Analysis of wild vascular plant resources and diversity in Taibai Mountains of Qinling area,Shaanxi Province
2024-01-11BingjunSunQingWngMinliRunAnhuWngJingmingJi
Bingjun Sun,Qing Wng,Minli Run,b,Anhu Wng,*,Jingming Ji,*
a School of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang 110016,China;
b University of Michigan,Ann Arbor.930 N University Ave,Ann Arbor,MI 48109,USA
Abstract Taibai Mountains,located at the northern foot of the Qinling Mountains,are composed of the Yuan Taibai Mountain (also known as East Taibai Mountain),Aoshan Mountain (also known as West Taibai Mountain) and their connection part.With its complex geographical and climatic conditions,Taibai Mountains are extremely rich in wild plant resources.Based on field investigation,literature review and specimen identification,wild vascular plants resources and their diversity in Taibai Mountains were studied by the sixth Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) Resources Scientific Expedition Team of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.222 species of vascular plants belonging to 163 genera and 63 families were collected during July 2012 in this area,and most of the plants are angiosperms.The families with more species are Liliaceae,Ranunculaceae,Asteraceae,Rosaceae,and Saxifragaceae,and the dominant genus are Aconitum, Sedum,Eleutherococcus,Pedicularis,Polygonatum,and Patrinia.In terms of life form,perennial herbs are the main species,accounting for 72.97% of the total species,with others being some annual (or biennial) herbs,shrubs and lianas.Among all the collected vascular plants,170 species of them are medicinal vascular plants,accounting for 76.58% of the total.Most of the medicinal parts are roots and rhizomes,followed by the whole plants.Finally,on the basis of investigation and study,some suggestions are put forward to strengthen the protection and utilization of plant resources in Taibai Mountains.
Keywords: Taibai Mountains;Aoshan Mountain;plant resources;plant diversity;medicine;protection and utilization
1 Introduction
Wild plant resources have always been the necessary material basis for human survival and development,an important part of the stable and balanced ecosystem and biodiversity,and the strategic resources for sustainable development in China.Investigation of wild plant resources is of great significance for solving ecological problems,realizing the harmonious coexistence between man and nature,and promoting the construction of ecological civilization.At the same time,as the main source of natural medicine,wild plant resources also play an irreplaceable role in the treatment and prevention of diseases.
Since ancient times,Taibai Mountains have been famous for its precipitousness,strangeness,and mysteriousness.Known as the “Asian Natural Botanical Garden” and “China Natural Zoo”,Taibai Mountains have a wide variety of animals and plants with complex flora and ancient origin.
Under the combined effects of complex and changeable geological factors and specific cosmic factors,the unique species of Taibai Mountains come into existence.Woody plants and herbs belonging to temperate zone,cold temperate zone and subtropical zone coexist and prosper in the same forest [1].At present,there are 126 families,597 genera,and more than 1850 species of seed plants in Taibai Mountains,including 25 endemic genera,110 species of ferns,and 257 species of mosses.In particular,the only relict plant in the world,Kingdonia uniflora,exists exlusively in Taibai Mountains.Besides,29 species of rare wild plants in Taibai Mountains are under national and provincial key protection,including the national first-class protected plants,Kingdonia unifloraandTaxus wallichiana,the second-class protected plants,Larix potaninii,Picea neoveitchii,Cercidiphyllum japonicum,Abies chensiensis,Tetracentron sinense,Fraxinus mandshurica,andGlycine soja,as well as 20 provincial-level protected plants.Therefore,it is of great significance to clarify the species composition and distribution pattern of the existing plant resources in Taibai Mountains for further effective protection,rational development and sustainable utilization of biodiversity.
The sixth TCM Resources Scientific Expedition Team of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University adopted the methods of field investigation,specimen collection,literature retrieval and specimen verification to preliminarily investigate the wild vascular plant resources and diversity in the Taibai Mountains.The aim of this study was to understand the species composition and distribution of wild plant resources in the Taibai Mountains,and provide an objective basis for the sustainable development and utilization of wild plant resources in the Taibai Mountains.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Overview of Taibai Mountains
Qinling Mountains are the transitional zone from warm temperate deciduous broad-leaved forest to subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest.They are the intersection of China forest subregion and China-Himalaya forest subregion in East Asian flora,and also the intersection of Northern Region and South China flora [2].
As the main peak of the famous Qinling Mountains in China,Taibai Mountains are located at the northern foot of the Qinling Mountains.Located in Baoji City,Shaanxi Province,Taibai Mountains are spanning through three counties,namely Taibai County,Mei County and Zhouzhi County,with geographical coordinates between 107°41'23”E-107°51'40”E and 33°49'31”N-34°08'11”N.The mountains extend from east to west across the central and eastern part of Taibai County,starting from Zutou Town in the west,reaching Laojun Ridge in Zhouzhi County in the east,bounded by Xishui River in the south and Yingge Town and Yingtou Town in the north.Taibai Mountains have the highest peak in the eastern part of mainland China and the highest section of the watershed between the Yellow River system and the Yangtze River system,with an altitude of 3767.2 m.It is composed of the Yuan Taibai Mountain (also known as East Taibai Mountain),Aoshan Mountain(also known as West Taibai Mountain) and the mountain ridge connecting the two.
Taibai Mountains have developed unique climate features.With the increase of altitude,the climate types are distributed in continuous bands according to certain rules,and the average vertical decline rate of air temperature is estimated to be between 0.4 ℃ and 0.5 ℃.Five obvious climate zones are formed from bottom to top: warm temperate,temperate,cold temperate,cold and alpine cold.The unique geographical location and the complex geology and landform,as well as the huge relative altitude difference of Taibai Mountains have created the diversity of the prosperous ecosystem and provide diverse habitats for living organisms [3].
Consistent with the vertical difference of climate,the distribution of plants and animals also presents the corresponding vertical band spectrum.Within the mountain range of 620 m to 3511 m above sea level,the area covers the climate,plant and animal zones that usually coexist only in places over thousands of kilometers [4].Therefore,Taibai Mountains are excellent sites for plant resources and diversity studies.
2.2 Research method
In July 2012,the sixth TCM Resources Scientific Expedition Team of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University went to Aoshan Mountain and Yuan Taibai Mountain,the main peak of the Qinling Mountains in Shaanxi province,for scientific investigation.Route survey was adopted for representative areas.We collected specimens along the way,took photos,and recorded the collection site,time,and main morphological characteristics of plants in detail.The longitude and latitude were recorded throughout the whole process with GPS recorder.According toFlora of China[5]andFlora of Qinling Mountains[6],the species of vascular plants in the two regions were identified,and the list of vascular plant resources was established.
On the basis of this list,the list of vascular plants that can be used as medicine was established according toNational Chinese Herbal Medicine Collection[7],Chinese Herbal Medicine[8],andIllustrated Handbook of Common Medicinal Plants in Qinling Mountains,China[9].The information of medicinal parts,efficacy and indications were recorded with reference to these documents.Finally,we analyzed and evaluated the diversity of vascular plant resources in Taibai Mountains,and put forward corresponding suggestions for development,utilization and protection.
3 Results
3.1 Analysis of vascular plant species composition in Taibai Mountains
According to the results of scientific investigation,we collected 222 species of vascular plants belonging to 163 genera and 63 families in Taibai Mountains,including 6 species of pteridophytes belonging to 5 genera and 5 families,2 species of gymnosperms belonging to 2 genera and 2 families,and 214 species of angiosperms belonging to 156 genera and 56 families (180 species of dicotyledon belonging to 130 genera and 49 families;7 families,26 genera and 34 species of monocotyledonous plants) (Table 1).Among them,angiosperms are the most abundant in families,genera and species,accounting for 88.89% of the total families,95.71% of the total genera and 96.40% of the total species.Majority of angiosperms are dicotyledres.Relatively few species are available for gymnosperms and ferns.
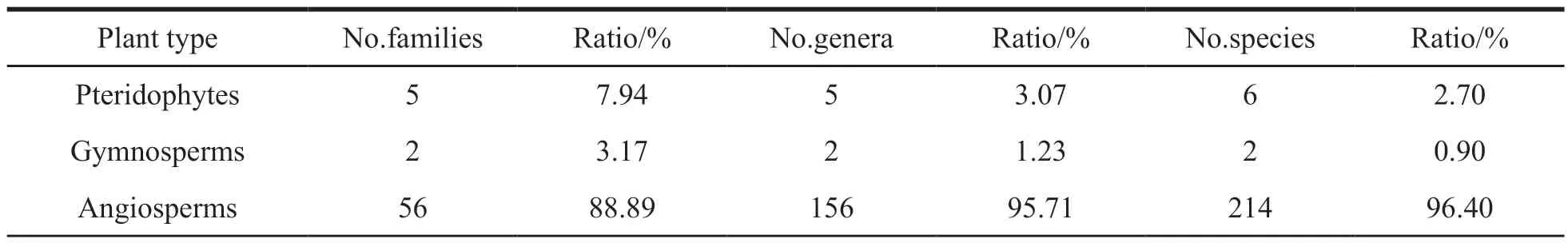
Table 1 Vascular plant species in Taibai mountains
3.2 Analysis of the genus composition of vascular plant families in the Taibai Mountains
According to Table 2,among the vascular plants collected in the Taibai Mountains,53 families contained 1 to 5 species,accounting for 84.13% of the total number of subjects.6 families contained 6 to 10 species,accounting for 9.52% of the total number of subjects.In particular,there are 4 families which contained more than 10 species,namely Liliaceae,Ranunculaceae,Asteraceae,and Rosaceae.Although the 4 families only represent 6.35% of the total number of families,the number of species contained in the family account for 33.78% of the total number of species.

Table 2 Species in different families of vascular plants in Taibai Mountains
As for genera,the genera containing only one species are obviously dominant.Table 3 shows that among 163 genera of vascular plants collected,129 genera have only one species,accounting for 79.14% and 58.11% of the total genera and species respectively.33 genera contain 2-5 species,accounting for 20.25% of the total genera.But the number of species contained in the 33 genera is relatively large,accounting for 38.74% of the total number of species.What's more,only 1 genus,Aconitum,has 7 species.
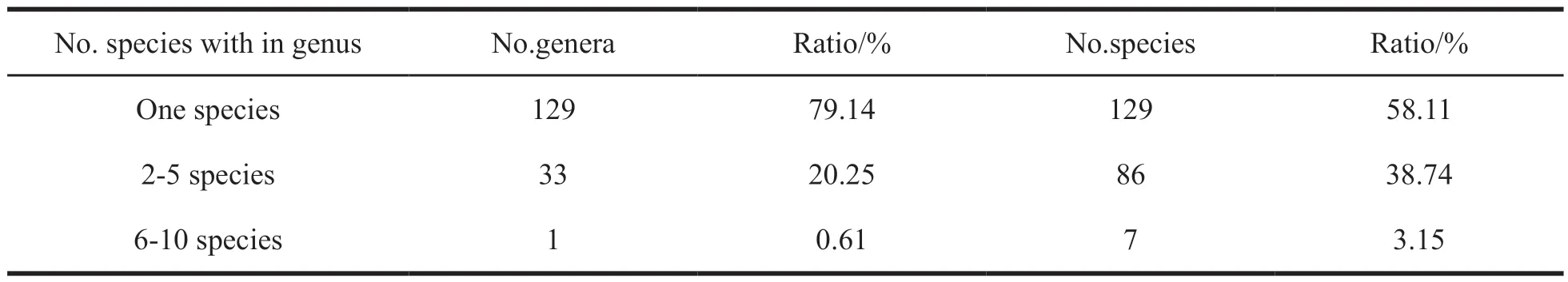
Table 3 Species in different genus of vascular plants in Taibai Mountains
3.3 Analysis of vascular plants in Taibai Mountains
The statistical analysis of different life types of vascular plants collected in Taibai Mountains shows that perennial herbs are dominant,with 162 species,accounting for 72.97% of the total species.The second dominant one is shrub,with 23 species,accounting for 10.36% of the total,followed by liana with 22 species,accounting for 9.91% of the total,and annual (or biennial) herbs with 15 species,accounting for 6.76% of the total species(Fig.1).
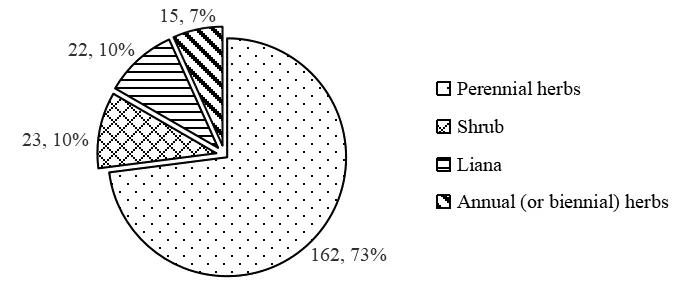
Fig.1 Different life forms of vascular plants in Taibai Mountains
3.4 Analysis of medicinal vascular plants in Taibai Mountains
Taibai Mountains are rich in traditional Chinese medicine resources.These resources have a very broad application prospect in the utilization of modern traditional Chinese medicine resources and have become an important driving force for local economic development.As the most primitive area,Aoshan Mountain is rich in animals and plants.It is said that Sun Simiao,a famous doctor of Tang Dynasty,lived in Aoshan Mountain for many years,studying medicine and writing books.Yuan Taibai Mountain,with its unique natural environment,has bred a large number of rare plants.Today,there are more than 100 herbs labeled with “Taibai”,such as theFritillaria taipaiensisandSouliea vaginata.Among them,more than 50 kinds of herbs have been recorded in the bookChinese Herbal Medicine in Shaanxi Province[10].
According to the records of literature,the sixth TCM Resources Scientific Expedition Team of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University investigated,collected and preliminarily identified the medicinal vascular plants in the Taibai Mountains (Fig.2).Meanwhile,by combining the information provided by local farmers and literature,the origin,medicinal parts and efficacy of the medicinal vascular plants in Taibai Mountains were systematically sorted out,summarized and revised.

Fig.2 Some medicinal vascular plants and their habitats in Taibai Mountains
In general,the medicinal vascular plants collected in Taibai Mountains are mainly used for heat-clearing and detoxifying,expelling wind,removing dampness,and promoting blood circulation to remove obstruction in the vessel channels (Table 4).
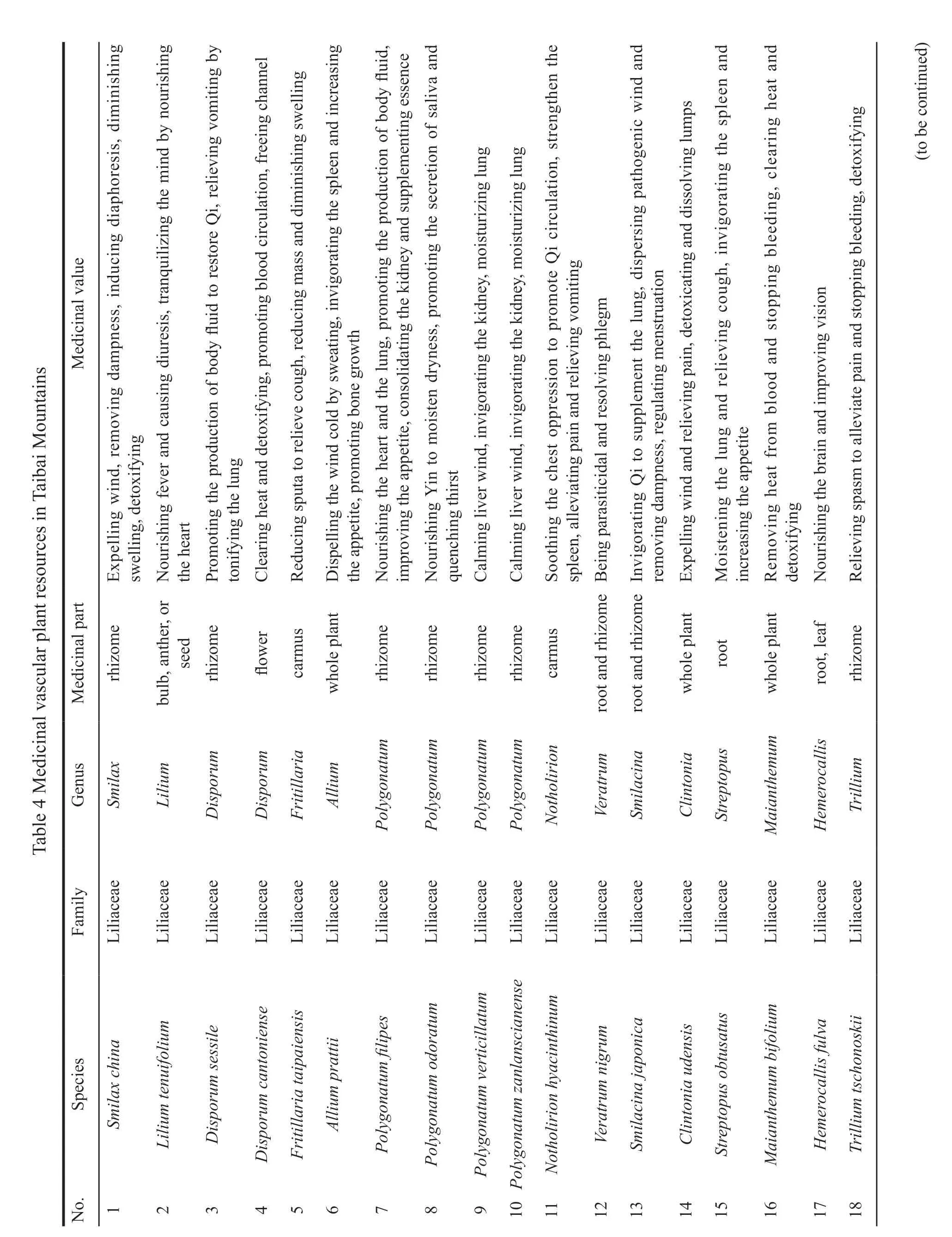
In this study,we collected 53 families,128 genera and 170 species of vascular plants with medicinal value in Taibai Mountains,accounting for 84.13% of the total families,78.53% of the total genera and 76.58%of the total species.The main families of medicinal vascular plants are Liliaceae (22),Ranunculaceae (13),Asteraceae (12),Lamiaceae (8),Saxifragaceae (8),and Crassulaceae (8),which account for 12.94%,7.65%,7.06%,4.71%,4.71% and 4.71% of the total species of medicinal vascular plants respectively.The main genera areAconitum(7),Sedum(5),Acanthopanax(5) andPedicularis(5).In addition,the life types of medicinal plants are also mainly perennial herbs,with 126 species,accounting for 74.12% of the total number of medicinal vascular plants.
The medicinal plants collected in Taibai Mountains were divided into whole plants,roots and rhizomes,flowers,branches and leaves,fruits and seeds.The results show that,the roots and rhizomes medicinal plants are the most abundant,with 93 species,accounting for 54.71% of the total species of medicinal vascular plants,followed by whole plants,with 71 species,accounting for 41.76%.Branches and leaves,flowers,fruits and seeds account for 6.47%,4.12%,2.35% and 0.59% respectively(Fig.3).Note: Some species have multiple medicinal parts and are counted together.The ratio is the ratio of species number to the total species number of medicinal vascular plants.
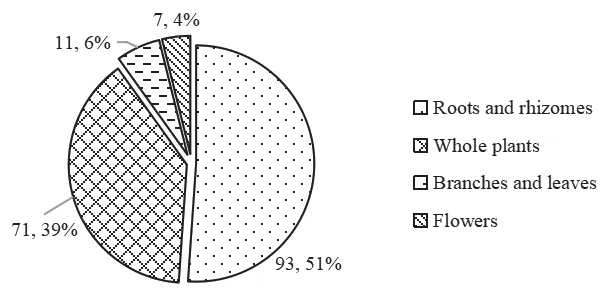
Fig.3 Different medicinal parts of medicinal vascular plants in Taibai Mountains
4 Discussion
Traditional Chinese medicine and traditional drugs with natural and long-term folk applications have become the hot spots in new drug development and investment.As the highest peak in the inland,Qinling Mountains are the dividing line of the warm temperate zone in eastern Asia and the monsoon marginal zone influenced by the intersection of the South Asian monsoon and the East Asian monsoon.Different circulation systems have caused great differences in the north and south climate of the Qinling Mountains [11],resulting in rich species diversity and medicinal materials resources.Taibai Mountains,the main peak,have extremely rich Chinese herbal medicine resources,known as the“No idle grass in the Qin land”.
Through our preliminary investigation and diversity analysis of vascular plant resources in Taibai Mountains,222 species of vascular plants were collected,belonging to 63 families and 163 genera.Angiosperms are dominant in this area because of their strong adaptability to environment,while pteridophytes and gymnosperms are rarely distributed.
In terms of plant families and genera,the main families are Liliaceae,Ranunculaceae,Asteraceae,Rosaceae,and Saxifragaceae,and the six main genera areAconitum,Sedum,Eleutherococcus,Pedicularis,Polygonatum,andPatrinia.It may be related to their superior reproductive structure and strong environmental adaptability.From the perspective of plant life type,herbs,shrubs and perennial herbaceous plants are the most distributed ones.With low plants and dense clumps,they can adapt well to unfavorable conditions,such as short growth period,frequent thawing and freezing.
There are abundant vascular plant resources with medicinal value in Taibai Mountains.According to the investigation,there are 53 families,128 genera and 170 species of vascular plants with medicinal value in this area.The main medicinal families are Liliaceae,Ranunculaceae,Asteraceae,Lamiaceae,Saxifragaceae,and Crassulaceae,and the main medicinal genera areAconitum,Sedum,AcanthopanaxandPedicularis.The analysis results are similar to the dominant families and genera of local vascular plants,which further show that the vascular plants in Taibai Mountains are an important source of medicinal resources.In terms of medicinal parts,roots and rhizomes are the most,followed by whole plants.The unique climate characteristics and geographical advantages of Taibai Mountains provide favorable conditions for the growth of all kinds of medicinal materials.
Although there are abundant plant resources in Taibai Mountains,due to the influence of topography and harsh environment,the field resources survey is still facing great challenges,which hinders the protection of plant resources.On the other hand,because of the climate warming in the region,the demand for natural resources is increasing,and the ecosystem is continuously destroyed,which has seriously damaged the diversity of plant resources,and a large number of species have become endangered or even extinct [12].
Therefore,the following suggestions are made.Firstly,policies to strengthen biodiversity conservation and sustainable use should be formulated.These policies include local laws and regulations in the fields of wildlife protection and nature reserves [13]and guidance of biodiversity conservation planning and sustainable management.Mechanism for identification and assessment of biodiversity damage should be established,and the system for combating illegal trade in wild animals and plants should be improved.Secondly,protection planning policies for rare and endangered species should be formulated too.Continuous biodiversity investigation and monitoring should be promoted to improve diversity conservation and detection information platform,and integrated analysis should be performed and basic biodiversity data should be shared and the analysis results should be applied [14].When the database of endangered species is built,the inspection and measurement network is improved,and the dynamic of ecological environment change and species growth and decline in real time is grasped,basis for scientific formulation of protection measures is established.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Professor Wu Chunfu of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University for the design and arrangement of the scientific expedition route,thank Mr.Dong Xiaoming and Mr.Xue Baizhong for their funding,and also thank all the scientific expedition members of the 6th Chinese Medicine Scientific Expedition Team of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University for their hard work.
