexisting curves are displayed in Fig.2(dashed curves) based onρj=ρc±D.Then, one sees three regions of the phase diagram covering the stable region, the metastable region and the unstable region, which states that the neutral and the coexisting curves fall down due to the SLE amplifying.
5.Numerical simulation
In this section,the periodic boundary condition is applied and the initial conditions are employed as
First of all, the spatiotemporal evolution of density waves is described at differentvlimas shown in Fig.3, corresponding density profiles displayed in Fig.4 at 10300 time step,whereN=100,ρ0=0.25,γ=0.05, anda=2.58.According to Figs.3 and 4,the amplitude of density waves magnifies as the limited speed decreases and the kink-antikink density wave occurs in Figs.3(a)-3(c),which reveals that the lower limited speed will deteriorate the stability of traffic flow.
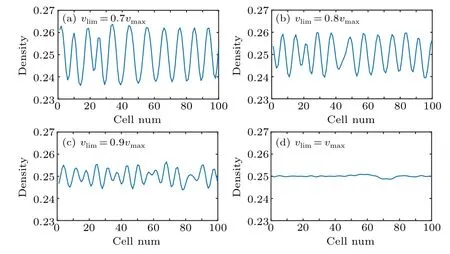
Fig.4.The density profiles at 10300 time step corresponding to Fig.3.
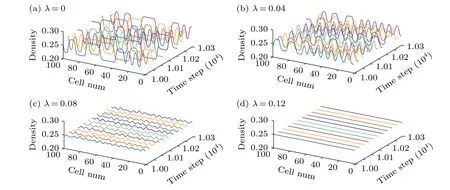
Fig.5.The spatiotemporal evolution of density waves for different λ.
Moreover, the three dimensional density evolution is exhibited for different reaction coefficientsλin Fig.5.And Fig.6 represents the density profiles related to Fig.5 at the 10300th time step for all sites, wherevlim=0.8vmax.From Figs.5 and 6, the density vibration lessens by amplifyingλ-value, which states that traffic jam can be effectively restrained by ascending the intensity of the SLE in two-lane system.Also, a stable state has emerged in Figs.5(d) and 6(d)asλ=0.12, which demonstrates that the SLE promotes the stability of two-lane traffic flow.

Fig.6.The density profiles at 10300 time step for different λ corresponding to Fig.5.

Fig.7.The hysteresis loop of the 55th lattice between flux and density.
Finally, due to the asynchronous flow and density during the acceleration and deceleration processes of the traffic flow,a hysteresis loop phenomenon occurs.Therefore,we get hold of the hysteresis loop according to flux and density displayed in Fig.7.Observing Fig.7, the hysteresis loop obviously shrinks by enlarging theλ-value,which certificates that the SLE contributes to the stable situation of two-lane traffic system.Moreover, asλ=0.12, the hysteresis loop vanishes owing to the stable state of two-lane traffic flow in this case.
6.Conclusion
Due to road bottlenecks,it is often necessary to limit the speed of vehicles for safety reasons.Accordingly,V2X communication is adopted to convey information of the speed limit effect in building two-lane lattice model.Also,we obtain the stability condition closely related to the speed limit effect on two lanes.Moreover, nonlinear analysis is performed to derive the mKdV equation connected with the speed limit effect.Additionally,it is confirmed that the speed limit effect can be applied to suppress traffic congestion with the advantage of the two-lane freeway.Consequently, it is completely necessary to consider the speed limit effect in traffic flow modeling on two lanes.Surely,how to consider a reasonable speed limit range based on the physical conditions of traffic roads is an interesting topic in future research.
Acknowledgments
Project supported by the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation, China (Grant No.2022GXNSFDA035080), the Central Government Guidance Funds for Local Scientific and Technological Development, China (Grant No.Guike ZY22096024), and the National Natural Science Foundation,China(Grant No.61963008).
杂志排行
Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- A multilayer network diffusion-based model for reviewer recommendation
- Dynamics of information diffusion and disease transmission in time-varying multiplex networks with asymmetric activity levels
- Modeling the performance of perovskite solar cells with inserting porous insulating alumina nanoplates
- Logical stochastic resonance in a cross-bifurcation non-smooth system
- Experimental investigation of omnidirectional multiphysics bilayer invisibility cloak with anisotropic geometry
- Exploration of the coupled lattice Boltzmann model based on a multiphase field model: A study of the solid–liquid–gas interaction mechanism in the solidification process
