Structural characteristics and influencing factors of spatial correlation network for regional high-quality development in China
2023-12-19LIUJianjunLIUHe
LIU Jian-jun,LIU He
School of Geography Sciences,Liaoning Normal University,Dalian 116029,CHINA
Abstract: On the basis of measuring the regional high-quality development in China from 2011 to 2020,this study uses gravity model to build spatial correlation network,and uses social network analysis method to analyze the structural characteristics and influencing factors of correlation network.The results are shown as follows.First,from 2011 to 2020,the level of regional high-quality development in China is rising gradually,and the discrete characteristics between regions are gradually obvious,showing a step-like distribution structure decreasing from east to west.Second,the network density of regional high-quality development is generally low and tends to decline,but it has strong stability and correlation strength.Third,the spatial correlation network has an obvious core-edge structure.Shanghai is always at the center of the network and plays a significant intermediary role,while Qinghai and Xinjiang are always at the edge of the network.Fourth,the regional high-quality development association network can be divided into four major sectors: main benefit,net benefit,net spillover,and broker,showing the spatial correlation characteristics of inter-plate contact and intra-plate agglomeration.Fifth,the level of economic development,the level of urbanization and geographical proximity have a significant impact on the formation of regional high-quality development correlation network.
Key words: high quality development;spatial association network;influencing factors;social network analysis
1 Introduction
The report of the 19th National Congress of the Communist Party of China clearly pointed out that“China’s economy has shifted from the stage of high-speed growth to the stage of high-quality development”.At present,the country attaches great importance to the realization of high-quality regional development.However,due to the vast territory of China,the different development bases among different regions lead to the obvious difference in the level of high-quality regional development in China (Zhao and Hao,2022).In addition,with the gradual strengthening of the trend of regional integration,the flow of information,economy and other elements between regions becomes more and more frequent,which makes the connection between regions become closer and closer.“Flow space”begins to replace“field space”,and the spatial correlation features of high-quality inter-regional development become more and more complex(Liu and Jia,2019).Since high-quality regional development has obvious spatial spillover effect (Xiao et al.,2020),it is inevitable that exploring the path to improve high-quality development level from an isolated perspective will continue to widen the regional development gap to a certain extent,thus leading to a serious imbalance in China’s high-quality development level.Therefore,deconstructing the structural characteristics and influencing factors of the spatial correlation network of high-quality provincial development in China from the perspective of network has important practical significance for improving the quality of life of residents and promoting the realization of high-quality development in China.
At present,the research on high quality development has gradually expanded from theoretical analysis,quantitative measurement and influencing factors to spatial flow and interaction.Firstly,it is generally believed in theoretical research that high-quality development is the pursuit of more efficient,greener and fairer development,whose ultimate goal is to meet people's growing demand for a better life (Zhang et al.,2022).Including innovation,coordination,green,openness and sharing (Qu et al.,2022);Secondly,most quantitative researches build evaluation index system based on new development concepts,and adopt entropy method,principal component analysis and other methods to conduct comprehensive evaluation of high-quality development level under national,urban agglomeration,provincial and municipal scales (Wei and Li,2018;Chen and Huo,2022;He et al.,2022;Lin and Xu,2022),found that the level of high-quality development on the whole presents an upward trend,but the regional differences are gradually obvious (Sun et al.,2022);Finally,in the study of spatial interaction,kernel density estimation,exploratory spatial data analysis,convergence model and other methods are used to analyze the spatial distribution characteristics,correlation characteristics and convergence characteristics of high quality development level (Liu and Shang,2021;Zhou et al.,2022;Chen and Qing,2022) found that the spatial agglomeration characteristics of high-quality development are obvious (Zhang and Wang 2022).As regional connections become closer and closer,some scholars begin to explore the complexity characteristics of spatial correlation network structure of high quality development level,and find that its network density is low and still at a low level(Ma Jing et al.,2021).However,the research on the influencing factors of the spatial correlation network of high-quality development is mainly based on a single year,and neglects to explore the dynamic change characteristics of the factors that affect the formation of the spatial correlation network of high-quality development (Wang et al.,2022).There are differences in the strength and significance of the influencing factors at different development stages.Exploring the dynamic change of influencing factors is more beneficial to provide targeted suggestions for regional planning.
In summary,the entropy method is used to measure the high-quality development level of 31 provinces in China during 2011-2020,and the modified gravity model is used to build the high-quality spatial correlation network.On this basis,social network analysis is used to explore the structural characteristics and influencing factors of the correlation network,so as to provide a basis for shortening the regional development gap.And then realize the high quality development of the region.
2 Data sources and methods
2.1 Measurement of regional high-quality development
2.1.1 Construction of index system of regional high-quality development
Most of the existing studies build a high-quality development evaluation index system from five aspects: innovation,coordination,green,openness and sharing (Sun et al.,2020;Chen et al.,2022;Wang et al.,2022;Yang et al.,2022),referring to existing studies(Shi and Wang,2022;Xiao and Li,2022) believe that the innovation dimension includes three aspects: innovation input,innovation output and innovation potential;the coordination dimension consists of urban-rural coordination,industrial coordination and economic coordination;the green dimension includes energy consumption,environmental pollution,green environmental protection and environmental governance;and the open dimension is mainly the degree of regional openness.The sharing dimension consists of area sharing,service sharing and facility sharing.On this basis,China’s regional high quality development index system contains 37 indicators.The specific indicators are shown in Table 1.
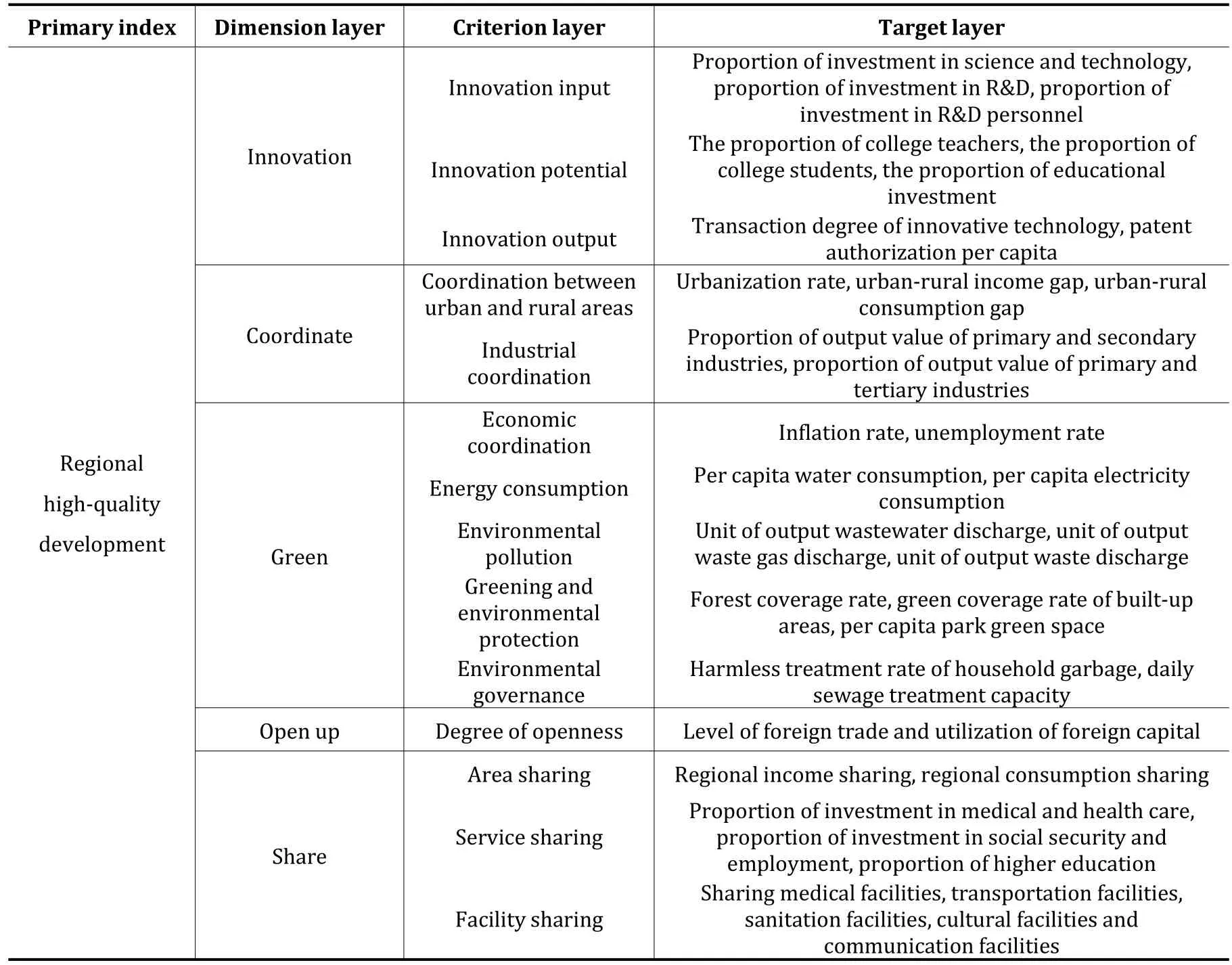
Table 1 China’s regional high-quality development level evaluation index system
2.1.2 Measurement of regional high-quality development
Entropy method can effectively avoid the randomness of subjective weighting,so this study adopts entropy method for objective weighting.First,the range standardization was used to standardize the original indicators,then the entropy method was used to obtain the weight of each indicator,and finally,the linear weighted summation was used to calculate the regional high quality development level.The relevant calculation process was referred to the literature (Chen and Li,2022).
2.2 Spatial association network construction and analysis
2.2.1 Building spatial association networks
In this paper,by referring to relevant studies(Wang et al.,2022),the revised gravity model is adopted to construct the spatial correlation network of high-quality regional development in China.The calculation process is as follows:
WhereFijis the correlation strength between regioniand regionj,Kijis the gravitational coefficient,GiandGjare the actual GDP of regioniand regionjrespectively,PiandPjare the number of permanent residents of regioniand regionjrespectively,HQDiandHQDjare the high-quality development index of regioniand regionjrespectively,andDijis the distance between regioniand regionj.On this basis,with reference to the research of Wang and Liu (2021),binarization of the network matrix is carried out.
2.2.2 Social network analysis
Social network analysis can deeply analyze complex network relationships and explore spatial correlation effect.It has been widely used in studies on spatial correlation networks such as tourism efficiency(Cheng et al.,2020),human settlements(Shao and Wang,2022),tourism carbon emissions(Wang et al.,2020),and high-quality development(Liu and Ma,2020).
Four indexes,network density,network correlation,network rank and network efficiency,were used to explore the overall characteristics of regional high-quality development correlation network.The individual characteristics of spatial association networks were analyzed using degree centrality,proximity centrality and intermediate centrality (Table 2).In addition,the clustering characteristics of spatial correlation network are analyzed by using block model,and the plates are divided into “net benefit” plate,“net overflow” plate,“main benefit” plate and “broker” plate by referring to relevant studies(Liu and Ma,2020).On this basis,QAP regression analysis was used to explore the influencing factors of spatial association network.The relevant calculation process was referred to the literature(Jia et al.,2021;Zhao et al.,2021).

Table 2 Calculation and description of the characteristic index of the spatial correlation network
2.3 Data sources
The study area of this paper mainly includes 31 provinces in China(excluding Hong Kong SAR,Macao SAR and Taiwan Province),and the data mainly comes fromChinaStatisticalYearbook,China StatisticalYearbookofScienceandTechnology,provincial statistical yearbook and statistical bulletin from 2012 to 2021.Partial missing data are supplemented by interpolation method.
3 Result analysis
3.1 Analysis of high-quality regional development in China
As can be seen from Figure 1,China's regional high-quality development level shows a steady rising trend during 2011-2020.From the average point of view,China’s regional high-quality development level is 0.3556,increasing from 0.3055 in 2011 to 0.4115 in 2020.The standard deviation showed an upward trend on the whole,from 0.0880 in 2011 to 0.1035 in 2020,indicating that the discrete feature of regional high-quality development level in China was gradually obvious during 2011-2020.In addition,from the perspective of regional development level,the eastern region has the highest level of high-quality development,followed by the northeast region,the central region and the western region,which presents a step-like structure decreasing from east to west in space.

Figure 1 Evolutionary trend of regional high-quality development level from 2011 to 2020
3.2 Structural characteristics of spatial correlation network for high-quality regional development
3.2.1 Overall feature
Gephi is used to carry out visualization analysis on the spatial association network of regional high-quality development.Due to space limitation,two sections in 2011 and 2020 are selected for analysis.The results are shown in Figure 2,where the depth of the color of nodes and connections represents the importance and connection strength of each region in the spatial association network.As can be seen from Figure 2,Tianjin,Beijing,Shanghai and Jiangsu occupy important node positions in 2011-2020,further demonstrating that the eastern coastal region is the core of China’s high-quality development.In addition,the network structure of high quality development in China has obvious differences.
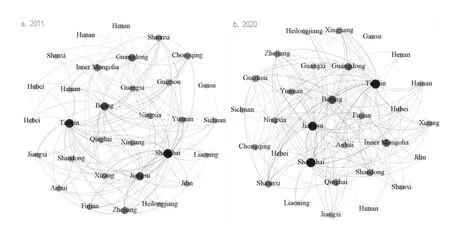
Figure 2 Topology of spatial correlation network for high-quality regional development in 2011 and 2020
As can be seen from Table 3,the network density of regional high-quality development is generally low and shows a downward trend,indicating that there is a relatively obvious unbalanced development trend of high-quality development in provinces,and the connection strength between regions still needs to be strengthened.During 2011-2020,the network correlation degree is all 1,indicating that there is no isolated region for high-quality development in China,and there are direct or indirect connections among all regions,with good connectivity.The level of network decreases from 0.8588 to 0.8384 on the whole,indicating that the level structure of spatial correlation network of regional high-quality development in China is developing towards equilibrium trend.From 2011 to 2020,the network efficiency was greater than 0.7494 and showed an increasing trend,indicating that the spatial correlation of high-quality regional development in China was gradually increasing,and the stability of network structure was gradually enhanced.
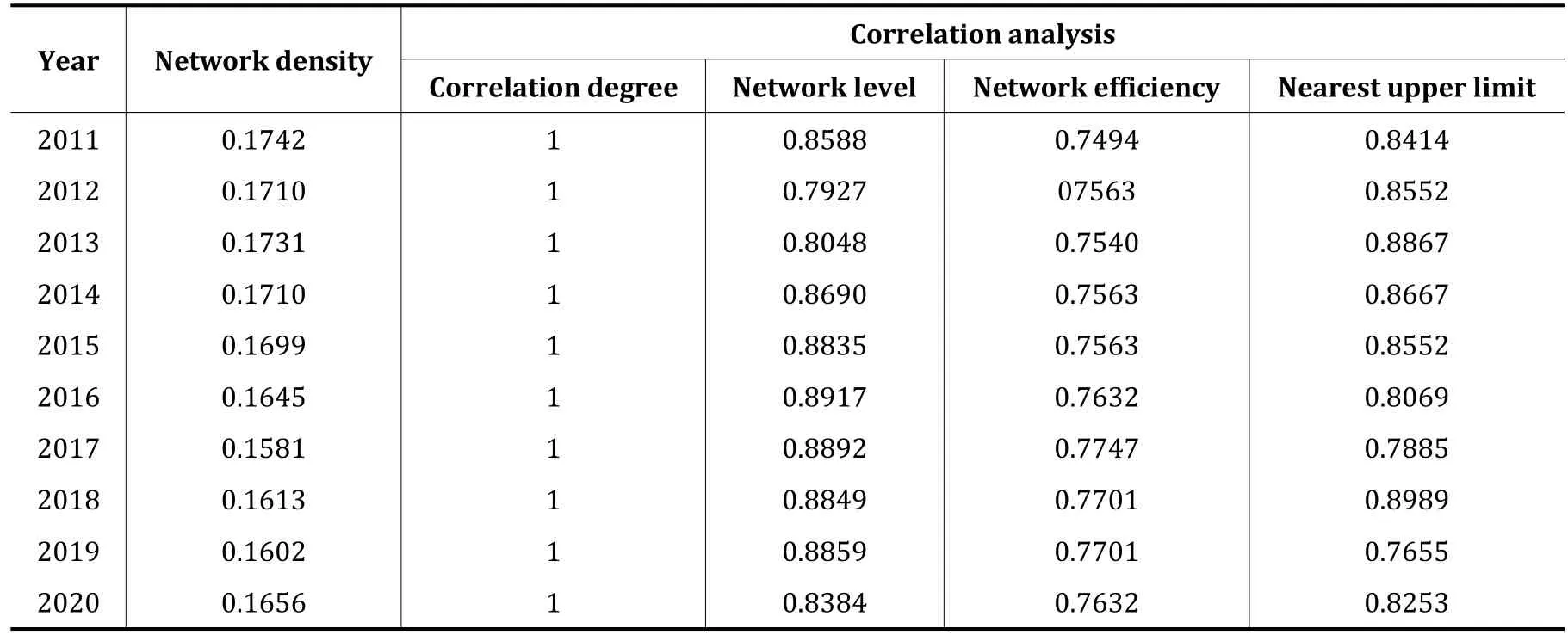
Table 3 Structural index of regional high-quality development
3.2.2 Individual network characteristics
Ucinet software was used to analyze the individual network characteristics of spatial association networks of high-quality regional development in China in 2011 and 2020,and the results were shown in Table 4.
(1)Degree centrality:Tianjin,Shanghai,Jiangsu and Beijing occupy the central position in the network,because these provinces are located in the eastern coastal areas of China,with certain policy advantages,superior geographical conditions and high level of regional development.Hunan,Gansu and Henan ranked relatively low in degree centrality,and were less connected with other regions,so they were in a marginal position in the association network.In summary,the mean degree centrality of correlation network showed a decreasing trend from 2011 to 2020,indicating that the connections between different regions were gradually sparse.
(2)Proximity centrality:The proximity degree of Tianjin,Anhui,Shandong and Beijing always ranks the top 5,indicating that these provinces have strong independence in the association network,can have direct contact with other regions,and play the role of central actor in the association network.The proximity degree of Heilongjiang,Hubei,Hebei and Henan is always in the bottom 5,indicating that the connection between these provinces and other regions is mainly indirect,and they are passive in the network.From 2011 to 2020,the mean degree of proximity to centrality of correlation networks showed an upward trend,indicating that the status of central actors was weakened and that of passive actors was improved.
(3) Intermediate centrality: the intermediate centrality of Inner Mongolia,Shanghai,Sichuan and Yunnan always ranks top 5,indicating that these provinces occupy a key position in the association network and play a regulating and controlling role in the connection between other regions.The intermediate centrality of Heilongjiang,Hubei,Qinghai and other regions is always 0,indicating that they are in a relatively obvious marginal position in the network.From 2011 to 2020,the mean mediating centrality of correlation networks showed an increasing trend,indicating that individual cities have enhanced the degree of control over regional connections,and the trend of network disequilibrium is obvious.
3.2.3 Analysis of board characteristics
Using UCINET software to set 2 as the maximum segmentation depth and 0.2 as the convergence criterion,the spatial correlation network of regional high-quality development in 2020 is divided into four plates,in which Beijing,Inner Mongolia,Gansu,Guangdong,Sichuan,and Chongqing together form plate one,Jiangsu,Tianjin,Shanghai,Zhejiang,Anhui,Fujian,and Shandong together form plate two,Hebei,Liaoning,Xinjiang,Hubei,Yunnan,Xizang,Heilongjiang,Jiangxi,Jilin,Qinghai,Guizhou,Hainan,Ningxia together to form plate three,Guangxi,Hunan,Shanxi,Shaanxi,Henan together to form plate four.
The spatial correlation network of regional high-quality development in 2020 includes 154 relationships,including 31 relationships within the plate and 123 relationships between the plates,which indicates that the correlation characteristics and spillover effects between the plates are more obvious.As can be seen from Table 4,the number of spillover relationships of plate 1 is significantly less than the number of receiving relationships,and the proportion of its expected internal relationships is larger,which is the “main benefit” plate.The actual internal relationship ratio is 4.46 times of the expected internal relationship ratio,which means that the spatial spillover effect of plate 2 is significant and belongs to the “net benefit” plate.The number of accepting relationships in panel 3 is 10,the number of spillover relationships is 89,and the expected internal relationship ratio is 17.78 times of the actual internal relationship ratio,therefore,panel 3 is a"net spillover"panel.The difference between the number of accepted relationships and the number of spillover relationships in panel 4 is not large,and the actual internal relationship ratio is smaller than the expected internal relationship ratio,so it belongs to the“broker”panel(Table 5).
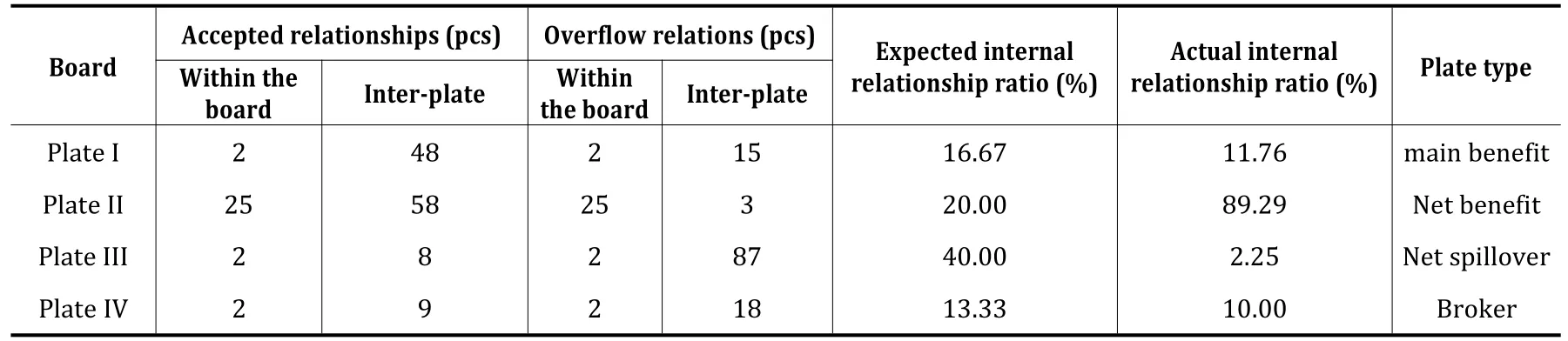
Table 5 Spatial correlation network plate spillover effects of regional high-quality development in 2020
To further analyze the association relationship between plates,the overall network density(0.1656)in 2020 is taken as the cut-off value,and if the plate density is greater than 0.1656,it is 1,which indicates that there is connection between plates,and if the plate density is less than 0.1656,it is 0,which indicates that there is no connection between plates,so the like matrix is obtained(Table 6).As can be seen from Table 6,Plate I gradually shifts from isolated development to the existence of spillover effect on Plate IV during 2011-2020,Plate II always focuses on internal linkage,Plate III shifts from the existence of spillover effect on Plate I to the existence of spillover effect on Plate I and Plate II,Plate IV always maintains the existence of spillover effect on Plate I,and the spillover effect on Plate II gradually disappears.On the whole,China's regional high-quality development presents the spatial correlation characteristics of inter-plate linkage as the main feature and intra-plate agglomeration as the supplement.
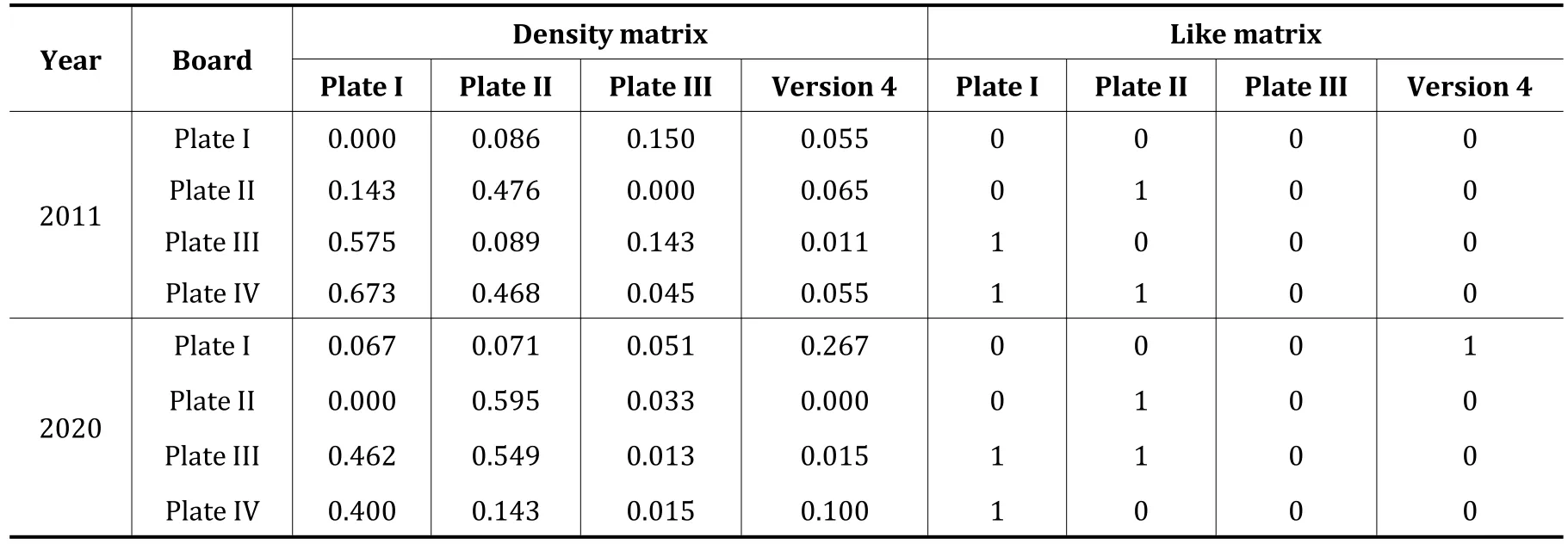
Table 6 Density and image matrices
The inter-plate linkage map is drawn to visually reflect the linkage between the plates,and the results are shown in Figure 3.Plate I mainly receives overflow from plate III,which has richer energy resources and provides impetus for the high-quality correlation network;plate II not only has more internal connections,but also receives overflow from the other three plates,indicating that the eastern coastal regions such as Jiangsu and Zhejiang have strong adsorption capacity;plate III sends out relationships mainly in plate I and plate II,where the distance between plate I and plate III is is closer,and the regional high quality development level of plate two is higher.However,plate three receives fewer relationships,which means that plate three's network transmits more resources to other regions,but it introduces fewer resources;plate four,as a “broker” plate,assumes a more important“bridge”role in the network.
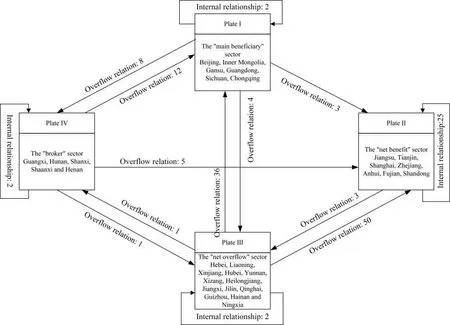
Figure 3 The correlation between regional high-quality development segments
3.3 Analysis of factors influencing the spatial correlation network of regional high-quality development in China
3.3.1 Selection of indicators
Referring to existing studies and the characteristics of spatially linked networks for high-quality development (Zeng et al.,2022;Li et al.,2022).In this study,economic development level,urbanization level,industrial structure,geographic proximity,transportation conditions,human capital and environmental quality were selected as influencing factors to investigate the formation mechanism of the spatial correlation network of high quality development in Chinese regions.Among them,GDP per capita,proportion of urban population,proportion of tertiary industry,spatial proximity,road network density,proportion of scientific and technological employees,and per capita industrial wastewater,SO2,and smoke and dust emissions are selected to characterize the influencing factors.On this basis,a difference matrix was constructed using the corresponding indicators,and QAP correlation and regression analyses were conducted using UCINET software.
3.3.2 Correlation analysis
QAP correlation analysis was conducted using UCINET software,and 2000 times was selected as the number of random permutations,the results of which are shown in Table 7.

Table 7 QAP correlation analysis
Among them,economic development level,urbanization level,industrial structure,geographical proximity and transportation conditions pass the significance test in 2011 and 2020,indicating that the above five factors have a significant influence on the formation of regional high-quality development association network.Human capital passes the 1% significance test in 2020,which indicates that the importance of human capital factors is gradually highlighted.In addition,environmental quality does not pass the significance test in both 2011 and 2020,indicating that environmental quality does not affect the formation of regional high-quality development network.
3.3.3 Regression analysis
QAP regression analysis was conducted using UCINET software,and 5000 times was selected as the number of random permutations,the results of which are shown in Table 8.The verdict coefficients are 0.143 and 0.108,which both pass the 1%significance level test,and the model fits well,indicating that the selected factors can in some way explain the formation of regional high-quality development association network.
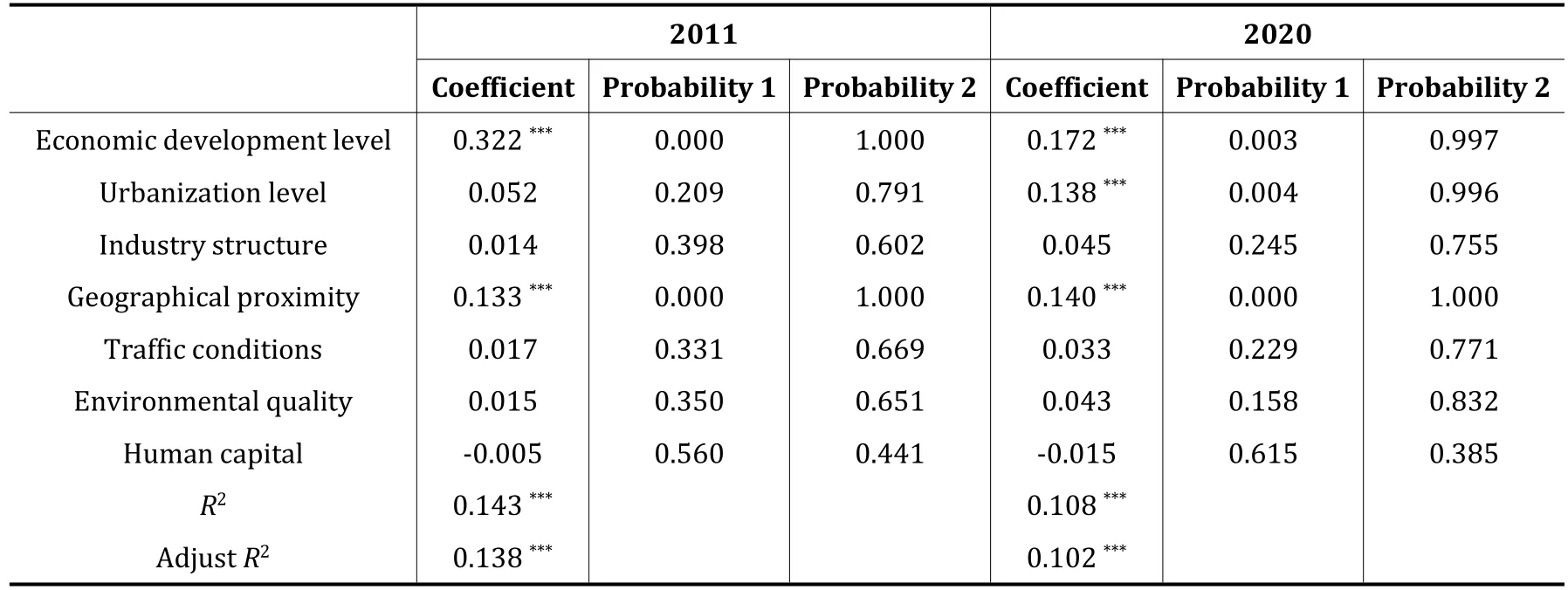
Table 8 QAP regression analysis
The level of economic development has a significant positive influence on the network of regional high-quality development linkages and the degree of its influence gradually decreases,but its regression coefficient is the largest in 2011 and 2020,indicating that the level of economic development is the main factor in the formation of the network of regional high-quality development linkages,and the higher the level of regional economic development,the more it can attract the flow of factors,which leads to the linkage of cities.The positive influence of urbanization level and geographical proximity on the network of regional high-quality development linkage gradually increases,indicating that population concentration and regional proximity are important factors leading to the linkage of cities,and the greater the difference in population size and geographical proximity between regions,the easier it is to create linkage between regions.The regression coefficients of industrial structure,transportation conditions and environmental quality are positive,and the regression coefficient of human capital is negative,but they do not pass the significance test on the formation of regional high-quality development network,indicating that the above factors do not have significant effects on the formation of regional high-quality development network.
4 Conclusions and recommendations
On the basis of measuring the level of regional high-quality development,the study uses a modified gravity model to construct a spatial correlation network of high-quality development,based on which the structural characteristics of the spatial correlation network are explored using social network analysis and the influencing factors of the spatial correlation network are explored using QAP regression analysis.Conclusions are found as follows.First,the level of regional high-quality development in China from 2011 to 2020 shows a linear increase,with an average annual growth rate of 3.16%,and the spatial divergence is obvious,showing a decreasing distribution pattern from east to west.Second,the spatial network density of regional high-quality development is low,with the average value of 0.1669,which is still at a low level,but there is no isolated development area in the network,and the spatial network is gradually developing towards the trend of equalization,and the robustness of the network is gradually obvious.Third,the spatial correlation network of regional high-quality development from 2011 to 2020 has a more obvious core-edge structure,with regions such as Tianjin,Shanghai and Beijing more easily connected with other regions due to their superior location conditions and development base,and located in the center of the network;central and western regions such as Qinghai,Xinjiang and Hubei are less connected with other regions due to their remote locations,and are located in the edge of the network.The network is located at the edge.Fourth,the spatial linkage network of regional high-quality development can be divided into four major segments,namely the “net benefit”segment,the “net spillover” segment,the “main benefit” segment and the “broker” segment.The“broker”segment.On the whole,the spillover effect between the segments is obvious,while there is less connection within the segments.Fifth,the level of economic development,urbanization and geographical proximity have significant positive effects on the formation of spatially linked networks for high-quality development in China,while industrial structure,transportation conditions,environmental quality and human capital have insignificant effects on the formation of spatially linked networks.
Based on the findings of the article,the following suggestions are made as follows.First,the spatial correlation network of regional high-quality development has already appeared,so it is necessary to consider not only the region’s own conditions,but also focus on cooperation with its neighboring regions to promote inter-regional communication and collaboration.In addition,it is also necessary to pay attention to the central actors in the spatially linked network and the regions that assume the role of bridges,so as to give full play to their driving role.Second,when dividing the regions and implementing precise policies,we should break the traditional geographical division of “east-northeast-central-west” and implement precise policies based on the types of segments in the network,giving full play to the"main benefit"segments and“net benefit”segments.The central position of the“net beneficiary”segment will drive the development of other segments,enhance the absorption capacity of the “net spillover” segment,guide the “broker” segment to establish the concept of coordinated development,and increase the opening-up efforts.Fully consider the influence of economic development level,urbanization level and geographical proximity on the spatial association network,and promote the flow of population and economic factors between the core and peripheral regions.In addition,it is also necessary to pay attention to shortening the gap between regions in terms of industrial structure,transportation conditions and human capital,so as to enhance the intensity of regional linkage while helping the peripheral regions to integrate into the linkage network more quickly and better.
杂志排行
Ecological Economy的其它文章
- Assessing the impact of manufacturing agglomeration on environmental pollution in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region using spatial panel data model
- NDVI characteristics and precipitation sensitivity of urban agglomeration in Central Shanxi Basin
- Determinates of the competitiveness of provincial forest health care industry in China
- Spatial and temporal heterogeneity of the impact of per capita income on household indirect carbon emissions in western China
- Carbon emission reduction effect and mechanism test of carbon emission trading pilot
- Regulatory mode selection and legal governance of China's response to climate change risk
