The mechanism of regulating macrophage polarization based on Notch1 signaling pathway to improve joint inflammation in adjuvant arthritis rats
2023-03-06CHENGJingWANLeiZHAOLeiLIShuLIFangzeHUSaisaiCHENYingying
CHENG Jing, WAN Lei, ZHAO Lei, LI Shu, LI Fang-ze, HU Sai-sai, CHEN Ying-ying
1. Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230031, China
2. Department of Rheumatology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230031, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To study the impact of the Notch1/Jagged1/RBP-Jκ/Hes1 signaling pathway on macrophage polarization and its role in modulating the inflammatory response in rats with adjuvant arthritis (AA).Methods: The rats were randomly divided into three groups (6 rats): the healthy group (NC), the model group (MC), and the Notch1 inhibitor group (FLI).Medication was administered after 12 days of inducing inflammation.After 30 days, the arthritis index (AI) and degree of swelling in the right hind foot joint (E) were measured in each group.The expression levels of CD80+ and CD163+ cells in peripheral blood macrophages of rats were analyzed by flow cytometry.The standards of IL-4, IL-10, IL-1β, and TNF-α in rat serum were gauged by Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.The expression of Notch1,Jagged1, RBP-Jκ, and Hes1 proteins in rat synovial tissue was detected using Western blot.Results: The degree of swelling (E) and arthritis index (AI) in the MC group rats with AA were significantly higher than those in the NC group (P<0.01).CD80+ cell expression was significantly higher compared to the control group (P<0.01), while CD163+ cell expression was significantly lower than the control group (P<0.01).IL-1β and TNF-α expression levels were significantly elevated (P<0.01), whereas IL-4 and IL-10 expression levels were significantly decreased (P<0.01).Notch1, RBP-Jκ, Jagged1, and Hes1 protein expression levels were significantly increased (P<0.01).In comparison to the MC group, the rats in the Notch1 inhibitor group exhibited a significant reduction in toe swelling and arthritis index(P<0.01).CD80+ cell expression was significantly decreased (P<0.01), while CD163+ cell expression was significantly increased (P<0.01).IL-1β and TNF-α expression levels were significantly decreased (P<0.05), whereas IL-4 and IL-10 levels were significantly increased(P<0.01).Notch1, Jagged1, Hes1, and RBP-Jκ protein expression levels were significantly decreased (P<0.05).Correlation analysis revealed a positive association between CD80+ and Notch1, Jagged1, Hes1, and RBP-Jκ (P<0.01), while CD163+ showed a negative correlation with the expression of these proteins (P<0.01).Conclusion: The Notch1/Jagged1/RBP-Jκ/Hes1 signaling axis regulates macrophage polarization to M2 type and reduces inflammation in AA rats.
1.Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disease caused by an abnormal attack of the immune system on its own joint tissue[1].The synovial tissue of RA patients is proliferative and hypertrophic, and there are many infiltrating inflammatory cells.Aggregated immune cells are directly involved in the development of synovitis by promoting the proliferation of synovial fibroblasts and activating osteoclasts[2].Most of the immune cells in the synovium of RA are macrophages, which can produce the main proinflammatory cytokines involved in the pathological development of RA[3].Domestic and foreign studies have shown that macrophages(Mφ) can be differentiated into M1 and M2, M1 type Mφ is represented by CD80+and CD86+, M2 type Mφ is represented by CD206+and CD163+.M1 macrophages can participate in the development of RA by releasing pro-inflammatory factors such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-a (TNF-a).M2 macrophages release anti-inflammatory factors such as IL-4, IL-10, and IL-13 to reduce inflammation[4,5].
Studies have shown that Notch is an important molecule that regulates the function of macrophages.Activation of Notch signaling can regulate the polarization of Mφ to M1 type and play a pro-inflammatory effect ; blocking Notch signaling can induce Mφ to M2 polarization and exert anti-inflammatory effects[6].The expression and activation of Notch signaling pathway can stimulate synovial cells, thereby promoting the production of pro-inflammatory factors in RA[7].Previous animal studies have shown that the activation of Notch signaling can regulate the M1 polarization of macrophages, thereby promoting the occurrence of adjuvant arthritis (AA)[8].In this study, the effects of Notch1 signaling pathway on arthritis index, toe swelling, serum cytokines(IL-4, IL-1β, IL-10, TNF-α) and M1 / M2 macrophage expression in AA rats were investigated by replicating AA rat model.The role and molecular mechanism of Notch1 / Jagged1 / RBP-Jκ / Hes1 signaling axis in the polarization of synovial M1 / M2 macrophages in AA rats were further studied.
2.Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental animals
Eighteen clean grade SD male rats, weighing (195 ± 15) g.Animals were purchased from Experimental Animal Center of Anhui Medical University.This study followed the provisions of the Experimental Animal Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, animal ethics number AHUCM-rats-2021022.
2.2 Main reagents and instruments
Freund’s complete adjuvant (Sigma, USA, item number MB9887);interleukin-4 (IL-4), IL-10, IL-1β, TGF-α kits (Wuhan gene beauty company, number: JYM0651Ra, JYM0297Ra, JYM0636Ra,JYM0612Ra); rabbit Notch1, Jagged1 and Hes-1 antibodies were purchased from abcam, and the product numbers were ab53457,ab108293 and ab120934, respectively.Rabbit RBP-Jκ antibody:bioss, item number: bs-3906R.Notch1 pathway inhibitor (FLI-06):Shanghai Bluewood Chemical Co., Ltd., Sales No.: S8894.Flow cytometry (Beckman company); inverted microscope (OLYMPUS);centrifuge (Shanghai Hexin Science and Education Equipment Co.,Ltd.); electrophoresis apparatus, electrophoresis tank (Shanghai Tianneng Technology Co., Ltd.).
2.3 Grouping, modeling and administration
Eighteen rats were divided into three groups according to the random control table, namely healthy group, model group and Notch1 inhibitor group, with 6 rats in each group.MC and FLI rats were used to construct AA rat model[9].After 2 weeks, the drug was administered.Notch1 inhibitor group : 0.224 mg / ml mixture was made, 0.056 mg / 0.25 mL / 100 g tail vein injection, once every other day ; healthy group and model group : normal saline 2 mL /only gavage 1 times / day.Administration for 30 day.
2.4 Determination of joint inflammatory symptoms
The right hind foot joint volume of SD rats in each group was measured 1 day before modeling and 30 days after inflammation,and the swelling degree (E) of the right hind foot joint of each group was calculated[10].On the 30 th day after inflammation, the systemic observation was carried out and the arthritis index (AI)was calculated.AI score, normal for 0 points, 1 joint swelling for 1 points, 2 joint swelling for 2 points, more than 2 joint swelling for 3 points, all limb swelling for 4 points.
2.5 Determination of macrophage polarization markers by flow cytometry
100 μL fresh blood of rats was added with anti-mouse CD80-PE 0.25 μg and CD163-AF647 0.25 μg.According to the operation manual, the expression of CD80+and CD163+cells was detected by flow cytometry.
2.6 Determination of the expression of inflammatory cytokines by ELISA
Blood samples were collected from the abdominal aorta, and the OD values of inflammatory cytokines were detected according to the ELISA instructions.The standard curves of IL-4, IL-1β, IL-10 and TNF-α were drawn, and the concentrations of IL-4, IL-1β, IL-10 and TNF-α in rat serum were calculated.
2.7 Western Blot was used to determine the expression level of related proteins
The total protein of synovial membrane was extracted with protein extraction kit, separated by electrophoresis, transferred from gel to membrane by semi-dry method, and blocked with 5 % skim milk powder at room temperature for 2 h.Immunoreaction : At room temperature, Notch1, Jagged1, Hes1, and RBP-Jκ antibody were diluted by 1 / 2 000 and incubated with the membrane for 2 h.The gray values of Notch1, Jagged1, Hes1 and RBP-Jκ bands in each group were calculated.The ratio of the gray value of the target band to the internal reference β-actin was used as the relative expression of Notch1, Jagged1, Hes1 and RBP-Jκ proteins in the synovial membrane.
2.8 Statistical methods
Using SPSS27.0 statistical software, Correlation Analysis method was used to detect correlation, ANOVA method was used to detect variance analysis, and independent sample t test was used to compare the two groups.P < 0.05 was statistically significant.
3.Results
3.1 Effects of Notch1inhibitor on E and AI in AA rats
The E and AI of AA rats in the model group were significantly higher than those in the healthy group (P < 0.01).The E and AI in the Notch1 inhibitor group were significantly lower than those in the model group (P < 0.01).See Table 1.
Tab 1 Comparison of E and AI in each group of rats (n=6, ±s)

Tab 1 Comparison of E and AI in each group of rats (n=6, ±s)
Note : Compared with NC group, △△P <0.01 ; compared with MC group,▲P<0.05, ▲▲P <0.01.
Peer group Swelling degree of right hind foot joint(%) Arthritis index (points)NC 44.74±11.92 0.00±0.00 MC 80.26±17.53△△ 6.85±1.69△△FLI 47.30±17.59▲▲ 4.97±0.75▲
3.2 Effects of Notch1inhibitor on M1, M2surface markers in AA rats
The expression of CD80+cells in AA rats in MC group was significantly higher than that in NC group, while the expression of CD163+cells was significantly lower than that in NC group (P <0.01).In Notch1 inhibitor group, the expression of CD80+cells was significantly lower than that in MC group, and the expression of CD163+cells was significantly higher than that in MC group (P <0.01).See Table 2, Figure 1, Figure 2.
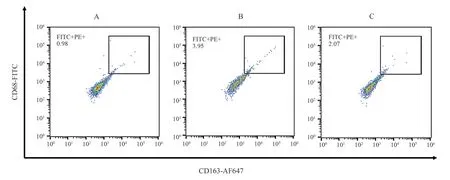
Fig 1 CD80 + flow cytometry of each group
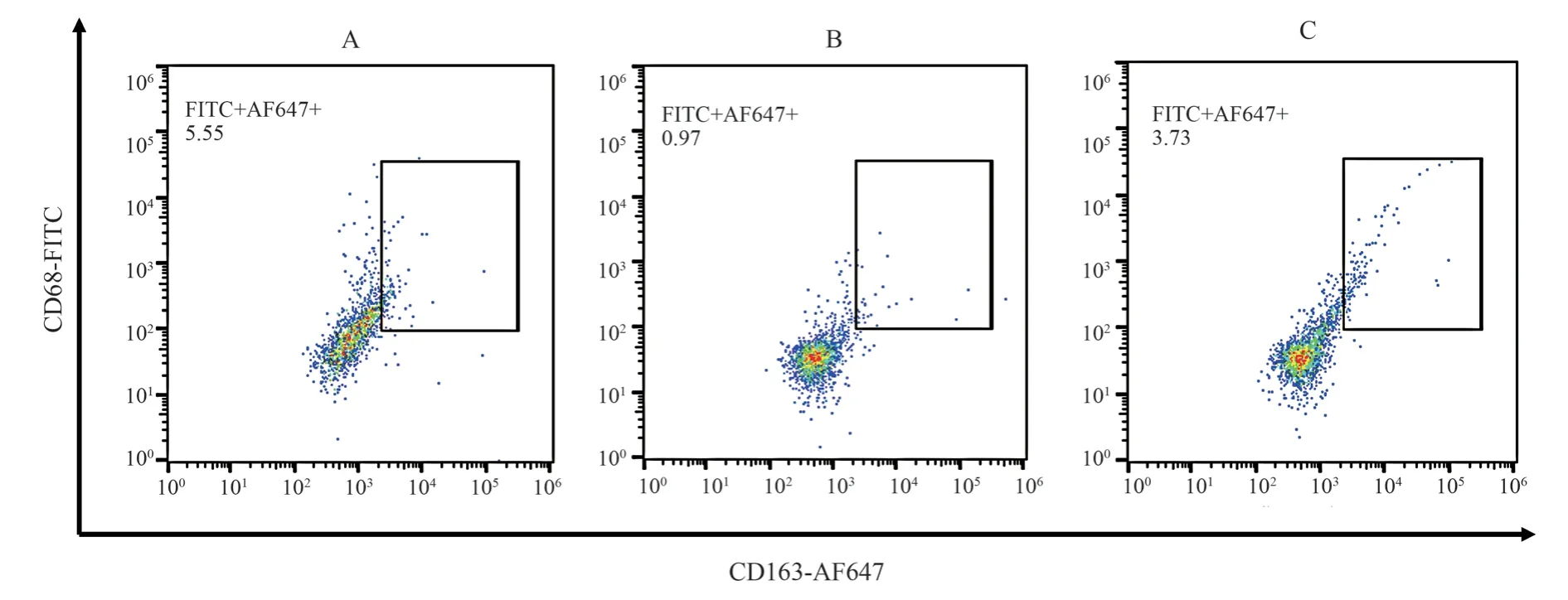
Fig 2 CD163+ flow cytometry of each group
Tab 2 Comparison of Macrophage Polarization Markers in Different Groups (n=6,±s)
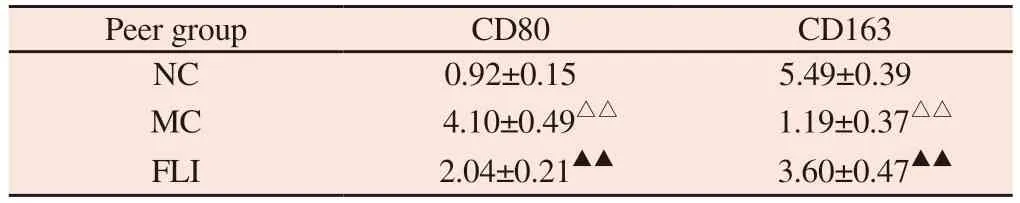
Tab 2 Comparison of Macrophage Polarization Markers in Different Groups (n=6,±s)
Note : Compared with NC group, △△P<0.01 ; compared with MC group,▲▲P<0.01.
Peer group CD80 CD163 NC 0.92±0.15 5.49±0.39 MC 4.10±0.49△△ 1.19±0.37△△FLI 2.04±0.21▲▲ 3.60±0.47▲▲
3.3 Effects of Notch1 inhibitor on the levels of IL-4, IL-1β,IL-10 and TNF-α in AA rats
Compared with NC group, the expression of IL-1β and TNF-α in MC group was significantly increased (P < 0.01), while the expression of IL-4 and IL-10 was significantly decreased (P < 0.01).The expression of IL-1β and TNF-α in FLI group was significantly lower than that in MC group (P < 0.05), and the expression of IL-4 and IL-10 was significantly higher than that in MC group (P < 0.01).See Table 3.
3.4 Effect of Notch1 inhibitor on Notch1, Jagged1, Hes1 and RBP-Jκ protein in synovial tissue of AA rats
The expressions of Notch1, Jagged1, Hes1 and RBP-Jκ in MC group were significantly higher than those in NC group (P < 0.01).The expression of Notch1, Jagged1, Hes1 and RBP-Jκ in synovial tissue of Notch1 inhibitor group was significantly lower than that of MC group (P < 0.05).See Table 4, Figure 3.

Fig 3 The protein expression of Notch1 / Jagged1 / RBP-Jκ / Hes1 in each group of rats
3.5 Correlation analysis of macrophage polarization markers and Notch1, Jagged1, Hes1, RBP-Jκ protein in AA rats
Correlation analysis showed that CD80 was positively correlated with Notch1, Jagged1, Hes1 and RBP-Jκ protein (P < 0.01), and CD163 was negatively correlated with Notch1, Jagged1, Hes1 and RBP-Jκ protein (P < 0.01), as shown in table 5.
Tab 3 Comparison of inflammatory cytokine levels in rats of each group (n=6, ±s)

Tab 3 Comparison of inflammatory cytokine levels in rats of each group (n=6, ±s)
Note: Compared with NC group, △△ P<0.01 ; compared with MC group, ▲P<0.05,▲▲P < 0.01.
Peer group IL-4 IL-1β IL-10 TNF-α NC 10.71±0.55 46.23±5.89 67.81±3.91 42.00±7.99 MC 2.87±0.28△△ 153.60±13.02△△ 19.36±2.25△△ 177.41±7.94△△FLI 6.82±0.23▲▲ 72.67±5.66▲ 30.00±0.99▲▲ 87.41±5.33▲
Tab 4 Comparison of Notch1, Jagged1, Hes1 and RBP-Jκ expression levels in each group of rats (n=6, ±s)

Tab 4 Comparison of Notch1, Jagged1, Hes1 and RBP-Jκ expression levels in each group of rats (n=6, ±s)
Note: Compared with NC group, △△ P<0.01 ; compared with MC group,▲P<0.05.
Peer group Notch1 Jagged1 Hes1 RBP-Jκ NC 0.15±0.13 0.10±0.04 0.19±0.01 0.41±0.13 MC 0.73±0.12△△ 0.54±0.12△△ 1.45±0.50△△ 0.90±0.21△△FLI 0.44±0.19▲ 0.35±0.01▲ 0.46±0.08▲ 0.61±0.16▲

Tab 5 Correlation analysis of CD80, CD163 and other indicators
4.Discussions
RA is an autoimmune inflammatory disease related to the irreversible destruction of the affected joints.The main features are immune cell infiltration and synovial inflammation.In RA,activated synovial fibroblasts produce pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, leading to characteristic joint inflammation and cartilage destruction[11,12].Studies have found that IL-4, IL-10 and TNF-α are key factors in the development of RA, and they are involved in Th1-mediated inflammatory response, leading to cartilage and bone destruction[13].M1 macrophages are the key regulatory molecules of RA articular cartilage inflammation.M2 macrophages exert anti-inflammatory activity by secreting cytokinessuch as IL-10 and are conducive to tissue repair.IL-4 can induce the decreaseof M1 macrophage marker and the increase of M2 macrophage marker[14-16].Studies have shown that the treatment of inducing polarization from M1 to anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages may be better to control the abnormal inflammatory response of RA[17].The results of this study showed that compared with the NC group, the expression levels of IL-1β and TNF-α in the MC group were significantly increased, and the expression levels of IL-4 and IL-10 were significantly decreased.The expression of CD80+cells was significantly increased, and the expression of CD163+cells was significantly decreased.The expression levels of Notch1, Jagged1, Hes1 and RBP-Jκ protein were significantly increased, indicating that macrophages in AA rats were polarized to M1 macrophages, inhibiting the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines and promoting the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines.Abnormal activation of Notch1 / Jagged1 / RBP-Jκ /Hes1 signaling axis in AA rats.At the same time, it verified the previous research of the research group that Notch signaling pathway was closely related to the regulation of macrophage polarization in the pathogenesis of RA.
Notch signaling pathway includes Notch receptor (Notch1) and Notch ligand (Jagged-1)[18].Activation of Notch signaling may negatively regulate the immune defense mechanism in macrophages,and can promote cytokine secretion and aggravate RA[19].After Notch1 and Jagged1 are combined, they are combined with the transcription factor RBP-Jκ to form a transcription complex, which in turn regulates the expression of the target gene Hes1, leading to the differentiation of inflammatory polarization of macrophages to M1 type, and promoting the formation of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1β and TNF-α, which may be involved in the development of RA.Inhibition of Notch signaling pathway causes macrophage polarization to differentiate from M1 type to M2 type, which may be involved in the treatment of RA[20-22].This experimental study found that the expression levels of IL-1β and TNF-α in the Notch1 inhibitor group were significantly lower than those in the MC group, and the expression levels of IL-4 and IL-10 were significantly higher than those in the MC group ; the results are similar to those of Su et al[23].
RBP-Jκ-dependent Notch pathway is a new way to participate in joint maintenance and articular cartilage homeostasis[24].Yang et al.found that inhibiting the expression of Notch1 receptor, Jagged1 ligand and Hes1 promoted the polarization of macrophages into M2 macrophages[25].Correlation analysis showed that CD80 was positively correlated with Notch1, Jagged1, Hes1 and RBP-Jκ protein, and CD163 was negatively correlated with Notch1, Jagged1,Hes1 and RBP-Jκ protein.It can be seen that after Notch1 binds to Jagged1, it binds to RBP-Jκ to form a transcription complex,thereby regulating the expression of target gene Hes1, which can polarize macrophages to M1.The results showed that the Notch1/ Jagged1 / RBP-Jκ / Hes1 axis was related to M1 and M2.The results of this study showed that Notch1 inhibitor group could significantly down-regulate the expression of Notch1, Jagged1, Hes1 and RBP-Jκ protein in synovial tissue.Compared with MC group,the swelling degree and arthritis index of right hind foot joint in Notch1 inhibitor group were significantly decreased.The expression of CD80+cells was significantly decreased, and the expression of CD163+cells was significantly increased.Compared with previous studies, it was further clarified that inhibition of Notch1 signaling pathway can improve the inflammatory response of AA rats by regulating the polarization of macrophages to M2 type, upregulating the expression of IL-4 and IL-10, and down-regulating the expression of IL-1β and TNF-α.
In summary, by inhibiting the Notch1 / Jagged1 / RBP-Jκ / Hes1 signaling axis, regulating the polarization of M1-type to M2-type macrophages, and improving the immune inflammatory response of AA rats.It provides a technical and scientific basis for future clinical research.
The author’s contribution shows :
Cheng Jing: complete the test, analyze the data, write papers;wanlei: Conducting experimental design to provide direction for the paper; zhao Lei collected specimens; li Shu, Li Fangze, Hu Saisai,Chen Yingying: Collecting data.
All the authors declared no conflict of interest.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Effects of Tribulus terrestris saponins on proliferation and invasion of A549 cells
- Compound fufangteng mixture affects the expression of CD69 on CD11b + monocytes in immunosuppressed mice
- Mechanism of Sanshi decoction in the treatment of gouty arthritis by NLRP3 inflammasome
- Predictive value of controlling nutritional status score for progression to chronic critical illness in elderly patients with sepsis
- SPHK1 expression in gastric cancer and clinical value based on bioinformatics analysis
- Meta-analysis of the effects of high-intensity intermittent exercise on cardiopulmonary function rehabilitation in patients with stroke
