Study on the mechanism of P2X receptors involved in electroacupuncture treatment of neuropathicpain in dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord
2023-12-25SIShuhan司书晗TANGWenchao唐文超WANGFan王凡
SI Shuhan (司书晗), TANG Wenchao (唐文超), WANG Fan (王凡)
Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 201203, China
Abstract
Keywords: Acupuncture Therapy; Electroacupuncture; Acupuncture Analgesia; Ganglia, Spinal; Receptors, Purinergic P2X;Neuralgia
Pain, based on the course of disease, can be divided into acute pain and chronic pain, and the latter can be further divided into inflammatory pain, cancerous pain,and neuropathic pain (NP)[1].Among them, 20%-25% of patients with chronic pain are diagnosed with NP[2].NP,a common symptom of a great number of diseases, has an incident rate of 7%-10% in the general population[3].NP is defined as “caused by a lesion or disease of the somatosensory system”, and it may originate from a variety of central and peripheral diseases or injuries,such as stroke, spinal cord injury, trigeminal neuralgia,herpes zoster, and diabetes.Clinical manifestations of NP include hyperalgesia, allodynia, spontaneous pain,numbness, hypoesthesia, and so on[2,4-5].NP has a long course and is often accompanied by emotional disorders, sleep disorders, and even disabilities, so it seriously affects the daily living of the patients.
Analgesic drugs such as lidocaine and morphine are clinically preferred for the treatment of NP.Despite alleviating pain to a certain extent, such analgesic drugs are short-lived and have certain dependence and side effects[6].In view of this, the treatment of NP has become an urgent problem to be solved in the medical community.Acupuncture therapy can provide definite efficacy in the treatment of NP, such as sciatica,trigeminal neuralgia, postherpetic neuralgia, and diabetic peripheral neuralgia, and can relieve the side effects of chemical medicine[7].A meta-analysis indicated that acupuncture significantly relieved the symptoms of low back pain compared with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs[8].In the results of another meta-analysis, it was shown that acupuncture was more capable of improving the efficacy and reducing the sciatica recurrence rate than carbamazepine[9].
In view of the satisfactory therapeutic effect of acupuncture for NP, many studies have been carried out on its analgesic mechanism in many countries.Among these studies, the role of purines and their receptors in the analgesic effect of acupuncture for NP has attracted widespread attention and has become one of the research hot spots in recent years.In this paper, the mechanism of acupuncture for NP was reviewed from the perspective of purinergic P2X receptors, providing a new research idea and basis for further exploring the mechanism of acupuncture analgesia.
1 P2X Receptors
Purinergic P2 receptors include ionotropic (P2X)receptors and metabotropic G protein-coupled (P2Y)receptors[10].In vertebrates, P2X receptors have 7 subtypes (P2X1-7) encoded by genes with 40%-50%homology in terms of amino acid sequence[11].P2X receptors are membrane ion channels that open in response to binding to extracellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP), with preferential permeability to sodium, potassium, and calcium.P2X receptors are widely distributed and participate in numerous physiological and pathological reactions, such as synaptic transmission, rapid transmission of neuroglial cell signals, muscle contraction, inflammation, and NP[12-14].
2 P2X Receptors and NP
It is increasingly evidenced that the extracellular ATP induces the downstream signaling by activating purinergic P2X receptors, having a close bearing on the generation and transmission of NP signals[15].Under pathological conditions, ATP is the strongest mediator of P2X receptor activation.In case of tissue damage, a large amount of ATPs will be released out of the cells to bind to P2 receptors on the free nerve endings of peripheral tissues and activate P2 receptors, causing the inward flow of Ca2+, Na+, and K+ions, generating action potentials, and resulting in pain sensitization[16].Several P2X receptor subtypes, including P2X3, P2X4, and P2X7,have been proven to play different roles in the pathogenesis of NP, specifically in mediating rapid transmission in the peripheral nervous system and regulating neuronal activities in the central nervous system[17].P2X3 monomer receptor (P2X3R) and P2X2/3 heterogeneous receptor (P2X2/3R) in primary sensory neurons and P2X4 monomer receptor (P2X4R) in microglia of spinal dorsal horn play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of NP after peripheral nerve injuries.P2X receptor antagonists can reverse allodynia and nociceptive behavioral responses caused by spared nerve injuries (SNI)[18].Spinal cord injury (SCI) and stroke are important causes of central NP.Microglia express a large number of purinergic receptors, while P2X4R and P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) exert an important role in central NP by activating the microglia[17].
3 P2X Receptors and Acupuncture Analgesia
Pain is the dominant indication of acupuncture treatment.In Chapter Nine, Needles and Twelve Yuanprimary Points, of Ling Shu (Miraculous Pivot)[19], the principle of acupuncture analgesia of “unblocking meridians and regulating blood and Qi” and“eliminating prolonged stagnation” was proposed.The mechanism of acupuncture analgesia has not yet been fully clarified due to its complexity.However, it has been shown in studies that acupuncture analgesia can inhibit peripheral and central sensitization and regulate the expression of cell signaling pathways, ion channels,neurotransmitters, immunological inflammatory factors,the expression of pain-related receptors (such as P2X receptors), and pain emotions[20-22].Purinergic signaling is one of the important cellular mechanisms of acupuncture analgesia, and P2 receptors, as one of two primary receptors of purinergic signals, play an important regulatory role in acupuncture analgesia.Purinergic signaling converts acupuncture signals into electrical signals.Acupuncture can down-regulate the expression of P2X receptors or up-regulate the expression of adenosine A1 receptors to play an analgesic effect[23].P2X3[24-31], P2X4[32-39], and P2X7[40-52]receptors are closely related to NP and involved in the analgesic mechanism of acupuncture for NP at different levels in the peripheral and central nervous system(Table 1).
3.1 P2X3R
P2X3R is a non-selective cation channel that is highly specifically expressed in the dorsal root ganglion (DRG)of some primary afferent nerves and small- and moderate-sized neurons in the trigeminal ganglion[24].In the case of NP, the ATP released from the damaged tissue or spinal cord will activate P2X3R in the sensory nerve endings and DRG[25], causing an increase in Ca2+influx, which may mediate the hyperalgesia after the peripheral nerve injuries by further activating the level of cytoplasmic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2), a key molecule involved in signaling in the inflammatory response[18].
Experiments showed that the 2 Hz/100 Hz alternating wave electroacupuncture (EA) at Zusanli (ST36) and Yanglingquan (GB34) on the affected side downregulated the overexpression of P2X3R proteins in the DRG neurons in chronic constriction injury model of the sciatic nerve (CCI) and improved the thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical hyperalgesia of CCI rats.Interestingly, EA on the healthy side (contralateral insertion) can achieve the same analgesic effect[26-27].As demonstrated in some studies that further combined the patch-clamp technique, the 2 Hz/100 Hz alternating wave EA treatment inhibited the ATP-generated currents in DRG neurons of CCI rats, thereby inhibiting the up-regulation of P2X3R.In addition, EA was more effective in reducing the ectopic mechanical pain and thermal hyperalgesia when combined with the intrathecal application of P2X3R inhibitor A-317491[28].A rat model of L5spinal nerve ligation found that the expression of P2X3R in the damaged L5DRG was significantly reduced, and EA had no significant effect on it.However, the expression of P2X3R was significantly up-regulated in the adjacent ipsilateral undamaged L4DRG, and the overexpression of P2X3R was reversed by 2 Hz EA treatment[29].Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is a usual complication of diabetes and a common pathogeny of NP.A study was conducted on the expression of DRG neuron P2X3R and hyperalgesia in an animal model of diabetic neuropathic pain (DNP), and the results showed that EA at 2 Hz could also down-regulate the expression of P2X3R to mediate analgesia, providing a theoretical basis for clinical EA treatment of DNP[30].It has been found that EA at 2 Hz, 100 Hz, and 2 Hz/100 Hz can relieve NP in SNI rats.Its analgesic effect may be related to its effective inhibition of transient receptor potential vanilloid (TRPV) 1, phosphorylated TRPV1, and P2X3 protein expression in spinal cord dorsal horn (SCDH)[31].
In summary, EA can play an analgesic role by inhibiting the overexpression of P2X3R in DRG and SCDH neurons, and both 2 Hz/100 Hz alternating wave and 2 Hz continuous wave are effective.See Figure 1.
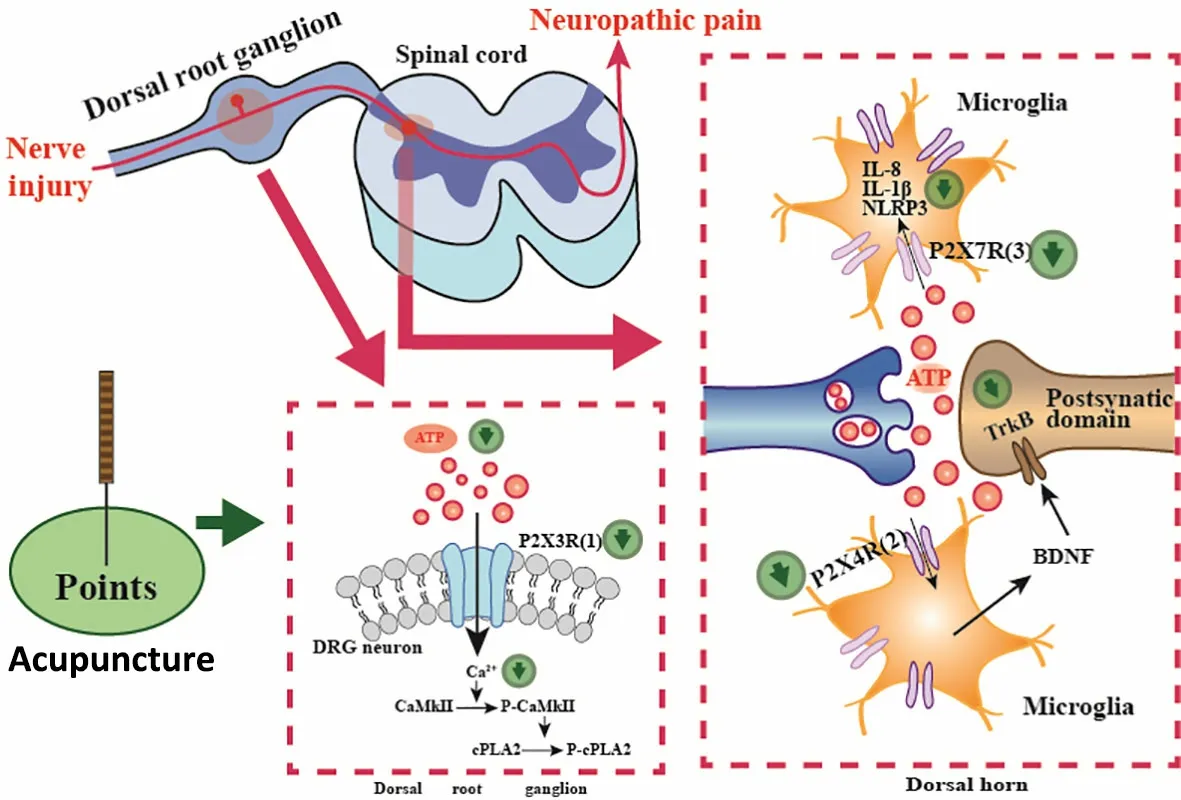
Figure 1 Involvement of P2X receptors in acupuncture treatment of NP
3.2 P2X4R
P2X4R is a fast and sensitive purinergic receptor that is widely expressed in central and peripheral neurons,microglial cells, a variety of epithelial tissues, and endothelial cells[32].P2X4R is the most abundant P2XR subtype expressed in the central nervous system[33].After peripheral nerve injuries, spinal microglia are activated, and P2X4R induces the synthesis and release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) under the action of ATP and then acts on the receptor of tyrosine kinase B (TrkB) across the postsynaptic membrane of pain neurons, which leads to increased Cl-efflux and neuronal depolarization and mediates the central sensitization of NP[13].
In the CCI rat model, excessive release of interferon-γ(IFN-γ) activates the resting spinal microglia, resulting in NP, while 2 Hz EA at Huantiao (GB30) can downregulate the overexpression of IFN-γ in the spinal cord,thereby reducing the expression of P2X4R in the spinal microglia and improving the tactile hypersensitivity after the peripheral nerve injuries[34].It was found that 2 Hz/100 Hz alternating wave EA at Zusanli (ST36)-Yanglingquan (GB34) also played a certain analgesic role by inhibiting the expression of P2X4R in the spinal cord[35].The purinergic signaling between neurons and glial cells is also involved in NP.Under the action of activated microglia, the expression level of P2X4R can be induced or promoted, the production and diffusion of biologically active factors such as cytokines and neurotrophic factors can be mediated, and the depolarization of sensory neurons in the spinal dorsal horn can be induced[36].2 Hz/100 Hz EA at Zusanli(ST36)-Kunlun (BL60) can increase the mechanical withdrawal threshold and thermal withdrawal latency of rats with L5spinal nerve ligation, and reduce the overexpression of P2X4R proteins and genes in the spinal cord.Simultaneously, the frequency of the spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic current in substantia gelatinosa (SG) neurons in the spinal dorsal horn of spinal nerve ligation model (SNL) rats can be weakened by EA, which confirms that EA may inhibit the nociceptive transmission of the SG neurons by regulating P2X4R in the spinal microglia[37].EA at points Feishu (BL13), Pishu (BL20), and Shenshu (BL23) has an obvious analgesic effect on DPN rats.At the same time,the expression of P2X4R in the spinal microglia and spinal inflammatory factors are significantly downregulated[38].With EA at Hegu (LI4), the overexpression of P2X4R mRNA in the trigeminal ganglion and dental pulp of a rat model of dental pulp pain induced by Escherichia coli endotoxin lipopolysaccharide can be reduced, thus supporting the involvement of P2X4R in the analgesic mechanism of EA for dental pulp pain[39].
The above studies attempt to clarify the mechanism of P2X4R in acupuncture analgesia at the spinal cord level.Acupuncture can directly down-regulate the overexpression of P2X4R in sensory neurons of the spinal dorsal horn.More importantly, acupuncture inhibits nociceptive transmission of spinal cord neurons by regulating P2X4R in spinal microglia.See Figure 1.
3.3 P2X7 receptor (P2X7R)
P2X7R is mainly located in the microglia of the central nervous system, and a small amount in glial cells, such as astrocytes and oligodendrocytes.P2X7R is the main driver of inflammation and mediates neurodegenerative diseases[40].P2X7R has also been found to be associated with NP in recent years.The expression of P2X7R is up-regulated in DRG and injured nerves in patients with NP.Pharmacological blockage of P2X7R can alleviate the hyperalgesia in NP[41-42].In addition,hippocampal P2X7R may play an important role in pain signaling and the development of depressive behavior in DNP associated with depression in rats[43-44].Unlike other subtypes of P2XR, P2X7R can only be activated by high concentrations of ATP.Activated P2X7R contributes to the inflammatory response to injuries or bacterial invasion, mediates apoptosis, and sustainably promotes the release of ATP, causing further damage to the body[45-46].
As P2X7R is relatively late in the discovery of NP mechanisms, there is limited research on the analgesic mechanism of acupuncture.For peripheral NP, EA has the function of inhibiting the activation of P2X7Rpositive microglia in the spinal cord, as well as suppressing the overexpression of interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-18 in the spinal cord, thereby alleviating the tenderness and thermal hyperalgesia induced by nerve injuries[47-48].For central nerve injuries, it has been observed that EA at Jiaji (EX-B2) inhibits the activation of P2X7R and the expression of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptor protein 3 in rats with SCI and acute SCI, thereby improving the inflammatory injury of spinal cord tissues and motor function[49-51].Those studies confirmed that acupuncture could improve motor dysfunction after central nerve injuries by inhibiting the expression of P2X7R and alleviating inflammatory responses.However, whether P2X7R is involved in the treatment of NP after spinal cord injuries remains to be further studied.The study has shown that 2 Hz EA at Zusanli(ST36)-Kunlun (BL60) can down-regulate the expression of P2X4 and P2X7 and play a certain analgesic effect on DNP, which provides a theoretical basis for clinical EA treatment of DNP[52].
Therefore, EA can exert an analgesic effect by inhibiting the overexpression of P2X7R in SCI, the chronic compression injury of the sciatic nerve, and diabetic neuropathy.See Figure 1.
4 Discussion
Extracellular ATP is a purine signal molecule of the intercellular signaling pathway.It mainly triggers its downstream signal transmission by activating P2 purinergic receptors, facilitating the information transmission in the peripheral and central nervous system.In 2009, BURNSTOCK G[53]proposed the hypothesis that ATP purine signal may be involved in the mechanism of acupuncture action.More than ten years of research have gradually made clear the relationship between purine signals and acupuncture’s analgesic effect on NP.Acupuncture, as a kind of nociceptive stimulus, may give rise to a large amount of local extracellular ATPs released in the point area and activate P2 purinergic receptors[54].P2X3R, located in local sensory nerve endings of DRG and trigeminal ganglion neurons, can project to the higher center of the brain through the collateral inhibition of painrelated pathways in ascending dorsal horn spinal cord neurons.Secondly, P2X4 or glial P2X7 receptors, located in spinal cord neurons and microglia, can also be activated[55].Purinergic receptors convert acupuncture signals into electrical signals.Acupuncture exerts its analgesic effect by down-regulating the expression of P2X receptors or up-regulating the expression of adenosine A1 receptor[23].Extracellular ATP is extremely unstable and easily degraded into adenosine diphosphate (ADP), adenosine monophosphate (AMP),adenosine (ADO), etc.Particularly, the level of ADO can be increased by nearly 24 times.ADO can activate A1 receptors and negatively regulate ATP in sensory nerve conduction pathways such as DRG and spinal dorsal horn.In this way, pain mediated by ATP binding to the P2X3, P2X4, and P2X7 receptors can be reduced under their analgesic effects[56].
The mechanism of P2X receptors participating in acupuncture treatment of NP is different, mainly determined by their various distributions in the sensory nerve conduction pathway and their characteristics.The P2X1 receptor is mainly expressed in smooth muscles and mediates the influx of calcium ions in platelets,which may contribute to thrombosis.The P2X5 receptor is mainly expressed in skeletal muscles and can play a supporting role in inflammation[57].The P2X6 receptor is widely expressed in the central nervous system, and it has been proved that it can form heterogeneity.The expression is increased in the CCI model in an unclear way[58-59].The P2X2 receptor is mainly located in existent neurons and plays a major role in taste and auditory transduction.In many cell types, P2X2 receptor subunits are co-expressed with other P2X subtypes,such as P2X2/3 heterogeneous receptors involved in pain signal transduction[57,60].The latest study on the initiation mechanism of EA shows that EA can inhibit the expression of P2X2 receptors in the local muscle of point, and bilateral sciatic nerve resection can reverse the inhibition of EA on P2X2 receptors.This study suggests that the P2X2 receptor may be involved in the analgesic mechanism of EA for NP, but its specific target needs to be further studied[61].P2X3R is specifically expressed in the DRG of primary afferent nerve and small-sized and moderate-sized neurons of trigeminal ganglia.Acupuncture can directly mediate analgesia by down-regulating the expression of P2X3R in neurons.P2X4R, however, is widely distributed in spinal cord neurons and microglia.Acupuncture has been proven to inhibit the nociceptive transmission of neurons mainly by down-regulating P2X4R in the spinal microglia.P2X7R is mainly located in the microglia of the central nervous system and is closely related to inflammation.Therefore, acupuncture may relieve NP by inhibiting the secretion of inflammatory factors by reducing P2X7R in the spinal microglia.
Despite great progress having been made in the research on the analgesic effect mechanism of acupuncture for NP, acupuncture treatment can increase the pain threshold, suppress somatic pain,relieve acute and chronic pain, and reduce or even eliminate deep pain and emotional reactions to pain[62].There are still many unsolved problems in this field.Firstly, neuro-glia communication is involved in NP via purinergic signals.For example, ATP overexpression in DRG can activate glial cells via P2X7R, which in turn activates P2X3R in adjacent neurons to cause pain[63].It has been proved that EA inhibits the expression of P2X7R in the spinal microglia.Further experiments are needed to confirm how acupuncture further affects the neuro-glial communication to exert analgesic effects.Secondly, current studies indicate that P2X is also expressed in the cerebral cortex and can mediate NP[64].However, relevant analgesic mechanisms of acupuncture need to be developed.Thirdly, priority has been given to the study of EA in the analgesic mechanism of acupuncture for NP, while the study of manual acupuncture is relatively rare.In traditional acupuncture therapy, great attention has been paid to the application of manipulation.A study[65]has instructed that the lifting-thrusting and twirling-rotating manipulations in acupuncture are beneficial to promoting the release of ATP and are involved in the transformation of acupuncture signals from mechanical stimulation to biological signals.However, acupuncture without manipulation will not release enough ATP.So, is there a dose-effect relationship between acupuncture manipulation and local ATP release in the point area?How does this dose-effect relationship relate to ATP/P2X receptors in the ascending pathway? The answers to those questions are of great significance to unveil the mystery of acupuncture manipulation.
5 Conclusion
In this paper, a review was conducted on the relationship between P2X receptors and analgesic effects of acupuncture for NP.P2X receptors closely related to NP mainly include P2X3, P2X4, and P2X7 receptors, which have been shown to be involved in mediating acupuncture in the treatment of NP.In the DRG and trigeminal ganglia of primary afferent nerves,acupuncture mediates analgesia by down-regulating the expression of P2X3R in neurons.In the spinal cord,acupuncture reduces NP by down-regulating P2X4R and P2X7R in the spinal microglia, as well as P2X4R in neurons.It remains to be explored how acupuncture further influences neuro-glial communication via purine signals to exert analgesic effects.In addition, the doseeffect of P2X receptors in manual acupuncture analgesia deserves further research in the future.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (国家自然科学基金项目, No.81603687); Budgeted Project of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (上海市教育委员会预算内课题, No.2021LK099).
Authors’ Contributions
WANG Fan provided the instruction for the design of this study.SI Shuhan collected studies and wrote the paper.TANG Wenchao made the map of mechanisms.WANG Fan reviewed and edited the manuscript.All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Received:15 December 2022/Accepted: 18 May 2023
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Effects of electroacupuncture at Baihui (GV20) and Yintang (GV29) on endoplasmic reticulum stress in depressive rats caused by chronic unpredictable mild stress
- Effects of acupuncture and moxibustion on PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway in substantia nigra of Thy1-αSyn transgenic mice with Parkinson disease
- Acupuncture compound anesthesia for traditional thyroidectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Effects of abdominal Tuina on behavioral function and 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor/synapsin-1 in hippocampal CA1 region of rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain injuries
- Effects of auricular point sticking on labor pain and anxiety
- Clinical study of Tuina combined with functional training to improve the clinical symptoms and balance function in patients with meniscus injury
