Research progress on cardiotoxicity mechanism of doxorubicin and prevention and treatment of traditional Chinese medicine
2023-12-06SUJingLIUDonglingHAIYangLIUXiaofengHOUWenqianDONGJingquXULan
SU Jing, LIU Dong-ling✉, HAI Yang, LIU Xiao-feng, HOU Wen-qian, DONG Jing-qu,XU Lan
1.College of Pharmacy, Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, China
2.Scientific Research and Experimental Center, Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Doxorubicin is an anthracycline antibiotic.As a broad-spectrum antitumor drug, it is widely used in clinic.However, doxorubicin is dose-dependent and shows obvious cardiotoxicity,which limits its clinical application.At present, the mechanism of doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity has not been fully clarified.Reducing cardiotoxicity and improving the scope of clinical application have become the focus of research in recent years.This paper reviews the mechanism of doxorubicin cardiotoxicity and the prevention and treatment of doxorubicin cardiotoxicity with traditional Chinese medicine, in order to provide reference for the combined application of doxorubicin.
1.Introduction
Doxorubicin (DOX) is a first-line chemotherapy drug with anthracycline structure.It is widely used in the treatment of solid tumors such as malignant lymphoma, breast cancer, prostate cancer,bladder cancer, osteosarcoma, lung cancer and neuroblastoma[1].DOX mainly plays an anti-tumor role by embedding DNA and inhibiting topoisomerase II, but the low selectivity of DOX can also cause apoptosis or necrosis of normal tissues, involving multiple organs such as brain, heart, liver and kidney, causing toxic damage[2].Clinical studies have found that DOX induced cardiotoxicity is dose-dependent.When the concentration of DOX reaches 400 mg/m2, 500 mg/m2and 550 mg/m2respectively, the incidence of heart failure is positively correlated with the cumulative dose, increasing to 5%, 16% and 26%[3], resulting in progressive heart failure and irreversible cardiac insufficiency[4].Current studies suggest that DOX induced cardiotoxicity is related to oxidative stress, inflammatory response, mitochondrial damage, imbalance of Ca2+homeostasis, apoptosis, autophagy and other mechanisms[5].This paper reviews the toxic mechanism of DOX and the role of traditional Chinese medicine in the prevention and treatment of DOX cardiotoxicity, in order to provide reference for the clinical application of DOX.
1.Molecular mechanism of doxorubicin induced myocardial injury
1.1 Oxidative stress and inflammatory response
Oxidative stress is a state of imbalance between reactive oxygen species (ROS) and antioxidation in the body.When the body tends to oxidative reaction, it can lead to neutrophil inflammatory infiltration, increase protease secretion, and produce oxidative intermediates such as superoxide anion (O2-), hydroxyl radical(-OH)[6].Under normal conditions, the main site of reactive oxygen species generation is online particle.ROS enzyme in mitochondria can convert the quinone part of DOX into semiquinone form.DOX in semiquinone form is easy to react with oxygen molecule (O2)to generate superoxide anion (O2-).O2-combines with superoxide dismutase (SOD) to form relatively stable and low toxic hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and then produce highly active - oh.ROS oxidizes with DNA, protein and lipid, resulting in DNA damage and lipid peroxidation, and finally cell damage[7].
There is a positive correlation between inflammatory response and oxidative stress, which accelerates myocardial injury.Abdelgawad et al.[8] showed that DOX can stimulate the inflammatory factors interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor of cardiomyocytesα (TNF-α) Expression and release of.Zhang et al.[9] found that DOX can over activate TLR4/MAPKs/NF-κB signaling pathway in myeloid differentiation protein 1 (MD-1) gene knockout mice to accelerate cardiomyocyte apoptosis.Wang et al.[10] showed that DOX stimulates the transient receptor potential A1 (TRPA1) ion channel and causes cardiotoxicity by promoting oxidative stress and inflammation.
1.2 Mitochondrial damage
As a place for aerobic respiration and providing energy for cell metabolism, mitochondria have the ability to regulate cell growth,which is very important to maintain the normal function of cells and the balance of energy metabolism[11].Dox can cause damage to mitochondrial tissue structure, affect mitochondrial metabolism and reduce cell energy supply.DOX has high affinity with cardiolipin located on the inner membrane of mitochondria.They combine to form an irreversible complex and accumulate in cardiomyocytes.When the concentration of DOX in mitochondria exceeds 50~100 μmol/L, ROS production increased[12].Mitochondrial phosphate transporter (MPT) is an important protein located on the inner mitochondrial membrane.MPT is responsible for transferring the metabolic substrate inorganic phosphate from the cytoplasm to the mitochondrial matrix through the inner mitochondrial membrane[13].MPT pore (MPTP) can lead to changes in mitochondrial intimal potential, cessation of mitochondrial adenosine triphosphate (ATP)synthesis, uncoupling of respiratory chain, promoting mitochondrial osmotic swelling and rupture and cell death through DOX induced mitochondrial oxidative damage and calcium overload[14].Catanzaro et al.[15] pointed out that DOX can also enhance mitochondrial lysis and accelerate the degradation of mitochondria by lysosomes,eventually leading to cardiotoxicity.
1.3 Calcium homeostasis imbalance
DOX and its metabolites can cause the increase of intracellular Ca2+concentration, imbalance the Ca2+homeostasis in cardiomyocytes,and damage the function of cardiomyocytes.Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR), a special form of endoplasmic reticulum of cardiomyocytes, is mainly responsible for regulating Ca2+channels and controlling excitation contraction coupling[16], and participates in the development of DOX induced cardiotoxicity.Glucose regulated protein 78 (GRP78) is not only the central mediator of unfolded protein response during endoplasmic reticulum stress,but also the regulator of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+homeostasis.Overexpression of GRP78 can reduce calmodulin dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) activation and p53 accumulation, and protect cardiomyocytes from DOX induced apoptosis[17].Llach et al.[18]showed that low-dose DOX can reduce ejection fraction, slightly expand and destroy cardiac function.Its mechanism may be related to the decrease of intracellular free Ca2+concentration.
1.4 Autophagy
Autophagy is a catabolic process that eliminates misfolded proteins and damaged or aging organelles by regulating autophagy related genes (ATG) and lysosomal proteolysis to maintain cell homeostasis[19].Dox can induce autophagy initiation of cardiomyocytes through endoplasmic reticulum stress, oxidative stress and other pathways[20].Mammalian rapamycin target protein (mTOR) is one of the main negative regulators of autophagy.DOX increases the expression of microtubule associated protein 1A/1B light chain 3- II (LC3-II),ATG5, atg6, Atg8 and atg12 by activating AMPK and inhibiting p38 mitogen activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK), inhibits the expression of mTOR and promotes autophagy[21].In addition, DOX can stimulate autophagy by increasing the ratio of LC3-II/LC3-I,stimulate the expression of c-jun amino terminal kinase 1 (JNK1)and p70S6 kinase (P70S6K), up regulate the expression of p62,beclin-1 and ATG5, and promote autophagy[16].
1.5 Apoptosis
Apoptosis is a programmed cell death controlled by genes.It plays an important role in the evolution of organisms, the homeostasis of internal environment and the renewal of normal cells.Dox induced cardiotoxicity is related to p53 nuclear translocation and p53 dependent apoptosis.Dox activates extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) and phosphorylates p53 at ser15.Phosphorylation of p53 can lead to cardiomyocyte apoptosis by down regulating anti apoptotic B-cell Lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2), up regulating Pro apoptotic Bcl-2 related X protein (Bax) and activating cysteine protease-3(caspase-3), caspase-9 and ADP ribose polymerase[22].In addition,E2F transcription factor 1 (E2F1)/AMPK α The activation of 2 signaling pathway is also involved in DOX induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis[23].Although the effect and mechanism of DOX on cardiomyocyte apoptosis have been widely studied, the specific signal pathway involved in DOX induced apoptosis has not been completely clear.The schematic diagram of the mechanism related to dox induced cardiotoxicity is shown in Figure 1.
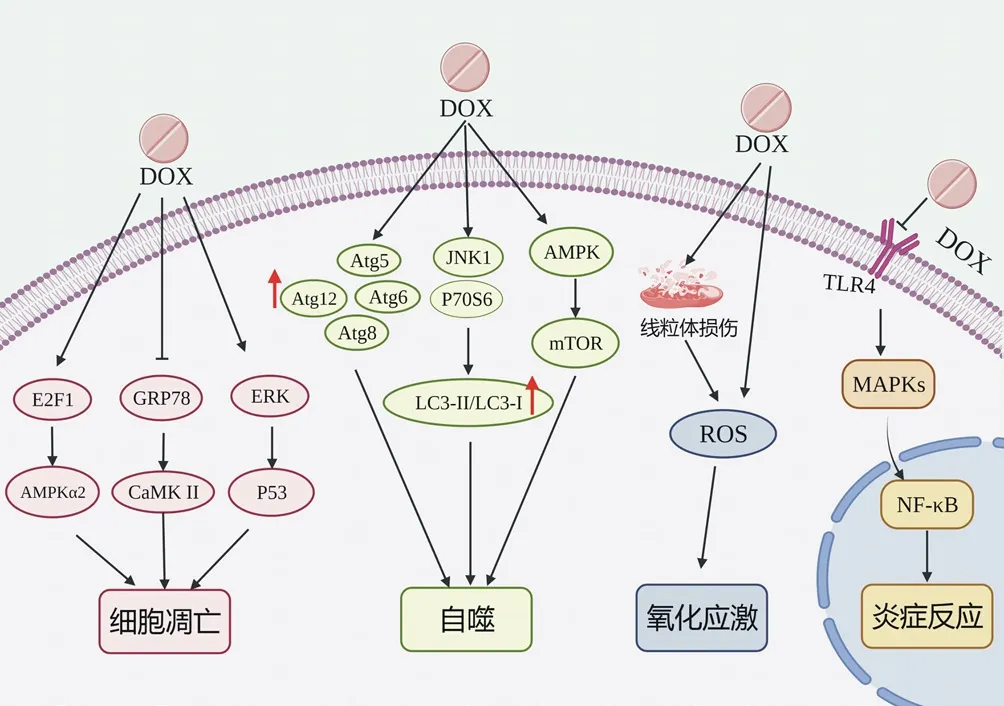
Fig 1 Schematic diagram of the mechanism related to dox induced cardiotoxicity
2.Preventive and therapeutic effects of traditional Chinese medicine and its active components on doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity
Although the records of symptoms, accumulation, rash, addiction,rock and other diseases in traditional Chinese medicine books of past dynasties are similar to modern malignant tumors, there is no clear record of the toxicity caused by anti-tumor drugs.The clinical manifestations of doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity are chest tightness, palpitation, shortness of breath, fatigue, sweating and cold limbs.Traditional Chinese medicine classifies them into the categories of “palpitation”, “chest arthralgia” and “heart failure”according to clinical symptoms.The pathogenesis of myocardial injury caused by doxorubicin is mostly deficiency of Qi and Yin and deficiency of Qi and blood.Based on the idea of “concept of righteousness and evil” in the Yellow Emperor’s Internal Classic,the treatment is mainly to support righteousness and eliminate evil,which should replenish qi, nourish blood, warm yang and nourish yin; Dispelling evil should promote blood circulation, remove phlegm, regulate qi and remove blood stasis.
2.1 Tonic drugs
2.1.1 Tonic
Ginseng, astragalus, licorice, seabuckthorn, Rhodiola and acanthopanax senticosus participate in the treatment of heart injury caused by DOX through antioxidant, regulating autophagy and improving thread body function.
Ginseng has the effects of tonifying vital energy, tonifying spleen and lungs, calming nerves and benefiting intelligence.It can treat the syndrome of deficiency of heart, lung, spleen and kidney qi.In tonifying heart qi, ginseng can improve the symptoms of heart qi deficiency and failure such as palpitation, chest tightness, shortness of breath and pulse deficiency.Its main effective component is ginsenoside.Liu et al.[24] showed that ginsenoside Rb1 can eliminate the delayed depolarization induced by high calcium in rabbit ventricular myocytes, inhibit the increase of intracellular calcium ions, alleviate calcium overload, and play the role of anti arrhythmia and protecting cardiomyocytes.
Astragalus membranaceus has the effect of Supplementing Qi,generating blood and supporting healthy qi.It can treat various syndromes of Qi and blood deficiency.Its main component is Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharide, which can enhance the immune function and hematopoietic function of the body.Cao et al.[25] found that Astragalus polysaccharides could reduce DOX induced cardiotoxicity by regulating AMPK/mTOR pathway by establishing DOX induced rat cardiomyocyte injury model and mouse heart failure model.
Licorice has the effects of Tonifying the spleen and lungs and harmonizing various drugs.It can treat pulse node generation and palpitation caused by insufficient heart qi.The main effective component glycyrrhizic acid can inhibit AMPK/mTOR autophagy signal pathway mediated by high mobility group protein B1(HMGB1) and reduce DOX induced cardiotoxicity[26].
Seabuckthorn has the effect of promoting blood circulation and dispersing stasis.It can treat chest arthralgia and heartache.Its effective component Seabuckthorn total flavonoids can reduce myocardial oxygen consumption and improve myocardial microcirculation.Studies have shown that[27], seabuckthorn total flavonoids can improve myocardial antioxidant capacity and reduce myocardial injury caused by DOX by inhibiting lipid peroxidation caused by free radicals.Zhou et al.[28] established a DOX induced apoptosis model of H9c2 cells and found that coumarin-4-aminobutanol (alk-A) and rare pyridine indole alkaloid (alk-B) can inhibit the production of ROS, inhibit cell apoptosis and improve mitochondrial function, so as to protect cardiomyocytes.
Rhodiola has the effects of Supplementing Qi, promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis.Its main effective component is salidroside.Cao Xiangming et al.[29] established doxorubicin myocardial injury model and found that Rhodiola could improve DOX induced cardiotoxicity by increasing cardiac troponin I (cTnI),B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and cardiomyocyte apoptosis index(AI).
Acanthopanax senticosus has the effect of tonifying heart qi.The main effective components are a variety of glycosides.Acanthopanax senticosus and its glycoside extracts have anti stress and anti arrhythmia effects, and can reduce cellular lipid peroxidation[30].Zhang Shan et al.[31] intervened with different doses of Acanthopanax senticosus injection through DOX induced cardiac toxicity model in rats.The results showed that Acanthopanax senticosus injection could enhance cardiac systolic dysfunction,improve cardiac configuration and reduce ultrastructural damage of myocardial tissue in rats with myocardial injury caused by DOX.
2.1.2 Yang tonic
Yang tonifying drugs pilose antler, Festuca arundinacea, Cordyceps sinensis and Morinda officinalis can effectively improve the cardiac function injury caused by DOX through antioxidant, antiinflammatory and anti apoptosis mechanisms.
Pilose antler has the effect of Supplementing Qi and blood and benefiting essence.It mainly becomes pilose antler polypeptide.Shi et al.[32] showed that pilose antler can restore cardiac function by improving myocardial fibrosis and ventricular remodeling in rats.Li Xin et al.[33] showed that pilose antler polypeptides regulate transforming growth factors- β (TGF-β1), the expression of Smad7 and PKC protein can protect H9c2 cells from DOX induced injury.
Citronella has the effect of warming kidney yang.The main effective components are citronelloside, citronellosin and so on.Modern pharmacological studies have found that Festuca arundinacea has the effect of antioxidant stress and is related to NF-B signaling pathway[34].Yao Jia et al.[35] showed that Festuca arundinacea polysaccharide can increase the activities of serum creatine kinase (CK), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and nitric oxide synthase (NOS) in mouse myocardial injury model, increase the activity of myocardial SOD and reduce the content of malondialdehyde (MDA), and has obvious protective effect on myocardial injury caused by DOX.
Psoralea corylifolia has the effects of Tonifying the kidney and Yang, warming the spleen and stopping diarrhea.The main effective components are psoralen phenol and isopsoralen.Zhuang Huamei et al.[36] showed that Psoralea corylifolia can reduce myocardial injury, improve SOD activity and reduce MDA level in rats with chronic heart failure by regulating Bcl-2/Bax, Caspase-9 and caspase-3 transcription levels, and protect cardiomyocytes.Any other[37] studies have shown that psoralen can inhibit oxidative stress injury and apoptosis caused by DOX by activating SIRT3/SOD2 signaling pathway.
Cordyceps sinensis has the effects of tonifying lung and kidney,relieving cough and resolving phlegm.The main effective components are adenosine, polysaccharide and so on.Jijiachai et al.[38] found that cordycepin can inhibit NF-κB signaling pathway reduces DOX induced inflammatory response and cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and improves DOX induced cardiac insufficiency.
Morinda officinalis has the effects of Tonifying Kidney Yang and strengthening muscles and bones.The main effective components are anthraquinone, oligosaccharide and so on.Gu Bing[39] showed that Morinda officinalis oligosaccharide can reduce the degree of myocardial injury caused by DOX and protect damaged cardiomyocytes through antioxidant effect.
2.1.3 Blood tonic
Angelica sinensis, a blood tonic, can improve the cardiac function injury caused by DOX by anti apoptosis and enhancing ATPase activity.
Angelica sinensis has the effect of promoting blood circulation and relieving pain.The main effective components are Angelica sinensis polysaccharide, volatile oil and so on.Jeon et al.[40] showed that Angelica sinensis neutral oil has obvious protective effect on myocardial ischemia.Chang Yanna[41] et al.showed that Angelica ultrafiltration with different concentrations (3.75, 7.5, 15 g/L)antagonized the cardiotoxicity caused by DOX by enhancing cellular ATPase activity, reducing intracellular LDH activity and inhibiting the release of apoptotic factors.
2.1.4 Yin tonifying drugs
Lycium barbarum and Ophiopogon japonicus can effectively improve the damage of heart function caused by DOX through antioxidant and anti apoptosis mechanisms.
Lycium barbarum has the function of nourishing liver and kidney.The main effective component is Lycium barbarum polysaccharide.Deng et al.[42] showed that Lycium barbarum polysaccharide can reduce the immunotoxicity of DOX and enhance its antitumor activity.Liu Kaixi et al.[43] showed that different concentrations of Lycium barbarum polysaccharides can significantly reduce the damage of DOX to cardiomyocytes and reduce the degeneration and necrosis of cardiomyocytes.
Ophiopogon japonicus has the effects of benefiting the stomach,nourishing Yin, clearing the heart and removing annoyance.The main effective component is Ophiopogon japonicus saponin.Meng Chen et al.[44] showed that Ophiopogon japonicus saponin d had a protective effect on cardiomyocytes by reducing the accumulation of ROS induced by DOX and alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress.
2.2 Drugs for promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis
Ligusticum chuanxiong, Salvia miltiorrhiza, safflower, motherwort and Turmeric can effectively improve the damage of heart function caused by DOX through antioxidant, regulating autophagy,protecting mitochondrial function and other mechanisms.
Ligusticum chuanxiong has the effects of promoting blood circulation and Qi, dispelling wind and relieving pain.The main effective component is Ligustrazine.Ding Xueming et al.[45] showed that Ligustrazine up regulates cell 14-3-3γ And the expression of Bcl-2 in mitochondria, inhibit the oxidative stress of cardiomyocytes,protect the function of mitochondria and reduce the apoptosis of cardiomyocytes induced by DOX.
Salvia miltiorrhiza has the effect of promoting blood circulation,removing blood stasis and relieving pain.The main effective component is tanshinone.Tanshinone IIA can reduce cardiomyocyte oxidative stress and prevent cardiomyocyte injury caused by DOX,regulating autophagy mediated by AMPK signaling pathway[46, 47].
Safflower has the effect of promoting blood circulation, removing blood stasis and relieving pain.The main effective components are tanshinone, tanshinol and so on.Tong Cailing et al.[48] showed that different concentrations of safflower yellow pigment (2.5, 5, 10 g/kg/d) can significantly increase the expression level of myocardial Cx43, and its mechanism is to play a protective role by up regulating the expression of Cx43.
Motherwort has the effect of promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis.The main effective component is motherwort base.Chen Yuping et al.[49] showed that motherwort can reduce the damage of myocardial cell membrane caused by oxygen free radicals through anti lipid peroxidation, reduce the permeability of cell membrane and protect myocardial injury induced by DOX.
Turmeric has the effect of promoting blood circulation and Qi.The main effective component is curcumin.Zhang Xinwei et al.[50]showed that curcumin protects cardiomyocytes by increasing SOD activity and reducing MDA level and Caspase-3 expression.
2.3 receiving astringent drugs
Yin tonifying drugs Jinyingzi and Schisandra chinensis can effectively improve the cardiac function injury caused by DOX through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti apoptosis mechanisms.
Rosa laevigata has the effect of solidifying collapse and stopping belt.The main effective components are polysaccharides and flavonoids.Luo Weimin et al.[51] showed that Rosa laevigata reduced the levels of AST, LDH, CK-MB and TC in rat serum through antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti apoptotic pathways,and had a protective effect on DOX induced myocardial injury.
Schisandra chinensis has the effects of Supplementing Qi,generating fluid, tonifying the kidney and calming the heart.The main effective components are lignans.Zhang Minyu et al.[52]showed that Schisandra chinensis extract can improve SOD activity and inhibit DOX induced lipid peroxidation of cardiomyocytes, so as to reduce the toxicity of DOX to the heart.Chen Hongzhu et al.[53]showed that Schisandra chinensis lignans can reduce LDH and CK levels and improve DOX induced myocardial injury.
2.4 hemostatic drugs
Hemostatic drugs wormwood leaf and Panax notoginseng can effectively improve the cardiac function damage caused by DOX through antioxidation.
Wormwood leaf has the effects of warming meridians, hemostasis,dispersing cold to relieve pain.It mainly contains volatile oil and brass.Wang Zhongxiao et al.[54] showed that wormwood leaf extract can reduce the levels of LDH, AST, CK-MB, CK and MDA, improve the level of SOD, enhance the antioxidant stress ability of rats, and reduce the degree of myocardial injury caused by DOX.
Panax notoginseng has the effects of dispersing blood stasis,hemostasis, detumescence and pain.The main effective component is Panax notoginseng saponin.Li Weili et al.[55] showed that different concentrations (50, 100 mg/kg) of Panax notoginseng saponins effectively reduced the levels of LDH, CK and CK-MB in rats,improved the loose and atrophic morphology of myocardial tissue caused by DOX, and had a protective effect on myocardial injury caused by adriamycin.
2.5 Antipyretic
Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi can effectively improve the damage of heart function caused by DOX through antioxidant, antiinflammatory, anti apoptosis and regulating autophagy.
Scutellaria baicalensis has the effect of clearing heat and hemostasis.The main effective component is baicalein.Zhou et al.[56] showed that Scutellaria baicalensis root extract can protect cell apoptosis by inducing autophagy.Dai Yuan et al.[57] showed that baicalein can inhibit the phosphorylation level of NF-κB and JNK and reduce cardiomyocyte apoptosis caused by DOX
2.6 Other traditional Chinese Medicine
Evodia rutaecarpa, Euphorbia officinalis and Siraitia grosvenorii can effectively improve the cardiac function injury caused by DOX through antioxidant and anti apoptosis mechanisms.Wang Li et al.[58] showed that evodiamine can protect H9c2 cardiomyocytes from DOX induced injury by enhancing the vitality of H9c2 cells, inhibiting the release of ROS and inhibiting apoptosis.Yu Jing[59] and other studies showed that the alcohol extract of Herba Lysimachiae can reduce the heart coefficient, increase the heart rate, reduce the biochemical indexes in serum (CK, LDH, TC)and improve the cardiac toxicity induced by DOX.Huang Wenwei et al.[60] showed that Siraitia grosvenorii saponin can increase the expression of Bcl-2 protein, reduce the expression of mRNA,enhance the antioxidant capacity of DOX myocardial injury rats and inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis.
3.Summary and Prospect
The etiology of DOX induced cardiotoxicity lies in “deficiency”.The Yellow Emperor’s Internal Classic says that “deficiency will make up for it, and those who lose will benefit it”.The treatment is mainly “tonifying deficiency, protecting the heart and reducing toxicity”.At present, it is found that the toxicity of DOX does not exist only in the form of cardiac toxicity, but traditional Chinese medicine takes into account the whole, which can effectively improve the overall toxicity while reducing the cardiac toxicity.Traditional Chinese medicine systematically treats the body from the perspective of the whole and takes into account the damage of multiple organs, which has unique advantages in the toxic reactions caused by DOX.Traditional Chinese medicines such as tonifying deficiency drugs and promoting blood circulation and removing blood stasis can effectively prevent DOX induced cardiotoxicity by strengthening the body and expelling evil.Their mechanisms are mostly related to antioxidant stress and inflammatory response,preventing mitochondrial damage, maintaining Ca2+homeostasis,inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis and so on.However, traditional Chinese medicine has the characteristics of multi-component, multichannel and multi-target in treatment, which leads to the complexity and correlation of the detoxification mechanism.Therefore, the specific pharmacodynamic material basis and action mechanism need to be further studied.
Authors’ contribution
Topic selection and writing: Jing Su, paper revision: Dong-ling Liu,Yang Hai, literature collection: Jing-Qu Dong, Lan Xu, literature collation: Wen-Qian Hou, Xiao-Feng Liu.
Conflict of interest statement for all authors
The author declares that there is no conflict of interest in the publication of this paper.
Referencs
[1] He H, Wang L, Qiao Y, et al.Epigallocatechin-3-gallate pretreatment alleviates doxorubicin-induced ferroptosis and cardiotoxicity by upregulating AMPKα2 and activating adaptive autophagy.Redox Biol 2021, 48: 102185.
[2] Saleh MF, Elsayad ME, Goda AE.Mitigation of doxorubicin -induced cardiotoxicity by dichloroacetate: Potential roles of restoration of PGC- 1α/SIRT3 signaling and suppression of oxidative stress and apoptosis.Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2021, 25(21): 6573-6584.
[3] Vejpongsa P, Yeh ET.Prevention of anthracycline - induced cardiotoxicity: Challenges and opportunities.J Am Coll Cardiol 2014,64(9): 938-945.
[4] Koss-Mikołajczyk I, Todorovic V, Sobajic S, et al.Natural products counteracting cardiotoxicity during cancer chemotherapy: The special case of doxorubicin, a comprehensive review.Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22 (18):10037.
[5] Li YY, Li JJ, Ge FX, et al.Research progress on in vitro models of cardiomyocyte injury.Chin J Chin Mater Med 2021, 46(13): 3257-3269.
[6] Mu HM, Liu HW, Zhang JY, et al.Ursolic acid prevents doxorubicininduced cardiac toxicity in mice through eNOS activation and inhibition of eNOS uncoupling.J Cell Mol Med 2019, 23: 2174-2183.
[7] Wenningmann N, Knapp M, Ande A, et al.Insights into Doxorubicininduced Cardiotoxicity: Molecular Mechanisms, Preventive Strategies,and Early Monitoring.Mol Pharmacol 2019, 96: 219-232.
[8] Abdelgawad Ibrahim Y, Grant Marianne KO, Popescu Flavia E, et al.Doxorubicin Paradoxically Ameliorates Tumor-Induced Inflammation in Young Mice.Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22(16): 9023.
[9] Zhang YJ, Huang H, Liu Y, et al.MD-1 Deficiency Accelerates Myocardial Inflammation and Apoptosis in Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity by Activating the TLR4/MAPKs/Nuclear Factor kappa B(NF-κB) Signaling Pathway.Med Sci Monit 2019, 25: 7898-7907.
[10] Wang Z, Wang ML, Liu JF, et al.Inhibition of TRPA1 Attenuates Doxorubicin-Induced Acute Cardiotoxicity by Suppressing Oxidative Stress, the Inflammatory Response, and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress.Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018, 2018: 5179468.
[11] Ji WH, Tang X, Du W, et al.Optical/electrochemical methods for detecting mitochondrial energy metabolism.Chem Soc Rev 2022, 51(1):71-127.
[12] Saleh M F, Elsayad M E, Goda A E.Mitigation of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by dichloroacetate: potential roles of restoration of PGC-1α/SIRT3 signaling and suppression of oxidative stress and apoptosis.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2021, 25: 6573-6584.
[13] Zhou Y, Wang LE, Yu W, et al.Research progress of mitochondrial autophagy in doxorubicin cardiotoxicity.J Hubei Univ Sci Tech (Med Sci)2021, 35(04): 356-360.
[14] Barajas M, Wang AL, Griffiths K, et al.The newborn Fmr1 knockout mouse: a novel model of excess ubiquinone and closed mitochondrial permeability transition pore in the developing heart.Pediatr Res 2021,89: 456-463.
[15] Catanzaro Michael P, Weiner A, Kaminaris A, et al.Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocyte death is mediated by unchecked mitochondrial fission and mitophagy.FASEB J 2019, 33: 11096-11108.
[16] Xu ZM, Li CB, Liu QL, et al.Ginsenoside Rg1 Prevents Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity through the Inhibition of Autophagy and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Mice.Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19(11): 3658.
[17] Tscheschner H, Meinhardt E, Schlegel P, et al.CaMKII activation participates in doxorubicin cardiotoxicity and is attenuated by moderate GRP78 overexpression.PLoS One 2019, 14: e0215992.
[18] Llach A, Mazevet M, Mateo P, et al.Progression of excitation-contraction coupling defects in doxorubicin cardiotoxicity.J Mol Cell Cardiol 2019,126: 129-139.
[19] Shabalala S, Muller CJF, Louw J, et al.Polyphenols, autophagy and doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity.Life Sci 2017, 180: 160-170.
[20] Bagchi Ashim K, Malik A, Akolkar G, et al.Study of ER stress and apoptotic proteins in the heart and tumor exposed to doxorubicin.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 2021, 1868: 119039.
[21] Wang X, Wang XL, Chen HL, et al.Ghrelin inhibits doxorubicin cardiotoxicity by inhibiting excessive autophagy through AMPK and p38-MAPK.Biochem Pharmacol 2014, 88: 334-50.
[22] Cunha-Oliveira T, Ferreira L, Coelho Ana R, et al.Doxorubicin triggers bioenergetic failure and p53 activation in mouse stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2018, 348: 1-13.
[23] Gu J, Fan YQ, Zhang HL, et al.Resveratrol suppresses doxorubicininduced cardiotoxicity by disrupting E2F1 mediated autophagy inhibition and apoptosis promotion.Biochem Pharmacol 2018, 150: 202-213.
[24] Liu ZP, Song L, Zhang PP, et al.Ginsenoside Rb1 exerts antiarrhythmic effects by inhibiting I and I in rabbit ventricular myocytes.Sci Rep 2019,9: 20425.
[25] Cao Y, Shen T, Huang XQ, et al.Astragalus polysaccharide restores autophagic flux and improves cardiomyocyte function in doxorubicininduced cardiotoxicity.Oncotarget 2017, 8: 4837-4848.
[26] Lv XL.Investigation on HMGB1-mediated autophagy involved in protective effects of Glycyrrhizin against cardiotoxicity induced by Doxorubicin.Southern Medical University 2020.
[27] Gulimire A, Ybadaiti T, Rena K, et al.Protective effect of total flavonoids of H.rhamnoides L.subsp.turkestanica Rousi against adriamycininduced cardiotoxicity in rats.J Xinjiang Med Univ 2010, 33(04): 383-385.
[28] Zhou W, Ouyang J, Hu N, et al.Protective effect of two alkaloids from Hippophae rhamnoides Linn.against doxorubicin-Induced toxicity in H9c2 cardiomyoblasts.Molecules 2021, 26(7): 1946.
[29] Cao XM, Xi L, Shen WS, et al.The effect of different dosage of Rhodiola decotion on cardiac troponin I, brain natriuretic peptide,myocardial apoptosis of rats withDoxorubicin induced cardiomyocyte injury and establishment of mathematical model.J Clin Exp Med 2017,16(24): 2402-2405.
[30] Su J, Wang Q, Li Z, et al.Acanthopanax senticosusDifferent Metabolites in the Roots, Seeds, and Leaves of and Their Role in Alleviating Oxidative Stress.J Anal Methods Chem 2021, 2021: 6628880.
[31] Zhang S, Hao CH, Ge YM, et al.Effect of Ciwujia Injection on decrease of cardiac contractile function induced by doxorubicin hydrochloride.Chin Tradit Herb Drugs 2018, 49(17): 4071-4077.
[32] Shi H, Zhao T, Li Y, et al.Velvet Antler Ameliorates Cardiac Function by Restoring Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca-ATPase Activity in Rats With Heart Failure After Myocardial Infarction.Front Pharmacol 2021, 12:621194.
[33] Li X, Lv GF, Han D, et al.Study on the protective effect of pilose antler polypeptide on adriamycin induced H9c2 cell injury.Chin J Hosp Pharm 2020, 40 (10): 1089-1093.
[34] Liu M, Liu S, Zhang Q, et al.Curculigoside attenuates oxidative stress and osteoclastogenesis via modulating Nrf2/NF-κB signaling pathway in RAW264.7 cells.J Ethnopharmacol 2021, 275: 114129.
[35] Yao J, Peng M, Hu JY, et al.Protective effects of polysaccharide from Curculigo orchioides Gaertn on adriamycin-induced cardiotoxicity in mice.Chin J Gerontol 2014, 34 (21): 6079-6081.
[36] Zhuang HM, Chen XJ, Wang JF, et al.Effect of psoralen on myocardial injury in rats with chronic heart failure.Chin J Integr Med Cardio-Cerebrovasc Dis 2021, 19 (06): 930-934.
[37] Ren H, Wang CY.Protective effects of bakuchiol against doxorubicininduced cardiotoxicity and its underlying mechanism.J Shanxi Med Univ 2020, 51 (1): 39-45.
[38] Ji JC, Chen J, Fu CG.Effect of cordycepin on doxorubicin induced acute heart failure and its mechanism.Chin J Geriatr.Heart Brain Vessel Dis 2019, 21 (8): 804-809.
[39] Gu Bing.Effects of Morinda Officinalis Oligosaccharide on Serum Myocardial Enzyme of Rats with Myocardial Injury Induced by Doxorubicin.J Basic Clin Oncol 2019, 32 (3): 194-196.
[40] Jeon YJ, Shin JI, Lee S, et al.Angelica gigas Nakai Has Synergetic Effects on Doxorubicin-Induced Apoptosis.Biomed Res Int 2018, 2018:6716547.
[41] Chang YN, Li WJ, Sun SB, et al.Study on the Effect of Angelica Eextract on Ultrafiltration Membrane on Adriamycin Damage in Cardiomyocytes.J Med Res 2014, 43(5): 55-58.
[42] Deng X, Luo S, Luo X, et al.Fraction from Lycium barbarum Polysaccharides Reduces Immunotoxicity and Enhances Antitumor Activity of Doxorubicin in Mice.Integr Cancer Ther 2018, 17(3): 860-866.
[43] Liu KX, Yang XR, Liang T, et al.Effects of Lyceum Barbarum Polysaccharides on Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis in Adriamycin-Induced Cardiomypathy in Rat.The J Medical Theory and Practice 2014, 27 (14):1821-1822.
[44] Meng C, Yuan CH, Zhang CC, et al.Ophiopogonin D protects cardiomyocytes against doxorubicin-induced injury through suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress.Acta Pharm Sin 2014, 49 (8): 1117-1123.
[45] Ding XM, Chen TP, Xu Q, et al.Tetramethylpyrazine attenuates doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity through 14-3-3γ/Bcl-2.Chin J Clin Pharmacol Ther 2021, 26 (04): 361-367.
[46] Yuan LL, Xiao HQ, Li H, et al.Tanshinone ⅡA attenuates doxorubicininduced cardiomyocyte oxidative stress injury through autophagy 1.Chin J Clin Pharmacol 2019, 35 (19): 2289-2291.
[47] Wang CH, Xu Q, Xiao HQ, et al.Tanshinone ⅡA attenuates doxorubicin-induced injury in H9c2 cardiomyocytes via AMPKmediated autophagy.Chin J Pathophysiol 2019, 35 (03): 406-410.
[48] Tong CL, Liu JY, Huang M, et al.Effect of Safflower Yellow on Myocardial Connexin Expression in Mice with Doxorubicin-induced Cardiotoxicity.J Guangzhou Univ Tradit Chin Med 2014, 31(02): 272-274+323.
[49] Chen YP.The protective effect of the extracts of Leonurus artemisia on the adriamycin-induced myocardial injury.Shanghai Med Pharm J 2014,35 (21): 52-54.
[50] Zhang XW, Li L, Wang Y, et al.Protective Effects of Curcumin on Cell Injury induced by Doxorubicine in H9c2 Cell and Its Mechanism.J Mudanjiang Med Univ 2017, 38 (02): 25-27.
[51] Luo WM, Liu YF, Luo XY, et al.Antioxidant and antiapoptosis effect of Rosa Laevigata Michx.on Doxoru-bicin-induced cardiac injury rats.Chin Med Her 2014, 11 (07): 15-18.
[52] Zhang MY, Wu HW, Xu LP, et al.Pharmacological effect of Schisandrae Chinensis Fructus and relative active components on cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.Chin J Chin Mater Med 2018, 43 (8): 1536-1546.
[53] Cheng HZ, Lin JX, Pan Y, et al.Effect of Schisandra chinensis lignans on myocardial injury.J Jilin Med Univ 2016, 37 (3): 196-198.
[54] Wang ZX, Qu ZL, Wang B, et al.Preventive and protective effects of wormwood leaf extract on adriamycin induced myocardial injury in rats.Modern Med J Chin 2021, 23 (7): 50-52.
[55] Li WL, Huo RM.Mechanism of Notoginsenoside in Preventing and Treating Myocardial Damage in Rats Induced by Adriamycin.China Pharm 2017, 26 (21): 15-17.
[56] Zhou J, Luo Y, Kang X, et al.The root extract of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi promotes β cell function and protects from apoptosis by inducing autophagy.J Ethnopharmacol 2022, 284: 114790.
[57] Dai Y, Hu Y, Ju SH, et al.Baicalein Inhibits Doxorubicin-Induced Inflammation and Cytotoxicity in Rat Cardiomyocytes by Modulating Activation of NF-κB and JNK Pathway.J Chengdu Univ Tradit Chin Med 2014, 37 (02): 26-28.
[58] Wang L, Dong X, Xu HF, et al.Protective effect of rutaecarpine on Adriamycin-induced rat embryonic cardiomyocytes H9c2 injury.West Chin J Pharm Sci 2020, 35 (06): 621-625.
[59] Yu J, SU SW, Yang JZ, et al.Protective Effects of Ethanol Extracts from Siegesbeckiae herba on Doxorubicin-induced Chronic Myocardi-al Injury in Mice.Chin Pharm 2017, 28 (10): 1320-1323.
[60] Huang WW, Hong LF, Guo F, et al.Effect of Mogmside on Oxidative Stress and Cell Apoptosis in Myocardium of Adriamycin Myocardial Injury Rat.J Liaoning Univ Tradit Chin Med 2019, 21 (06): 39-42.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Establishment of extensively drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia model in rat
- MiR-873 regulates cell autophagy by targeting Beclin1 to promot inflammation and apoptosis of bronchial epithelial cells
- Monitoring and analysis of contamination of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio alginolyticus in seafood in Haikou
- Study on regulating mechanisms of oxocrebanine obtained from Stephania hainanensis H.S.Lo et Y.Tsoong on microtubule sites and tubulin in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells
- Effect of acupuncture on acupoint "Yingxiang-Hegu" on Th1, Th2 cytokines and T-bet/GATA-3 of allergic rhinitis rats
- Study on the mechanism of Fuzi in the treatment of allergic rhinitis based on network pharmacology and experimental validation
