Mechanisms of action of natural products on type 2 diabetes
2023-11-26TaoWangYangYangWangMengYueShiLianLiu
Tao Wang,Yang-Yang Wang,Meng-Yue Shi,Lian Liu
Abstract Over the past several decades,type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has been considered a global public health concern.Currently,various therapeutic modalities are available for T2DM management,including dietary modifications,moderate exercise,and use of hypoglycemic agents and lipid-lowering medications.Although the curative effect of most drugs on T2DM is significant,they also exert some adverse side effects.Biologically active substances found in natural medicines are important for T2DM treatment.Several recent studies have reported that active ingredients derived from traditional medicines or foods exert a therapeutic effect on T2DM.This review compiled important articles regarding the therapeutic effects of natural products and their active ingredients on islet β cell function,adipose tissue inflammation,and insulin resistance.Additionally,this review provided an in-depth understanding of the multiple regulatory effects on different targets and signaling pathways of natural medicines in the treatment of T2DM as well as a theoretical basis for clinical effective application.
Key Words: Type 2 diabetes;Natural product;β cell;Adipose tissue inflammation;Insulin resistance
lNTRODUCTlON
According to the International Diabetes Federation,the number of patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) worldwide was 536 million in 2021,which is expected to reach 783 million by 2045[1].Globally,China has the highest number of patients with DM,whose prevalence is increasing steadily.By 2045,the total number of patients with DM in China is expected to exceed 174 million[1].Based on its etiology,mechanism,and clinical manifestations,DM can be classified into type 1 DM,type 2 DM (T2DM),specific types of DM due to other causes,and gestational DM[2].In China,T2DM accounts for 90% of all DM cases[3].T2DM is mainly caused by insulin resistance (IR) associated with obesity,deficiencies in insulin secretion (INS),and reduction in islet cell numbers due to apoptosis[3].DM and its complications are serious health and economic problems that affect individuals worldwide and require urgent prevention and early intervention.
Through diet management,lifestyle changes,and oral use of biguanides and sulfonylureas,blood sugar levels can be effectively controlled to treat T2DM.Although these treatment modalities can relieve symptoms and improve patients’ conditions to a certain extent,they cannot completely prevent the occurrence and progression of complications;moreover they exert toxic side effects[4].Natural medicines have become a hotspot in the exploration of alternative treatments for DM owing to their minimal side effects.Natural products mainly refer to small or macromolecular active substances with pharmacological properties and are extracted from plants,animals,or microorganisms.They can be used to treat DM and its complications through multiple targets and pathways.The antidiabetic ingredients of natural products include monomeric compounds such as flavonoids,alkaloids,terpenes,polyphenols,saponins,and quinines[5].
The current literature on T2DM treatment with natural products is mostly based on their different active ingredients;however,reviews on their regulation mechanisms are lacking.This review aimed to summarize the mechanism of natural products and/or their monomers on T2DM treatment (Table 1).It also provided a theoretical basis for comprehensively understanding the mechanism and clinical application of natural medicines in the treatment of T2DM by summarizing the signal pathways involved in the regulation.
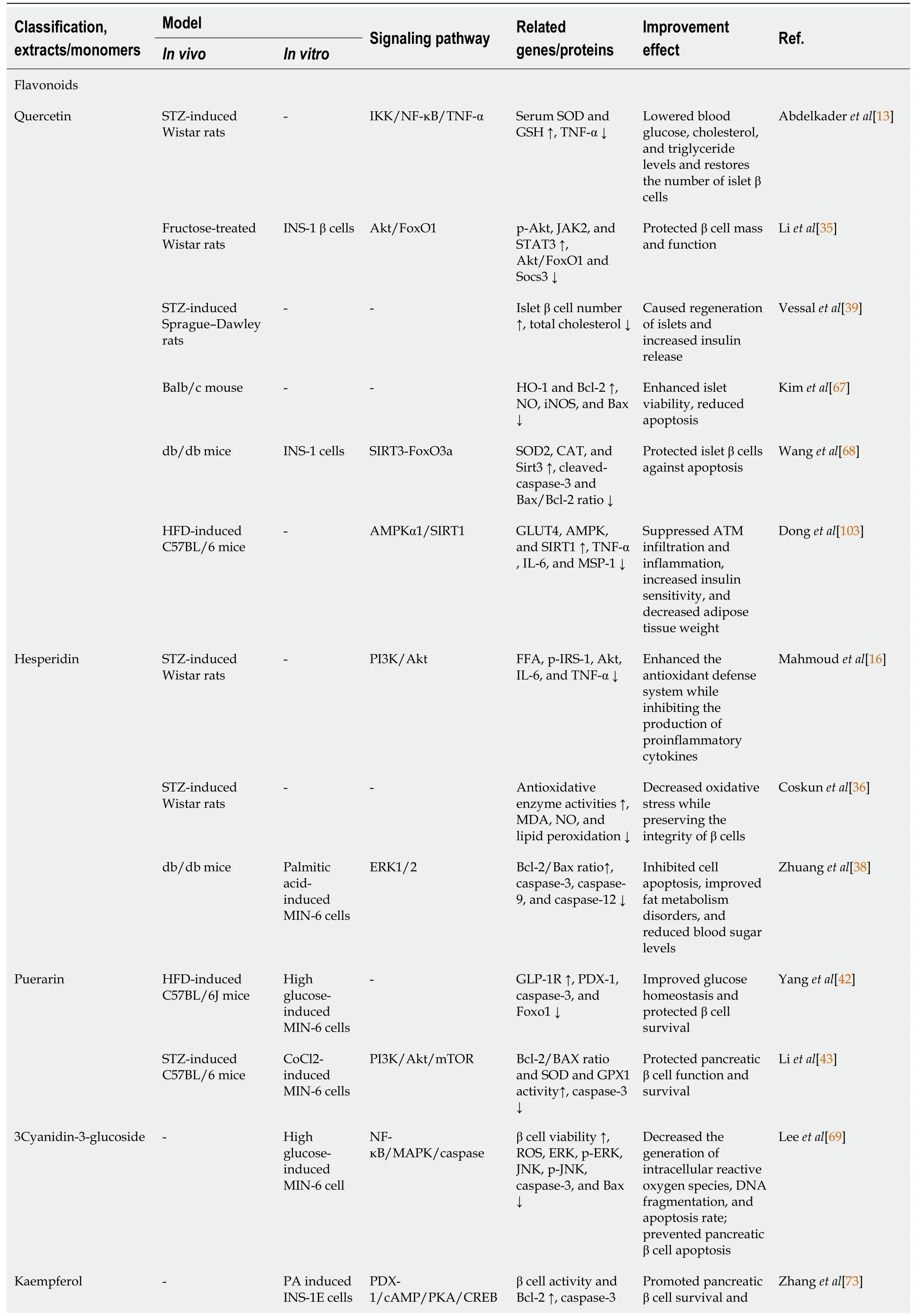
Table 1 Mechanism of natural products in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus
PROTECTlON OF lSLET B CELLS
Inhibition of islet β cell function is a prerequisite for T2DM occurrence.β cell impairment and IR are crucial in the development and pathogenesis of T2DM[6].During the course of the illness,islet β cell function failure is observed along with frequent episodes of exacerbation[7,8].Natural products exhibit notable effectiveness in reducing the inflammation,promoting the regeneration,and inhibiting the apoptosis of islet β cells (Figure 1).
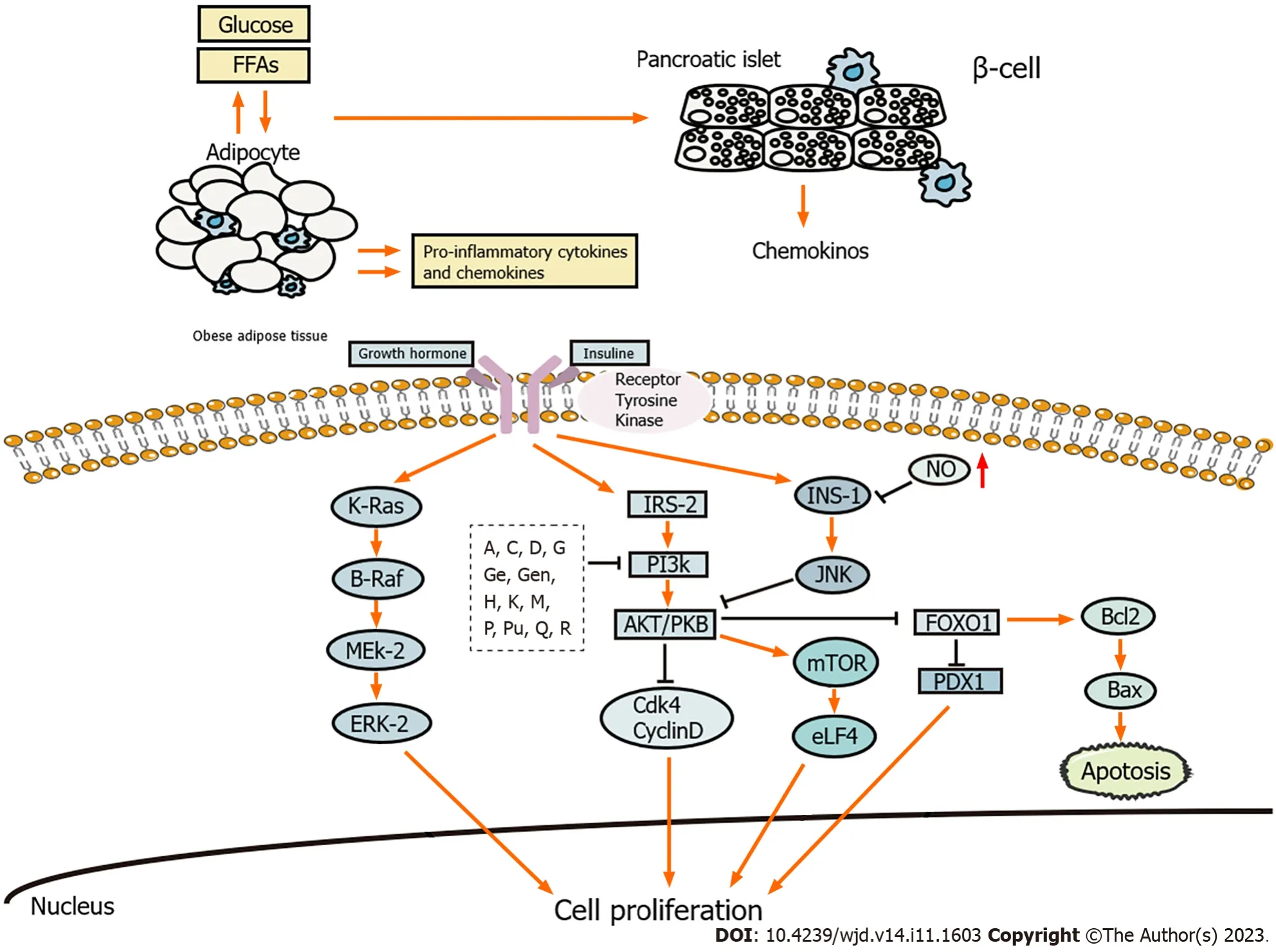
Figure 1 Mechanism of natural products in promoting the regeneration and inhibiting the apoptosis of islet β cells. The letters inside the black squares refer to natural products.Inhibitory effects are shown by black pathways.A: Alpha-mangostin;C: Caffeic acid;D: Dioscorea batatas extract;G: Gallic acid;Ge: Genistein;Gen: Geniposide;H: Hesperidin;K: Kaempferol;M: Mulberry anthocyanin extract;P: Paeoniflorin;Pu: Puerarin;Q: Quercetin;R: Resveratrol;FFA: Free fatty acids;FOXO: Forkhead box class O;JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase;mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin;NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B;NO: Nitric oxide;PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase;ROS/RNS: Reactive oxygen/nitrogen species.
Reduction in the inflammation of islet β cells
The accumulation of intra-islet macrophages is observed in T2DM,which represents the primary source of proinflammatory cytokines within the islets[9].Activated monocytes and macrophages release proinflammatory mediators,such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α),interleukin-6 (IL-6),and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1)[10],which activate inflammatory signaling pathways,such as the inhibitor of kappa B kinase and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK),and impair the insulin signaling pathway by regulating the levels of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)and protein kinase B(Akt).
Flavonoids: Quercetin is one of the most important bioflavonoids found in vegetables,cereals,fruits,and other plants.It is widely detected in green tea,onions,and apples and exerts antioxidative,anti-inflammatory,and antifibrotic effects[11].A previous study reported that the anti-inflammatory effect of quercetin is mediated by the upregulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated γ (PPAR-γ),which interferes with proinflammatory transcriptional factors,such as signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB),and reduces the expression of IL-1β,IL-6,and TNF-α[12].Abdelkaderet al[13] also demonstrated that the anti-inflammatory effect of quercetin decreased the expression of IκB-α by inhibiting the expression of IKK-α and IKK-β in islets β cells,thereby inhibiting NFκB activation and decreasing TNF-α levels.
Naringin and hesperidin are abundant in citrus fruits and exert antioxidative,antidiabetic,lipid-lowering,anti-atherosclerotic,and anti-inflammatory effects[14,15] They can reduce the expression of TNF-α and IL-6,regulate the level of nitric oxide (NO),activate the JNK pathway,inhibit the PI3K/Akt pathway,inactivate the lipid peroxide reaction,and reduce the levels of free radicals in high-fat diet/streptozocin (HFD/STZ)-induced rats with diabetes[16].
Polyphenols: Curcumin is a bioactive molecule found in the rhizome of turmeric plants;it exhibits extensive pharmacological and biological activities,such as exerting anti-inflammatory and hypoglycemic effects,improving β cell function,preventing β cell death,and improving IR[17].It has been reported that curcumin indirectly inhibits the NF-κB pathway to prevent inflammation by inhibiting IκB-α degradation as well as reduces the levels of IL-6,MCP-1,and TNF-α in the serum of rats with diabetes[18].Another study reported that curcumin decreased the expression of JNK,cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2),protein kinase C,extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK),and p38,reduced the level of malondialdehyde (MDA),and prevented inflammation[19].
Gallic and p-coumaric acids are found in plants such as tea,mango,and cocoa;they exert anti-inflammatory,antioxidative,and antiobesity effects[20,21].IL-1β reportedly induces NO production,increases NF-κB DNA binding,activates inducible NO synthase (iNOS) in islet β cells,and aggravates the inflammatory injury in islet β cells.Oral administration of gallic and p-coumaric acids also increases the expression of PPAR-γ[22],suppresses the expression of NF-κB,decreases the levels of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1,IL-6,and TNF-α),iNOS expression,and nitrite production,and increases insulin sensitivity[23].
Luteolin is widely found in vegetables,fruits,and natural herbs,such as parsley,thyme and celery.It exerts various antitumor and anti-inflammatory effects by inducing cell apoptosis and inhibiting NF-κB activation,respectively[24].Luteolin reportedly inhibits the NF-κB pathway and increases IL-10 levels in lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophagelike cell lines,thus exerting its anti-inflammatory effect[25].
Resveratrol is detected in cereals,fruits,and plant derived-beverages.It exerts antidiabetic,anti-inflammatory,and antioxidative effects[26].Resveratrol also inhibits the production of inflammatory factors by activating sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) and inhibiting p65/RelA acetylation,which results in decreased mRNA expression ofICAM-1,MCP-1,andTNF-α[27-29].
Genistein is an isoflavone found in legumes and herbs.It is a natural estrogen and tyrosine kinase inhibitor with potential hypolipidemic,antioxidative,and antiapoptotic effects[30].Genistein reportedly inhibits p65 acetylation by activating SIRT1 to reduce the levels of IL-1β,IL-6,and TNF-α in ovariectomized rats with diabetes as well as the expression of NF-κB[31].
Alkaloids: Brucea javanica belongs to the bitter wood family,which is generally used for the treatment of DM[32].A previous study showed that it effectively reduced the levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in rats,inhibited the NF-κB pathway,enhanced the expression of insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1),and GLUT4 and played an anti-inflammatory role[33].
Promotion of β cell regeneration
β cells are key to maintaining balance in glucose metabolism.A decrease in the number of β cells leads to insufficient insulin production,which is one of the key factors in the pathogenesis of T2DM.β cell regeneration can be considered a new approach for treating T2DM[34].
Flavonoids: Quercetin promotes the differentiation and regeneration of β cells[13].Previous studies have revealed that quercetin decreases the phosphorylation of Akt and FoxO1 in fructose-fed rat islets and increases the expression of nuclear FoxO1 in fructose-treated INS-1 cells[35].Quercetin significantly decreases MDA and NO levels,increases antioxidative enzyme activities,and enhances insulin staining and β-cells preservation[36].Oyedemiet al[37] reported that quercetin increased the number of pancreatic islets and β cells and can normalize the weight ratio of rat pancreas,suggesting that quercetin has the potential to regenerate pancreatic β cells.Furthermore,Zhuanget al[38] reported that quercetin improved the vacuolation of β cells and increased the number of pancreatic islets in db/db mice,consistent with the regeneration of pancreatic islets in STZ-induced rats with diabetes after 7 d of treatment with quercetin[39].
Puerarin,the dry root of pueraria,exerts neuroprotective,antioxidative,anti-inflammatory,and antiapoptotic effects[40].It reportedly increases the mass and proliferation of mouse β cells,leading to the activation of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor signaling[41].Another study confirmed that puerarin protects pancreatic β cell function and promotes survival by mediating the PI3K/Akt pathway,thereby exhibiting resistance to the toxicity of cobalt chloride[42,43].
Polyphenols:Sargassumis a brown macroalgae found in shallow sea meadows.It exerts anti-inflammatory,antioxidative,and immune regulatory effects[44].Pathological analysis of the islets revealed that the water extract ofSargassumcan restore the damaged islet structure.Previous studies have revealed that the islet area and regeneration percentage increased and the regeneration function of pancreatic β cells improved after 30 d of supplementation with hydroalcoholic extract ofSargassum[45,46].
Genistein intake can improve hyperglycemia,increase insulin levels,and enhance glucose tolerance in mice with diabetes[47].Akt and ERK1/2 are markers of cell proliferation and growth[48].Genistein reportedly increases the expression of p-ERK1/2,p-Akt,and Bcl-2 and suppresses the expression of caspase-3,concomitant with improved morphology and mass of islet β cells[49].
Mangiferin is a polyphenolic compound isolated fromAnemarrhena.C-glycoside,which is isolated from mango leaves,is a type of mangiferin exhibiting biological activities.It reduces blood glucose levels and contributes to the regeneration of pancreas and islet cells in rats with diabetes[50].Neurogenin-3 (Ngn3) is a marker of new endocrine progenitor β cells[51].A previous study reported that mangiferin increased the expression of Ngn3,FoxO-1,and PDX after partial pancreatectomy in mice and contributed to the proliferation of β cells.Mangiferin can also regulate the cell cycle through the activation of p16INK4a and promote islet regeneration in rats[52,53].
Terpenoids: Geniposide is widely found in herbs.It exhibits anti-inflammatory,antioxidative,and antidiabetic effects[54].T cell transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) is a key factor involved in the Wnt/β-catenin pathway,which is an important regulator of β cell survival and regeneration.Geniposide reportedly increases the expression of TCF7L2 by activating Wnt signaling[55].Furthermore,it inhibits GSK3β activity as well as promotes the nuclear translocation of βcatenin and regeneration of β cells.Geniposide can also induce ductal cell differentiation by upregulating TCF7L2 expression and activating the JAK2/STAT3 pathway.Thus,it can promote β cell survival and regeneration by activating β-catenin/TCF7L2 signaling[56].
Astragalusbelongs to the legume family and possesses many pharmacological properties,including antidiabetic,antioxidative,anti-inflammatory,and antiapoptotic effects[57].A previous study reported thatAstragalusstrengthens the structure of pancreatic islet cells;the researchers also reported the appearance of new pancreatic islet cells and abundant capillaries around the islets,which promote β cell regeneration in HDF/STZ-induced Wistar rats with diabetes[58].
Quinones: Thymoquinone is the most abundant constituent in the volatile oil ofNigella sativaseeds.It exerts antioxidative,anti-inflammatory,and immunomodulatory effects[59].In rats with diabetes,treatment with thymoquinone can efficiently ameliorate the histomorphological deteriorations of pancreatic islets,replenish the mass of β cells;and restore the function of β cells[60].It has also been shown that thymoquinone inhibits COX-2 activity,relieves lipid peroxidation,and enhances antioxidative enzyme activity,thereby protecting pancreatic β-cells[61].
Inhibition of β cell apoptosis
β cell apoptosis is a common pathological feature of T2DM.Mass production of superoxide ions and endoplasmic reticulum stress caused by high concentrations of free fatty acids lead to β cell apoptosis and dysfunction.Furthermore,the impaired balance between oxidation and antioxidation promotes β cell apoptosis and dysfunction[62,63].Excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species induces IR and chronic inflammation through abnormal changes in intracellular signaling pathways[64].Inflammation also promotes β cell apoptosis and dysfunction[64,65].
Flavonoids: The decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential is an early indicator of apoptosis[66].Previous studies have reported that quercetin reverses the decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential,inhibits the activation of caspase-3,caspase-9,and caspase-12,and increases the Bcl-2/Bax ratio,thereby suppressing apoptosis[38,67].Quercetin also protects islet β cells from oxidation-induced apoptosisviaSIRT3.After treating INS-1 cells and mice with diabetes were treated with quercetin,superoxide dismutase 2 and SIRT3 proteins levels increased,whereas the cleaved caspase-3 levels and Bax/Bcl-2 ratio decreased,along with reduced blood glucose levels and elevated insulin levels[68].
According to a previous study,cyanidin-3-glucoside decreased the apoptotic rate,intracellular ROS generation,and caspase-3 activity as well as reduced MAPK phosphorylation in MIN-6 cells treated with high levels of glucose[69].The same results were observed in MIN-6 cells treated with H2O2[70].A previous study revealed that anthocyanins protected the pancreatic tissue from STZ-induced apoptosis by regulating the levels of caspase-3,Bax,and Bcl-2 proteins in rats with diabetes[71].
Kaempferol is a flavanol compound found in various Chinese medicinal herbs[72].It has been reported that kaempferol protects β cells and human islets from palmitate-induced apoptosisviathe upregulation of the PDX-1/cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling cascade[73],increases the expression of Bcl-2viaCREB to activate the PI3K/Akt pathway,maintaining β-cell survival under high-glucose conditions,and reduces the expression of caspase-3[74].
Icariin is the main active ingredient of the natural medicine epimedium.It is considered a potential therapeutic agent for various diseases and is known to exert antioxidative,antineuroinflammatory,and antiapoptotic effects[75].Icariin reportedly increasesGLUT4mRNA expression and promotes AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) phosphorylation to reduce the loss of islets in the pancreatic tissue[76].
Puerarin promotes the proliferation and reduces the apoptosis of pancreatic β-cells.It also reverses the effect of impaired glucose tolerance[41,42].Isoflavone glycosides (the main component of puerarin) inhibit apoptosis and protect β cellsviaAkt phosphorylation[43].
Polyphenols: Resveratrol reportedly alleviates uric acid-induced apoptosis,reduces the expression of Bax,cleavedcaspase-3,and iNOS,and activates the PI3K/Akt pathway by upregulating the expression of miR-126[77].A previous study demonstrated that ROS overproduction affected cell apoptosis by destroying the mitochondrial membranes,releasing cytochrome C,and stabilizing HIF-1 and p53[78].Previous research has also revealed that resveratrol inhibited the production of ROS and HIF-1α[79].Another study showed that the PI3K/Akt pathway reduced ROS production and inhibited p53 expression and pancreatic islet cell apoptosis[80].
Curcumin possesses antiapoptotic activity and improves the function of pancreatic islets.On the one hand,it interferes with the interaction among Beclin1,Bcl-2,and Bim through the signal pathway mediated by JNK-1 and AMPK,thereby regulating the transition between apoptosis and autophagy[81,82].On the other hand,it decreases palmitate-induced oxidative stress in pancreatic islet cells by regulating the NADPH pathway,increases insulin levels,reduces the expression of cleaved caspase-3 and Bax,and protects cells from apoptosis[83].
Alkaloids: In a previous study,overexpression of independent phospholipase A2β and treatment with berberine significantly attenuated palmitate-induced apoptosis.Furthermore,silencing independent phospholipase A2β partially abolished the antiapoptotic effect of berberine and inhibited cardiolipin/Opa1 signaling in MIN6 cells[84].In another study,coffee ingestion protected β cells from STZ cytotoxicity,suppressed hyperglycemia,inhibited β cells apoptosis,and maintained the pancreatic insulin content by inhibiting the activity of poly ADP ribose polymerase[85].Based on a previous research,caffeic acid,naringin and quercetin increased the expression of GLUT2,Ins1,β2,Pdx1,Akt1,Bcl2 and Hsp70/90,reduced the expression of caspase-3 and Bax,and inhibited apoptosis of INS-1E cells[86].
Terpenoids: Mangostin reduces ROS,p38,and JNK phosphorylation,restores the impaired secretory function of pancreatic β cells,and exerts its antiapoptotic effect on STZ-induced INS-1 cells[87].Geniposide inhibits the apoptosis of INS-1 cells induced by high levels of glucose,thereby preventing caspase-3 cleavage.Further research demonstrated that AMPK siRNA attenuated the effects of geniposide on apoptosis-associated proteins and cell viability,suggesting that AMPK plays a key role in protecting β cells from high-glucose-induced apoptosis[88].According to a previous study,pretreatment with licorice extract inhibited the expression of caspase-3,caspase-8,caspase-9,and other apoptotic factors as well as the expression of p-STAT1,thereby hindering STZ-induced β cell apoptosis[89].
Paeoniflorin is a glycoside extracted from the root ofPaeonia lactifloraPall.It inhibits the activation of the p38MAPK and JNK signaling pathway and reduces the phosphorylation of p38MAPK and ERK1/2 by increasing the expression of Bcl-2 and inhibiting the expression of Bax and caspase-3.It also increases the survival rate of STZ-induced INS-1 cells[90].
REDUCTlON OF ADlPOSE TlSSUE lNFLAMMATlON
Adipose tissue is an important endocrine organ that regulates insulin sensitivity and energy homeostasis throughout the body.It can secrete various hormones such as adiponectin,leptin,resistin,and visfatin as well as typical cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6.It can also activate the MAPK and NF-κβ pathways[10,91].Adipose tissue inflammation is a mechanistic pathogenesis of T2DM.Fat-infiltrated macrophages,basophils,and regulatory T cells cooperate with adipocytes to mediate adipose tissue inflammation by secreting proinflammatory factors[92].Activation of monocytes and release of MCP-1 cause the transformation of white fat cells into the proinflammatory phenotype[93].MCP-1 recruits macrophages into adipose tissue,which in turn produce inflammatory cytokines.PPARα/γ agonists also reduce the expression of IL-6,CXC-L10,and MCP-1 in human adipocytes[94].
Flavonoids
Butein is isolated from the bark of the sumac tree.It exerts antioxidative,anti-inflammatory,antidiabetic,and neuroprotective effects[95].It has been reported that pretreatment with butea results in the complete blockade of TNF-α-induced IκB-α degradation,prevents p65 phosphorylation at Ser311 and Ser536,and inhibits ERK,JNK,and p38MAPK phosphorylation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes[96].These results are consistent with the previous findings,indicating that butein suppresses the expression of IL-6,TNF-α,and MCP-1,increases the expression of HO-1,and activates the p38MAPK/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in the epididymal white adipose tissue of HFD-fed mice[97].These findings suggest that butein plays an anti-inflammatory role in adipocytesin vitroandin vivo.
Naringin possesses strong antioxidative activity.Previous studies have demonstrated that naringin suppresses TNF-α-induced activation of NF-κB and ERK pathways in 3T3-L1 adipocytes[98].Naringenin presumably exerts an anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting IκB-α degradation and p-JNK expression,thereby inhibiting the expression of TLR2 in TNF-α induced adipocytes[99].It was found to suppress macrophage infiltration into the adipose tissue by inhibiting MCP-1 production[100].A recent study demonstrated that naringenin suppresses neutrophil infiltration into the adipose tissue by regulating MCP-3 expression and macrophage infiltration[101].
SIRT1 activators suppress inflammatory responses by promoting p65 deacetylation and inhibiting NF-κB activity in adipocytes[102].Quercetin increases antioxidative activity as well as p-AMPK and SIRT1 expression in the adipose tissue of HFD-fed mice.Moreover,it reduces proinflammatory enzymatic activity and cytokine levels[103].
Polyphenols
Cranberry contains various types of bioactive components with high antioxidative and anti-inflammatory potentials.It also exerts beneficial effects on adipogenesis and lipid metabolismin vitro[104].Cranberries reportedly reduce lipid accumulation during adipocyte differentiation by decreasing the levels of acid-binding protein,lipoprotein lipase,fatty acid synthase,and perilipin 1[105].In addition,they reduce H2O2-induced inflammation in 3T3-L1 cells by decreasing the expression of IL-6,PAI-1,MCP-1,and leptin in adipose tissue[106].
Peanut skin extract is a rich source of polyphenols[107].It is effective in the treatment of various diseases,such as DM,obesity,and inflammation[108-110].A previous study reported that peanut skin extracts significantly alleviate adipose tissue inflammation by reducing the expression of TNF-α,IL-1β,IL-6,and PAI-1[109].
According to another study,the combined use of curcumin and resveratrol inhibited the activation of NF-κB,decreased the expression of IL-1β,TNF-α,IL-6,and COX2,and reduced the damage induced by chronic inflammation in adipocytes[111].Based on a previous study,luteolin increases the expression of p-AMPK and SIRT1,suppresses the expression of pp65,and decreases the mRNA expression ofTNF-α,IL-6,andMCP-1in 3T3-L1 cells[112].Studies have shown that SIRT1 inhibits NF-κB activation[113],and AMPK antagonizes inflammation through SIRT1[114].
NATURAL PRODUCTS CAN TREAT T2DM BY lNHlBlTlNG lR
IR usually refers to the reduction in insulin-induced glucose uptake and utilization efficiency in the muscle,body fat,and liver,leading to compensatory INS,which ultimately results in a series of clinical manifestations such as hyperglycemia,hyperinsulinemia,and dyslipidemia[115,116].A previous study reported that lipid accumulation in the liver and adipose tissue accelerated IR in patients with T2DM[117].Inflammatory factors such as TNF-α and IL-6 activate the NF-κB pathway and inhibit the expression of IRS-1 and GLUT4,thereby promoting IR[118,119].IL-1β also inhibits the IRS-1 pathway and promotes IR[120].In general,IR is related to the NF-κB,JNK,p38MAPK,and PI3K/Akt pathways.When the energy intake is high,the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway can alleviate obesity and IR[121](Figure 2).
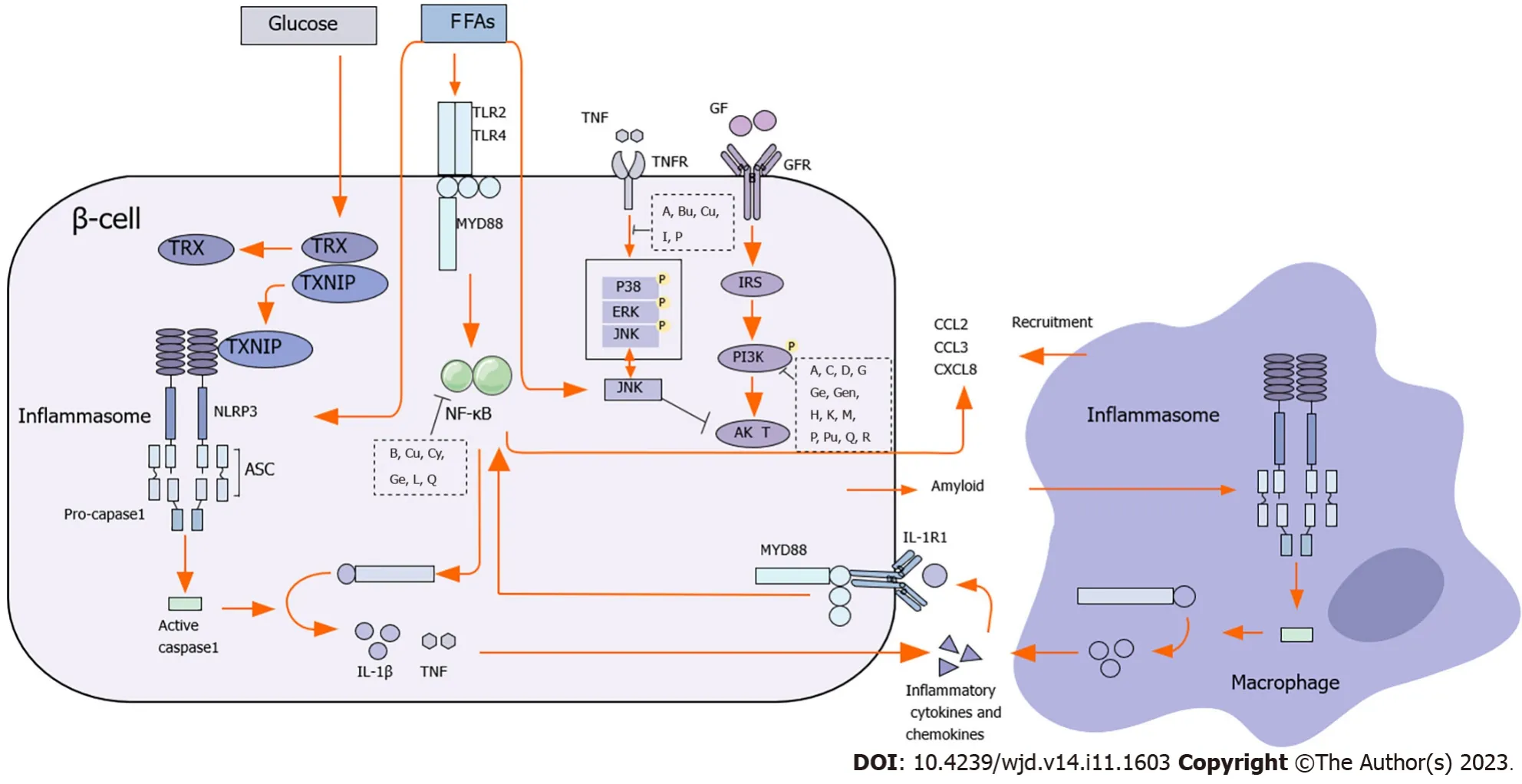
Figure 2 The mechanism of natural products suppresses insulin resistance. The letters inside the black squares refer to natural products.A: Alphamangostin;B: Berberine;Bu: Butein;C: Caffeic acid;Cu: Curcumin;Cy: Cyanidin-3-glucoside;D: Dioscorea batatas extract;G: Gallic acid;Ge: Genistein;Gen: Geniposide;H: Hesperidin;I: Icarrin;K: Kaempferol;L: Leteolin;M: Mulberry anthocyanin extract;P: Paeoniflorin;Pu: Puerarin;Q: Quercetin;R: Resveratrol;CHOP: CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein homologous protein;ER stress: Endoplasmic reticulum stress;FFA: Free fatty acids;FOXO: Forkhead box class O;GFR: Growth factor receptor;GR: Growth factor;IKK: Inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappa B kinase;IL-1β: Interleukin 1β;IL-1: Interleukin 1;iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase;IRAK: Interleukin 1 receptor-associated kinase;JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase;mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin;NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B;NO: Nitric oxide;PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase;ROS/RNS: Reactive oxygen/nitrogen species;STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription;STAT1: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1;STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3;TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha;TNFR: Tumor necrosis factor receptor.
Flavonoids
Anthocyanins reportedly improve INS and IR[122].A previous study showed that mulberry anthocyanin extract activates the PI3K/Akt pathway,increases the phosphorylation of its downstream target GSK3β,activates GYS2,and alleviates IR in HepG2 cells induced by high levels of glucose and palmitic acid.According toin vivoexperiments,mulberry anthocyanin extract reduces the secretion of leptin and insulin and increases the levels of adiponectin in the serum,thereby improving IR[123].
According to a previous study,baicalein reduced the expression of TNF-α and F4/80,activated AMPK,p-AKT,and IRS-1,and induced dephosphorylation of ERK,NF-κB and JNK,thereby reducing IR[124].A study by Puet al[125] confirmed that the inhibitory effect of baicalein on IR was mediated by the inhibition of the MAPK pathway and activation of the IRS1/PI3K/Akt pathway.
Naringin possesses strong antioxidative activity.It reportedly increases the expression of GLUT4,adiponectin,and Ch-REBPβ in white adipocytes,promotes energy consumption and insulin sensitivity,and inhibits the proliferation of fat cells[126].
Polyphenols
Gallic acid increases the expression of PPAR-γ in the adipose tissue,liver,and skeletal muscle,enhances tyrosine kinas activity,promotes IRS phosphorylation,and improves insulin-dependent glucose transport through GLUT4 in the PI3K/p-Akt dependent pathway in the adipose tissue,thereby improving IR in rats[127].Adiponectin plays an important role in regulating insulin function as well as the occurrence and development of T2DM[128].Gallic acid reduces the levels of serum total cholesterol and triglycerides by inhibiting adipogenesis and increasing adiponectin activity.The combined use of gallic acid and p-coumaric acid increases the levels and mRNA expression of PPAR-γ and reduces the levels of serum adiponectin in STZ-induced rats with diabetes[23].
Luteolin reportedly reduces blood lipid and glucose and improves hyperinsulinemia and IR through PPAR-γ[129].It increases the absorption of circulating free fatty acids and reduces liver fat toxicity by increasing the protein expression of PPARγ in the adipose tissue[130].In HFD-fed mice,luteolin reduces lipid formation,increases fatty acid oxidation,and significantly reduces the levels of IL-1,IL-6,and PAI-1,thereby improving obesity and metabolic disorders[131].
Terpenoids
HFD-induced IR in mouse visceral adipose tissue is characterized by increased p-ERK and decreased p-Akt expression.The therapeutic effect of theDioscorea batatasextract decreased the protein expression of p-ERK and p-S6K1 and enhanced the translocation of GLUT4 to the plasma membrane of the visceral adipose tissue in mice.It has been speculated that theDioscorea batatasextract attenuates IR by upregulating the expression of GLUT4 in the plasma membrane of the visceral adipose tissue in HFD-fed mice[132].The discoloration mixture ofAstragalus membranaceusandPotentilla anserinareportedly increases the mRNA expression ofPPARγandPI3Kin the liver,reduces FPG levels,and improves IR in mice[133].
CLlNlCAL STUDY ON NATURAL PRODUCTS lN THE TREATMENT OF DM
To date,only a few clinical studies have been reported on natural medicines for treating DM.Most previous studies have focused on the addition of natural medicines to the diet to examine their effects on blood glucose levels,blood lipid levels,and body mass index in patients with T2DM.The addition of soluble fibers from psyllium to the normal diet of patients with T2DM significantly improved the levels of fasting blood sugar,hemoglobin A1c,C-peptide,Homeostasis Model Assessment-IR,and Homeostasis Model Assessment-B after 8 wk of administration[134].A study by Noureddinet al[135] also showed that psyllium supplementation decreased the body weight,blood glucose levels,and cholesterol levels and increased the high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in patients with T2DM.Similar results were reported in other clinical trials[136,137].
A previous study showed that dietary raspberries significantly reduced serum glucose levels at 2 h and 4 h after intake and decreased the serum levels of IL-6 and TNF-α[138].These results indicated that propolis increased the serum activity of superoxide dismutase and GPx,decreased the levels of fasting blood sugar,2-h postprandial glucose and insulin,and alleviated IR[139].In a previous study,based on the results of the area under the curve,the consumption of bitter melon for 3 mo increased INS and decreased the body weight,body mass index,and glucose in patients with T2DM,possibly by increasing uncoupling protein expression or inhibiting PPAR-γ[140].
These results indicated that quercetin intake was inversely correlated with T2DM prevalence in the Chinese population.Moreover,quercetin intake reduced pancreatic β-cell inflammation,thus successfully treating T2DM[141].
CONCLUSlON
Accumulating studies including clinical trials and animal experiments have confirmed the effectiveness of natural products.In vivoandin vitrostudies have demonstrated that the active ingredients of monomeric compounds,such as flavonoids,polyphenols,alkaloids,terpenes,and quinones in natural medicines can inhibit the release of inflammatory mediators and reduce oxidative stress.Thus,reduction in IR and lipid accumulation can protect islet cells and treat T2DM.The mechanisms by which natural medicines treat T2DM include the following: (1) β cell inflammation was mainly inhibited by IKK/IκB/NF-κB,PI3K/Akt,and SIRT1/NF-κB pathways;(2) β cell regeneration was mainly promotedviaERK1/2/MDA,PI3K/Akt/mTOR,Wnt/β-catenin,and JAK2/STAT3/Ngn3 pathways;(3) β cell apoptosis was inhibited through MAPK/caspase-3,PI3K/Akt/caspase-3,and SIRT1/HIF-1/P53 pathways;(4) Adipose tissue inflammation was attenuated by PPAR-γ/SREBP,TGF-β/STAT3/Smad2/3,P38MAPK/Nrf2/HO-1,JNK/MCP-1,and AMPK/SIRT1 pathways;and (5) IR was alleviated mainly through IRS1/PI3K/Akt,TGF-β/Smad,LKB1/AMPK/PGC1α,and mTOR/S6K1 pathways (Figure 3).
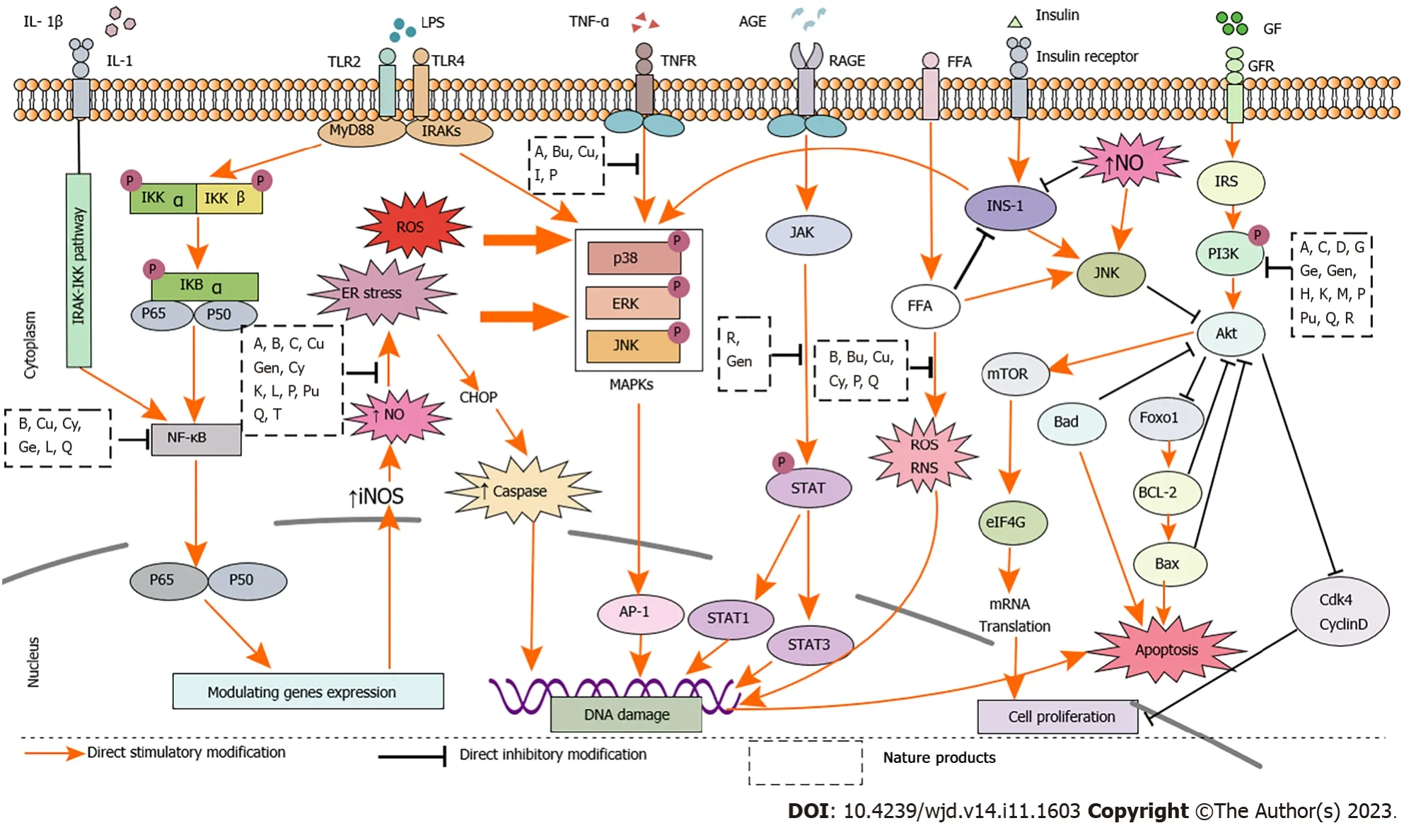
Figure 3 Mechanisms of natural products for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. The letters inside the black squares refer to nature products.Inhibitory effects were shown by black pathways.A: Alpha-mangostin;B: Berberine;Bu: Butein;C: Caffeic acid;Cu: Curcumin;Cy: Cyanidin-3-glucoside;D: Dioscorea batatas extract;G: Gallic acid;Ge: Genistein;Gen: Geniposide;H: Hesperidin;I: Icarrin;K: Kaempferol;L: Leteolin;M: Mulberry anthocyanin extract;P: Paeoniflorin;Pu: Puerarin;Q: Quercetin;R: Resveratrol;Akt: serine/threoninekinase;AGE: Advanced glycation end products;AP-1: Activator protien-1;Bad: Bcl2 associated death promoter;Bax: BCL2-Associated X;Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma-2;Cdk4: Cyclin dependent kinase 4;CHOP: CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein homologous protein;eIF4G: Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4G;ER stress: Endoplasmic reticulum stress;FFA: Free fatty acids;FOXO: Forkhead box class O;GFR: Growth factor receptor;GR: Growth factor;IkBa: Inhibitory subunit of NF Kappa B Alpha;IKK: Inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappa B kinase;IL-1β: Interleukin 1β;IL-1: Interleukin 1;iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase;IRAK: Interleukin 1 receptor-associated kinase;JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase;mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin;NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B;NO: Nitric oxide;PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase;ROS/RNS: Reactive oxygen/nitrogen species;STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription;STAT1: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1;STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3;TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha;TNFR: Tumor necrosis factor receptor.
Commonly used drugs for treating T2DM,such as α-glutaminase inhibitors,sulfonylureas,biguanides,and glitalactone,can be used alone or in combination to regulate blood glucose levels.However,the multiple side effects and high cost of these drugs have led to the urgent need to explore natural medicines to treat T2DM.In recent years,an increasing number of studies have explored various effective active ingredients of natural medicines for treating T2DM to discover a new alternative medicine.The plants and their main components reported in this review can alleviate the effects of T2DM on the body to a certain extent and provide a theoretical basis for the development of new drugs.Further studies in the following areas are still warranted: (1) The potential toxicity of natural medicines and the interactions between drug compatibilities remain unclear.Common adverse effects associated with the intake of natural medicines include gastrointestinal disturbances such as abdominal pain,diarrhea,constipation,nausea,and vomiting[142-145].However,more severe toxicities may occur and affect patients’ cardiovascular systems,auditory functions,or reproductive health[146,147].Furthermore,the concomitant use of natural medicines and established antidiabetic drugs may increase the risk of hypoglycemia in patients with T2DM[148].Thus,further studies are warranted on the specific mechanism of action and long-term toxic side effects of these natural products;and (2) Although some natural products have shown positive effects in cell and animal models,their activities have not yet been verified.Thus,further clinical studies are warranted to confirm the efficacy of natural medicines.
FOOTNOTES
Co-first authors:Tao Wang and Yang-Yang Wang.
Author contributions:Wang T and Wang YY reviewed and summarized the literature and wrote the paper;Shi MY revised the manuscript;Liu L designed and revised the manuscript;Liu L is the guarantor of this work.All authors were involved in the critical review of the results and have contributed to,read,and approved the final manuscript.Wang T and Wang YY contributed equally to this work as co-first authors.The reasons for designating Wang T and Wang YY as co-first authors are threefold.First,the research was performed as a collaborative effort,and the designation of co-corresponding authorship accurately reflects the distribution of responsibilities and burdens associated with the time and effort required to complete the study and the resultant paper.This also ensures effective communication and management of post-submission matters,ultimately enhancing the paper's quality and reliability.Second,the overall research team encompassed authors with a variety of expertise and skills from different fields,and the designation of cocorresponding authors best reflects this diversity.This also promotes the most comprehensive and in-depth examination of the research topic,ultimately enriching readers' understanding by offering various expert perspectives.Third,Wang T and Wang YY contributed efforts of equal substance throughout the research process.The choice of these researchers as co-first authors acknowledges and respects this equal contribution,while recognizing the spirit of teamwork and collaboration of this study.In summary,we believe that designating Wang T and Wang YY as co-first authors of is fitting for our manuscript as it accurately reflects our team's collaborative spirit,equal contributions,and diversity.
Supported bythe Nature Science Foundation of Hubei Province,No.2023AFB839.
Conflict-of-interest statement:The authors declare having no conflicts of interest.
Open-Access:This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers.It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license,which permits others to distribute,remix,adapt,build upon this work non-commercially,and license their derivative works on different terms,provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial.See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Country/Territory of origin:China
ORClD number:Tao Wang 0009-0006-7818-6062;Yang-Yang Wang 0000-0003-3010-8613;Meng-Yue Shi 0000-0002-3890-8335;Lian Liu 0000-0001-6489-227X.
S-Editor:Lin C
L-Editor:Filipodia
P-Editor:Yu HG
杂志排行
World Journal of Diabetes的其它文章
- Cellular and molecular overview of gestational diabetes mellitus: ls it predictable and preventable?
- Exploring the targets and molecular mechanism of glycyrrhetinic acid against diabetic nephropathy based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
- Molecular targets and mechanisms of Jiawei Jiaotai Pill on diabetic cardiomyopathy based on network pharmacology
- Vascular endothelial growth factor B improves impaired glucose tolerance through insulin-mediated inhibition of glucagon secretion
- Reduced risk of dementia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus using Chinese herbal medicine: A nested case-control study
- Molecular mechanisms of noncoding RNA and epigenetic regulation in obesity with consequent diabetes mellitus development
