配位环境对有机钛化合物催化聚酯缩聚反应的影响
2023-11-22苏亚王勇军陈文兴吕汪洋
苏亚 王勇军 陈文兴 吕汪洋






摘 要:为探究不同配位环境下有机钛化合物在聚酯缩聚反应过程中的催化性能,采用密度泛函理论(DFT)并结合对苯二甲酸双羟乙酯(BHET)合成聚酯的反应动力学实验,对四甲基酚合钛(Ti·[C7H7O]4,Cat1)、乙酰丙酮氧化钛(TiO·[C5H7O2]2,Cat2)、异丙基三(二辛基焦磷酸酰氧基)钛酸酯(C51H112O22P6Ti,Cat3)3种有机钛化合物进行研究,分析配位基团的电子效应和空间位阻对有机钛催化活性的耦合影响。DFT计算结果表明,3种活性种的中心钛原子的Hirshfeld电荷数值分别为0.661、0.524、0.600,其亲电能力从大到小的顺序为Cat1、Cat3、Cat2。结构分析结果表明,中心钛原子的配位空间从大到小的顺序为Cat2、Cat1、Cat3。催化反应动力学实验表明,Cat1、Cat2、Cat3催化BHET合成聚酯的反应活化能分别为72.41、80.16、102.47 kJ/mol,Cat1的催化活性最高,说明配位基团的电子效应和空间位阻共同影响钛催化剂的催化活性。研究结果可为钛系催化剂的设计及调控提供一定的理论基础和参考依据。
关键词:聚酯;有机钛化合物;缩聚反应;催化活性;配位基团
中图分类号:TQ314.2 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1009-265X(2023)06-0092-08
聚酯具有优异的物理化学性能,广泛应用于工业生产和日常生活中。其中,聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)具有优良的机械性能和可回收性能,是目前使用最为普遍的一种聚酯材料[1]。PET合成分为酯化和缩聚两个阶段,精对苯二甲酸(PTA)的H+离子可以自催化发生酯化反应,所以酯化阶段可以不添加催化剂[2]。缩聚阶段需要催化剂来提高反应速度,故缩聚催化剂在聚酯的生产过程中起着关键的作用。目前,聚酯合成工业中最普及的催化剂是锑系化合物。然而重金属锑对环境和人体存在一定的危害,因此国内外研究人员一直在探索性能优异、经济环保的其他金属类催化剂。钛系催化剂具有环保、催化活性强和价格便宜等优点[3],有望替代锑系催化剂。
钛系催化剂的高活性不仅提高了PET缩聚过程的反应速率,同时也会加速热降解、热氧化降解等
副反应,这种副反應成为制约钛系催化剂应用于聚酯合成中的最为突出的问题之一[3]。因而,调控钛系催化剂的催化活性至关重要。目前主要的调控方法有:一是复配法,即与其他种类催化剂复配[4];二是水解法,即制备以TiO2为主要成分的固相催化剂[5];三是负载化[6],即将钛负载在比表面积比较大的载体上;四是合成复杂的有机钛化合物,利用配位基团去调控钛的催化活性[7-9]。
基于第4种方法,本文选择了四甲基酚合钛(Ti·[C7H7O]4,Cat1)、乙酰丙酮氧化钛(TiO·[C5H7O2]2,Cat2)、异丙基三(二辛基焦磷酸酰氧基)钛酸酯(C51H112O22P6Ti,Cat3)3种不同配位环境下的有机钛化合物,通过密度泛函理论(DFT)方法和反应动力学实验,探究配位基团的电子效应和空间位阻效应对有机钛化合物催化合成PET活性的影响,揭示催化剂结构与催化性能之间的构效关系。
1 实 验
1.1 主要原料与仪器
实验原料:对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(BHET),梯希爱(上海)化成工业发展有限公司;四甲基酚合钛、乙酰丙酮氧化钛、异丙基三(二辛基焦磷酸酰氧基)钛酸酯,天津希恩思生化科技有限公司;无水乙醇AR,上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司。
实验仪器:乌氏黏度计(VISCO070,德国Julabo公司),超高效聚合物色谱(ACQUITY,美国Waters公司),差示扫描量热仪(DSC1,瑞士Mettler-Toledo公司)。
1.2 样品制备
将Cat1、Cat2、Cat3三种催化剂溶解在无水乙醇中,超声使其分散均匀,然后将催化剂加入熔融的BHET(3~5 g)中(Ti含量为50 mg/kg),搅拌蒸发除去无水乙醇,制备得含催化剂的BHET。
在温度260~265 ℃,压力1800~2000 Pa条件下进行预缩聚反应。预缩聚后减压至体系压力低于400 Pa,选取265~285 ℃中的4个温度,30~120 min中的4个时间进行终缩聚反应。
1.3 计算方法
采用密度泛函理论(DFT)中常用的B3LYP杂化泛函,通过Gaussian 09软件对催化剂分子进行结构优化。其中钛原子使用LANL2DZ基组,氧、碳、氢和磷原子使用6-31G**基组,色散校正采用DFT-D3(Zero-damping)方法。在优化的结构上进行频率计算,计算结束时,若得到的虚频数为0,表示优化后的结构是能量处于极小值的稳定结构。Hirshfield电荷和表面距离投影均在Multiwfn软件包中计算。
1.4 催化剂性能测试
将催化剂与BHET混合均匀(Ti含量为50 mg/kg),取5~8 mg放在20 μL铝制坩埚中进行DSC测试:40 mL/min氮气氛围,升温速率10 ℃/min,温度25~300 ℃,得到催化剂活性曲线。
1.5 PET性能测试
特性黏度:以25 mL苯酚/四氯乙烷(质量比1∶1)溶液为溶剂,称取(125±5) mg样品,110 ℃条件下溶解15 min,然后冷却至室温,用乌氏黏度计在25 ℃下测定特性黏度。
数均分子量测试:流动相和溶剂为含5 mmol/L三氟乙酸钠的六氟异丙醇溶液,待测试样品质量浓度为2 mg/mL,使用APC进行测试,色谱柱温度55 ℃,样品室温度25 ℃,流速0.4 mL/min,进样量50 μL。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 配位基团的电子效应和对催化活性影响的理论计算分析
在PET的缩聚反应过程中,催化剂配体先与单体或低聚物的端羟基之间发生交换反应,生成金属醇盐;另一分子中的羟乙酯基中的氧进攻羰基碳原子,酯羰基氧对中心钛原子的亲核进攻会增加羰基碳的正电性,从而提高反应速率。
优化后的3种有机钛化合物的结构模型如图1所示。在此结构基础上使用Gaussian 09软件对3种钛醇盐活性种进行优化计算,为了简化计算过程,选择苯甲酸β-羟乙酯(BAHET)作为模型反应物进行配体交换反应。通过Multiwfn软件包[10]对3种钛醇盐活性种的Hirshfeld电荷[11]进行计算,Hirshfeld电荷与原子的亲电能力有很强的相关性[11]。配体的给电子能力不同导致中心钛原子的电荷不同[12],电荷值越大,钛原子的亲电性越强,即酯羰基氧原子对钛的亲核反应越容易发生。计算Cat1、Cat2和Cat3这3种钛醇盐活性种的Hirshfeld电荷值分别为0.661、0.524、0.600。所以,从电子效应角度分析,3种有机钛化合物的催化活性从大到小为Cat1、Cat3、Cat2。
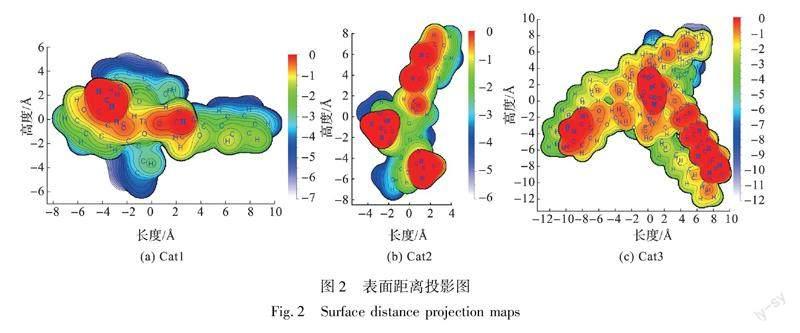
2.2 配位基团的位阻对催化活性影响的理论计算分析
除电子效应外,空间位阻效应也会影响催化剂催化缩聚PET的难易程度,对于位阻效应的考量,通过Multiwfn软件包计算其范德华表面的距离投影来评估[13]。从表面距离投影图(见图2)中可看出:3种化合物的钛原子都被包埋于配体之间,从配体间的距离可看出包埋程度为Cat3、Cat1、Cat2。所以其配位空间从大到小依次为:Cat2、Cat1、Cat3。结合图1中Cat3分子的催化剂模型可知,Ti原子周围存在PO键,在反应过程中PO键比BHET中酯羰基氧原子更易与活性钛中心配位,从而占据更多的配位空间,使得Cat3的空间位阻要比Cat1和Cat2大得多,大大抑制了钛的活性[10]。因此从空间位阻效应角度考虑,催化活性从大到小为Cat2、Cat1、Cat3。
2.3 催化活性分析
2.3.1 催化BHET过程分析
为了进一步探索3种具有不同配体催化剂的活性,采用DSC实验进行了活性测试。图3显示了Cat1、Cat2、Cat3分别与BHET混合后的DSC加热曲线。从图3中可以看出,每个试验都会得到两个吸热峰,其中第1个峰在110 ℃左右,对应的是BHET的熔融峰,不会随催化剂的不同而改变;第2个反映了缩聚过程中乙二醇蒸发时吸收的热量,峰的位置会随着催化剂的不同而有所改变[7]。催化剂的活性越高,最大反应速率发生得越早,该吸热峰温度越低。3种催化剂的吸热峰温度从低到高依次为:225.8、229.5、257.7 ℃,从中可以判断出3种催化剂的活性从大到小为Cat1、Cat2、Cat3。
2.3.2 催化BHET产物分析
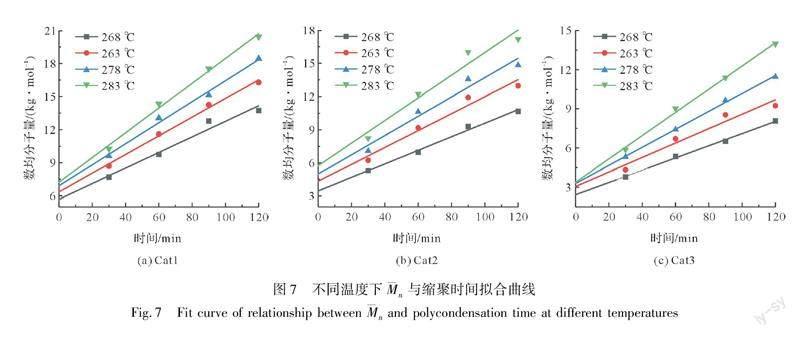
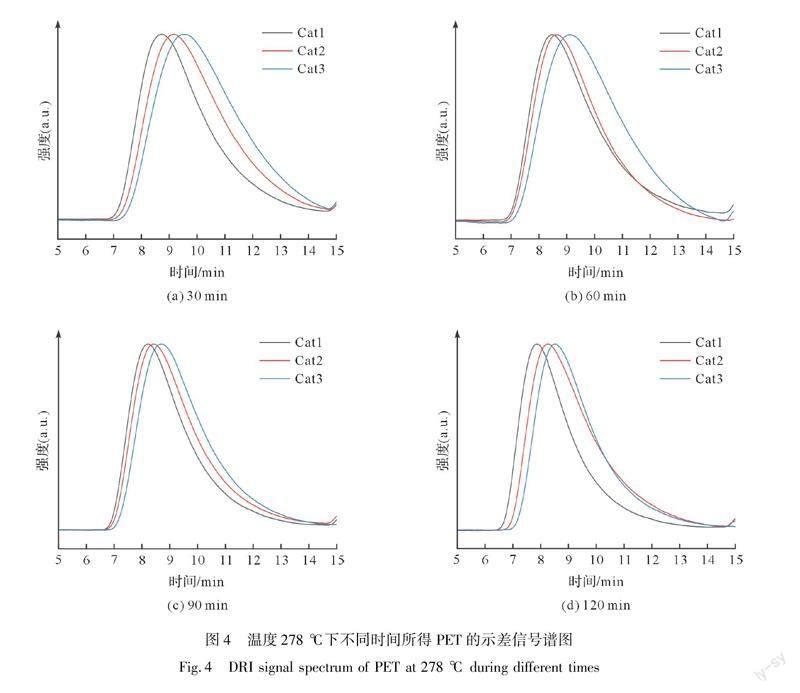
使用APC对温度278 ℃下所得的样品和时间90 min下所得的样品进行数均分子量[14]测定。比较3种不同有机钛化合物所得产物的分子量变化,在温度278 ℃下不同时间所得PET的示差信号谱图如图4所示,在时间90 min下不同温度所得PET的示差信号谱图如图5所示。从图4和图5中可以看出,在相同条件下,使用Cat1的洗脱峰最先出来,随后是Cat2和Cat3,所以,数均分子量从大到小顺序是Cat1、Cat2、Cat3。即在同一反应条件下,分子量的增长速率从大到小的顺序为Cat1、Cat2、Cat3。分子量的表征结果与上述DSC活性测试结果相吻合。
为了验证以上结果,对产物的特性黏度进行测试分析。3种不同有机钛化合物在不同温度、不同聚合时间下的特性黏度的变化如图6所示。从图6中可看出,在273 ℃、90 min的反应条件下,Cat1、Cat2、Cat3所得PET产物特性黏度分别为0.53、0.46、0.35 dL/g。当Cat2、Cat3所得产物黏度达到0.50 dL/g左右时,所需温度和时间分别为278 ℃、90 min和283 ℃、120 min。所以3种有机钛化合物的催化活性从大到小为:Cat1、Cat2、Cat3。这与上述DSC和分子量测试分析结果相一致。
两种分析结果说明催化剂的催化活性受到电子效应和空间位阻效应的共同影响。Cat1的Hirshfield电荷值大于Cat2,Cat2的空间位阻小于Cat1,Cat1的催化活性高于Cat2表明电子效应的影响要大于空间位阻效应。Cat3雖然具有较高的电荷值,但其体积大且烷基链很长,同时又因为在反应过程中会分解形成磷酸酯基,PO键会与金属中心配位占据更多的配位空间来增加反应物与其接触的难度,从而导致Cat3的空间位阻要远大于Cat1和Cat2。所以Cat3的活性要小于Cat1和Cat2。这也是在实际工业生产中选择磷酸酯化合物作为稳定剂来制备催化剂的可能原因之一[9]。
2.4 熔融缩聚反应动力学
熔融缩聚过程中,可以用活化能ΔE来表征缩聚反应的难易程度,以此来判断不同催化剂的催化活性。根据相关文献报道[15-16],Ti离子催化PET的反应属于二级反应,热降解和副反应可忽略不计,只考虑链增长反应,再根据Mark-Houwink方程,通过不同反应时间和温度的产物特性黏度[η],计算其数均分子量n:
式中:A表示频率因子,是一个常数;ΔE表示反应活化能,kJ/mol;R是气体常数,取值为8.31 J/(mol·K);T表示热力学温度,K。
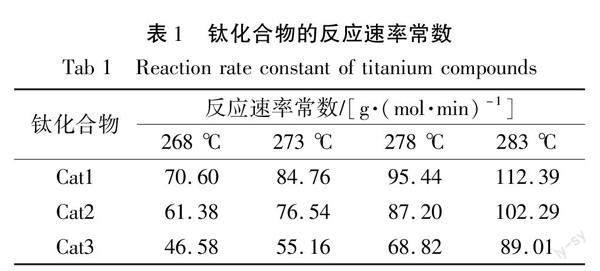
拟合不同反应温度下n与t的关系曲线(见图7),得该缩聚反应温度下的反应速率常数K,数据详见表1所示。从表1中可看出,在熔融缩聚过程中,反应速率常数会随着温度的升高而增大,在同一反应条件下,Cat1反应速率常数要大于Cat2和Cat3。
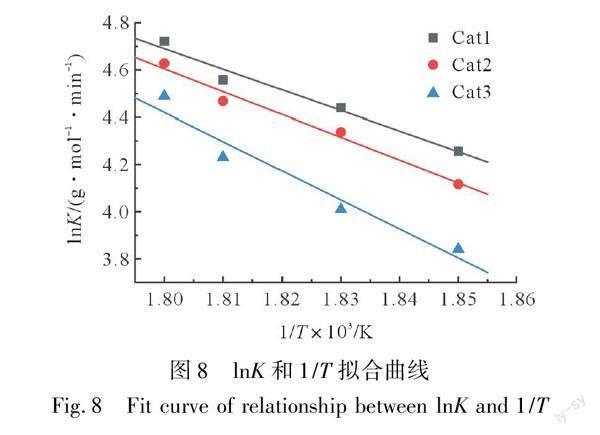
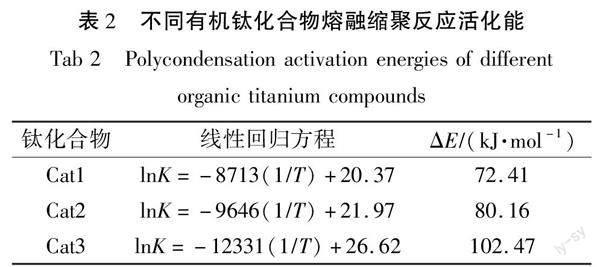
根据Arrhenius方程,拟合得到lnK/T线性关系,拟合曲线如图8所示,并从直线斜率计算出反应活化能ΔE,计算结果如表2所示。
由表2可知,在催化熔融聚合过程中,相同条件下3种钛系催化剂的反应活化能的大小顺序为:Cat1、Cat2、Cat3,即3种催化剂的活性大小顺序为:Cat1、Cat2、Cat3。这与理论计算分析、DSC实验和产物分子量分析结果相吻合,表明配位基团的电子效应和空间位阻共同耦合影响催化剂的催化活性。因此,在设计聚酯钛系催化剂时要考虑到这两个因素的影响。
3 结 论
为了探究不同配位环境对有机钛化合物催化活性的影响,采用量子化学方法和反应动力学实验对3种有机钛化合物在缩聚合成PET过程中的催化性能进行了研究,探究其分子结构和性质对催化活性的影响,从而为钛系催化剂的设计提供思路。
理论计算表明:从电子效应角度考虑,3种有机钛化合物的催化活性大小顺序为Cat1、Cat3、Cat2;从空间位阻角度考虑,催化活性大小顺序为Cat2、Cat1、Cat3;由于Cat3中位阻效应过于强烈,严重阻碍了反应物与中心钛原子的接触,造成其反应活性大大降低。
DSC测试结果和产物数均分子量分析表明:3种有机钛化合物的催化活性从大到小为Cat1、Cat2、Cat3,并通过反应动力学实验对其进行了验证。
以上结果说明,电子效应和空间位阻是设计和优化有机钛聚酯催化剂需要考虑的两个重要因素。
参考文献:
[1]FLORES I, DEMARTEAU J, MüLLER A J, et al. Screening of different organocatalysts for the sustainable synthesis of PET[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2018, 104: 170-176.
[2]CAI Q, BAI T, ZHANG H, et al. Catalyst-free synthesis of polyesters via conventional melt polycondensation[J]. Materials Today, 2021, 51: 155-164.
[3]张大省.钛系催化剂在聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯合成中的应用[J].纺织导报,2020(1):48-52.
ZHANG Daxing. Titanium catalyst for the synthesis of polyethylene terephthalate[J]. China Textile Leader, 2020(1): 48-52.
[4]SAVITHA K S, SENTHIL KUMAR M, JAGADISH R L. Ti(OBu)4 in combination with Sn(Oct)2: An efficient catalyst system for high molecular weight poly(butylene succinate) synthesis[J]. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2023, 34(5): 1492-1496.
[5]THAKUR A, HAMAMOTO T, IKEDA T, et al. Microwave-assisted polycondensation for screening of organically-modified TiO2/SiO2 catalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2020, 595: 117508.
[6]陈慕华,陈燕青,陈思,等.活性炭负载钛酸四丁酯催化合成二甘醇二苯甲酸酯[J].化工进展,2014,33(5):1201-1204.
CHEN Muhua, CHEN Yanqing, CHEN Si, et al. Synthesis of diethylene glycol dibenzoate catalyzed by Ti(OBu)4/AC[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2014, 33(5): 1201-1204.
[7]LIN Q, GAO F, WANG Y, et al. Ethylene glycol-soluble Ti/Mg-citrate complex catalyst for synthesis of high intrinsic viscosity poly(ethylene terephthalate)[J]. Polymer, 2022, 246: 124741.
[8]LI, S J, TANG Y C, ZHAO C X. Preparation method and application of titaunium-phosphorus catalyst for polyester sythesis: WO2022217818[P]. 2022-10-20.
[9]莊颖,杜玮辰,王文,等.钛系聚酯催化剂的研究进展[J].化学反应工程与工艺,2021,37(5):467-473.
ZHUANG Ying, DU Weichen, WANG Wen, et al. Progress of study on titanium catalyst for polyester synthesis[J]. Chemical Reaction Engineering and Technology, 2021, 37(5): 467-473.
[10]LU T, CHEN F. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2012, 33(5): 580-592.
[11]LU T, CHEN F. Atomic dipole moment corrected hirshfeld population method[J]. Journal of Theoretical and Computational Chemistry, 2012, 11(1): 163-183.
[12]WANG B, RONG C, CHATTARAJ P K, et al. A comparative study to predict regioselectivity, electrophilicity and nucleophilicity with Fukui function and Hirshfeld charge[J]. Theoretical Chemistry Accounts, 2019, 138(12): 1-9.
[13]FU Y, LIU H, YANG D, et al. Boosting external quantum efficiency to 38.6% of sky-blue delayed fluorescence molecules by optimizing horizontal dipole orientation[J]. Science Advances, 2021, 7(43): eabj2504.
[14]刘梅,刘雄,陈世昌,等.联合超高效聚合物色谱和激光光散射法的聚酯分子质量及其分布测定[J].纺织学报,2016,37(5):11-16.
LIU Mei, LIU Xiong, CHEN Shichang, et al. Determination of polyester molecular weight and its distribution by advanced polymer chromatography and laser light scattering detection[J]. Journal of Textile Research. 2016, 37(5): 11-16.
[15]关震宇,周文乐,张玉梅,等.基于钛镁催化剂合成瓶用聚酯的动力学研究[J].纺织学报,2021,42(3):64-70.
GUAN Zhenyu, ZHOU Wenle, ZHANG Yumei, et al. Kinetic study on synthesis of bottle polyester using Ti-Mg catalyst[J]. Journal of Textile Research, 2021, 42(3): 64-70.
[16]JI H, GAN Y, KUMI A K, et al. Kinetic study on the synergistic effect between molecular weight and phosphorus content of flame retardant copolyesters in solid-state polymerization[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2020, 137(38): 49120.
Effect ofcoordination environment on polycondensation of polyester catalyzed by organic titanium compounds
SU Ya1, WANG Yongjun CHEN Wenxing LU Wangyang1,2
Abstract: Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) has excellent physical and chemical properties and is the most commonly used polyester material. The polycondensation stage of polyester synthesis requires the participation of catalysts. At present, antimony-based catalysts are widely used in industrial production. Antimony-baseds, as a kind of heavy metal compound, have biological toxicity and will cause harm to human health and ecological environment. With the increasing awareness of healthy, the design and development of non-toxic and non-hazardous polyester catalysts has become an important hotspot in the field of polyester research. The titanium-based catalysts are expected to replace the antimony-based catalysts due to the advantages of environmental protection, strong catalytic activity and abundant resources. The high activity of titanium-based catalysts not only increases the reaction rate of the PET polycondensation process, but promotes side reactions such as thermal degradation and thermo-oxidative degradation, which is one of the most prominent problems limiting the application of titanium-based catalysts in polyester synthesis. The regulation of the catalytic activity of titanium-based catalysts is therefore crucial. To investigate the catalytic performance of organotitanium compounds in the condensation synthesis of polyesters under different coordination environments, firstly, density functional theory (DFT) quantum chemistry method was used to study tetramethylphenol titanium(Ti·[C7H7O]4, Cat1), acetyl acetone titanium oxide (TiO·[C5H7O2]2, Cat2), isopropyl tri (dioctylpyrophosphoxy) titanate (C51H112O22P6Ti, Cat3), and the coupling mechanism of electronic effects and steric hindrance of coordination groups on catalytic activity of organotitanium was analyzed theoretically. The Gaussian software was used to carry out structural optimization and energy calculations for the three organotitanium compounds, and the wave functions were extracted from the calculation results. The wave function analysis was carried out by using the Multiwfn software package to obtain the Hirshfeld charge values of the titanium metal centers and the surface distance projection maps were used to assess the effect of steric hindrance. Theoretical calculations show that Cat1 is more capable of forming titanium alcohol salt active species than Cat2 and Cat3; the Hirshfeld charge values for the central titanium atoms of the three active species are: 0.661, 0.524 and 0.600, respectively, and the Hirshfeld charge is strongly correlated with the electrophilic ability of the atoms: the higher the charge value, the stronger the electrophilic ability. It is found by analyzing the distance between ligands in the surface distance projection that the size of the coordination space is Cat2, Cat1 and Cat3, respectively. The catalytic reaction kinetics experiments results show that the reaction activation energies of Cat1, Cat2 and Cat3 for the synthesis of polyesters from BHET(Dihydroxyethyl terephthalate) are 72.41, 80.16 and 102.47 kJ/mol, respectively, and the highest catalytic activity is obtained for tetramethylphenolato-titanium (Ti·[C7H7O]4, Cat1), indicating that the electronic effect of the ligand group and the spatial site resistance jointly affect the catalytic activity of the titanium-based catalysts, with the electronic effect being more influential than the spatial site resistance. This study is a of certain guiding significance for screening of ligands in adjusting the activity of titanium catalysts in the future.
Keywords: polyester; organic titanium compounds; polycondensation; catalysis; coordination group
收稿日期:20230504 網络出版日期:20230804
基金项目:浙江省重点研发计划项目(2021C01020)
作者简介:苏亚(1998—),女,河南商丘人,硕士研究生,研究方向为钛系聚酯催化剂。
通信作者:吕汪洋,E-mail:luwy@zstu.edu.cn
