Effects of abdominal Tuina on behavioral function and 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptor/synapsin-1 in hippocampal CA1 region of rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain injuries
2023-12-25WANGWei,HUANGYumei,WANGDejun等
Abstract
Keywords: Tuina; Massage; Abdomen; Brain Injuries; Muscle Strength; 5-Hydroxytryptamine 1A Receptor; Synapsins; Rats
Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injuries (HIBI) refer to craniocerebral injuries caused by perinatal neonatal asphyxia, which is a common cause of neonatal death and nervous system dysfunction[1].Studies have shown that mental retardation and abnormal behavioral function of limbs caused by HIBI are mostly caused by hippocampal neuron apoptosis and synapse number reduction[2-4].Abdominal Tuina (Chinese therapeutic massage), a common treatment technique in traditional Chinese medicine, has been proven to promote synaptic remodeling, repair the regeneration of neurons in the hippocampus, and accelerate the recovery of brain injuries.However, how hippocampal neurons are regulated and the synaptic remodeling mechanism are not clear[5].The repair process of nervous tissue injury includes angiogenesis, neurogenesis, synaptic remodeling, and so on.Neuronal morphogenesis,integration with circuits, and synaptic connection remodeling are mostly regulated by synaptic protein expression[6].The 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1A(5-HT1AR) is an important signal molecule in the development of the nervous system and nerve conduction.It up-regulates the expression of synapsin-1(Syn1) and increases the synapse number to realize synaptic structural remodeling, neuron repair, and regeneration[7].In this study, we observed the effects of abdominal Tuina on the behavior of upper limbs and the expression levels of 5-HT1AR and Syn1 in neonatal HIBI rats and explored the neuro-remodeling mechanism of abdominal Tuina on the hippocampus of neonatal HIBI rats.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Animals
Five healthy pregnant (13-17 d) Sprague-Dawley rats were provided by Hunan SJA Experimental Animal Co.,Ltd., China [Animal License No.SYXK (Xiang) 2019-0009]and fed normally until delivery.Forty rat pups were delivered by the pregnant rats and weighed on the 7th day of birth; rats with a body mass of 12-17 g were selected.The feeding conditions of experimental animals were in accordance with the relevant experimental requirements and regulations, so as to reduce pain and death.The experiment was conducted in accordance with the Guiding Opinions on the Treatment of Experimental Animals issued by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China in 2006.This study has been approved by the Animal Experiment Ethics Committee of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine (Approval No.LLBH-202007080001).
1.2 Main experimental reagents and instruments
Isoflurane (Hebei Yipin Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.,China); 92% N2+ 8% O2mixed gas (Changsha Fanggang Gas Co., Ltd., China); trichloromethane, absolute ethanol, and isopropanol (Cat.No.B830240, E809056,and I811932, Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd.,China); hematoxylin dye and eosin dye (Cat.No.G1004 and G1001, Servicebio Company, China).
XCell SureLock Mini-Cell electrophoresis cell, iBright CL750 imaging system (Servicebio Company, China);5-HT1AR primary antibody (Cat.No.bs-1124R, BIOSS Company, China); Syn1 polyclonal primary antibody and β-actin polyclonal primary antibody (Cat.No.AF6201 and AF7018, Affinity Corporation, USA); goat anti-rabbit immunoglobulin (Ig) G [Cat.No.S004F, Beijing TDY Biotech Co., Ltd., China].
1.3 Model preparation and grouping
Forty neonatal rats were randomly divided into a sham operation group (12 rats) and a group for modeling (28 rats).Only blood vessels were exposed without ligation, cutting, and hypoxia treatment in the sham operation group.The newborn HIBI rat model was established according to the modified Rice modeling method in the group for modeling[8].The 7-day-old rats were anesthetized by isoflurane inhalation and sterilized with 75% ethanol, followed by cutting the neck skin in the middle, blunt separation of the left common carotid artery, electrocoagulation, penicillin treatment, and skin suture[4].The rats were kept warm for 1 h after the operation, placed in an anoxic chamber containing 92% N2+ 8% O2at 37 ℃ for 2 h, in a cage with the smell of mother rats for 15 min, and then returned to the cage and reared with mother rats.Whether the rats had tail clipping or left-rotation behaviors during hypoxia was observed.The rats were evaluated by the method developed by LONGA E Z,et al[9]after resuscitation.The model was judged to be successful if the score was higher than 2 and the above behaviors occurred.Twenty-four successful model rats were randomly divided into a model group and an abdominal Tuina group, with 12 rats in each group.
1.4 Intervention methods
The abdominal Tuina group was given abdominal Tuina for 28 d from 24 h after model establishment,once a day for 7 min/time (Figure 1).
Rubbing abdomen for 2 min: The manipulation started gently without driving subcutaneous tissues at a frequency of 120 times/min.
Kneading abdomen for 3 min: The thumb acted on the abdomen with relatively gentle manipulations in the beginning by slightly driving subcutaneous tissues, and then pressed deeply and moved slowly by gradually driving deep tissues at a frequency of 120 times/min.
Swinging abdomen 5-10 times: Pushed back and forth from left to right on the abdomen with the thumb and forefinger with increasing pressure, having the function of cleaning stools.
Pressing abdomen 4-6 times: Separated the abdomen into the upper and lower abdomen by the dichotomy, and pressed about 3 mm down (which could be deepened to 5 mm as the young rats grew up) at the upper abdomen and lower abdomen with the thumb,4-6 times at each position.
Parting abdomen Yin-Yang 5-10 times: Pushed 5-10 times from the subxiphoid along the costal arch edge to both sides.
Rats in the other groups were fed under the same conditions without other treatments.The feeding conditions were routinely a light/dark cycle of 12 h/12 h,20-25 ℃ temperature, and humidity of 50%-65%.

1.5 Observation items and detection methods
1.5.1 Behavioral test: suspension test
The suspension test was performed on the 7th, 14th,21st, and 28th days of intervention to detect the upper limb behavior function and muscle strength of neonatal rats[2].
Suspension test: The young rats were made to hold a glass rod with a length of about 50 cm and a diameter of about 0.5 cm by their forepaws, and their bodies and hind limbs were 50 cm away from the desktop or the ground.The falling time of the rats was recorded and scored according to the scoring standard.The suspension time <10 s was 1 point; during 10-30 s was 2 points; >30 s but <2 min was 3 points; during 2-5 min was 4 points; >5 min was 5 points.The higher the suspension test score, the better the behavioral function and muscle strength of the upper limbs[10].
1.5.2 Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining
After 28 d of interventions, 3 rats from each group were anesthetized; the left hippocampus was separated and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde.After routine dehydration, transparency, waxing, and embedding, the CA1 region of the left hippocampus was stained with HE and observed under the microscope[4].
1.5.3 Immunohistochemistry
After 28 d of interventions, the CA1 region of hippocampus from 3 rats in each group was sectioned.The endogenous peroxidase was inactivated by 3% H2O2for 10 min after the slices were dewaxed and placed in water; after being washed with PBS for 3 min × 3 times,the labeled area was delineated with a marker pen, the 5-HT1AR primary antibody (1:200) was added, and then put into an incubator at 37 ℃ for 1 h; after being washed for 3 min × 3 times with PBS, the second antibody (rabbit anti-sheep IgG) was added dropwise and incubated at 37 ℃ for 30 min, followed by coloration with the DAB chromogenic kit, hematoxylin re-staining, dehydration, transparency, and sealing[10].The integrated optical density (IOD) was calculated by Image-Pro 6 software, and the average optical density(AOD) was used as the expression results for statistical analysis (AOD = IOD ÷ Visual field area)[11].
1.5.4 Syn1 expression was measured by Western blotting (WB)
After 28 d of interventions, the hippocampus of 6 rats in each group was lysed on ice and the protein stock solution was extracted.The protein concentration was determined using the BCA standard method and the protein sample solution was prepared.The protein was denatured at 100 ℃ for 20 min, then loaded,electrophoresed, electro-transferred, blocked with 5%skim milk for 60-90 min, washed with TBST for 15 min[4],then added Syn1 (1:1 000) or β-actin (1:8 000) primary antibody, respectively, and incubated overnight on a shaking table at 4 ℃.Washed with TBST 3 times,15 min/time, added 4-6 mL of IgG (1:8 000), incubated on a shaking table at room temperature for 90 min.Then, washed with TBST 3 times and dropwise added the developer.The gray value was measured by Image Lab 3.0[12].β-actin was used to analyze the relative Syn1 expression in each group.
1.6 Statistical methods
The SPSS version 25.0 statistical software was used to analyze the data.The measurement data conforming to normal distribution were expressed as mean ± standard deviation, and those satisfying homogeneity of variance were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance,and the least significant difference method was used for
pairwise comparisons between groups.Those not conforming to normal distribution were expressed as median (interquartile range) [M (IQR)] and analyzed by nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis H test.P<0.05 indicated that the difference was statistically significant.
2 Results
2.1 Suspension test results
There was no significant difference in the suspension test score between the 7th and the 14th days of intervention (P>0.05).Compared with the sham operation group, the suspension test scores were decreased (P<0.05), while the behavioral function and muscle strength of upper limbs were worse in the model group after 21 d and 28 d of interventions.Compared with the model group, the suspension test scores were significantly higher (P<0.05), while the behavior function and muscle strength of upper limbs were better in the abdominal Tuina group after 21 d and 28 d of interventions (Figure 2).

Figure 2 Comparison of the suspension test score of each group after intervention (n=12)
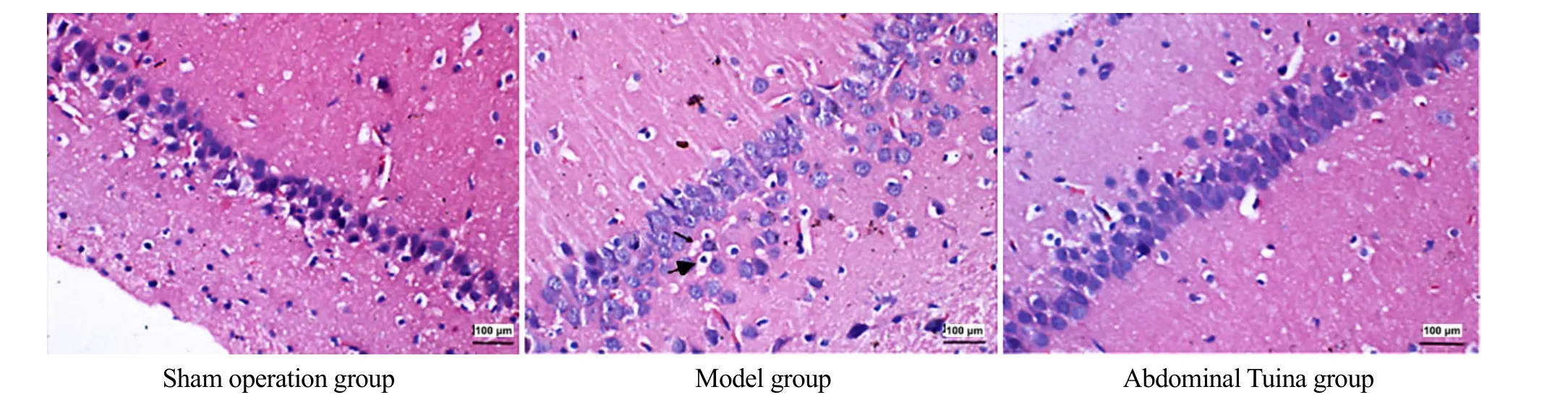
2.2 Pathological changes in hippocampal CA1 region observed by HE staining
Cells in the hippocampal CA1 region were complete in morphology and structure and arranged neatly without necrosis in the sham operation group.Cell structure in the hippocampal CA1 region was disordered with edema and necrosis in the model group.The arrangement of cells in the hippocampal CA1 region was clear, and the edema was improved obviously in the abdominal Tuina group (Figure 3).
2.3 Immunohistochemical analysis of AOD changes in 5-HT1AR positive cells in the hippocampal CA1 region
After 28 d of interventions, the 5-HT1AR positive cells in the hippocampus of the sham operation group rats were significant.Compared with the sham operation group, the 5-HT1AR positive cell number in the hippocampus of rats in the model group decreased significantly (P<0.05).Compared with the model group,the 5-HT1AR positive cell number in the hippocampus of the abdominal Tuina group rats increased significantly(P<0.05).See Figure 4 and Figure 5.
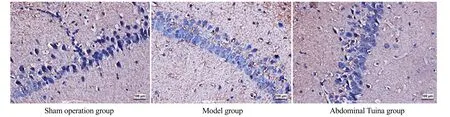
Figure 5 Comparison of the average optical density of 5-HT1AR positive cells in the hippocampus among groups(n=3)
2.4 Protein quantitative detection of Syn1 expression by WB
After 28 d of interventions, the Syn1 expression in the hippocampus of the sham operation group rats was obvious.Compared with the sham operation group,Syn1 expression in the hippocampus of the model group rats decreased significantly (P<0.05); compared with the model group, the Syn1 expression in the hippocampus of the abdominal Tuina group rats increased significantly (P<0.05).See Figure 6 and Figure 7.
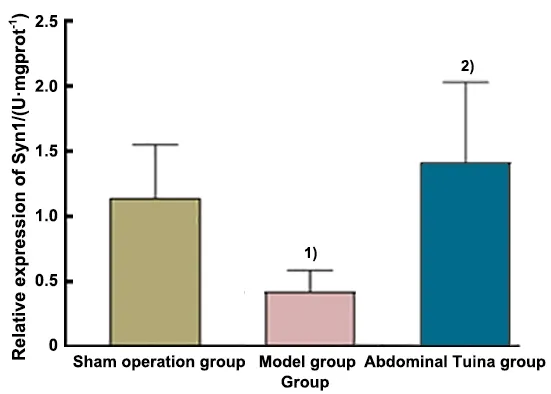
Figure 7 Comparison of the relative expression of Syn1 in the hippocampus of each group (n=6)

3 Discussion
HIBI occurrence is closely related to neuronal apoptosis and synaptic dysfunction[13].Studies have shown that HIBI-induced neuronal apoptosis changes the synaptic structure and number.With the decrease of the synaptophysin expression level, the release and binding of transmitters such as signal transduction and neurotrophic factors are abnormal, which aggravates brain dysfunction[14].It has been reported that on the same or roughly the same brain injury sites, the severity of the disease is correlated with the levels of 5-HT1AR and Syn1[15-17].Increasing the expression levels of 5-HT1AR and Syn1 can promote synaptic remodeling,accelerate the rehabilitation of brain function, and alleviate the clinical symptoms of brain injury[7,18-19].
As a unique therapy of traditional Chinese medicine,abdominal Tuina is easy to operate and safe.The application of abdominal Tuina therapy is based on the traditional meridian theory of traditional Chinese medicine and the theory of “brain-gut axis” of modern medicine.Tuina stimulates the abdomen of rats and regulates the intestinal flora and brain-gut peptide factors, thus regulating the brain through the gut-brain interaction, including the sympathetic nervous system,the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, and the immune system[20].Our previous research showed that abdominal Tuina effectively promoted brain injury repair and the growth and development of young HIBI rats[21].The main operation site of abdominal Tuina is the abdomen.According to the meridian theory of traditional Chinese medicine, abdomen is the place where the Zang-Fu Front-Mu points aggregate, as well as where the Conception Vessel, Stomach Meridian,Spleen Meridian, and Kidney Meridian pass through.The Conception Vessel is the sea of Yin meridians,maintaining Yin in the whole body.The spleen and stomach are the postnatal foundation, and the kidney is the congenital foundation, and these four are closely related to the brain.Abdominal Tuina acts on the Conception Vessel, Kidney Meridian, Spleen Meridian,and Stomach Meridian, stimulating Zang-fu Front-Mu points at the same time.This method unblocks meridians, regulates Zang-Fu organs, wakes up the heart, and opens orifices to treat mental diseases[22].
The hippocampus is the most sensitive site to HIBI[23].Studies have shown that ischemia and hypoxia cause severe hippocampal neuron apoptosis in rats, which eventually leads to declined coordination, integration,and control functions of hippocampal neurons over limbs, resulting in abnormal behaviors and functions of upper limbs[2,4].In this study, after 21 d and 28 d of interventions, compared with the sham operation group, the suspension test score decreased, and the performance of upper limb muscle strength and behavior function was worse in the model group, which was consistent with the research results of many scholars[2,24].ELDOMIATY M A, et al[25]showed that after limb exercise training, brain-derived neurotrophic factor and upper limb muscle cytokines in the hippocampus increased significantly, and the degenerated neurons in the hippocampus reduced significantly.It also proves that hippocampal injury and upper limb behavioral function influence each other pathologically and regulate each other functionally.This study showed that after 21 d and 28 d of abdominal Tuina interventions,the scores of the suspension test in the Tuina group were higher than those in the model group, and the motor function and muscle strength of upper limbs were improved, suggesting that Tuina intervention promotes the regulation of hippocampal neurons on limb coordination and control, thus promoting the normal behavior function of upper limbs.
The brain tissues of HIBI rats undergo degeneration,necrosis, inflammation, edema, neuron atrophy or apoptosis, white matter transformation around the ventricle, and other pathological changes[26].Astrocytes are activated 15 d after hypoxic-ischemic injuries to inhibit neuronal apoptosis and accelerate neuronal repair and synaptic remodeling by releasing a large number of neurofactors, thus promoting the rehabilitation of brain injuries[27].The HE staining showed that after 28 d of interventions, compared with the model group, the pathological changes such as edema and inflammation in the hippocampus of abdominal Tuina group rats were improved, suggesting that abdominal Tuina can accelerate the repair of HIBI neurons and synaptic remodeling, and promote the rehabilitation of brain function.
5-HT1AR is an important signal molecule in nervous system development and nerve conduction.It can inhibit neuronal apoptosis, increase the number of synapses, and promote nerve signal conduction and neuron development[28-29].It is found that 5-HT1AR can directly feedback and regulate the 5-HT system to inhibit neuronal apoptosis in rodent models of global brain and focal cerebral ischemia.Meanwhile, it activates adenylate cyclase, regulates cAMP/PKA pathway and downstream signal molecules, and increases synaptophysin secretion, thus realizing neuroprotective effects[30-31].Previous studies have shown that Tuina intervention up-regulates 5-HT/5-HT1AR protein-positive cells in brain injury model rats,affects neurogenesis, stimulates nerve plasticity,reduces neuron deaths, plays an anti-inflammatory role,and improves memory and limb control ability of rats[32-33].Immunohistochemical results showed that after intervention, compared with the model group, the number of 5-HT1AR positive cells in the injured hippocampus of the abdominal Tuina group rats increased significantly, suggesting that abdominal Tuina can increase the expression of 5-HT1AR in the hippocampus to achieve neurological rehabilitation.
Syn1 is the main protein involved in structural synaptic plasticity, located on the adventitia of synaptic vesicles and participating in signal transduction and neurotrophic transmitter release, and it can directly reflect the number and density of synapses.Syn1 is also a sign of presynaptic development and activity, playing an important role in synaptic remodeling and cognitive processes[34].Here, WB showed that compared with the model group, the expression level of Syn1 in the injured hippocampus of the abdominal Tuina group rats was significantly higher, which indicated that abdominal Tuina had a certain regulatory effect on synaptic protein in the hippocampus and promoted the repair of brain injuries in HIBI rats.
In conclusion, abdominal Tuina improves the behavioral function of upper limbs in HIBI rats,up-regulates the expression levels of 5-HT1AR and Syn1 in the hippocampus, and promotes synaptic remodeling to realize the rehabilitation effect of brain function.Abdominal Tuina is easy to operate and has great potential to be used in the treatment of neonatal HIBI.However, the behavioral dysfunction of upper limbs caused by HIBI in newborns is a complex pathological process, which involves the cortical motor region.Due to the limitation of experimental technology and cycle,this study failed to observe the changes in the cortical motor region, which needs further exploration.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the General Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (国家自然科学基金面上项目, No.81874508); University-level Scientific Research Fund Project of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine (湖南中医药大学校级科研基金项目,No.2021CX40).
Statement of Human and Animal Rights
This study has been approved by the Animal Experiment Ethics Committee of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine (Approval No.LLBH-202007080001).The treatment of animals in this experiment conformed to the ethical criteria.
Received: 7 March 2022/Accepted: 25 November 2022
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Effects of electroacupuncture at Baihui (GV20) and Yintang (GV29) on endoplasmic reticulum stress in depressive rats caused by chronic unpredictable mild stress
- Effects of acupuncture and moxibustion on PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway in substantia nigra of Thy1-αSyn transgenic mice with Parkinson disease
- Acupuncture compound anesthesia for traditional thyroidectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Effects of auricular point sticking on labor pain and anxiety
- Clinical study of Tuina combined with functional training to improve the clinical symptoms and balance function in patients with meniscus injury
- Study on the mechanism of P2X receptors involved in electroacupuncture treatment of neuropathicpain in dorsal root ganglion and spinal cord
