Neutrophil-lymphocyte and platelet-lymphocyte ratios for assessing disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving tofacitinib treatment
2023-11-14TANGJuanCHENJuanLINGuoxinZHANGHaoGUIMingLINannanGUYihongLUOLinjuanSUNJian
TANG Juan ,CHEN Juan,2 ,LIN Guoxin ,ZHANG Hao ,GUI Ming ,LI Nannan ,GU Yihong,LUO Linjuan,SUN Jian
1Department of Nephrology and Rheumatology,3Department of Anesthesiology,Third Xiangya Hospital,Central South University,Changsha 410013,China;2Department of Nephrology,Yuyao People's Hospital,Yuyao 315499,China
Abstract: Objective To evaluate the value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) for assessing disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis(RA)treated with tofacitinib.Methods This retrospective study was conducted among 98 RA patients in active stage treated with tofacitinib in Third Xiangya Hospital and 100 healthy control subjects from the Health Management Center of the hospital from 2019 to 2021.We collected blood samples from all the participants for measurement of erythrocyte sedimentation rate(ESR),high-sensitivity C-reactive protein(hs-CRP),interleukin-6(IL-6)and other blood parameters 1 month before and 6 months after tofacitinib treatment.We further evaluated PLR and NLR before and after tofacitinib treatment in the RA patients,and analyzed their correlations with RA disease activity.Results PLR and NLR increased significantly in RApatients as compared with the healthy controls.In the RApatients,PLR and NLR were positively correlated with the levels of hs-CRP,ESR,IL-6,Disease Activity Score of 28 joints-ESR(DAS28-ESR),anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide(CCP),and rheumatoid factor (RF) before and after tofacitinib treatment.Tofacitinib treatment for 6 months significantly decreased hs-CRP,ESR,IL-6,CCP,RF and DAS28-ESR levels in the RA patients.Conclusion NLR and PLR can be useful biomarkers for assessing disease activity in RApatients treated with tofacitinib.
Keywords:neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio;platelet-lymphocyte ratio;rheumatoid arthritis;tofacitinib
INTRODUCTION
As a chronic,inflammatory,and systemic autoimmune disease characterized by bone destruction and joint synovitis,rheumatoid arthritis (RA) causes joint deformities and attacks multiple organs to result in irreversible physical disabilities and interstitial lung fibrosis in severe cases[1,2].The assessment of disease activity is critical before initiation of therapeutic intervention and for evaluation of treatment responses of RA patients.Disease Activity Score of 28 jointserythrocyte sedimentation rate (DAS28-ESR) is commonly used for disease activity assessment of RA[3,4],but this assessment contains complex contents and involves expensive tests,and thus more convenient and cost-effective methods are needed for more efficient assessment of RA activity.
The etiology of RA has not been fully clarified.Precious studies[5-7]have shown that inflammation is involved in the pathogenesis of RA,and the pro-inflammatory cytokines,including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)[8-10]and interleukin (IL)-6[11],can result in joint pain,swelling and bone destruction.Elevation of the levels of the autoantibodies including anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) and rheumatoid factor (RF)can occur before disease onset and is vital in diagnosis of RA according to 2010 ACR/EULAR RA classification criteria[12].The goal of RA treatment is to achieve structural and functional remission with low disease activity.Therapeutic interventions of RA include disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)[13,14],biological agents[15]and small-molecule targeting drugs[16,17].Tofacitinib is a Janus kinase inhibitor used in a new optional medicine regimen for RA[18],and its treatment efficacy can be assessed by evaluating the acute inflammatory proteins such as C-reactive protein(CRP)[19]and ESR[20]and the inflammatory factor IL-6[11].
Accumulating evidence suggests that increased neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and plateletto-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) are associated with multiple autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)[21],ulcerative colitis[22],Sjögren's syndrome (pSS)[23],Takayasu's arteritis[24]and RA[25],and are thus considered as novel markers of the inflammatory status[26].In addition,emerging evidence indicates that PLR and NLR are reliable markers for assessing treatment response in RA patients receiving biological agent therapy[27,28].In this retrospective study,we aimed to define the correlation of NLR and PLR with the disease activity and levels of IL-6,CCP and RF antibodies in RA patients before and after tofacitinib treatment.
METHODS
Patients and treatments
This retrospective study was conducted among the patients with RA treated in the Department of Nephrology and Rheumatology,Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University from 2019 to 2021.For all the patients,the diagnoses of RA were established according to the criteria for classification of RA developed by the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) in 2010.The patients with malignant tumors,hematological disorders,acute or chronic infectious diseases,tuberculosis,and cardiac,liver and kidney dysfunctions,those receiving non-RA medications that may affect blood cell counts,and those with other connective tissue diseases were excluded from the study.All the included patients were treated with tofacitinib at 5 mg twice a day,and they also received steroid and methotrexate treatment before and after tofacitinib treatment.One hundred age-and sex-matched healthy adults were recruited from the Health Management Center of the Third Xiangya Hospital to serve as the healthy control group.
The protocol of this study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University (No.23677),which waived informed consent from the patients in this retrospective study.The demographic characteristics and laboratory data of the RA patients and healthy controls were collected at baseline and at 6 months after the initiation of tofacitinib treatment.
Blood sample collection
At 1 month before tofacitinib treatment and at 6 months during the treatment,4 mL venous blood samples were collected from the subjects in the morning after fasting for 8-10 h.A blood cell analyzer was used to detect routine blood parameters,and the levels of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP)and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) were determined using a biochemical analyzer and a capillary microscopic imaging system (Zhejiang Quake Biotechnology Company),respectively.BD FACS Canto II flow cytometry was applied for detection of IL-6 level(Agilent kit).CCP (Shenzhen Yahuilong Biotechnology Company,China) and RF (Anhui Ipunokang Biotechnology Company,China) were measured using commercial detection kits according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Statistical analysis
SPSS 23.0 software was used for statistical analysis of the data.Normally distributed data are presented asMean±SDand compared between the two groups using Student'sttest and Mann-WhitneyUtest.Skewed distribution data are presented as median with quartiles (Q1,Q3) and compared using non-parametric test.The categorical data are presented as percentage (%) and compared using χ²test.Spearman's correlation analysis was performed to determine the correlation of NLR and PLR with biomarkers including hs-CRP,ESR,IL-6,CCP,and RF before and after treatment with tofacitinib in RA patients.Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to analyze the predictive value of the model.APvalue less than 0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
RESULTS
Basic characteristics of the study subject
A total of 98 patients with RA were enrolled in this study,who were all in active stage with an average DAS-28-ESR score of 6.60 (5.82,7.27) (Tab.1).Among the RA patients,25 had concurrent interstitial pneumonia,32 had anemia,6 were diagnosed with Sjogren Syndrome,and 5 had renal tubular acidosis.The demographic data and laboratory results of all the participants are shown in Tab.1.There were no significant differences in age or gender distribution between the RA patients and the control subjects.Platelet and neutrophil counts were significantly higher while lymphocyte count was lower in the RA patients (allP<0.001).PLR,NLR and serum hs-CRP level were markedly higher in the RA patients than in the control subjects(P<0.001).

Tab.1 Demographic characteristics and laboratory test results in healthy control group and patients with rheumatoid arthritis(RA)
PLR and NLR are positively correlated with RA disease activity before and after tofacitinib treatment
As shown in Tab.2,the inflammatory biomarkers ESR and hs-CRP levels were decreased dramatically after 6 months of tofacitinib treatment,which also resulted in a decrease of the mean DAS28-ESR to 3.81.Tab.3 and Tab.4 show that PLR of the RA patients was positively correlated with the baseline ESR,hs-CRP and DAS28-ESR,and such correlations were still significant after the 6-month tofacitinib treatment.Similarly,Tab.3 and Tab.5 show positive correlations of NLR with ESR,hs-CRP,DAS28-ESR in the RA patients both before and after tofacitinib treatment.

Tab.2 DAS28-ESR,ESR,hs-CRP,and blood parameters in RA patients before and after tofacitinib treatment(n=98)
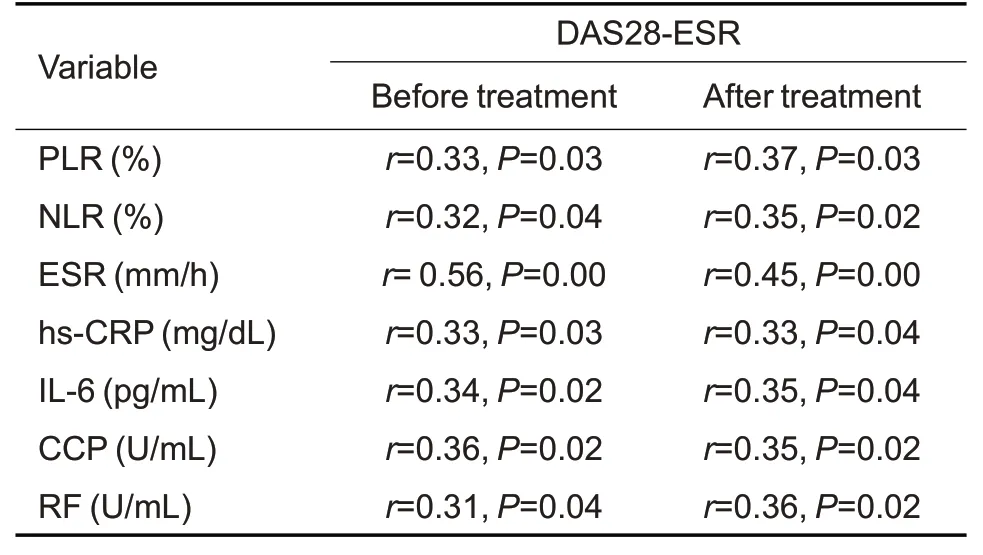
Tab.3 Spearman's correlation analysis of DAS28-ESR with ESR,hs-CRP,NLR,PLR,IL-6,CCP,and RF in RA patients before and after 6 months of tofacitinib treatment(n=98)
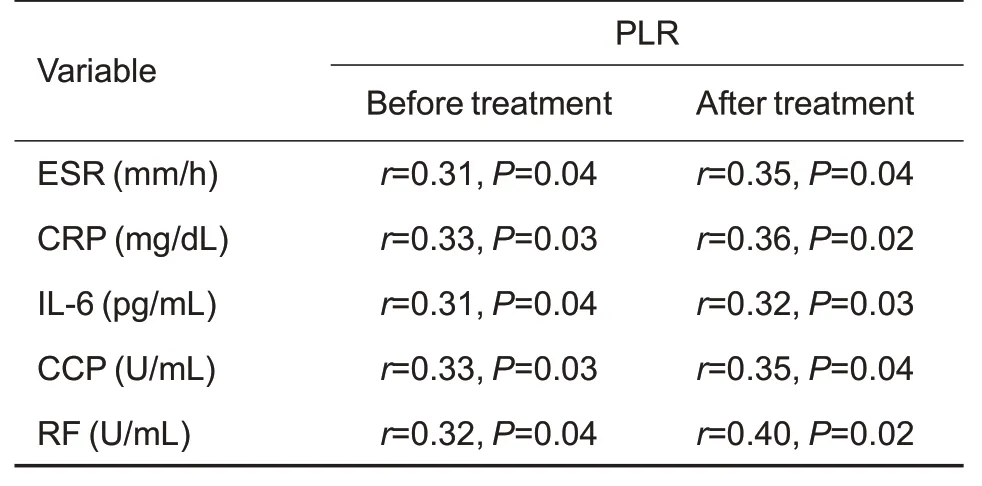
Tab.4 Spearman's correlation analysis of PLR with ESR,hs-CRP,IL-6,CCP,and RF in RA patients before and after 6 months of tofacitinib treatment(n=98)
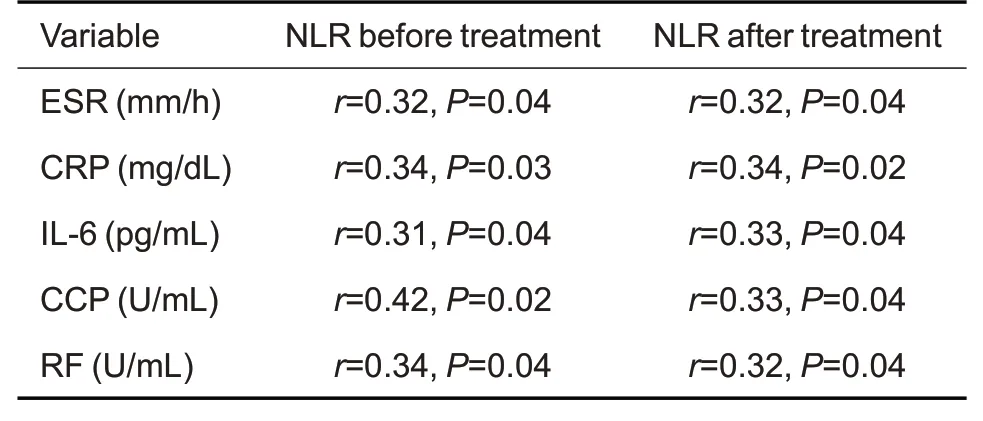
Tab.5 Spearman's correlation analysis of NLR with ESR,CRP,IL-6,CCP,RF in RA patients before and after 6 months of tofacitinib treatment(n=98)
PLR and NLR are positively correlated with IL-6,CCP,and RF in RA patients before and after tofacitinib treatment
Spearman correlation analysis showed that PLR was positively correlated with IL-6,CCP,and RF levels of the RA patients both before and after the 6-month tofacitinib treatment (Tab.4).NLR was also found to positively correlate with NLR and IL-6,CCP,and RF both before and after the treatment(Tab.5).These data indicated that both PLR and NLR are positively correlated with IL-6,CCP,and RF in RA patients before and after tofacitinib treatment for 6 months.
ROC curves of PLR and NLR for RA disease activity
With DAS28-ESR as the standard,we performed ROC analysis to determine the optimal cut-off values of PLR and NLR for predicting RA disease activity (Fig.1).Our results showed that for predicting the disease activity,the area under the curve (AUC) of PLR was 0.921 (95%CI:0.863-0.979,P=0.000)and at the optimal cut-off value of 2.56,its sensitivity and a specificity was 81% and 77%,respectively.For NLR,the AUC was 0.882 (95%CI:0.863-0.979,P=0.000),the optimal cut-off value was 2.84,and its sensitivity and specificity was 89% and 79%,respectively.These results suggest that both PLR and NLR are valid indicators for assessing RA disease activity.

Fig.1 Receiver operating characteristic curve(ROC)analysis of the sensitivity and specificity of PLR and NLR for determining RA disease activity with DAS28-ESR as the standard.
DISCUSSION
Our results show that PLR and NLR increase significantly in RA patients in active stage,and they are both positively correlated with hs-CRP,ESR,IL-6,DAS28-ESR,CCP,and RF levels before and after tofacitinib treatment.These findings suggest that PLR and NLR may potentially serve as markers for disease activity assessment in RA patients treated with tofacitinib.
Previous studies suggest that leukocyte counts and subtypes can be used to predict inflammatory responses[29,30].The pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1,TNF-α,and IL-6 are responsible for acute phase protein production[9,11,31].The changes in ESR and CRP levels are associated with RA disease activity[18],and the hematological indicators including platelet,lymphocyte,and neutrophil counts are also related with immune response in RA[30,32,33].Platelets secrete inflammatory cytokines and play a critical regulatory role in rheumatic diseases including RA,and increased platelet counts were reported to be associated with RA disease activity[34],which is consistent with our results.As a Janus kinase(JAK) inhibitor,tofacitinib was reported to decrease platelet counts,similar to tocilizumab and rituximab[27,28].In our patients,steroid and methotrexate were also administered both before and after tofacitinib treatment,but they did not seem to produce significant effect on leukocyte or platelet counts of the patients(Tab.1).
PLR and NLR are two common hematological markers widely used for prediction and assessment of treatment efficacy in rheumatic diseases[35].They also serve as inflammatory biomarkers closely associated with the activity of different inflammatory diseases,such as Takayasu's arteritis,psoriatic arthritis,and systemic lupus erythematosus[36].In line with previous studies[27,28],we found that NLR and PLR increased significantly in RA patients in comparison with healthy individuals,and treatment with tofacitinib effectively lowered NLR and PLR in the patients as compared with their baseline levels.JAK/STAT signaling plays an important role in immune cell activation and pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion[37].In this study,we found that tofacitinib treatment significantly decreased IL-6 levels in RA patients,and NLR and PLR were positively correlated with IL-6 level after tofacitinib treatment,suggesting that the changes in these latter two parameters may represent the intensity of inflammation responses and hence the therapeutic efficacy in RA patients.
CCP and RF are acknowledged diagnostic markers of RA,but they both have limitations: CCP test is expensive and not widely carried out in hospitals[38,39],and RF has a relatively low specificity and can be found in other autoimmune diseases,even in healthy individuals[40].Here we demonstrate that both PLR and NLR are increased significantly in patients with active RA in close correlation with the inflammatory indicators and disease activity.ROC curve analysis showed high diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of PLR and NLR for RA and for determining the disease severity.Therefore,both PLR and NLR can be used as convenient,cost-effective,and reliable biomarkers for RA diagnosis and activity assessment.
This study has limitations due to its retrospective nature and the relatively small sample size from a single center.The clinical observation time of the patients is short,and potential confounding factors during RA treatment should be eliminated by linear regression analysis.Future prospective,multi-center studies with larger sample size are warranted to further validate the role of PLR and NLR in disease activity assessment in RA patients receiving tofacitinib treatment.
Conclusion
PLR and NLR increase significantly in RA patients with active disease and can be effectively lowered by tofacitinib treatment.Both PLR and NLR are positively correlated with hs-CRP,ESR,IL-6,DAS28-ESR,CCP,and RF levels before and after tofacitinib treatment,suggesting the potential of PLR and NLR as biomarkers for RA disease activity assessment in tofacitinib-treated RA patients.