Research progress on the regulation mechanism of non-coding RNA on ankylosing spondylitis
2023-12-23HUANGYangjunZHOUHonghaiCHENLonghaoLIJilinLUQingwangLIDongyang
HUANG Yang-jun, ZHOU Hong-hai, CHEN Long-hao, LI Ji-lin, LU Qing-wang, LI Dongyang
College of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Guangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic progressive inflammatory immune disease, which mainly affects the spine and sacroiliac joints, with a high rate of late disability.At present,because the pathogenesis of the disease is not clear, its treatment targets are not clear, and there is no consensus on intervention measures.Therefore, further exploration of the mechanism of the disease has certain guiding significance for clinical application.At the same time, noncoding RNA can regulate protein translation, participate in the physiological and pathological changes of AS, and is closely related to the progress of AS.Its internal mechanism and potential targets are worthy of in-depth study.This article summarizes the research progress of non-coding RNA involved in AS through the regulation of bone metabolism, inflammation,cell death and autophagy, in order to provide a theoretical basis for exploring potential clinical diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets of AS.
Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) is a chronic progressive inflammatory immune disease.The incidence in the Chinese population is about 0.2-0.4%.It is mostly young men.It mainly affects the spine and sacroiliac joints.The fusion of the spine and sacroiliac joints leads to reduced spine mobility and severely affects the patient’s quality of life[1].At present, it is believed that the onset of AS may be related to the interaction of multiple factors such as genetics,environment, or immunity.The mechanism of action is still unclear,and the therapeutic target is not clear.There is currently no standard treatment and maintenance of remission.Therefore, exploring the mechanism of AS and new therapeutic targets is of great significance for the prevention and treatment of AS.
Non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is the RNA that regulates protein translation in the gene regulatory network, including microRNA(miRNA), long-chain non-coding RNA (lncRNA), circular RNA(circRNA), etc.Recent studies have shown that miRNA, LncRNA and circRNA are abnormally expressed in the tissues of patients with AS, and they play an important regulatory role in the development of AS, suggesting that ncRNA is closely related to AS[2].Therefore,this research focuses on the research progress of miRNA, lncRNA,and circRNA in the diagnosis of AS and the mechanism of action.
1.miRNA and ankylosing spondylitis
miRNA is a group of endogenous short-stranded non-coding RNA molecules, most of which are transcribed by RNA polymerase II, and their upstream regions contain typical core promoters and enhancers regulated by transcription factors to control multiple gene targets The expression of, plays a vital role in biological regulation[3].With the development of high-throughput sequencing technology, more and more studies have shown that miRNA is involved in the pathogenesis of AS[4].
1.1 miRNA is involved in AS bone metabolism regulation
In the pathogenesis of AS, there are two contradictory bone metabolism processes: one is the pathological new bone formation of vertebrae, face joints and ligament structures, and the other is the loss of trabecular bone mass in the vertebral body, leading to osteoporosis..Studies have shown that miRNAs play an important role in the regulation of bone metabolism in AS[5], suggesting that miRNA may be involved in the bone metabolism process of AS.
1.1.1 miRNA regulates the Wnt/β-catenin osteogenic pathway
The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is a highly conserved pathway that is closely related to bone metabolism.It mainly binds to the Frizzled receptor and LRP5/6 co-receptor through Wnt protein to inhibit glycogen synthase kinase-3 ( GSK-3β) β-catenin phosphorylates and degrades the APC-Axin-GSK-3β complex,increases the stability and accumulation of β-catenin (β-catenin) in the cytoplasm, enters the nucleus and enhances T cell factors/lymph Factors (TCF/LEF) combine to play the transcription and expression functions of target genes[6].It has been confirmed that miR-29a,miR-17-5p, miR-96, and miR-495 participate in the pathogenesis of AS by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.HUANG et al.[7] experimentally confirmed the high expression level of miR-29a in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PMBC) of AS patients,and was positively correlated with the course of AS and the modified Stoke AS column score (mSASSS) Because the mSASSS index is a composite index reflecting the formation of new bone in the spine, it suggests that miR-29a may be involved in the process of new bone formation in AS.Fu Zhongchao et al.[8] found that while miR-29a was highly expressed in PMBC in AS patients, the expression of Dickkopf protein 1 (DKK1) and GSK-3β was significantly reduced, suggesting that miR-29a may regulate DKK1 and Factors such as GSK-3β participate in the formation of new bone in AS.This conjecture was confirmed in the research of LI et al.[9], LI et al.determined that DKK1 and GSK-3β are the direct targets of miR-29a through bioinformatics methods.DKK1 and GSK-3β are both negative regulators of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway,which inhibits its osteogenic effects by inhibiting the expression of this pathway.Among them, DKK1 inhibits Wnt by preventing the binding of Wnt protein to LRP5/6.Signal transduction, and GSK-3β destabilizes β-catenin by phosphorylating β-catenin at Thr-41, Ser-37, and Ser-33.The research results of LI et al.showed that miR-29a can target the expression of DKK1 and GSK-3β to increase TCF/LEF transcription activity and promote new bone formation in AS.QIN et al.[10] found that in AS-derived fibroblasts,the expression of miR-17-5p was significantly increased.While inhibiting the expression of DKK1, it also promoted the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).VEGF is a signal protein that plays a key role in angiogenesis, mainly involved in endochondral ossification, suggesting that miR-17-5p can promote osteogenic differentiation.Subsequent in vitro and in vivo experiments suggested that the tonic protein homolog (ANKH) is the functional target of miR-17-5p, and miR-17-5p regulates the ossification process of AS fibroblasts by targeting the 3'UTR of ANKH.Therefore, miR-17-5p can participate in AS progression by regulating ANKH, DKK1, and VEGF.Disheveled protein Dsh homolog (DVL) is a key positive regulator in the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.It mainly inhibits the function of APC-Axin-GSK-3β to reduce the phosphorylation of β-catenin and promote β in the cytoplasm.-catenin transfers to the nucleus and combines with TCL/LEF to form a transcriptional agonist.Studies have shown that overexpression of miR-96 up-regulates the expression of Wnt1,β-catenin and GSK-3β, and by inducing the phosphorylation of β-catenin and GSK-3β, the Wnt signaling pathway is activated,and miR-96 can also be targeted to regulate Wnt signal inhibitor SOST, thereby promoting the osteogenic factor alkaline phosphatase(ALP) activity of AS and the formation of calcium nodules[11].DU et al.[12] found that the expression of miR-495 in human fibroblastlike synovial cells (HFLS) cells extracted from AS patients' tissues was lower than that of healthy controls, and was determined by biosynthetic methods and luciferase activity It was confirmed that DVL-2 is the target gene of miR-495.By inhibiting DVL-2, miR-495 increased the expression of wnt3a, runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) and β-catenin, and promoted the osteogenic differentiation of HFLS cells.Therefore, miR-29a, miR-17-5p, miR-96, and miR-495 can all promote new bone formation in AS by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
1.1.2 miRNA regulates BMP/TGF-β osteogenic pathway
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2) is a member of the transforming growth factor β superfamily (TGF-β), which acts on the Smad protein by binding to the BMP receptor, causing the Smad 1/5/8 terminal serine residue to be phosphorylated It enters the nucleus, acts on the gene sequence of osteoblast-specific transcription factors RUNX2, Osterix and up-regulates its expression to play a role in osteogenic regulation[13].According to reports,miR-204, miR-204-5p, and miR-214-3p can participate in the osteogenic differentiation process of AS by regulating the BMP/TGF-β signaling pathway.Feng Zhongkai et al.[14] experimentally found that the expression of miR-204 was reduced in AS-derived fibroblasts, and predicted that the target gene of miR-204 was RUNX2 through bioinformatics analysis.After analysis, RUNX2 was highly expressed in AS-derived fibroblasts and BMP-2 and TGF-β1 treated fibroblasts, but after miR-204 transfection, its expression was significantly reduced.It is proved that miR-204 can effectively inhibit the ossification of fibroblasts by inhibiting RUNX2.ZHAO et al.[15] found that the expression of miR-204-5p was significantly reduced in AS tissues, while the expression of Notch2 was upregulated.TargetScan predicts that Notch2 is the target gene of miR-204-5p, miR-204-5p inhibits the expression of RUNX2 and BMP-2 in AS ligament fibroblasts by targeting Notch2,and inhibits the bone formation of AS.The latest research shows that miR-214-3p is down-regulated in AS fibroblasts and can inhibit the osteogenic differentiation of AS fibroblasts by targeting BMP-2 and blocking the BMP-TGFβ axis[16].It can be seen that miR-204,miR-204-5p, and miR-214-3p inhibit the osteogenic differentiation of AS ligament fibroblasts by blocking the BMP/TGF-β signaling pathway.
1.1.3 miRNA regulates JAK/STAT osteogenic pathway
In addition to the Wnt/β-catenin and BMP/TGF-β signaling pathways, the JAK/STAT signaling pathway is also an important pathway that regulates bone metabolism.Studies have shown that miR-21 regulates Janus kinase 2 (JAK2)/signal transduction and Activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is involved in the osteogenic differentiation process of AS[17].The study showed that the expression and osteogenic activity of miR-21 were negatively correlated with the concentration of TNF-α, and the osteogenic activity was the strongest at a concentration of 0.1 ng/mL, proving that the inflammatory environment is related to abnormal bone formation.At the same time, it was observed that the expression of JAK2 and STAT3 was increased in fibroblasts transfected with miR-21 mimics.In vitro injection of miR-21 in mice would cause new bone formation and fusion of sacroiliac joints, suggesting miR-21 Promote bone formation through the JAK2/STAT3 pathway.
1.1.4 miRNA regulates osteoclast production
Bone remodeling in the body also depends on the balance between osteoblasts and osteoclasts.When the dysfunction or abnormality of these two cells can cause bone homeostasis disorders, osteoclast dysfunction is also an important factor in AS bone metabolism disorders.one.In the experiment of LIU et al.[18], the mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) of AS patients showed a stronger ability to inhibit osteoclastogenesis than healthy donors.This phenomenon is consistent with CXC chemokine 5 The secretion of (CXCL5) is positively correlated.Bioinformatics analysis shows that CXCL5 is the target gene of miR-4284.When cells are transfected with miR-4284 inhibitor, CXCL5 secretion increases and significantly inhibits osteoclast production, confirming miR- 4284 by targeting CXCL5 makes the MSC of AS patients show stronger ability to inhibit osteoclastogenesis.Programmed cell death factor (PDCD)is an important factor that promotes apoptosis.HUANG et al.[19]found that the level of miR-21 in patients with AS was significantly increased, and its expression level was positively correlated with the duration of AS disease, activity, and bone density reduction,which may be related to miR-21 targeted inhibition PDCD4 in turn inhibits osteoclast apoptosis and promotes osteoclast differentiation,suggesting that miR-21 can serve as a relevant marker in AS pathological osteoclastogenesis.
Therefore, miRNA can participate in the bone metabolism regulation of AS by mediating Wnt/β-catenin, BMP/TGF-β, JAK/STAT and other signal pathways, as well as related osteogenic and osteoclast factors.Using these miRNAs as targets, the development of promotion/blocking agents for the conduction of miRNAs and related signal pathways or genes to inhibit the abnormal ossification of AS can greatly reduce the probability of bone fusion between joints in the later stage of AS, thereby improving patients Quality of life.
1.2 miRNA is involved in AS immune inflammatory response
AS is a complex chronic inflammatory disease.Studies have shown that miRNA is involved in the inflammatory response process of AS[20].Helper T cell 17 (Th17), as a subgroup of CD4[+] T cells,is characterized by the production of pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-17 (IL-17), which is involved in the pathogenesis of AS.CHEN et al.[21] studies have shown that miR-10b-5p increases expression in Th17 cells of AS patients, and overexpression of miR-10b-5p can reduce Th17 differentiation and IL-17A production in AS CD4+ T cells This is related to miR-10b-5p binding to the 3'UTR end to inhibit MAP3K7 in Th17 cells, and silenced MAP3K7 inhibits the production of IL-17A.
IL-23 is a heterodimeric cytokine secreted by monocytes,macrophages and dendritic cells.It mainly participates in the body’s immune response by promoting the differentiation of Th17 cells.LAI et al.[22] found that the expression levels of 12 miRNAs increased significantly in K562 cells cultured with IL-23, and the levels of 4 miRNAs decreased.Among these miRNAs regulated by IL-23, the expression of miR-29b-1-5p, miR-4449, miR-211-3p, miR-1914-3p and miR-7114-5p in T cells of AS patients was significantly increased.Among them, the transfection of miR-29b-1-5p can inhibit IL-23-mediated phosphorylation of STAT3 in K562 cells, and STAT3 is a key downstream transcription factor in the IL-23 signaling pathway required for Th17 cell differentiation.After NGS analysis and verification, it was found that miR-29b-1-5p can also up-regulate the expression of angiopoietin (ANG) and interferon-γ (IFN-γ).Therefore, miR-29b-1-5p inhibits IL-23-mediated phosphorylation of STAT3 and plays a negative feedback control role in the inflammatory response of AS.He Xiaoliang et al.[23] found that the expression of miR-146a increased in the peripheral blood of AS patients and was positively correlated with inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and disease activity, suggesting miR-146a It may be involved in AS disease activity by regulating inflammatory cytokines.This mechanism may be achieved by miR-146a inhibiting the expression of TRAF6 gene,but the specific mechanism needs to be further verified.
Because the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the miRNA sequence may change the expression of miRNA, and is related to the pathogenesis of AS.XU et al.[24] studied the relationship between miR-146a rs2910164G> C and miR-499 rs3746444T> C in the Han population and AS, in order to find candidate markers that can be used to identify early AS.The results show that miR-146a rs2910164G> C is associated with AS.However, after NIU et al.[25] expanded the sample size of the study, they got the opposite result, believing that this difference may be caused by the sampling of different cohorts, suggesting that miR-146a rs2910164G> C is used as a diagnostic marker for AS The research on objects still needs to be in-depth.It can be seen that overexpressed miR-29b-1-5p and miR-146a can promote the inflammatory response of AS by regulating inflammatory factors, and are expected to serve as potential targets for AS treatment.
1.3 miRNA is involved in the autophagy process of AS cells
Autophagy is the link between cell survival and death.It plays a cytoprotective role under most cell stresses (such as nutritional deficiencies), but can cause cell death under severe or prolonged stress.In addition, autophagy can also serve as an innate defense against infection or inflammation.In the middle and late stages of AS, the autophagy of macrophages can reduce the inflammatory response.let-7i is the first miRNA found to participate in the progression of AS by regulating autophagy[26].The researchers found that miRNA let-7i is overexpressed in Jurkat cells and can significantly inhibit the expression of its target insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R).IGF1R factor protects T cells from apoptosis through the transduction of phosphoinositide 3-kinase(PI3K)/Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)pathways.The study showed that inhibition of IGF1R-mediated signal transduction can reduce mTOR/Akt phosphorylation and Bcl-2 expression levels, and reduce the negative regulation of Bax/caspase-3/PARP, thereby subsequently inducing autophagy, while overexpression let-7i protects T cells from apoptosis by inhibiting IGF1R to induce autophagy.Wang et al.[27] observed a significant decrease in the expression of miRNA-199a-5p and autophagy-related genes (LC3, beclin1 and ATG5) in T cells of patients with AS, and the overexpression of miRNA-199a-5p could be suppressed Target gene Rheb and its downstream signal mTOR conduct abnormally,thereby promoting T cell autophagy.Wang Yahan et al.[28] found that miR-148a-3p was overexpressed in AS patients, while the expression level of its target gene DNMT1 was low.Overexpressed miR-148a-3p can promote the secretion of inflammatory factors(L-6, IL-17 and IL-23), and can significantly inhibit the expression of autophagy-related proteins (Beclin-1 and ATG5) and downregulate LC3 II The ratio of /LC3 I indicates that miR-148a-3p may participate in the regulation of T cell autophagy and inflammatory processes in AS by regulating the expression of DNMT1.Anthrax toxin receptor 2 (ANTXR2), as a membrane protein, participates in mediating extracellular matrix homeostasis through endocytosis and related signal transduction.XIA et al.[29] confirmed that the expression of ANTXR2 in the peripheral blood of AS patients was down-regulated, while miR-124 was up-regulated, and confirmed that ANTXR2 was the target gene of miR-124 by the luciferase reporter assay.In subsequent verification experiments, overexpressed miR-124 significantly inhibited the expression of ANTXR2 in Jurkat cells, and promoted the activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)and induced autophagy.
1.4 miRNA is involved in the process of programmed death of AS cells
Programmed cell death is a process that occurs in normal tissues throughout the life process (such as the physiological process of metabolism, the trauma process of the body).According to different ways of death, cell death is divided into programmed death and nonprogrammed death.Programmed death also includes apoptosis and pyrolysis.Among them, apoptosis is a process in which cells actively end their lives through exogenous, endogenous and endoplasmic reticulum stress induction pathways to eliminate damaged and senescent cells to maintain the stability of the internal environment,LI, etc.[30] It was observed that the expression of miR-130a-3p decreased in the T cells of AS patients, while the expression of its target gene HOXB1 increased.miR-130a-3p mimics can promote the proliferation of Jurkat T cells and inhibit cell apoptosis, but these effects can be reversed by HOXB1, so miR-130a-3p regulates the survival of T cells by targeting HOXB1.Pyrolysis relies on inflammatory caspase-1 (caspase-1) to form pores in the plasma membrane, leading to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and cell lysis.The study found that fibroblast-like synovial cells(FLS) treated with miR-204 mimics inhibited the pyrolysis rate and Caspase-1/PI cell differentiation, and reduced [Ca2+] and reactive oxygen species in FLS (ROS), pyrolysis-related genes (Caspase-1,Caspase-11 and NLRP3) levels, while up-regulating the target gene GSDMD of miR-204 can prevent the overexpression of miR-204 from affecting FLS.GSDMD happens to be a key factor in the caspase-1 pathway that triggers cell pyrolysis, so the up-regulated miR-204 inhibits the pyrolysis of FLS in AS by inhibiting GSDMD[31].
It can be seen that miRNAs mainly participate in the pathogenesis of AS by regulating bone metabolism, immune-inflammatory response, autophagy and programmed cell death pathways.
2.lncRNA, circRNA and ankylosing spondylitis
lncRNA and circRNA, as a member of the competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network, regulate target genes by competitively binding or sharing miRNA with miRNA response elements (miRNA response elements, MREs), thereby eliminating or reducing miRNA The effect on target genes (also known as “sponge effect”), which in turn affects the development of organisms and related diseases[32].
lncRNA is a type of RNA transcript with a length of more than 200 nucleotides, which contains one or more miRNA binding sites, regulates the expression of target mRNA through the ceRNA mechanism, and is mainly involved in epigenetics, gene transcription and post-transcriptional genes Expression regulation is also involved in the occurrence and development of AS[33].lncRNA MEG3 is an lncRNA that was found to be involved in the AS disease process earlier.LI et al.[34] found that MEG3 was down-regulated in AS patients, and the down-regulated MEG3 was negatively correlated with the levels of inflammatory factors IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α,but this inhibitory effect could be over-regulated by miR-146a.The expression was reversed, and qRT-PCR confirmed the targeting effect of miR-146a and MEG3.Therefore, MEG3 suppressed thelevel of inflammatory cytokines by sponging miR-146a.However,some scholars have pointed out that the expression level of MEG3 is negatively correlated with the course of the disease, and positively correlated with the level of autophagy-related gene Beclin 1 and IL-23.It is speculated that MEG3 may be involved in the pathogenesis and progression of AS by inhibiting the autophagy level of AS patients.However, its mechanism of action is currently unknown[35].lncRNA H19 is also related to the pathogenesis of inflammatory diseases.XU et al.[36] found that H19 is overexpressed in AS patients.Transfection of cells with H19 small interfering RNA (Si-H19-1484)can inhibit the expression of H19.And significantly down-regulate the expression of miR22-5p and increase the expression of miR675-5p, reducing the expression of vitamin D receptor (VDR) and IL-17A and IL-23 cytokines, thereby inhibiting the inflammatory response of AS.It is suggested that H19 can bind miR22-5p and miR675-5p multiple targets, and pass the H19-miR22-5p-VDR-IL-17A/IL-23 axis and H19-miR675-5p-VDR-IL-17A/IL-23 axis Promote the progress of AS inflammatory response.The NF-kB signaling pathway can regulate the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and play a key role in the inflammatory response.LOC645166 is an lncRNA that has recently been confirmed to participate in the AS inflammatory response through the NF-kB signaling pathway[37].The expression of LOC645166 in AS patients' T cells is reduced.It inhibits Toll-like receptor (TLR)-mediated autophosphorylation and activates IKK2 by binding to the polyubiquitin chain linked to K63, which in turn leads to the down-regulation of IkB by activated IKK2 Phosphorylation.The stable IkB binds to NF-kB, so that the NF-kB/IkB complex is retained in the cytoplasm.Therefore,LOC645166 activates the NF-kB pathway by binding to the K63-linked polyubiquitin chain to promote the inflammatory response of AS.In addition, LncRNA is also involved in the heterotopic ossification process of AS.XIE et al.[38] microarrays were used to identify lncRNAs differentially expressed in MSCs of osteogenic differentiation.The correlation analysis between CNC network and gene expression showed that lnc-ZNF354A-1, lnc-LIN54-1,lnc -FRG2C-3 and lnc-USP50-2 may participate in the abnormal osteogenic differentiation process of ASMSC through BMP2, which provides a basis for further exploring the regulation of lncRNA in AS patients with heterotopic ossification.Wang Chen et al.[39]screened out the lnc-NR_045553/miR-17-5p/FGD5 regulatory axis from thousands of differentially expressed lncRNA, miRNA and mRNA in the hip peri-articular ligaments of AS patients through a microarray chip, In the bone marrow MSCs of AS patients, it was found that lnc-NR_045553 competitively binds to miR-17-5p with FGD5 in the form of ceRNA, alleviating the negative regulation of miRNA on target genes, promoting the expression of FGD5,and activating Wnt/B-catenin signaling.Pathway, which positively regulates the process of osteogenic differentiation.It can be seen that lncRNA mainly participates in the inflammatory response and osteogenic differentiation process of AS by regulating the expression of Mrna by “sponging” miRNA.Therefore, compared with miRNA,the multi-target effects of lncRNA may benefit more in future clinical transformation and practical applications.

Tab 1 The regulatory role of miRNA in ankylosing spondylitis
CircRNA is a new type of endogenous non-coding RNA with a covalent closed loop structure.This closed loop structure makes them very stable, and because of its tissue specificity, it is highly conserved in many tissues and is a good treatment Targets and biomarkers.Gao Lihong et al.[40] found that circPDESA, circCCNY and circRASA1 were significantly up-regulated in AS patients'memory CD4+ T cells.Subsequent experiments proved that circCCNY and circRASA1 can act as sponges for miR-181c-5p.Regulating the expression of PKC-δ, interfering with the expression of circCCNY, circRASA1, or overexpressing miR-181c-5p mimics can all reduce the expression of PKC-δ, and the expression of autophagy-related genes ATG5, ATG7 and LC3B-II has been observed to decrease significantly, suggesting that Decrease in the level of autophagy.Therefore, circCCNY and circRASA1 regulate PKC-δ through sponge adsorption of miR-181c-5p to promote the level of autophagy.LI et al.[41] found that the expression levels of hsa_circ_0056558 and CDK6 in AS tissues were significantly higher than normal samples, and could positively regulate the levels of related proteins in the PI3K/AKT/NF-kB signaling pathway.This feedback can It is inhibited by miR-1290, therefore, hsa_circ_0056558 can inhibit cell proliferation and differentiation by targeting miR-1290 to promote the expression of CDK6 expression in AS.cicrRNA has stable function and strong specificity, and it plays an important role in multiple biological regulation.It is expected to become an early diagnostic marker and therapeutic target of AS.However, there are few reports on circRNA and AS in the literature, and research needs to be in-depth.
3.Summary
Due to the complexity of the etiology, pathogenesis and treatment targets of AS, the current intervention measures have not reacheda consensus.Therefore, clinical treatment is mainly to relieve symptoms and control the progress of the disease, which makes it difficult to treat, high disability rate, and serious impact The patient’s quality of life.With the development of high-throughput sequencing technology, more and more ncRNAs have been found to be closely related to the bone metabolism, inflammation, and cell survival process of AS, indicating that ncRNAs are involved in the physiological and pathological changes of AS, indicating that it has extensive research prospect.Therefore, finding ncRNAs that can be used as early diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets for AS,clarifying its mechanism of action, and formulating more effective intervention methods may become the direction of future research.In addition, there have been too few studies on circRNA and other ncRNAs (such as small interfering RNA, PiWi protein-interacting RNA, etc.) with stable functions and strong specificity.It is believed that as the research deepens, more relevant regulatory mechanisms will be revealed.
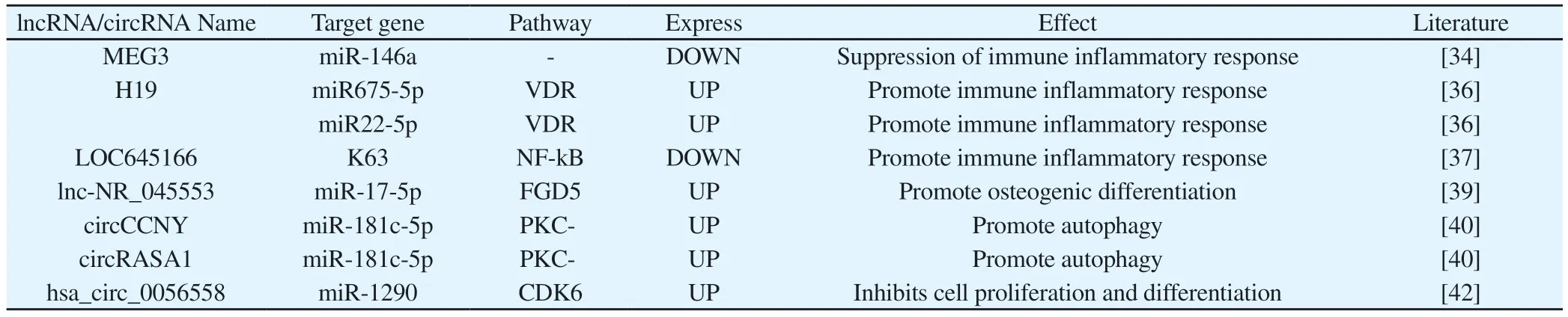
Tab 2 The regulatory role of lncRNA/cicrRNA in ankylosing spondylitis
Authors' contribution
Huang Yangjun: article thinking and writing;
Zhou Honghai: Check the quality, authenticity and feasibility of the article;
Chen Longhao: Provide guidance and analysis summary;
Li Jilin: search literature;
Lu Qingwang: sorting out the literature;
Li Dongyang: Organize the literature.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Anesthetic effect of phenobarbital sodium on female BALB/c mice
- Research progress of TCM regulation of Cajal interstitial cells in the treatment of functional Gastrointestinal diseases
- Abnormal expression and significance of circ-CBLB/miR-486-5p in patients with rheumatoid arthritis of spleen deficiency and dampness excess type
- Inhibitory effect of thymoquinone on neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease model by regulating NLRP3 inflammatory bodies
- Effect of Astragalus-hawthorn on ovarian reproductive function and inflammatory mechanism of action in rats with polycystic ovary syndrome
- Effect of estrogen pretreatment in GnRH antagonist protocol-Metaanalysis
