A comparative study of two methods for establishing a chronic non-bacterial prostatitis model in rats
2023-11-23TANGYiwenWANGXiongZHOUYanyanCHENHaoteZHANGZejiaWANGZhongGAOQingheLIUJiangangGAOZhan
TANG Yi-wen, WANG Xiong, ZHOU Yan-yan, CHEN Hao-te, ZHANG Ze-jia, WANG Zhong, GAO Qing-he, LIU Jian-gang, GAO Zhan✉
1.Graduate School of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine,Beijing 100029,China
2.Department of Urology, Xiyuan Hospital, Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100091, China
3.Department of Male Medicine, Xiyuan Hospital, Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100091, China
4.Institute of Cardiovascular Diseases, Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100091,China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To compare the biological characteristics and stability of the chronic non-bacterial prostatitis (CNP) model in rats induced by the depot combined with estrogen induction method and the autoimmune response induction method.Methods: The CNP rat model was prepared using the depot combined with 17β-estradiol induction method in the depot hormone group and three concentrations of prostate protein homogenate at 40 mg/mL, 20 mg/mL and 10 mg/mL in the autoimmune group, respectively.The degree of prostate tissue damage was evaluated by pathology (HE staining), and the immunoturbidimetric method was used to evaluate the contents of immunoglobulins IgA, IgM and IgG.ELISA was used to evaluate interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-10 (IL-10), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)and high-sensitivity-C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), and electrochemiluminescence was used to evaluate the expression level of testosterone (T), and the two model methods were compared.Results: Compared with the sham-operated group, the body mass of rats in both models was significantly lower in the depot hormone group and autoimmune group before extraction(P<0.01, P<0.01), and histopathology of the prostate in both models showed destruction of glandular structure and a significant increase in inflammatory cells.Compared with the depot hormone group and the autoimmune group, the histopathological changes and inflammatory pathological scores of prostate and the contents of immune indexes IgA, IgM and IgG were significantly different in the depot hormone group (P<0.05, P<0.05, P<0.05), and the levels of IL-1β, IL-10, TNF-α, hs-CRP and T were significantly changed in the autoimmune group (P<0.01).The comparison between the high, medium and low dose groups of the autoimmune group, in which the pathological changes in the medium dose of the autoimmune group were slightly better than the other two groups between the groups, but the changes in IL-1β, IL-10,TNF-α, hs-CRP, and T in the low dose of the autoimmune group were the most significant (P<0.05).Conclusion: The pathological tissues of the chronic non-bacterial prostatitis model established by the depot combined with estrogen induction method and the autoimmune response induction method both showed significant changes, and the comprehensive indexes indicated that the depot combined with estrogen induction method was a more appropriate modeling choice.
Chronic nonbacterial prostatitis (CNP) is a common urological disease that accounts for more than 90% of all prostatitis.[1, 2]It is the most common and most complex clinical syndrome of prostatitis because of the special anatomical and physiological characteristics of the prostate gland, resulting in a variety of clinical manifestations and recurrent symptoms that are difficult to heal.[3]The most common and complex clinical syndrome is prostatitis.It is a common and complex clinical syndrome in prostatitis.Current studies have found that pathogenic infections, urinary reflux,
1.Introduction
neuroendocrine factors, and oxidative stress are all associated with the development of prostatitis, with immune factors playing an important role in the development of CNP.[4, 5].The establishment of animal models of immune factors CNP is an important basis for conducting research on the etiology of CNP and drugs.Currently,animal models of prostate immune factors include depot combined with estrogen-induced, autoimmune response-induced, and spontaneous CNP models[6] In this study, we intend to use these two methods to establish CNP models, compare the characteristics,pathology and various indicators of the two models, explore the optimal choice of preparing CNP animal models, and provide better animal models for future experimental studies of drug prevention and treatment of CNP.
2.Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental materials
2.1.1 Experimental animals
Thirty-two healthy SPF-grade, male, Wistar rats, body mass (200± 20) g, provided by Spelford (Beijing) Biotechnology Co., Ltd[SYXK (Beijing) 2019-0030], were housed in the barrier-level laboratory animal room of Xiyuan Hospital, Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine [SYXK (Beijing) 2018-0018].Feeding environment: housed in a barrier system, temperature 22℃~26 ℃, humidity controlled at 40%~70%, by 12h light/dark cycle, ad libitum diet.The feed was provided by Beijing Science and Technology Co-operative Feed Co., Ltd [Beijing Feeding Certificate(2014) 06054].Drinking water: sterilized water in drinking bottles for experimental animals to drink freely.
2.1.2 Reagents
0.9% saline (Shandong Chenxin Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Lot No.1211040591); 10% chloral hydrate (International Group Chemical Co., Ltd., Lot No.20050805); estradiol benzoate (Solarbio, Lot No.WXBD0151V); Freund’s complete adjuvant (CFA) (Sigma, Lot No.C104202); BCA protein concentration kit (Shanghai Biyuntian Biotechnology Co.C104202); BCA Protein Concentration Kit(Shanghai Biyuntian Biotechnology Company, Lot No.P0010); IgA,IgG, IgM Kit (Beijing Huaying Institute of Biotechnology, Lot No.20220416BH); Interleukin-1β (IL-1β), Interleukin-10 (IL-10),Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α), High Sensitivity-C Reactive Agent (HACRA), and Estradiol Benzoate (Solarbio, Lot No.WXBD0151V).), high-sensitivity-C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) kits(Beijing Xinbosheng Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Lot No.20220428X);T kits (Shanghai Roche Diagnostic Products Co., Ltd., Lot No.48879601).
2.1.3 Instruments
Model 3-18K low temperature centrifuge (SiGma, USA); Model T18 disperser (IKA, Germany); Model DNP9082 electrothermal constant temperature flat incubator (Shanghai Jinghong Experimental Equipment Co., Ltd.); Model MultiSkan3 enzyme marker (Thermo, USA); Model EG1150 pathology embedding machine (Leica, Germany); Model 7160 automatic biochemistry instrument (HITACHI, Japan); DR-200BS type automatic enzyme standard analyzer (Wuxi Huawei Delong Instrument Co., Ltd.).
2.2 Experimental method
2.2.1 Model construction and grouping
After 7 d of acclimatization, the rats were divided into five groups according to a randomized control table, six in the sham-operated group, eight in the depot combined with estrogen-induced CNP model group (depot hormone group), and three in the autoimmune prostatitis (EAP) group, eight in the EAP protein high-dose group(high EAP group), The EAP protein medium dose group (medium EAP group) was 6, and the EAP protein low dose group (low EAP group) was 6.
The rats were anesthetized with 10% chloral hydrate intraperitoneally (0.2 mL/kg body mass), the limbs and head and neck were fixed in the supine position, the perineal area was fully exposed, the perineal area was prepared with skin and sterilized with towels, the skin of the scrotum was cut with ophthalmic scissors, the testes on both sides were separated to the sheath layer by layer, the testes and epididymis were separated bluntly, the root of the testes were ligated with silk, the spermatic cord was cut, and the testes were removed.Carefully observe the severed end of the ligature and confirm that there is no active bleeding.The wound was disinfected,sutured layer by layer, disinfected again, and put back into the rat cage.Penicillin was injected intramuscularly (dose 250,000 U-kg, 0.1 mL each) at 4 points on the back for 3 consecutive days after surgery to prevent infection.Estradiol benzoate was injected subcutaneously into the back of the rats at a dose of 0.25 mg·kg-1·d-1daily for 30 d starting on the second postoperative day.A model of chronic prostatitis in rats could be prepared on day 31, and the model could be maintained for not less than 30 d[7] The model can be maintained for not less than 30 d.In the sham-operated group, the surgical procedure was the same as before, but the only difference was that the testis and epididymis were separated bluntly, and the wound was sutured and put back into the cage.
For EAP modeling, the prostate tissue from the prepared rats was placed in saline, trimmed of fat, bladder and excess tissue, washed 2-3 times, cut and stirred prostate tissue, added saline solution containing 0.5% Triton-100, homogenized in ice bath, centrifuged at 12 000 r/min for 30 min at 4 ℃.After centrifugation, the upper layer of fatty tissue was aspirated, and the supernatant was sucked into a freezing tube for The supernatant was frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -20 ℃ for backup.The protein concentration was measured by BCA before use, and according to the measured protein concentration, the protein purification solution was diluted into 40 mg/mL, 20 mg/mL and 10 mg/mL high, medium and low concentrations respectively with 0.01 mmol/L PBS.0.5mL of prostate protein purification solution high, medium and low concentrations were mixed with 0.5 mL of complete Freund’s adjuvant in equal proportions, and a total of 1ml was used.On days 0, 15 and 30 of the modeling, 1ml of the high, medium and low concentrations were injected subcutaneously at 4 points on the back and 0.5mL of the vaccine was injected intraperitoneally for 45 d.The rat EAP model could be prepared on day 46, and the maintenance time of this model was not less than 30 d.[7] The maintenance time of this model was not less than 30 d.
2.2.2 Specimen collection
After the end of the modeling time for each group, the rats were weighed, anesthetized again, blood was taken from the abdominal aorta, and then centrifuged at 3 000 r/min for 10 min after 1 h of resting, and the serum was separated and stored at -80 ℃.The prostate tissue was removed from the rats, stripped of peritoneal and adipose tissue, washed 2~3 times with saline, blotted dry with filter paper, weighed on an electronic balance, and the prostate index was calculated for each group of rats, i.e.prostate wet weight/body mass, and treated by CO2anaesthesia after the end of sampling.The experimental process strictly followed the 2011 revised version of the Regulations for the Administration of Laboratory Animals and related regulations, and the animal experiments were approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Xiyuan Hospital, Chinese Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine (ethical approval number:2022XLC043-2).
2.3 Model evaluation
2.3.1 General
The rats were weighed and recorded weekly during the modeling period, and the amount of food and water intake, hair condition and general activity were observed daily.
2.3.2 Histopathological evaluation of the prostate
The prostate tissues of each group of rats were selected and stored in 10% formalin solution for 72 h, washed, dehydrated, transparent,waxed, embedded and baked at room temperature, then sealed with HE staining and observed the local pathological changes of the prostate under light microscope.The rest of the slices were kept as homogenate for prostate tissue index determination.
2.3.3 Prostate histopathology score for inflammation
The prostate tissue was evaluated from four indicators:inflammatory cells, fibroblasts, glandular lumen size, and secretions.Inflammatory cells: 0 points: no inflammatory cell infiltration, 2 points: mild infiltration of inflammatory cells, 4 points: moderate infiltration of inflammatory cells, 6 points: severe infiltration of inflammatory cells.Fibroblasts: 0 points: no fibroblast hyperplasia,1 point: mild fibroblast hyperplasia, 2 points: moderate fibroblast hyperplasia, 3 points: severe fibroblast hyperplasia.Glandular lumen:0 points: large glandular lumen, 1 point: medium glandular lumen,2 points: small glandular lumen, 3 points: atresia or disappearance of glandular lumen.Secretion: 0 points: much secretion, 1 point:moderate secretion, 2 points: little secretion, 3 points: no secretion[8].
2.3.4 Measurement of serum immunoglobulins in rats
The IgA, IgM and IgG levels were determined by immunoturbidimetric method according to the kit requirements.
2.3.5 Determination of serum inflammatory factors in rats
The levels of IL-1β, IL-10, TNF-α and hs-CRP were determined by enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) double antibody sandwich method according to the kit requirements.
2.3.6 Determination of hormone levels in rat prostate tissue
Testosterone (T) levels were measured by electrochemiluminescence according to the kit requirements.
2.4 Statistical methods
SPSS27.0 and Graphpad Prism9.4.1 software were used for data processing and statistical analysis processing, and the measurement data were in the form of mean ± standard deviation±s), and oneway analysis of variance (ANOVA test) was used for comparison between groups if the variances were equal, and correction test was used if the normal distribution was not satisfied or the variances were not equal, and the Bonferroni test was used for multiple comparisons between groups.P< 0.05 was considered a statistically significant difference.
3.Results
3.1 General information of each group
Wistar rats in each group were kept according to the corresponding modeling method.2 rats in the depot hormone group died on day 2, and 2 rats in the high EAP group died at 36 d.The rats in the depot hormone group and the rats in the high, medium and low EAP groups showed obvious yellowing of the fur, decreased glossiness and slightly slow response.All rats were weighed every 7 d.Compared with the sham-operated group, there was a significant difference (P< 0.05)betweenthe deactivated hormone group from the 1st week; the rats in the high EAP, medium EAP and low EAP groups had statistically different differences (P< 0.05) from the 2nd,4th and 5th weeks, respectively.See Table 1.
The prostate index was calculated by weighing the wet weight of the prostate at the time of sampling.The prostate gland of the rats in the depot hormone group was extremely atrophied, with soft glands,reduced volume and adhesions to surrounding tissues, and the prostate index of the rats was highly significantly different compared with the sham-operated and EAP groups (P< 0.01,P< 0.01).There was no significant change between the three groups of high, medium and low EAP and sham-operated groups by visual observation (P> 0.05), slightly smaller volume and slightly harder prostate gland than the sham-operated group; there was no significant difference between the three groups of rats in the high, medium and low EAP groups (P> 0.05).See Figure 1.
Tab 1 Changes in body mass of rats in each group during the modeling period (g, ±s)
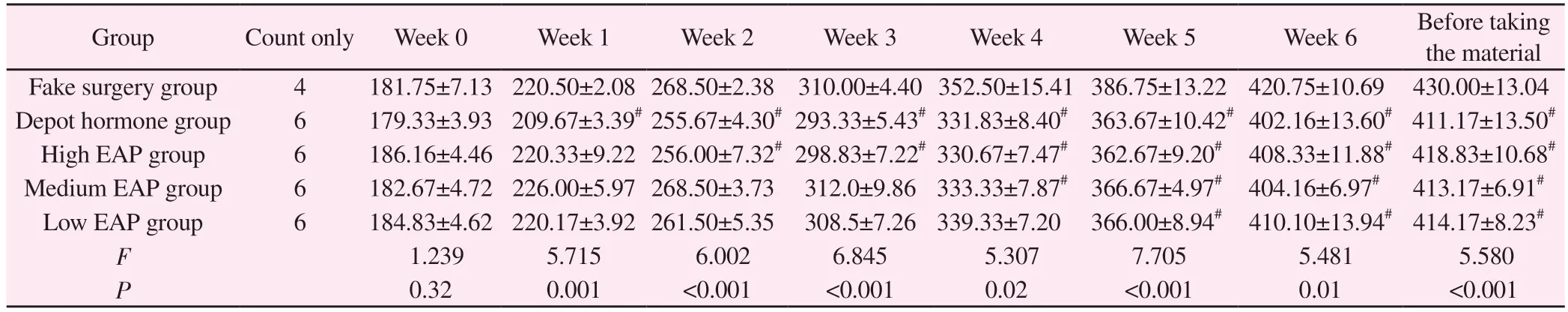
Tab 1 Changes in body mass of rats in each group during the modeling period (g, ±s)
Note: Compared with sham-operated group,# P < 0.05;## P < 0.01
Group Count only Week 0 Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Before taking the material Fake surgery group 4 181.75±7.13 220.50±2.08 268.50±2.38 310.00±4.40 352.50±15.41 386.75±13.22 420.75±10.69 430.00±13.04 Depot hormone group 6 179.33±3.93 209.67±3.39# 255.67±4.30# 293.33±5.43# 331.83±8.40# 363.67±10.42# 402.16±13.60# 411.17±13.50#High EAP group 6 186.16±4.46 220.33±9.22 256.00±7.32# 298.83±7.22# 330.67±7.47# 362.67±9.20# 408.33±11.88# 418.83±10.68#Medium EAP group 6 182.67±4.72 226.00±5.97 268.50±3.73 312.0±9.86 333.33±7.87# 366.67±4.97# 404.16±6.97# 413.17±6.91#Low EAP group 6 184.83±4.62 220.17±3.92 261.50±5.35 308.5±7.26 339.33±7.20 366.00±8.94# 410.10±13.94# 414.17±8.23#F 1.239 5.715 6.002 6.845 5.307 7.705 5.481 5.580 P 0.32 0.001 <0.001 <0.001 0.02 <0.001 0.01 <0.001
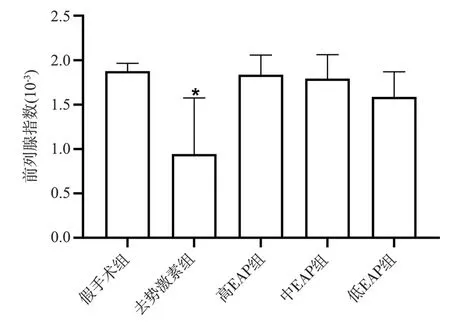
Fig 1 Prostate index of rats of each group
3.2 Comparison of the histopathology of the prostate gland in each group of rats
In the sham-operated group, the prostate tissue is structurally intact,with clear boundaries, regular lumen, normal glandular epithelial cell morphology, and no inflammatory reaction, see Figure 2A.In the high EAP group, the glandular structure was destroyed, the lumen was enlarged, and a small amount of inflammatory cell infiltration was seen, see Figure 2C.In the medium EAP group, the glandular structure was destroyed, the lumen was slightly enlarged,the glandular epithelium was reduced, and some inflammatory cell infiltration was seen in the interstitium, see Figure 2D.In the low EAP group, the glandular structure was destroyed, the lumen was loose, and a small amount of inflammatory cell infiltration was seen in the interstitium[8], see Figure 2E.
3.3 Comparison of inflammatory pathological scores of prostate tissue in various groups of rats
After modeling, compared with the sham-operated group, the inflammatory cells, fibroblasts, lumen size, and secretions in the lumen of the prostate tissue of the rats in the depot hormone group increased significantly, with significant differences (P< 0.05);compared with the sham-operated group, there was no significant difference in the inflammatory pathological score of the prostate tissue of the rats in the high, medium, and low EAP groups (P< 0.05); compared with the autoimmune group, there was no significant difference in the inflammatory pathological score of the rats in the depot hormone group compared with the high, medium,and low EAP groups.The inflammatory pathology scores of each index were significantly different between the three groups of depot hormone and high, medium and low EAP compared with the autoimmune group (P< 0.05); no significant difference was seen between the three groups of high, medium and low EAP compared with each other (P> 0.05).See Table 2.
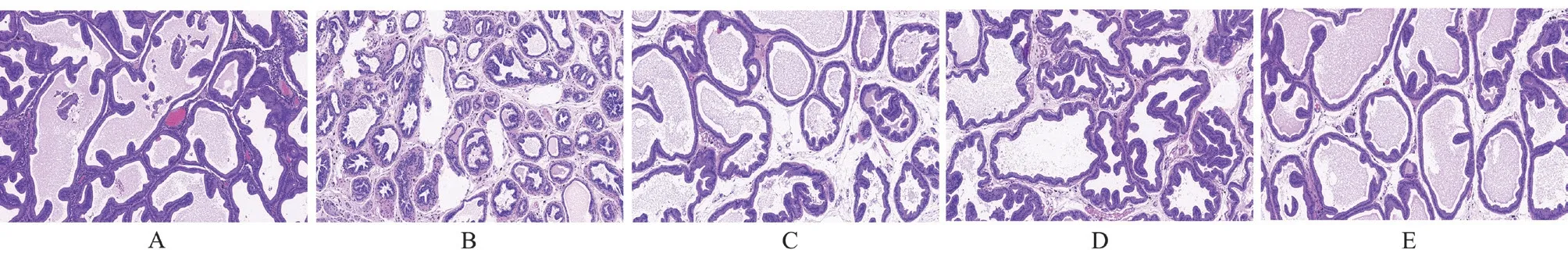
Fig 2 Observation of prostate tissue in rats of each group (HE,×100)
Tab 2 Comparison of inflammation scores of prostate tissue in each group of rats(±s)
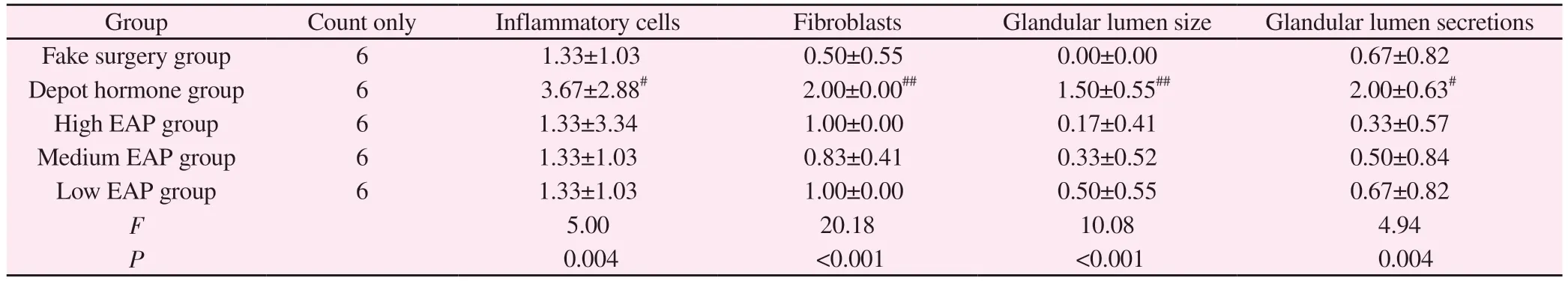
Tab 2 Comparison of inflammation scores of prostate tissue in each group of rats(±s)
Note: Compared with sham-operated group,# P < 0.05; ##P < 0.01
Group Count only Inflammatory cells Fibroblasts Glandular lumen size Glandular lumen secretions Fake surgery group 6 1.33±1.03 0.50±0.55 0.00±0.00 0.67±0.82 Depot hormone group 6 3.67±2.88# 2.00±0.00## 1.50±0.55## 2.00±0.63#High EAP group 6 1.33±3.34 1.00±0.00 0.17±0.41 0.33±0.57 Medium EAP group 6 1.33±1.03 0.83±0.41 0.33±0.52 0.50±0.84 Low EAP group 6 1.33±1.03 1.00±0.00 0.50±0.55 0.67±0.82 F 5.00 20.18 10.08 4.94 P 0.004 <0.001 <0.001 0.004
3.4 Comparison of serum immunoglobulins of rats in each group
Compared with the sham-operated group, IgA, IgG and IgM were significantly increased in the rats of the depot hormone group, and the difference was significant (P< 0.05); compared with the shamoperated group, only IgM was significantly different in the rats of the high, medium and low EAP groups (P< 0.05 ); compared with the autoimmune group, the indexes of inflammatory pathology scores were significantly different between the depot hormone group and the high, medium and low EAP groups (P< 0.05); no significant difference was seen in the comparison between the three groups of high, medium and low EAP, and there was no significant difference(P> 0.05).See Table 3.
Tab 3 Comparison of serum IgA, IgG and IgM levels of rats in each group (±s)
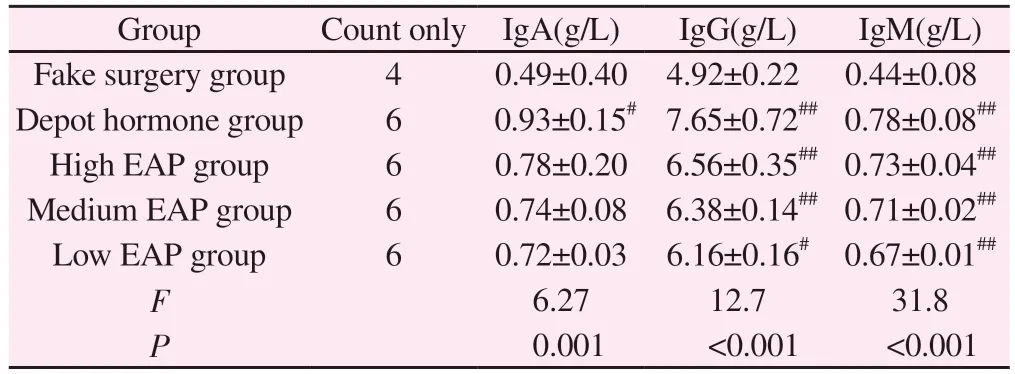
Tab 3 Comparison of serum IgA, IgG and IgM levels of rats in each group (±s)
Note: #P < 0.05; ##P < 0.01 compared with sham-operated group
Group Count only IgA(g/L) IgG(g/L) IgM(g/L)Fake surgery group 4 0.49±0.40 4.92±0.22 0.44±0.08 Depot hormone group 6 0.93±0.15# 7.65±0.72## 0.78±0.08##High EAP group 6 0.78±0.20 6.56±0.35## 0.73±0.04##Medium EAP group 6 0.74±0.08 6.38±0.14## 0.71±0.02##Low EAP group 6 0.72±0.03 6.16±0.16# 0.67±0.01##F 6.27 12.7 31.8 P 0.001 <0.001 <0.001
3.5 Comparison of serum inflammatory factors among groups of rats
Compared with the sham-operated group, no significant differences were seen in IL-1β, TNF-α, CRP and IL-10 in the depot hormone group (P>0.05); compared with the sham-operated group, IL-1β, TNF-α, CRP and IL-10 in the low EAP group rats were significantly changed, and the differences were highly significant(P<0.01), and IL-1β and TNF-α in the medium EAP group rats were Statistically significant (P< 0.05); no significant differences were seen in the indicators of rats in the high EAP group (P> 0.05);in the comparison between the three groups of high, medium and low EAP, the rats in the low EAP group were the most sensitive to the changes in indicators, with highly significant differences (P<0.01).See Table 4.
3.6 Comparison of hormone levels in the prostate tissue of rats in each group
Compared with the sham-operated group, respectively, no significant differences were seen in T levels of rats in the depot hormone and high EAP groups (P> 0.05), T levels of rats in the medium EAP group were significantly lower with significant differences(P< 0.05), and T levels of rats in the low EAP group were highly significant (P< 0.05) ; the most significant changes in T levels of rats in the low EAP group were observed among the three groups of high, medium and low EAP (P< 0.05).See Table 5.
4.Discussion
Chronic non-bacterial prostatitis (CNP) is a common disease in urology, the clinical etiology and pathogenesis are still not elucidated,and there are limitations in conventional western medicine treatment,so it is important to establish an ideal and suitable animal model rat that mimics the pathogenesis and pathological state of human CNP.
Tab 4 Comparison of serum IL-1β, IL-10, TNF-α and CRP levels of rats in each group (±s)
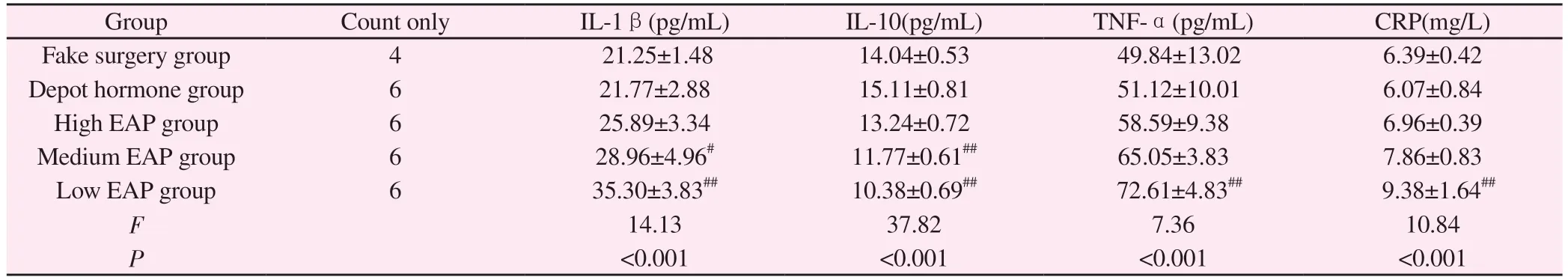
Tab 4 Comparison of serum IL-1β, IL-10, TNF-α and CRP levels of rats in each group (±s)
Note: #P < 0.05; ##P < 0.01 compared with sham-operated group
Group Count only IL-1β(pg/mL) IL-10(pg/mL) TNF-α(pg/mL) CRP(mg/L)Fake surgery group 4 21.25±1.48 14.04±0.53 49.84±13.02 6.39±0.42 Depot hormone group 6 21.77±2.88 15.11±0.81 51.12±10.01 6.07±0.84 High EAP group 6 25.89±3.34 13.24±0.72 58.59±9.38 6.96±0.39 Medium EAP group 6 28.96±4.96# 11.77±0.61## 65.05±3.83 7.86±0.83 Low EAP group 6 35.30±3.83## 10.38±0.69## 72.61±4.83## 9.38±1.64##F 14.13 37.82 7.36 10.84 P<0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001
Tab 5 Comparison of T levels in prostate tissue of rats in each group(ng/mL, ±s)
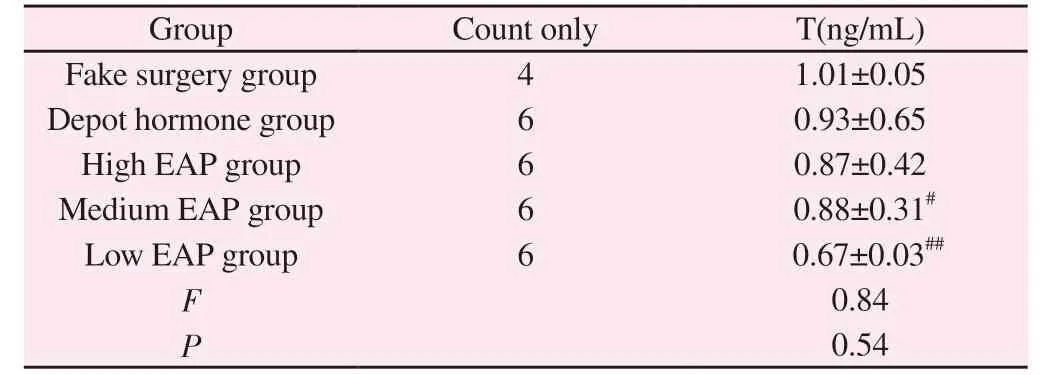
Tab 5 Comparison of T levels in prostate tissue of rats in each group(ng/mL, ±s)
Note: #P < 0.05; ##P < 0.01 compared with sham-operated group
Group Count only T(ng/mL)Fake surgery group 4 1.01±0.05 Depot hormone group 6 0.93±0.65 High EAP group 6 0.87±0.42 Medium EAP group 6 0.88±0.31#Low EAP group 6 0.67±0.03##F 0.84 P 0.54
The characteristics of depot combined with estrogen-induced chronic nonbacterial prostatitis rat model, immune factor CNP rat model mainly include depot combined with estrogen-induced CNP model, autoimmune response-induced CNP model, spontaneous CNP model, etc.The spontaneous CNP model uses aged male rats to produce CNP spontaneously.Although the pathological manifestations are similar to the clinical ones, with good pathological specificity and stability, its application in experimental studies is limited by the strict requirements on rat species and age, long modeling time, high cost, large individual deviation and difficulty in model replication.The combination of estrogen and testosterone can cause imbalance of testosterone hormone level and increase of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) in rats, causing local immune hyperfunction in prostate tissue and mediating immune inflammatory response,resulting in cell damage in prostate tissue and formation of CNP,which is simpler and less costly than spontaneous CNP model, and the pathological changes are not inferior to CNP model.It also has excellent characteristics in terms of model duration and stability.The main disadvantage of this method is that it is debatable whether the model is based on androgen deprivation and estrogen treatment, or a combination of spontaneous or genotypic factors that contribute to inflammation; moreover, this model severely affects the hormone levels in rats, and theoretically, testosterone decreases sharply after depotting, but it is not known whether this produces a negative feedback effect in vivo, therefore, when hormone level assessment or sexual function testing is required, this type of model should be used.Therefore, this type of animal model is not suitable when hormone level assessment or sexual function testing is required.[9]Therefore, this type of animal model is not suitable when hormone level assessment or sexual function testing is required.In the present study, we found that the T of the rats in the denervated hormone group decreased compared to the sham-operated group, but this was not statistically significant, which may be related to the adrenal glands in the rats making up for some of the function.
The induction of CNP by purified prostate protein stimulation is a common method for preparing a rat model of CNP, based on the principle that homozygous male gonad homogenate can induce an autoimmune response in rats, which selectively induces cellular immunity and infiltration of single nucleated cells in the prostate space to form CNP.The maintenance time of this model is comparable to that of the depot-combined estrogen method, but it is more tedious because the protein homogenate has to be retrieved from the rat prostate, which may take a longer time.There is no consensus in the literature on the choice of protein homogenate concentration and injection time, although the draft specification recommends the use of 20 mg/mL[7] GALMARINI et al.[10] found that all rats showed significant histological changes in target organs at d 35, 42 and 49, with inflammation in the prostate and adnexal glands.The histological changes in the target organs were evident at d 35, 42 and 49 in all rats.Zhou et al.[11] further explored this method and found that rats injected with 15 mg/mL of protein homogenate could form CNP model after 45 d, while no obvious pathological changes and inflammatory reactions were observed at 5 mg/mL and 10 mg/mL.Song Guohong et al.[12] The results showed that the protein homogenate concentrations of 40 mg/mL and 60 mg/mL produced good inflammatory responses and remained stable after 45 d of modeling in both groups.In conclusion, there are 15 mg/mL, 40 mg/mL and 60 mg/mL concentrations of prostate protein homogenate in rats, which can be injected in 1ml with 1:1 ratio of complete Freund’s adjuvant, and the injection interval can be as short as 1 d for 45 injections or as long as 15 d for 2~3 injections.In this study, three concentrations of 40 mg/mL, 20 mg/mL and 10 mg/mL were used to construct the rat CNP model, and no significant changes in immunoglobulin indexes were seen in the three groups after modeling; compared with the sham-operated group, the inflammatory factor indexes IL-1β, TNF-α, CRP and IL-10 were significantly changed in the 10 mg/mL group, and the pathological changes were more obvious in the 20 mg/mL group.
Both models showed a decrease in food and water intake during the modeling process compared with the sham-operated group, a decrease in body mass, and a significant decrease in prostate index in the depot hormone group.Among them, 2 rats died in the depot hormone group, considering that the rats might have died because of intolerance to the prescribed anesthetic dose; 2 rats died in the high EAP group, which might be related to wound infection and tearing by rats of the same kind.
The pathological changes in the two models were different, among which the destruction of prostate index glandular structure and diffuse distribution of inflammatory cells in the glandular lumen were the most obvious changes in the depot hormone group; the pathological changes in the high, medium and low EAP groups had their own advantages and disadvantages, the destruction of glandular structure and more inflammatory cell infiltration in the medium EAP group rats, the three groups had obvious changes compared with the sham surgery group, but still inferior to the depot hormone group.Comparing the two models, the depot hormone group was more consistent with the pathological changes of CNP, and the inflammatory cell infiltration was more obvious than that of the high,medium and low EAP groups.
Compared with the sham-operated group and the autoimmune group, the inflammatory cells, fibroblasts, lumen size, and secretions in the lumen of the gland were significantly abnormal in the shamoperated group; compared with the sham-operated group, no significant differences were found in the high, medium, and low EAP groups; the differences between the high, medium, and low EAP groups were not statistically significant.
Serum immunoglobulin IgA[13] , IgG[14] IgA, IgG, IgM[15] IgA is distributed locally in the mucosa of the body and is the first line of defense against infection; IgG can activate complement,phagocytosis and neutralize toxins, and is the main force of infection immunity, and can be maintained in the body for a long time; IgM is a marker of infection in the body, and activates the immune response at the first time after being stimulated by antigen, which is significant in the early immune defense of the body.Therefore, the level of serum immunoglobulin also indicates the strength of CNP immune response.In this study, we found that the levels of IgA, IgG and IgM of rats in the depot hormone group and high, medium and low EAP groups increased to different degrees compared with those in the sham-operated group, with the most significant changes in the depot hormone group, and the differences were all significant (P<0.05).
Pro-inflammatory cytokines include IL-1β[16] , TNF-α[17] and CRP[18] etc., play a role in promoting inflammation, accelerating intercellular adhesion factor expression, increasing prostaglandins and causing local damage to prostate tissue; anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 can strongly inhibit mononuclear macrophages,reduce inflammatory mediator production and achieve the function of repairing tissue.[19].In this study, compared with the shamoperated group, IL-1β, IL-10, TNF-α, and CRP were significantly changed in the low-EAP group rats, and the differences were all statistically significant (P< 0.05), and no significant differences were seen in the depot hormone group (P> 0.05).
Androgens play a leading role in the normal development of the prostate gland and have a role in suppressing humoral immunity,and when androgen levels are reduced, autoimmune reactions can be induced.[20] In the present study, the androgens in the medium and low EAP groups were more effective than those in the sham group.In this study, compared with the sham-operated group, the T levels of rats in the medium and low EAP groups were statistically significant(P< 0.05), and the T levels of rats in the depot hormone group were also decreased, but no significant difference was observed (P>0.05).
In summary, both desmoid combined with estrogen induction method and autoimmune response induction method can successfully construct CNP model.In general, the prostate index in the depot hormone group was significantly decreased; in pathology, the depot hormone group could lead to obvious glandular destruction,interstitial edema, and very obvious inflammatory cell infiltration in prostate tissue, which was more consistent with the pathological changes of CNP; in immune indexes, the rats in the depot hormone group were better than the high, medium and low EAP groups;in inflammatory factor indexes and sex hormone indexes, the low EAP group (10 mg/mL) rats were significantly better than the other groups of changes.The weights were calculated according to the draft preparation[7] The total score of the CNP model in the depot hormone group was 0.81, while the scores in the high, medium and low EAP groups were 0.62, 0.73 and 0.67, respectively.According to the results of this study, in general, the depot combined with estrogen induction method of modeling is a more appropriate method between the two.Specifically, the depot combined with estrogen induction method is more suitable for studying CNP pathology and changes in immune response, and more suitable for studying long-term changes in CNP; while for studying CNP inflammatory factor indexes and sex hormone indexes, 10 mg/mL of prostaglandin homogenate is a more suitable and ideal concentration for preparing CNP in rats,and more suitable for studying early inflammatory index changes in CNP.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Relationship between microRNA-29c expression and clinicopathological features of gastric cancer
- Experimental study on the synergistic inhibition of malignant biological behavior of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by the combination of DMDD and sorafenib
- Effect of small interference RNA on expression of the Skp2 in human chondrocytes cell
- Regulation of Quan Du Zhong capsule on VEGF/bFGF and expression of Bcl-2/Bax and Caspase-3 protein in the repairing process of canine femoral head necrosis
- Association of novel and legacy PFAS with reproductive hormones in women of child-bearing age
- Meta-analysis of influencing factors associating with treatment outcome of multidrug resistant tuberculosis
