Analysis of vascular plant resources and diversity in Machin County,Qinghai Province
2024-01-11HuChenDongdongWangQingWangAnhuaWangJingmingJia
Hu Chen,Dongdong Wang,Qing Wang,Anhua Wang,Jingming Jia
School of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang 110016,China
Abstract Machin County is situated in the Sanjiangyuan Nature Reserve in the southeastern part of Qinghai Province.Influenced by the special topography and climate of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau,Machin County has complex and diverse plant species. The vascular plant resources and diversity in Machin County were studied through field survey,literature review and specimen identification.The results show that there are 47 families and 127 genera and 256 species of vascular plants in the region,basically angiosperms,including those containing more species of the family Asteraceae,Buttercup,Genus Ginseng,Leguminosae and Rosaceae,and those containing more species of the genus Artemisia,Artemisia,Aster and Donzonia. In terms of life type,perennial herbs are the most dominant ones,accounting for 77.34% of the total number of species,followed by some annual (or biennial) herbs and shrub types.There are 191 species of medicinal vascular plants,accounting for 74.61% of the total number of species,including 48 species of Tibetan medicine. In terms of the medicinal parts of these plants,whole herb category is the most common one,followed by the root and rhizome category.Based on the investigation and research,we have proposed the conservation and utilization of plant resources in Machin County,Qinghai Province.
Keywords: plant resources;diversity;medicinal use;conservation and utilization;Tibetan medicine;Machin County
1 Introduction
Plant resources have always been the material basis for human survival,and these resources are also an important part of biodiversity and a major source of medicinal resources [1].It even plays an irreplaceable role in the treatment and prevention of diseases for ethnic minorities in remote areas [2].Machin County is located in the Sanjiangyuan Nature Reserve of Qinghai Province.Influenced by the special topography and climate of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau,the natural grassland ecological environment in the county is relatively complex [3].The highland environment provides unique geographical and climatic conditions for the growth of local vegetation,giving the vegetation in Machin County special distribution characteristics.However,at present,most studies on this area focus on ecological livestock development and grassland management [4,5],with only few reports on local plant resources and their medicinal values.Therefore,we performed a preliminary investigation using field survey,specimen collection,literature search and specimen to check plant resources and diversity in Machin County,aiming to help understand the species,distribution and utilization status of plant resources in the area,and to provide a scientific basis for rational development and effective conservation of vascular plant resources in Machin County.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Overview of Machin County
Machin County is located in the southeastern part of Qinghai Province and the northeastern part of Guoluo Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture,with latitude and longitude coordinates of N 33°43'-35°16',E 98°-100°56'.This location is within the national “sanjiangyuan” ecological reserve.The total area of Machin County is about 13,400 km2,with an average altitude of over 4,100 m and a typical plateau mountainous type [6].Influenced by the cold and humid climate in the plateau,the area is characterized by low heat,water and heat in the same season,stable rainfall,spring drought,small annual temperature difference,large daily temperature difference,long sunshine time,and short plant growth period.The average annual temperature is -3.8-3.5℃ and the annual precipitation is between 423-565 mm.The annual sunshine time is 2313-2607 h,with the relative sunshine around 45%-63%.Affected by natural factors such as topography,geomorphology and environment,the soil is still in the youth stage of development,and its texture is thin and coarse.Natural grassland in Machin County is divided into alpine meadow type,alpine swamp type,scrub type,mountain grassland type,alpine grassland type and sparse forest grassland type,which are widely distributed,accounting for 87.89% of the total land area of the county.Vegetation is affected by the strong fluctuation of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.The horizontal zonal distribution is disturbed,and the vertical zonal distribution is obvious.Some distribution patterns are closely related to specific topography and water,making them zonal types [7].The geographical location of the study area is shown in Fig.1.
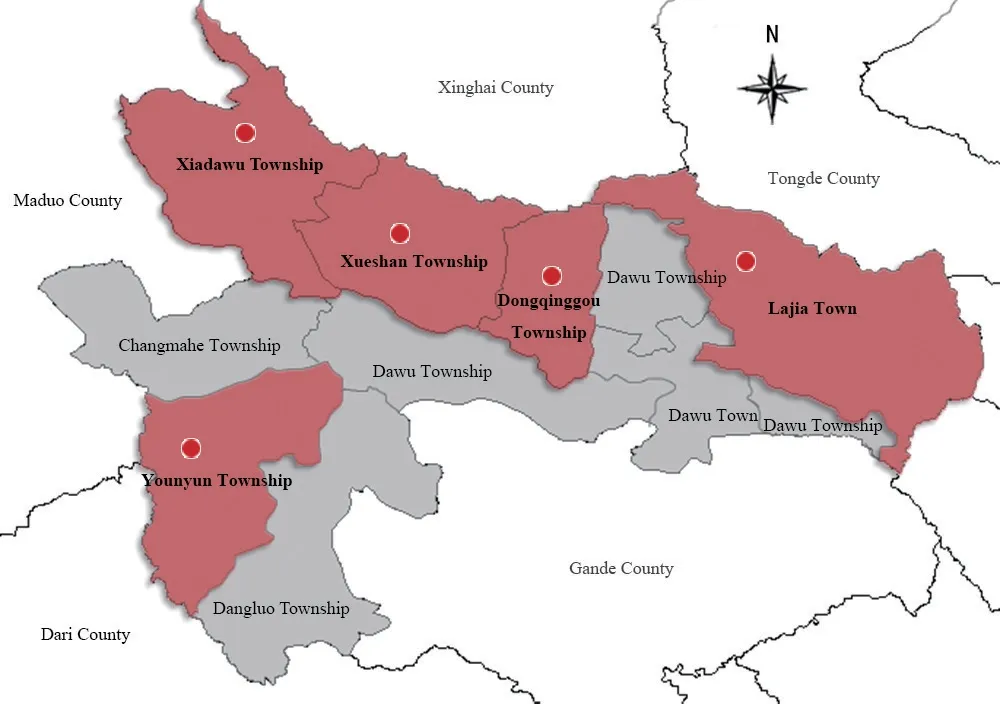
Fig.1 Geographic location and survey location of the study area
2.2 Research method
In July 2019,the 13th Scientific Expedition of Chinese Medicine Resources by Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,in conjunction with the People's Hospital of Machin County,Liaoning Jinqiu Hospital,Qinghai University and Qinghai University for Nationalities,adopted a route survey of representative areas in Machin County.The survey was performed by collecting specimens along the way,taking photographs,and recording detailed information on collection locations,time,and main morphological characteristics of plants,as well as using GPS recorder to record latitude and longitude.The species identification of vascular plants in Machin County was carried out according to literature such as “Flora of China” [8],“Flora of Qinghai” [9],and “Flora of Qinghai Economy” [10].The list of vascular plants that can be used as medicine was then established based on the National Compilation of Chinese Herbs [11],Chinese Materia Medica [12],Jingzhu Materia Medica [13],and Chinese Tibetan Medicine [14],with a total number of 191 species (48 species of Tibetan medicine included).Finally,the diversity of vascular plant resources in Machin County was analyzed and evaluated,and corresponding suggestions for development,utilization and conservation of vascular plant resources were made.
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Analysis of the composition of vascular plant species in Machin County
According to the results of the study,vascular plants in Machin County belong to 47 families,127 genera and 256 species,including 4 families,4 genera and 4 species of ferns,2 families,2 genera and 4 species of gymnosperms,and 41 families,121 genera and 248 species of angiosperms(36 families and 114 genera and 237 species of dicotyledons;5 families and 7 genera and 11 species of monocotyledons) (Table 1).The angiosperms are the most abundant at the family,genus,and species levels,accounting for 87.23% of the total number of families,95.28% of the total number of genera,and 96.88% of the total number of species,with dicotyledons being the second most abundant,and gymnosperms and ferns relatively few.

Table 1 Vascular plant species in Machin County
3.2 Analysis of the genus composition of vascular plant families in Machin County
According to Table 2,as many as 33 families contain 1-5 species,accounting for 70.22% of the total number of families;14 families contain 6-10 species,accounting for 19.15% of the total number of families;5 families contain more than 10 species:Compositae,Ranunculaceae,Ranunculaceae,Scrophulariaceae,Leguminosae,and Rosaceae.Although the 5 families (containing more than 10 species) only account for 10.65% of the total number of families,species contained within the family account up for 48.05% of the total number of species.
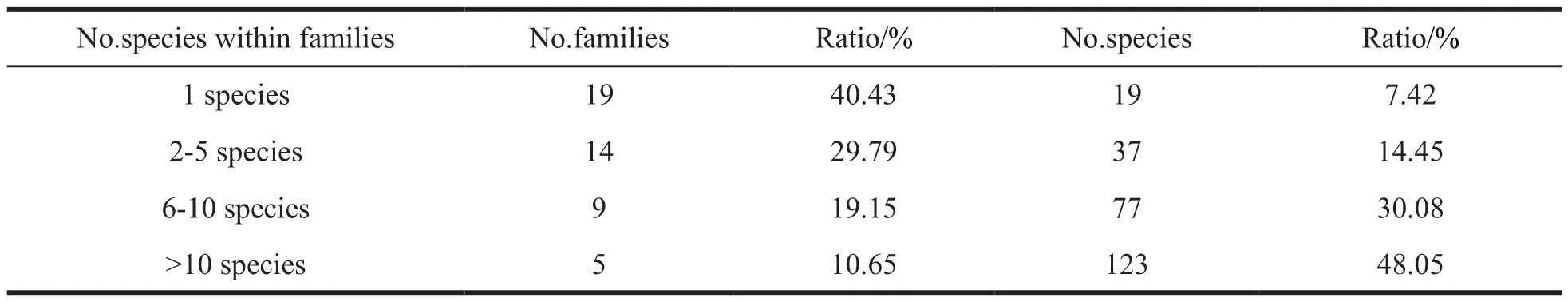
Table 2 Species in different families of vascular plants in Maqin County
As shown in Table 3,the dominance of genera containing only one species is obvious.Among the 127 genera of vascular plants,81 genera contain only one species,accounting for 63.78% and 31.64%of the total number of genera and species.36 genera contain 2-5 species,accounting for 28.35% of the total number of genera,but the proportion of the number of species included is larger,accounting for 37.50% of the total number of species.8 genera contain 6-10 species,accounting for 19.92% of the total number of genera,such asAster,ArtemisiaandThalictrum.Only 2 genera contain more than 10 species,namelySaussureaandPedicularis.In particulary,Pedicularishas 15 species.
3.3 Life type analysis of vascular plants in Machin County
Statistical analysis of different life types of vascular plants in Machin County showed that perennial herbs are the dominated plants,with up to 198 species,accounting for 77.34% of the total number of species (Table 4).This is followed by annual (or biennial) herbs,with 33 species,accounting for 12.89% of the total number of species.Shrubs have 24 species,accounting for 9.38% of the total number of species.Vines have only one species,the buttercup family Clematis spp.Herbs and shrubs are the main body of vascular plants in Machin County.
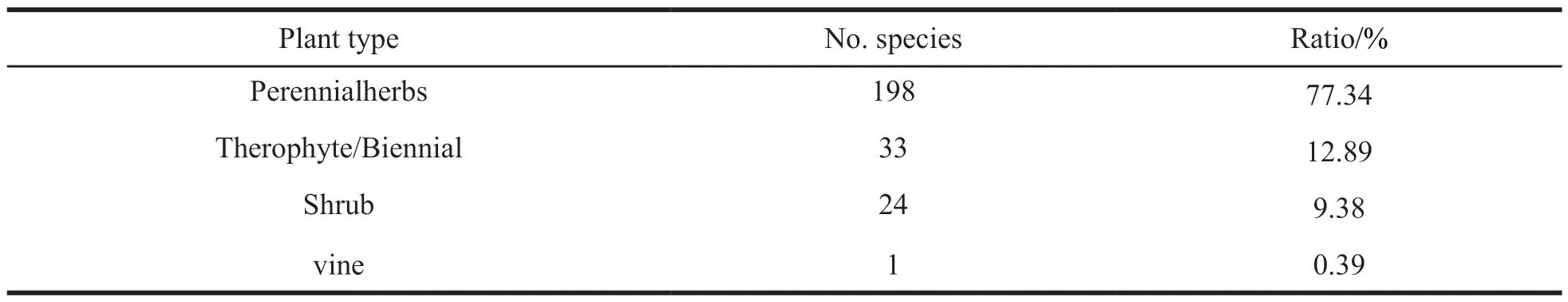
Table 4 Different life forms of vascular plants in Maqin County
3.4 Analysis of the diversity of medicinal vascular plants in Machin County
Table 5 shows that there are 191 species of vascular plants with medicinal value in 41 families and 105 genera in Machin County,accounting for 87.23% of the total number of families,82.68%of the total number of genera,and 74.61% of the total number of species,respectively.Among them,the main families of medicinal vascular plants are Compositae (36),Ranunculaceae (23),Leguminosae(15),Scrophulariaceae (11),and Papaveraceae (10),accounting for 87.80%,56.10%,36.59%,26.83%,and 26.83% of the total number of families of medicinal vascular plants,respectively.The main genera areSaussurea(7),Pedicularis(7) andThalictrum(7),which together account for 6.67% of the total number of medicinal vascular plant genera,followed byArtemisi(6) andAster(6),each accounting for 5.71%.In addition,the medicinal plant life type is also dominated by herbs,with 173 species,accounting for 90.58% of the total number of medicinal vascular plant species.
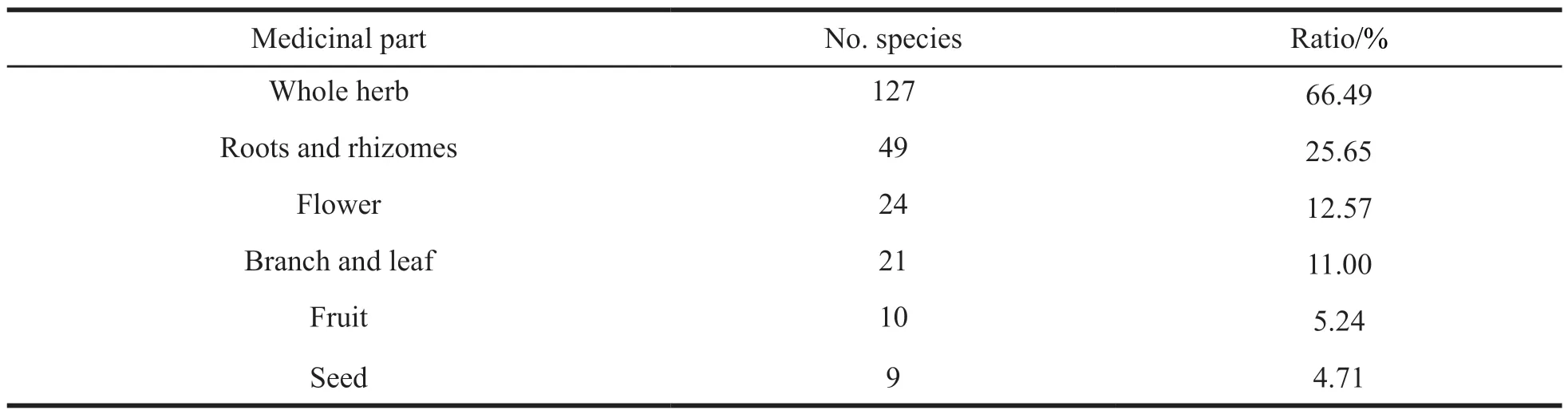
Table 5 Different medicinal parts of medicinal vascular plants in Maqin County
According to different medicinal parts,the medicinal plants of Machin County are divided into whole herbs,roots and rhizomes,flowers,branches and leaves,fruits and seeds.The results show that there are 127 species of medicinal plants in the whole herb category (Table 5).They account for 66.49% of the total number of species of medicinal vascular plants,followed by roots and rhizomes with 49 species,accounting for 25.65%.Flowers,branches and leaves,fruits,and seeds account for 12.57%,11.00%,5.24%,and 4.71%,respectively,with relatively fewer species.
3.5 Analysis of Tibetan medicine resources in Machin County
Tibetan medicinal resources are an important part of traditional medicine and have unique ethnic characteristics.From the statistical results of medicinal vascular plants in Machin County,there are 48 species used as Tibetan medicine (Table 6),accounting for 25.13% of medicinal vascular plants and containing 21 families and 40 genera.Among them,the family Asteraceae (10) and Buttercup family (9) predominate,accounting for 20.83%and 18.75% of the Tibetan medicinal resources,respectively.The number of species in the genus is small,with 32 genera containing 1 species and 8 genera containing 2 species.

Table 6 Tibetan medicine resources in Maqin County
4 Discussion
Due to the unique geographical environment,numerous precious plant resources are preserved in Machin County.The preliminary survey and diversity analysis of vascular plant resources in Machin County show that there are 256 species of vascular plants belonging to 47 families and 127 genera in Machin County.In terms of plant species,angiosperms dominate the area because of their strong adaptability to the environment,while ferns and gymnosperms are rarely distributed.In terms of plant families,the main families are Compositae,Ranunculaceae,Scrophulariaceae,Leguminosae,and Rosaceae,and the main genera areSaussurea,Pedicularis,Thalictrum,ArtemisiandAster.This may be related to their superior reproductive structure and strong environmental adaptability.In terms of plant life type,there are mainly herbs and shrubs,and perennial herbs are the most distributed,as their plants are low and often densely clustered,which are well adapted to unfavorable conditions such as short growing period,frequent thawing and cold temperatures.In addition,Machin County is rich in vascular plant resources with medicinal value.According to the survey,41 families,105 genera and 191 species of the local vascular plants have medicinal values,including 48 species of Tibetan medicinal resources,belonging to 21 families and 40 genera.Compositae,Ranunculaceae,Leguminosae,Scrophulariaceae,and Papaveraceae are the main medicinal families.Saussurea,Pedicularis,Thalictrum,Artemisi,andAsterare the main medicinal genera.The analysis results are similar to the dominant families of local vascular plants,further indicating that vascular plants in Machin County are important medicinal resources.In terms of medicinal parts,whole herbs are the most abundant,followed by roots and rhizomes.The extensive grassland vegetation in Machin County provides favorable conditions for the growth of whole herbs.Because of the accessibility to these herbs,they are widely used by local ethnic minorities as Tibetan medicine in the treatment of various lung,stomach,and liver diseases.
5 Conservation and utilization recommendation
Although Machin County is rich in plant resources,the degree of development and utilization is far from adequate.On one hand,the geographical influence,long distances and harsh environment pose a great challenge to field resource investigation and hinder the conservation of plant resources;on the other hand,the weak basic research on plants in the region greatly restricts their exploitation,leading to insufficient excavation of local Tibetan medicine resources.In addition,due to the warming climate in the region,population growth,overloading and overgrazing of livestock,and indiscriminate human extraction,the area of grassland degradation is increasing,and the rate is accelerating.Overall,the ecosystem is becoming increasingly fragile,causing serious damage to the diversity of plant resources.The grassland degradation in Lower Dawu Township is seriously affected by rodent infestation,while the land in Youyun Township has gradually become desertified.It is necessary to strengthen the exploitation of plant resources while taking into account the conservation work of resources and environment in order to achieve sustainable development.Therefore,the following recommendations are made.
Firstly,the scientific research on the botanical resources of Machin County should be strengthened.Strategies include increasing support for scientific researchers,improving funding for scientific research,strengthening local cooperation,and effectively solving the problem of difficult investigations in remote areas.Comprehensively exploring the situation of plant resources in the county area,digging deeper into Tibetan medicine resources,and mapping out the “home base” are good strategies too.In addition,basic research work should be carried out,such as chemistry and biology,and the plant resources development and utilization value of plant resources should be comprehensively evaluated.
Secondly,the protection of grassland in Machin County should be enhanced.This involves centralized treatment of already degraded grasslands using ecological restoration techniques,as well as livestock reduction and grazing restoration to restore grasslands,strengthening infrastructure construction,fencing and sealing to protect grasslands,rational drug collection to reduce man-made damage,improving the monitoring and early warning system for plateau rats and rabbits and comprehensive treatment to reduce damage to grasslands by rats,and increasing publicity to raise people's awareness of ecological protection.
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank Shenyang Zhuoyuehefa Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd,Nuokang Biology,Anhui Yatai Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd,Tianjin Yibei Biology,and Tianjin Modern Innovative Traditional Chinese Medicine Technology Co.,Ltd for sponsoring this scientific investigation.We express our gratitude to the strong support and assistance provided by Liaoning Jinqiu Hospital,Maqin County People's Hospital,Qinghai University,Qinghai Nationalities University Sha La Duo Jie,and the 13th Traditional Chinese Medicine Resource Science Research Team of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University during fieldwork.
