Validation of Molecular Detection Methods for Gluten Allergens in Infant Formula
2024-02-26ShuhuanZHAOYunxiaWANGCuizhiLI
Shuhuan ZHAO, Yunxia WANG, Cuizhi LI
Inner Mongolia Yili Industrial Group Co., Ltd., Inner Mongolia, Hohhot 010110, China
Abstract [Objectives] To verify the specificity, sensitivity, precision and negative-positive deviation of the foodproof gluten component detection kit for the detection of gluten allergens in milk powder matrix, and to establish a real-time fluorescent PCR legal method for the detection of gluten allergens in milk powder. [Methods] The specificity, sensitivity, precision and negative-positive deviation of the detection method of foodproof gluten component detection kit (PCR-probe method) were verified by artificially adding different concentrations of wheat bran and extracting sample DNA by kit method, and applied to sample detection. [Results] The specific detection results of two kinds of milk powder with wheat bran and buckwheat added showed that the foodproof gluten component detection kit (PCR-probe method) had good specificity for wheat gluten. The results of artificially added wheat bran positive samples showed that the false positive rate and false negative rate of the kit in the milk powder matrix were 0, and the sensitivity and precision were high. [Conclusions] The kit is simple to operate and has high accuracy, which is suitable for the detection of gluten allergen components in milk powder.
Key words Real-time fluorescent PCR, Gluten, Allergen, Infant formula
1 Introduction
Food allergy is a recurrent, adverse reaction caused by a specific immune response after exposure to a particular food and has become a global food safety issue[1-2]. The presence of natural allergenic components in food ingredients causes allergic reactions in 5%-8% of children and 2%-4% of adults, which can be severe and life-threatening[3]. Among them, gluten is one of the food allergen components and was the first food allergen to receive international attention and research. Gluten is a structural protein complex widely found in wheat grains, especially barley, wheat, oats and other grains, mainly composed of wheat alcohol soluble proteins and wheat gluten proteins, which account for 80%-85% of the total protein content of wheat[4-6]. Gluten proteins are the common antigens of celiac disease and immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated wheat allergy, and when an allergic individual is exposed to this protein for the first time, the body’s immune system produces antibodies that become IgE, and upon re-exposure to the same food proteins, the IgE antibodies and chemicals such as histamine are released, causing respiratory, gastrointestinal, dermal, or cardiovascular reactions that, in severe cases may even be fatal[7-8].
The techniques used for allergen detection can be categorized into two main groups,i.e., immunological detection techniques based on the protein level, and molecular biology detection techniques based on the gene level[9]. Molecular biology detection techniques based on the gene level include real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR, multiplex PCR, reverse transcription PCR, digital PCR,etc.Immunological detection techniques based on the protein level include electrophoresis, mass spectrometry, immunological methods and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The most widely used are mainly ELISA and PCR methods[10-11]. Since the accuracy and specificity of immunological detection methods mainly depend on the recognition of allergens by antibodies, certain food industries often utilize deep-processing techniques such as thermal processing, ultra-high pressure and enzymatic digestion to deform and degrade allergenic proteins, and changes in protein structure can interfere with protein extracts or antibody binding sites, which can also lead to the emergence of false-negative results[12]. Real-time fluorescence PCR method, as a new detection technology, has played an increasingly important role in allergen detection, and it effectively solves the problems of immunological methods, such as the inability to detect processed foods and high false-negative rate, and the instrument is relatively inexpensive, with low requirements for personnel experience and operation, and the detection cost is extremely low, high accuracy, good reproducibility, applicability, and easy to popularize the application[13]. The foodproof Gluten Composition Detection Kit (PCR-Probe Method) adopts real-time fluorescent PCR technology to design primers and probes for wheat- and barley-specific genes, and the probe bound to the template is broken down by Taq enzyme to produce fluorescent signals during PCR amplification, and the fluorescent quantitative PCR instrument plots real-time amplification curves based on the detected fluorescent signals, thus realizing the qualitative detection of gluten at the nucleic acid level. The qualitative detection of gluten at the nucleic acid level is realized.
In this study, the specificity, sensitivity and precision of the foodproof gluten detection kit were verified, and the false-positive and false-negative rates of the kit were also evaluated by milk powder samples artificially spiked with wheat gluten, with a view to providing more choices of detection protocols for the detection of gluten allergenic components in milk powder.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Samples and reagents
2.1.1Sample information. Infant formula, wheat bran, buckwheat, samples from Jingdong e-commerce and a market in Hohhot City.
2.1.2Reagents.foodproof gluten component detection kit (BIOTECON Diagnostics Company), plant gene extraction kit (Tiangen Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd.).
2.2 Instruments and equipmentPico17 benchtop centrifuge (Thermo-Fisher, USA), SLAN-96P real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR instrument (Shanghai Hongshi Medical Technology Co., Ltd.), A2 type biological safety cabinet (Thermo-Fisher, USA), BioDrop ulite micro nucleic acid protein assay (Bio-Drop, USA).
2.3 Experimental methods
2.3.1Extraction of template DNA. Weighed 30 mg of each infant formula sample and simulated gluten-containing sample in a 2 mL centrifuge tube, extracted and purified the template DNA using the DNA extraction and purification kit, and then used the micronucleic acid protein assay to determine the quality and concentration (OD260/OD280is in the range of 1.7-2.0) for fluorescence PCR detection.
2.3.2Foodproof gluten allergen component detection kit methods. First, the solution was thawed. To maximize recovery of the contents, shook the vial briefly in a microcentrifuge before opening. Removed the assay master mix, blew up and down to mix carefully, pipetted 20 μL of PCR Master Mix into each PCR tube, added 5 μL each of the negative control, sample DNA extract, and positive control into PCR tubes, covered the tube, centrifuged briefly, and immediately performed the PCR amplification reaction. The PCR tubes were placed on a PCR instrument, and the recommended reaction program was set as follows: reaction system 25 μL. The recommended reaction program is as follows: 25 μL of reaction system, fluorescence signal is detected at 60 ℃ in each cycle of the second step, and the detection channel is selected as FAM, and the detailed operation procedure is described in the instruction manual.
2.3.3Specificity verification. Took infant formula as the base, separately added 1% wheat gluten and buckwheat, extracted the DNA of the samples for specificity test according to the method described in the DNA extraction kit, and carried out the PCR reaction and interpretation of the results according to the method in Section2.3.2in the instructions of Foodproof Gluten Allergen Component Detection Kit to verify the specificity of the method.
2.3.4Sensitivity validation. Wheat gluten and infant formula were mixed in different proportions to obtain samples with different gluten contents, and the gluten contents were 100%, 10%, 1%, 0.1%, 0.01%, and 0.001%, with a total of 6 concentration gradient samples, and the DNA of the samples used for sensitivity testing was extracted in accordance with the method described in the DNA Extraction Kit, and the DNA of the samples was extracted in accordance with the method in Section2.3.2, and PCR reaction and result interpretation were performed according to the method in Section2.3.2to verify the sensitivity of the method.
2.3.4Precision verification. Took 2 samples of infant formula and infant formula with artificially added 0.1% wheat gluten, extracted the DNA of the samples used for the precision test according to the method described in the DNA extraction kit, and carry out PCR reaction 10 times for each sample according to the setting of the instruction manual of Section2.3.2Foodproof Gluten Allergen Ingredient Detection Kit to validate the precision of the method.
2.3.5Negative and positive bias experiment verification. Took 5 samples of infant formula, 20 samples of infant formula with 0.01% wheat gluten added artificially, and 5 samples of infant formula with 0.1% wheat gluten, extracted the DNA of the samples used in the negative-positive deviation experiment according to the method described in the DNA extraction kit, and carry out the PCR reaction and interpretation of the results in accordance with the setting of the instruction manual of Section2.3.2Foodproof Gluten Allergen Ingredient Detection Kit. PCR reaction and result interpretation were performed to calculate the false positive rate and false negative rate to verify the negative and positive deviation of the method.
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Specificity test resultsTheCtvalue of foodproof Gluten Allergen Detection Kit for infant formula containing 1% wheat gluten was less than 35, and the result was determined as "positive for gluten-containing cereal"; while no specificity was found for infant formula containing 1% buckwheat and infant formula without wheat gluten. TheCtvalue was NoCt, and the result was negative for gluten-containing cereal ingredients. The results are shown in Table 1, which indicates that the specificity of the kit is good.

Table 1 Test results of specificity for Foodproof Gluten Allergen ingredient test kit
3.2 Sensitivity test resultsThe results of the sensitivity test are shown in Table 2. From the results, it can be concluded that the content of wheat gluten can still be detected at 0.01%, which indicates that the sensitivity of this method can reach 0.01%, and that it can also detect wheat gluten at 0.01%. The sensitivity of this method can reach 0.01%.
3.3 Results of precision experimentUsing infant formula as the substrate, one negative sample without wheat gluten, one positive sample with artificial contamination of 0.1% wheat gluten, each sample was repeated 10 times. The results of the precision test are shown in Table 3. From the results, it can be concluded that the results of the precision experiment of the foodproof gluten allergen component detection kit are consistent.
3.4 Results of negative and positive deviation experiments
The results of the negative-positive deviation test are shown in Table 4. The results of the negative-positive deviation test are calculated from the results in Table 4. The false-positive rate of the results was 0. For positive results, the false-negative rate of the foodproof Gluten Allergen Ingredient Detection Kit test results was 0.
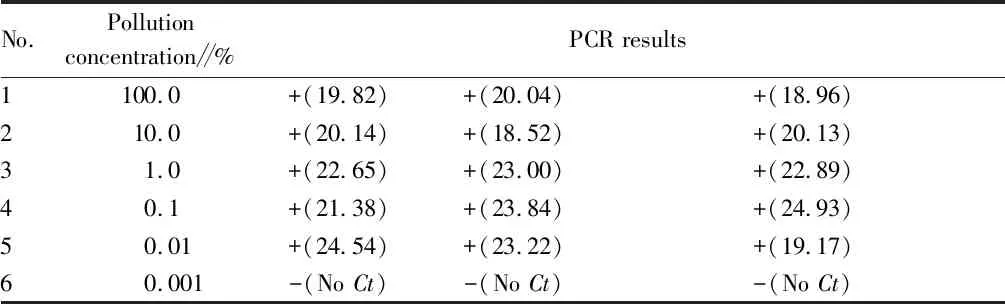
Table 2 Test results of sensitivity for Foodproof Gluten Allergen ingredient test kit

Table 3 Test results of precision for Foodproof Gluten Allergen ingredient test kit

Table 4 Test results of negative-positive deviation for Foodproof Gluten Allergen ingredient test kit
4 Conclusions and discussion
Abnormal or abnormal immune responses in the human body caused by food allergy have become a global public health and food safety issue of great concern[14]. With the rapid development of molecular technology at the DNA level, high-throughput and highly sensitive PCR technology has also played an important role in allergen detection, and the use of real-time fluorescent PCR to detect gluten allergen components is easier in the pre-treatment process and more accurate in the results compared with mass spectrometry methods, immunological methods, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay,etc[15-18].
This test was conducted to validate the specificity, sensitivity, precision and negative and positive deviations of the fluorescence quantitative PCR assay by measuring the mixed samples of adulterated wheat gluten. From the test results, it can be seen that the gluten components in milk powder can be detected quickly and accurately by real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR, and the foodproof gluten allergen component detection kit has good specificity, sensitivity, precision, and the results of the negative and positive deviations were all 0. The kit has the advantages of simple operation and rapidity, which can meet the needs of the rapid detection of infant milk powder samples, and it is suitable for monitoring the gluten allergen composition of milk powder used in the production and processing process, providing powerful technical support for the quality control of enterprise products.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Practice and Thinking of Agricultural Science and Technology Experts Serving the Grassroots to Promote Rural Revitalization
- Technique of Earthworms Restoring Soil in Greenhouse Cultivation
- Research Progress on Nutritional Requirements of Carp
- Discussion on Land Use Mode Reform in Coal Opencast Mining
- Guarantee Strategy for the Safety of Agricultural Industry in Hunan Province
- Study on Solid Fermentation and Antioxidant Function of Natto
