To investigate the effect of Shenqi Tiaoshen Formula on CSE induced inflammatory response of MH-S cells based on TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 pathway
2023-12-23WangHuiYangQinjunZHOUFanchaoYangChengTONGJiabingLIZegeng
Wang Hui, Yang Qin-jun, ZHOU Fan-chao, Yang Cheng, TONG Jia-bing, LI Zegeng,✉
1.Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230038, China
2.The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230031, China
3.Institute of Respiratory Diseases, Anhui Academy of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230031, China
4.Xin 'an Key Laboratory of Medical Science, Ministry of Education, Hefei 230038, China;
5.Key Laboratory of Application and Transformation of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Prevention and Treatment of Major Pulmonary Diseases,Hefei 230031, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To study the effects of Shenqi Tiaoshen Formula (SQTS) on the inflammatory response of MH-S cells induced by cigarette smoking extract (CSE) and its mechanism based on TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 pathway.Methods: MH-S cells were used as subjects to evaluate cell viability by CCK-8 method.The levels of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in the supernatant were detected by ELISA.ROS were detected by DCFH-DA fluorescence probe.Western blotting was used to detect the expression of TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 pathway protein, and TAK-242,a TLR4 inhibitor, was used to verify the role of SQTS in the TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 pathway.Results: Compared with blank group, the cell survival rate of CSE group was decreased, and the contents of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 were increased (P< 0.05),ROS fluorescence expression level was significantly increased (P< 0.01), TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 pathway protein expression was significantly increased (P< 0.05); Compared with CSE group, the survival rate of cells in SQTS groups was increased, and the expression levels of the above indexes were decreased (P<0.05), and TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 pathway protein decreased in TAK-242 groups (P<0.05).Conclusion: SQTS can reduce the inflammatory response of MH-S cells induced by CSE by inhibiting TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 pathway.
1.Introduction
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a common respiratory disease with chronic systemic inflammation, emphysema and megalopolysis as the main pathological changes.Macrophages are inflammatory cells derived from monocytes, and their number increases in airway, alveolar area and induced sputum in COPD patients, which are related to the inflammatory response and destruction of alveolar wall in COPD[1,2].At present, it is generally believed that oxidative stress caused by cigarette smoke plays a key role in the occurrence and development of COPD inflammatory response[3,4], which is characterized by the accumulation of inflammatory cells and the release of cytokines (such as ROS,TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β) in lung parenchyma, inducing exacerbation of COPD[5].Inhibition of cytokine production or function is a key mechanism for controlling inflammation.
SQTS was developed by Professor Han Mingxiang, a Chinese medical master, according to Xin ‘an theory of “strengthening the root and cultivating the yuan”, adding dogwood, peach kernel and white mustard seeds to the Liuwei Buqi capsule of Anhui Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine.Our research group's previous studies have shown that Liuwei Buqi can effectively play the role of immune regulation and inflammation inhibition[6,7], but the specific pharmacological mechanism of SQTS in the treatment of COPD is still unclear.Therefore, in order to further clarify the anti-inflammatory mechanism of SQTS, this study studied whether SQTS can reduce the CSE-induced MH-S cell inflammatory response through TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signaling pathway from the perspective of in vitro experiments, providing theoretical basis for the later TCM treatment of COPD by SQTS.
2.Materials
2.1 Cells
Mouse alveolar macrophage MH-S (Wuhan Procell, CL-0597).
2.2 Preparation of SQTS freeze-dried powder liquid
According to the methods reported in relevant literature[8].SQTS(ginseng, decocted Astragalus, Yizhiren, jade bamboo, orange peel,cinnamon, Cornus officinalis meat, white mustard seed, peach kernel.Purchased from the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine Pharmacy, identified as genuine by Professor Han Yanquan.) Add water and fry until 100 mL, mix well,then pack into sterile petri dish, freeze at -80 ℃, put into vacuum dryer for vacuum lyophilization for 36 h to obtain a puffed dry substance, grind into fine powder with mortar, and prepare SQTS freeze-dried powder mother liquor with serum-free DMED.The mother liquor was filtered by 0.22 μm filter membrane and frozen in-20 ℃ refrigerator for later use.
2.3 Reagents
DMEM high-sugar medium (Procell, PM150210); MH-S special medium (Procell, CM-0597); CCK-8(Shanghai, ES7011); IL-1β, TNF- ELISA kit (Wuhan Genmei Technology Co., LTD.,JYM0419RaH2DCFDA, JYM0635Ra); IL-6-ELISA kit (Hangzhou Lianke Biotechnology Co., LTD., EK306/3-96); ROS fluorescent probe (US MCE Corporation, HY-D0940); TLR4 inhibitor (TAK242,Selleck, S745502); TLR4 antibody (biossbs, AG05125500); NF-KB antibody (Proteintech, 10017763); p-NF-KB antibody (CST, USA,17); NLRP3 antibody (Abcam, GR3369573-3); Goat Anti-Mouse IgG (Zsbio, 140193).
3.Methods
3.1 Cell culture
MH-S cells were cultured in a 5% CO2 cell incubator at 37 ℃ with a 1:3 ratio.
3.2 CSE Preparation
According to the methods reported in relevant literature[9].Dujiang Brand cigarettes (Ingredients for each cigarette: Tar 10 mg, carbon monoxide 13 mg, nicotine 0.8 mg) lit, so that the smoke from the burning of 2 cigarettes uniform smoke through the glass bottle containing 20 mL serum-free DMEM medium, The absorbance value of DMEM medium at 320 nm was determined, and the OD value was adjusted to about 1.36±0.12.100% CSE stock solution was prepared and stored at -80 ℃ after subpacking.
3.3 CCK-8 detection
3.3.1 Selecting the optimal concentration and time for CSE molding
Single-cell suspension was prepared, inoculated on 96-well plates at a density of 2×105/mL per well, and cultured overnight.The original medium of the hole plate was discarded, and CSE 100 μL with different concentrations (1%, 2%, 4%, 6%, 8%, 10%, 12%)was added.Meanwhile, a blank group (without cells) and a control group (normal cells) were set up.After continuous culture for 24 h,CCK-8 reagent 10 μL was added to each hole to be tested.The light absorption values of each hole were measured at 450 nm wavelength.
3.3.2 Screening the optimal concentration and time of SQTS
The cell culture and seed plate operation were the same as “2.3.1”,and SQTS was added with different mass concentrations (10, 20, 40,80, 160, 320, 640 mg L-1) of 100 μL, and continued to be cultured for 24 h.CCK-8 test operation method and count are the same as“2.3.1”.
3.4 ELISA assay
The single-cell suspension was prepared and inoculated into the 12-well plate at a density of 2×105/mL.After the cells were fully attached to the wall, the liquid in the hole was discarded.They were randomly divided into blank group (normal culture), model group (8% CSE treatment), SQTS low-dose group (40 mg·L-1),SQTS medium-dose group (80 mg·L-1) and SQTS high-dose group(160 mg·L-1).The contents of IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6 in the cell supernatant of each group were detected 24h later.
3.5 DCFH-DA fluorescent probe detection
After the cells were cultured in groups for 24 h according to the method in “2.4”, the medium was discarded, PBS was washed twice,and 1 mL diluent was added to each well (DCFH-DA was diluted with DMEM high-glucose medium at the ratio of 1:1 000), and the cells were incubated in the incubator for 30 min, and then washed with PBS for 3 times.The excitation wavelength of 460 ~ 500 nm and the emission wavelength of 512 ~ 542 nm were set under the inverted fluorescence microscope for fluorescence imaging.ROS fluorescence relative level was analyzed by Image J software.
3.6 Western blot detection
Logarithmic growth of MH-S cells was divided into blank group, model group, SQTS high-dose group, TAK242 group,TAK242+CSE group, TAK242+CSE+SQTS group.With reference to relevant literature[10], TAK242 with a concentration of 20 mg·L-1was taken and pre-treated for 3 h before adding SQTS and CSE.Cell protein was extracted from each group, and the protein concentration was determined according to the instructions of BCA kit.After electrophoresis, the membrane was transferred for 90 min.After sealing PVDF membrane with 5% skim milk for 2 h, the first antibody was incubated at 4 ℃ overnight and the second antibody was incubated at 37 ℃ for 90 min.The protein was detected by ECL chemiluminescence substrate, and the gray values of each strip were analyzed by Image J software.
3.7 Statistical Methods
SPSS 22.0 software was used for statistical analysis.The data were expressed as±s, and one-way ANOVA was used to compare the data between multiple groups.P <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
4.Results
4.1 Suitable conditions for macrophage inflammation model induced by CSE
With increasing CSE concentration, cell viability decreased gradually compared with blank group (P<0.05); There was no significant change in cell viability when the concentration was 6%-8% (P>0.05), the activity was significantly decreased when CSE concentration reached 10% (P<0.05) and less than 80%.Therefore,8% CSE concentration was selected as the molding concentration for subsequent experiments.The results are shown in Fig.1 and Table 1.
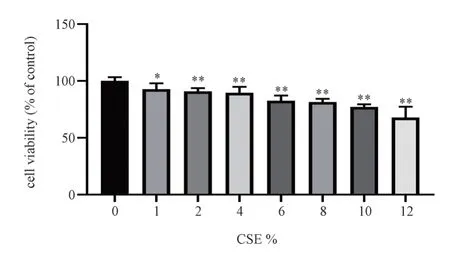
Fig 1 Effect of different concentrations of CSE on the viability of MH-S cells (±s, n=6)
Tab 1 Effect of different concentrations of CSE on the viability of MH-S cells (±s, n=6)
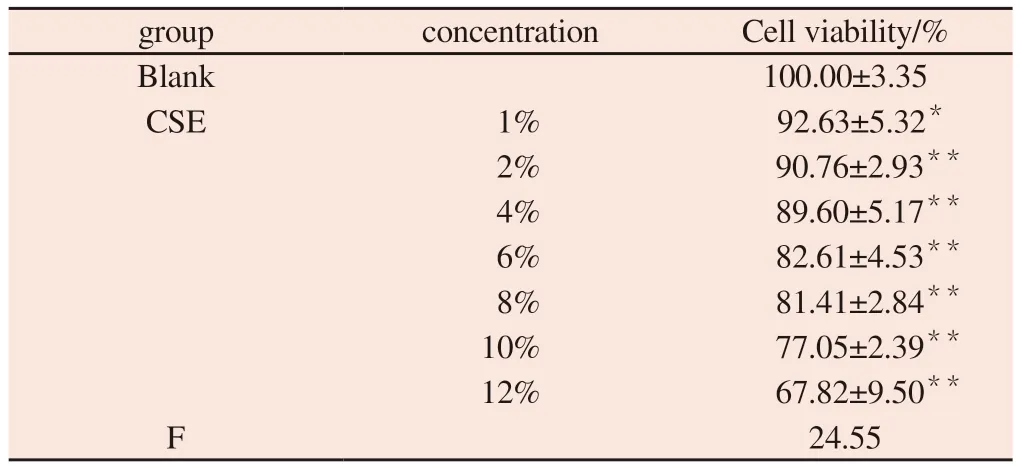
Tab 1 Effect of different concentrations of CSE on the viability of MH-S cells (±s, n=6)
Note:Comparison with blank group * P<0.05, ** P<0.01
group concentration Cell viability/%Blank 100.00±3.35 CSE 1% 92.63±5.32*2% 90.76±2.93**4% 89.60±5.17**6% 82.61±4.53**8% 81.41±2.84**10% 77.05±2.39**12% 67.82±9.50**F 24.55
4.2 Effects of SQTS on MH-S cell activity
When SQTS concentration ranged from 20 mg L-1 to 160 mg L-1,there was no significant difference in cell viability compared with blank group (P>0.05); When SQTS concentration exceeded 160 mg L-1, cell viability decreased significantly compared with blank group (P<0.05).Therefore, 40 mg L-1, 80 mg L-1, 160 mg L-1 were selected as SQTS low, medium and high dose groups for follow-up experiments.The results are shown in Fig.2 and Table 2.
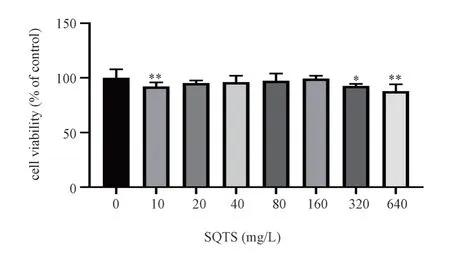
Fig 2 Effect of different concentrations of SQTS on the viability of MH-S cells (±s, n=6)
Tab 2 Effect of different concentrations of SQTS on the viability of MH-S cells(±s, n=6)

Tab 2 Effect of different concentrations of SQTS on the viability of MH-S cells(±s, n=6)
Note:Comparison with blank group * P<0.05, ** P<0.01
group concentration Cell viability/%blank 100.00±7.84 SQTS 10 mg·L-1 92.11±3.66**20 mg·L-1 95.16±2.41 40 mg·L-1 96.01±5.96 80 mg·L-1 97.31±6.57 160 mg·L-1 99.37±2.52 320 mg·L-1 92.94±1.24*640 mg·L-1 87.79±6.23**F 3.83
4.3 The levels of IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6 in cell supernatants of each group were determined by ELISA
Compared with blank group, the contents of IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6 in model group were significantly increased (P < 0.01).Compared with model group, the contents of IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6 in SQTS low, medium and high dose groups were significantly decreased (P <0.05).The results are shown in Fig.3 and Table 3.
4.4 Fluorescence probe DCFH-DA was used to detect the relative fluorescence level
Compared with the blank group, the relative fluorescence level of ROS in the model group was significantly increased (P< 0.01).Compared with model group, the relative levels of ROS fluorescence in SQTS low, medium and high dose groups decreased significantly(P< 0.01).The results are shown in Fig.4 and Table 4.
Tab 3 Effect of SQTS on the secretion of inflammatory factors in MH-S cells (±s, n=3)
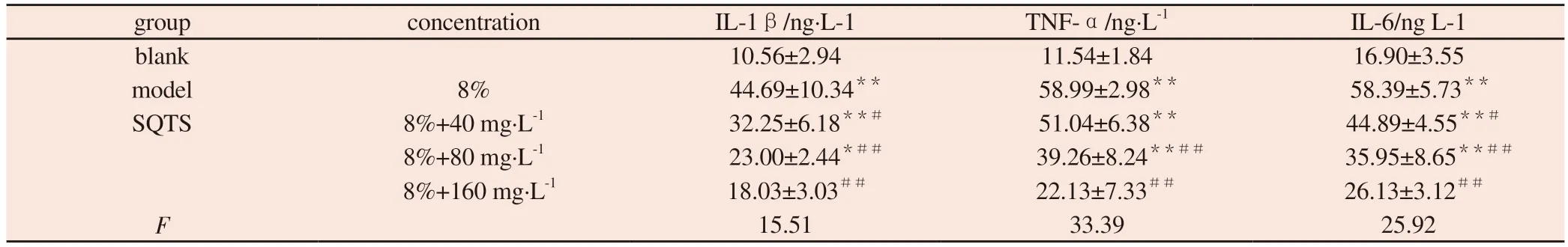
Tab 3 Effect of SQTS on the secretion of inflammatory factors in MH-S cells (±s, n=3)
Note:Comparison with blank group * P<0.05, ** P<0.01; Comparison with model group#P<0.05,##P<0.01
group concentration IL-1β/ng·L-1 TNF-α/ng·L-1 IL-6/ng L-1 blank 10.56±2.94 11.54±1.84 16.90±3.55 model 8% 44.69±10.34** 58.99±2.98** 58.39±5.73**SQTS 8%+40 mg·L-1 32.25±6.18**# 51.04±6.38** 44.89±4.55**#8%+80 mg·L-1 23.00±2.44*## 39.26±8.24**## 35.95±8.65**##8%+160 mg·L-1 18.03±3.03## 22.13±7.33## 26.13±3.12##F 15.51 33.39 25.92
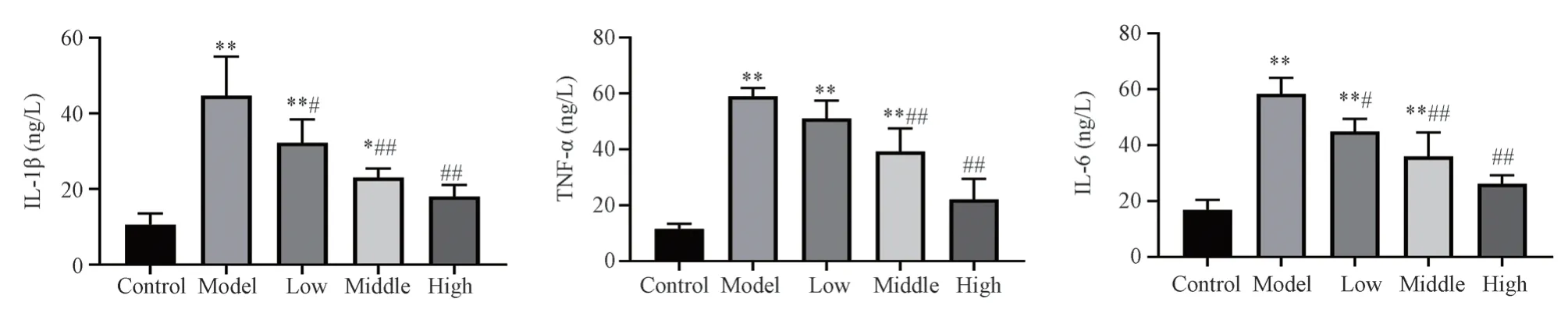
Fig 3 Effect of SQTS on the secretion of inflammatory factors in MH-S cells (±s, n=3)

Fig 4 Effects of SQTS on the relative fluorescence levels of ROS in MH-S cells(DCFH-DA ×200; ±s, n=3)
Tab 4 Effects of SQTS on the relative fluorescence levels of ROS in MH-S cells(±s,n=3)
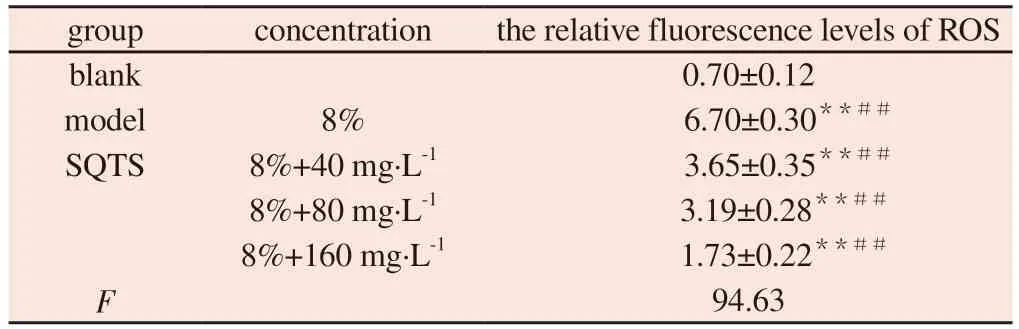
Tab 4 Effects of SQTS on the relative fluorescence levels of ROS in MH-S cells(±s,n=3)
Note:Comparison with blank group * P<0.05, ** P<0.01; Comparison with model group#P<0.05,##P<0.01
group concentration the relative fluorescence levels of ROS blank 0.70±0.12 model 8% 6.70±0.30**##SQTS 8%+40 mg·L-1 3.65±0.35**##8%+80 mg·L-1 3.19±0.28**##8%+160 mg·L-1 1.73±0.22**##F 94.63
4.5 Western blot assay was used to detect the protein expression levels of TLR4, NF-kB and NLRP3 in intracellular pathways
Compared with blank group, the protein expressions of TLR4,p-NF-kB and NLRP3 in model group were increased (P<0.01).Compared with model group, the expression levels of TLR4, p-NFkB and NLRP3 in SQTS group and TAK242+CSE group decreased(P<0.05), the protein expression levels of TLR4, p-NF-kB and NLRP3 in TAK242+CSE+SQTS group were decreased (P>0.01).Compared with TAK242+CSE group, there were no significant differences in TLR4, p-NF-kB and NLRP3 protein expression between SQTS group and TAK242+CSE+SQTS group (P> 0.05).The results are shown in Fig.5 and Table 5.

Fig 5 Effect of SQTS on TLR4、p-NF-κB、NLRP3 protein in MH-S cells relative expressions
Tab 5 Effect of SQTS on TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 protein in MH-S cells relative expressions (±s, n=3)

Tab 5 Effect of SQTS on TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 protein in MH-S cells relative expressions (±s, n=3)
Note:Comparison with blank group * P<0.05, ** P<0.01; Comparison with model group#P<0.05,##P<0.01
group concentration TLR4/GAPDH p-NF-κB/NF-κB NLRP3/GAPDH blank 0.32±0.03 0.36±0.06 0.45±0.06 Model 8% 0.95±0.09** 0.90±0.07** 0.90±0.03**SQTS 8%+160 mg·L-1 0.76±0.07**# 0.73±0.09*# 0.78±0.06**TAK242 20 mg·L-1 0.22±0.10## 0.21±0.01## 0.27±0.06##TAK242+CSE 8%+20 mg·L-1 0.59±0.05# 0.63±0.03# 0.66±0.03#TAK242+CSE+SQTS 8%+160mg·L-1+20 mg·L-1 0.42±0.03## 0.53±0.05## 0.55±0.05##F 53.53 98.61 63.54
5.Discussion
Inflammation and oxidative stress are interrelated processes that represent potential causes of COPD[11].Inflammatory response is the key driving and progression factor of COPD.It continues to exist in the stable period of COPD and is intertwined with immune imbalance and metabolic disorders.It is mainly characterized by the activation of immune inflammatory cells such as airway macrophages, neutrophils and mast cells.The secretion of intracellular factors such as IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6 and ROS as well as the activation of corresponding pathways lead to acute aggravation or persistence of airway inflammation, resulting in pathological changes such as alveolar separation and lung parenchyma changes,resulting in incomplete reversible and progressive airflow restriction[12,13,14].Exposure to CSE leads to inflammatory responses due to the production of high levels of cytokines such as ROS, TNF- , IL-6,and IL-1β[5,15].ROS is produced by cell physiology and is involved in maintaining cell homeostasis and oxidative stress.Excessive accumulation of ROS will lead to damage of cell components[16] and further aggravate the severity of inflammation[17].
In lung tissue, TLR4 is activated by cigarette smoke, bacterial and viral infection and other risk factors, and then activates NFkB and induces the expression of inflammatory mediators[18].After being activated by upstream TLR4, NF-kB releases TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and other cellular inflammatory factors, and activates into the nucleus[19].After NF-kB enters the nucleus, NLRP3 is activated to further induce the maturation and secretion of IL-1β, and participate in the regulation of inflammatory response in the body[20,21].Therefore, preventing the activation of the TLR4/NF-kB/NLRP3 signaling pathway is an important target for the treatment of inflammation.
Shenqi Tiaoshen formula is based on the clinical experience formula of Han Mingxiang, a Chinese medical master.It has the effect of tonifying lung and kidney, eliminating phlegm and removing blood stasis.Studies have found that the main components of SQTS include tangerine, cinnamic acid and ginsenoside Rg1[22].Tangerine has anti-inflammatory activity, which can inhibit the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in asthmatic rats to reduce the secretion of pro-inflammatory factors IL-lβ, IL-6 and TNF-α[23,24], thereby reducing airway inflammation.Cinnamic acid has various biological activities such as scavenging ROS/RNS, antiviral and antibacterial[25,26], and exerts anti-inflammatory effects by acting on inflammatory factors such as IL-1β and TNF[27].Ginsenoside Rg1 can reduce oxidative stress damage and inflammatory cell infiltration, and protect lung tissue[28,29].The effects of the above components are consistent with the therapeutic purpose of COPD.In this study, it was found that after CSE stimulation, the contents of inflammatory factors IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6 increased in normal MH-S cells.Meanwhile, the relative expression level of ROS fluorescence and the protein expressions of TLR4, p-NF-κB and NLRP3 increased significantly in cells, indicating that after CSE stimulation, the relative expression level of ROS fluorescence and the protein expression of TLR4, P-NF-κB and NLRP3 increased significantly.Induced an inflammatory model of MH-S cells.However, the expression of IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6 inflammatory factors in the cell supernatant and ROS fluorescence in the cells decreased after the treatment of Shenqi Tiaoshen Formula, indicating that the inflammatory response of the cells was improved after the treatment of Shenqi Tiaoshen formula.In order to further investigate the relationship between Shenqi Tiaoshen formula and TLR4/NFκB//NLRP3 during the regulation of inflammatory response, this study used TAK-242, an inhibitor of TLR4, to intervene.TAK242 can significantly down-regulate the expression of p-NF-κB and NLRP3 proteins downstream of TLR4.Shenqi Tiaoshen formula can also significantly down-regulate the expression of p-NF-κB and NLRP3 proteins downstream of TLR4, and there is no significant difference in the expression of these proteins compared with the inhibitor group, while Shenqi Tiaoshen formula combined with inhibitor can significantly inhibit the expression of these proteins, but there is no significant difference compared with the inhibitor group.The results showed that SQTS, similar to TAK242, also exerted antiinflammatory effects by inhibiting TLR4.Therefore, we conclude that SQTS may reduce CSE-induced MH-S cell inflammation by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway.
In conclusion, SQTS may improve CSE-induced MH-S cell inflammatory response by inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB//NLRP3 pathway, providing a new perspective for understanding the role and molecular mechanism of Shenqi Tiaoshen prescription in COPD.Therefore, Shenqi Tiaoshen prescription may be a new effective drug in the treatment of COPD.But further experiments are needed to assess the role of SQTS in vivo.
Author's contribution
Wang Hui: experimental operation, paper writing and final revision;Yang Qinjun: Put forward research ideas and guide the writing of the paper; Zhou Fanchao: data analysis and proofreading; Yang Cheng:Guiding experimental operation; Tong Jiabing, Li Zegeng: Financial support and technical guidance for all experimental reagents.
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Research progress on the regulation mechanism of non-coding RNA on ankylosing spondylitis
- Anesthetic effect of phenobarbital sodium on female BALB/c mice
- Research progress of TCM regulation of Cajal interstitial cells in the treatment of functional Gastrointestinal diseases
- Abnormal expression and significance of circ-CBLB/miR-486-5p in patients with rheumatoid arthritis of spleen deficiency and dampness excess type
- Inhibitory effect of thymoquinone on neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease model by regulating NLRP3 inflammatory bodies
- Effect of Astragalus-hawthorn on ovarian reproductive function and inflammatory mechanism of action in rats with polycystic ovary syndrome
