基于阻抗幅值波动差异的新型参数识别方向元件
2023-02-22牛伟民樊艳芳张鑫宇
牛伟民,樊艳芳,张鑫宇,马 健
基于阻抗幅值波动差异的新型参数识别方向元件
牛伟民1,樊艳芳1,张鑫宇2,马 健2
(1.新疆大学电气工程学院,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830046;2.国网新疆电力有限公司电力科学研究院,新疆 乌鲁木齐 830011)
针对故障分量方向元件在大规模双馈风机并网不适用的问题,提出了基于正序阻抗幅值波动差异的新型参数识别方向元件。首先,将风电场正序阻抗波动量化,分析阻抗波动对正序故障分量方向元件影响,得到正序故障分量方向元件在风电场送出线路的拒动边界。其次,基于Prony算法结合带通滤波器提取工频量,分析送出线路风电侧正、反方向故障正序阻抗幅值变化特征。最后,引入去趋势波动分析(detrended fluctuation analysis, DFA)计算波动函数,构造新型参数识别方向元件动作判据,实现故障方向判别。仿真结果表明,提出的参数识别方向元件不受风电场运行工况、故障类型和系统振荡的影响。当过渡电阻达到100W时,仍能正确判别故障方向,具有较强的抗干扰性能,适用于含风电接入的弱馈型电力系统。
双馈风电场;故障分量方向元件;阻抗波动;DFA;波动函数;参数识别
0 引言
在能源转型和电力电子技术日趋成熟的推动下,大规模风电接入电力系统[1-5]的故障特征与常规电网不同,使工频量保护存在适应问题[6-9]。故障分量方向元件在电力系统中应用广泛[10-13]。故障分量方向元件适用于线性网络及正负序阻抗相等的系统,而大规模风电接入使得电力系统由线性网络变为非线性网络,风电场正负序阻抗不相等且呈现波动特征,开展风电场送出线路故障分量方向元件适应范围分析及改进研究具有重要意义。
针对故障分量方向元件在风电接入的电力系统适应性分析,已有相关研究。文献[14-15]通过仿真验证了故障分量方向元件在大规模风电接入时存在适应问题,但未详细分析其故障特征对故障分量方向元件判别能力的影响。文献[16]提出正序故障分量方向元件除了受频偏特性影响,还受风电场正序阻抗波动影响,但未对影响机理、影响程度进行量化分析。文献[17]分析了故障稳态下Crowbar电路投入对双馈异步风力发电机(doubly fed induction generator, DFIG)正序阻抗的影响,但该正序阻抗公式不能表征故障暂态期间阻抗波动情况。针对故障分量方向元件在风电接入的电力系统改进方面,文献[18]提出利用故障相故障前后短路电流夹角余弦值差异构成新型方向元件,但该方法仅考虑频偏特性的影响,未考虑正序阻抗范围波动影响,单相接地故障下不具有正确判别故障方向的能力。文献[19]提出基于时域电压波形相似度的方向元件,但该方法易受异常数据影响。
综上,目前尚未提出较为契合风电接入电力系统的新型方向元件。本文首先基于双馈风电场接入电力系统,利用正序故障分量方向元件判据划分风电场侧正序阻抗允许波动区域,分析正序阻抗波动对正序故障分量方向元件影响,探寻风电场送出线路正序故障分量方向元件拒动边界。其次根据正、反方向故障下正序阻抗幅值波动迥异,引入DFA方法,提出基于正序阻抗幅值波动差异的新型参数识别方向元件。最后在PSCAD/EMTDC仿真中搭建双馈风电场接入电力系统模型,仿真结果结合Matlab验证了理论分析正确性。
1 阻抗波动对故障分量方向元件影响分析
1.1 正序故障分量方向元件理论基础
本文基于图1拓扑探讨风电场正序阻抗波动对风电场送出线路的正序故障分量方向元件影响。

图1 双馈风电场接入电力系统拓扑
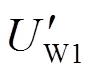
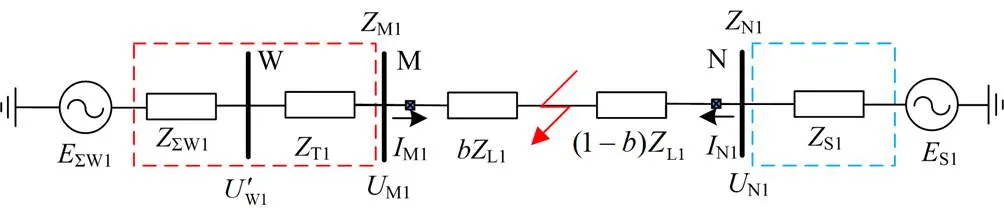
图2 正序故障网络分解图
f2处故障时,N侧电压电流不受风电接入影响[20],方向元件正常运行。本文针对M侧正序故障分量方向元件受阻抗波动影响展开分析并改进。
正序故障分量方向元件判据为

1.2 DFIG正序阻抗特征分析
当双馈风电场送出线路发生短路故障时,为防止风电场脱网运行致使电网有功缺额进一步恶化,通常将投入Crowbar电路进行低电压穿越[21]。故本文以正确提取工频量为前提,量化风电场投入Crowbar电路下正序阻抗波动情况,分析阻抗波动对M侧正序故障分量方向元件影响。
DFIG正序阻抗计算方法[22]为
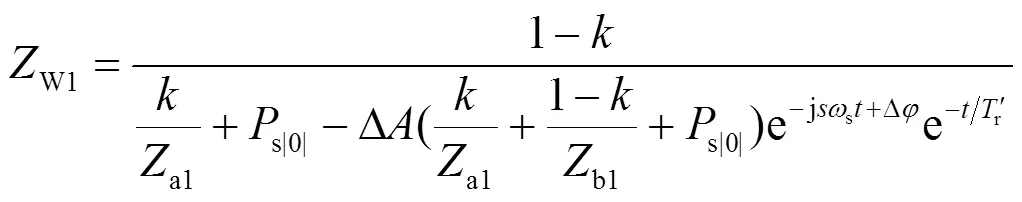
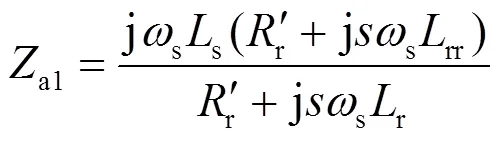
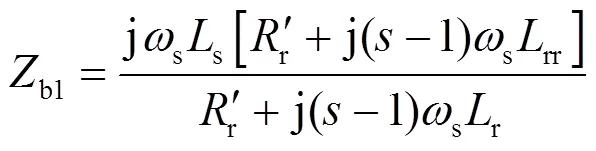
衰减转速分量幅值系数∆为
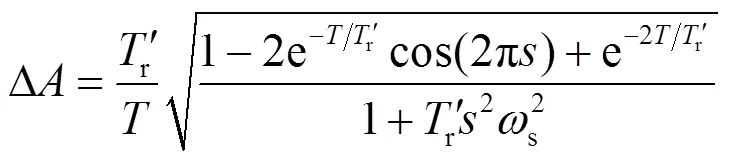
衰减转速分量相角变化量∆为
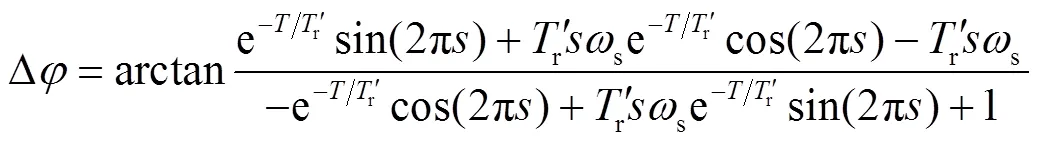
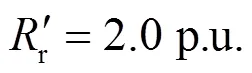


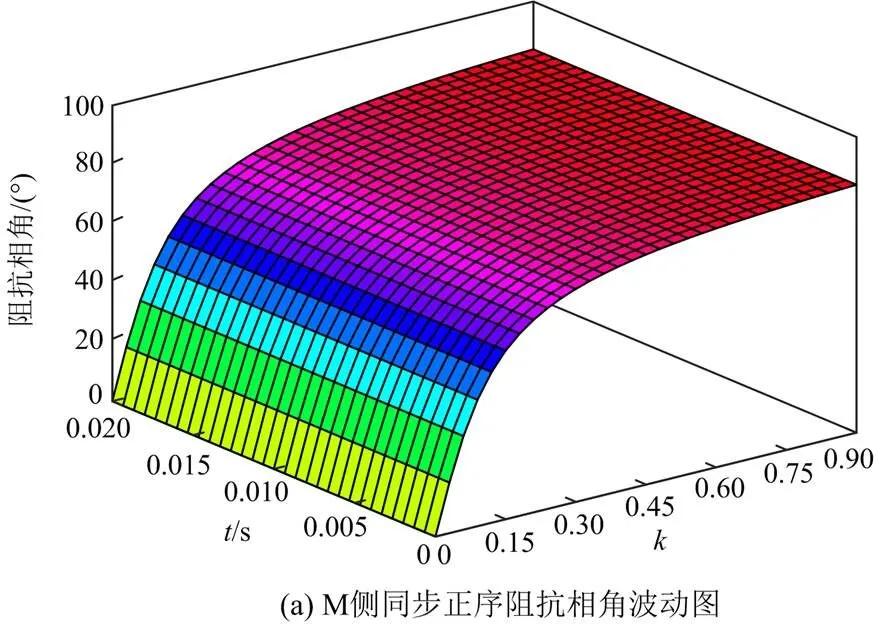
2 正序故障分量方向元件拒动边界
当风电场送出线路M侧发生正方向故障时,由式(1)可知,风电场正序阻抗角波动情况决定M侧正序故障分量方向元件动作与否。当风电场正序电抗ΣW1< 0时,正序故障分量方向元件动作。为探析正序故障分量方向元件拒动边界,将式(2)化简,结合ΣW1≥ 0,可得式(7)。

式中:
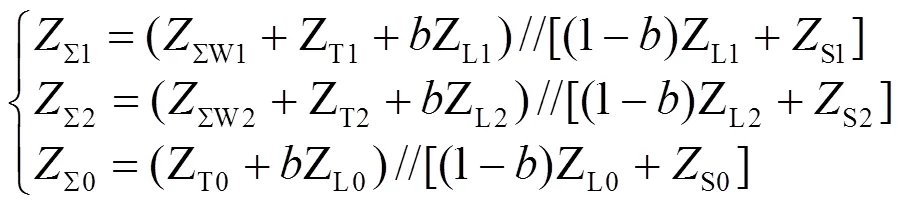
求解不同故障类型的故障点正序短路电流为

则故障点处正序电压为
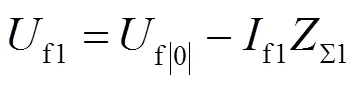
风电场提供的短路电流为
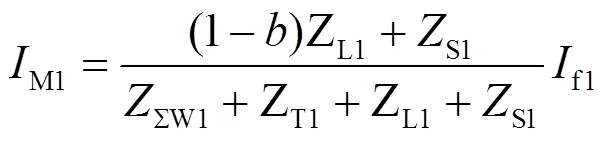
风电场正序电压为
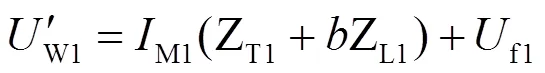

表1 实际电压跌落系数k1
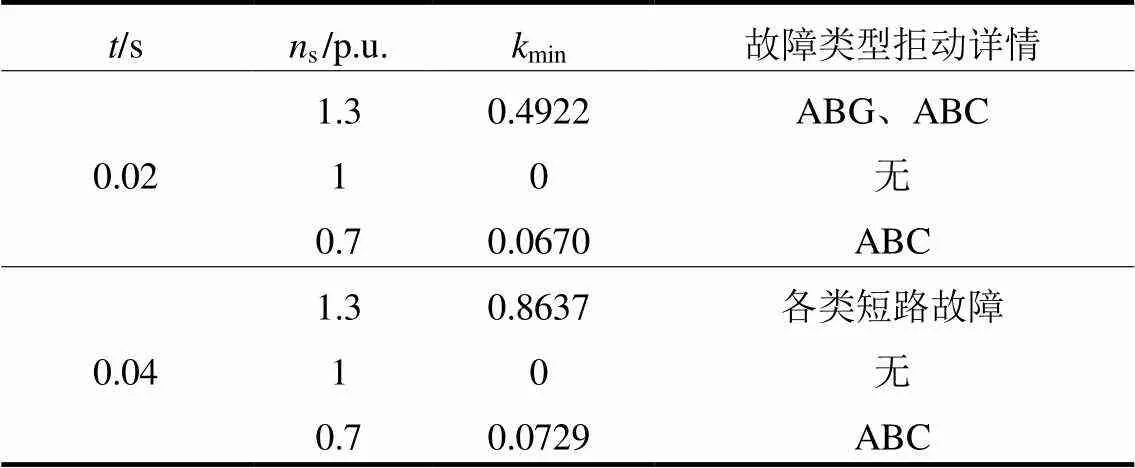
表2 受故障时间影响的拒动边界
结合上述分析可知,基于相角的正序故障分量方向元件不满足保护元件性能要求。因此,亟需提出适应于双馈风电场送出线路的新型方向元件。
3 新型参数识别方向元件
新型方向元件不可仅考虑短路电流频偏特性,也须考虑故障下阻抗波动影响。针对短路电流频偏特性影响,将采用Prony算法结合带通滤波器,保证工频量正确提取,避免频偏特性影响。解决风电场频偏特性影响后,利用故障情况下风电场正序阻抗幅值范围波动特征,引入DFA方法。该方法可分析非平稳时间序列,可平抑异常数据。基于其基本原理计算所得的DFA波动函数,可作为正、反方向故障下阻抗幅值波动程度的衡量指标。利用正、反方向故障下指标差异,构建适应于双馈风电场送出线路的新型参数识别方向元件。
3.1 DFA方法的引入
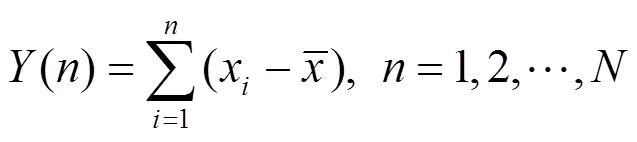
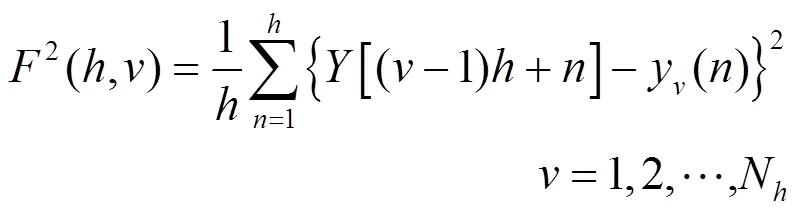
反向划分的子区间局部去趋势结果为

步骤五:计算DFA波动函数。
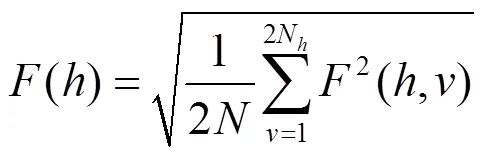
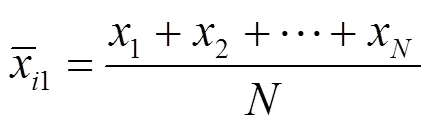
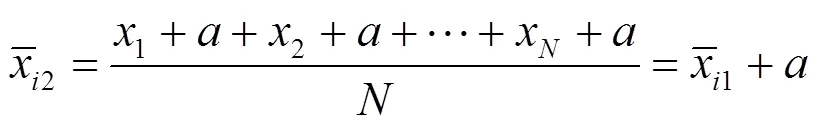


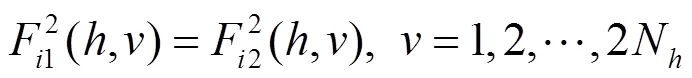
基于DFA方法计算x1及x2的波动函数可得:
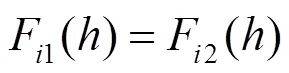
通过上述分析可知,依据DFA方法计算波动函数时,其波动函数大小由非平稳序列波动状况决定,与非平稳序列中的固定常量无关。
3.2 保护判据构造
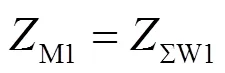

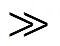
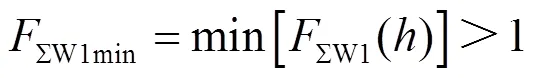
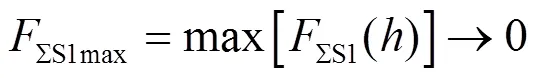
对于M侧发生正方向故障时,M侧背侧正序阻抗分量主要为ΣW1,结合式(25)可得M侧方向元件正方向故障判据为
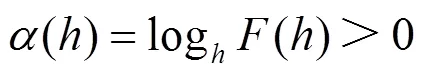
对于M侧发生反方向故障时,M侧背侧正序阻抗分量主要为S1,结合式(26)可得M侧反方向故障下()参数为负。
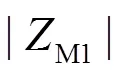
新型参数识别方向元件继承了故障分量方向元件方向性明确、不受风电场运行工况、系统振荡、过渡电阻影响的优点,结合DFA方法计算局部去趋势,使得该方向元件受异常数据影响较小。
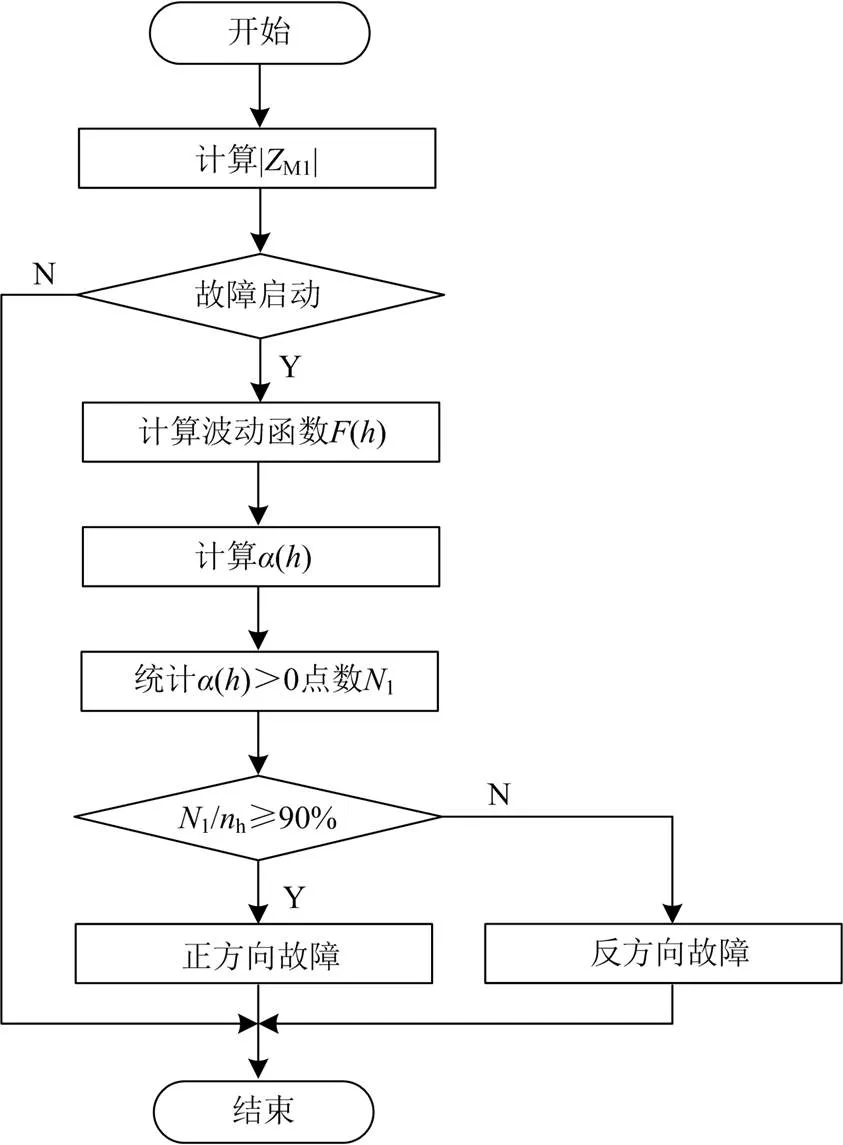
图4 新型参数识别方向元件判别流程图
4 仿真验证
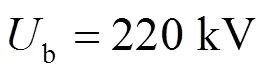
4.1 正序阻抗波动特征
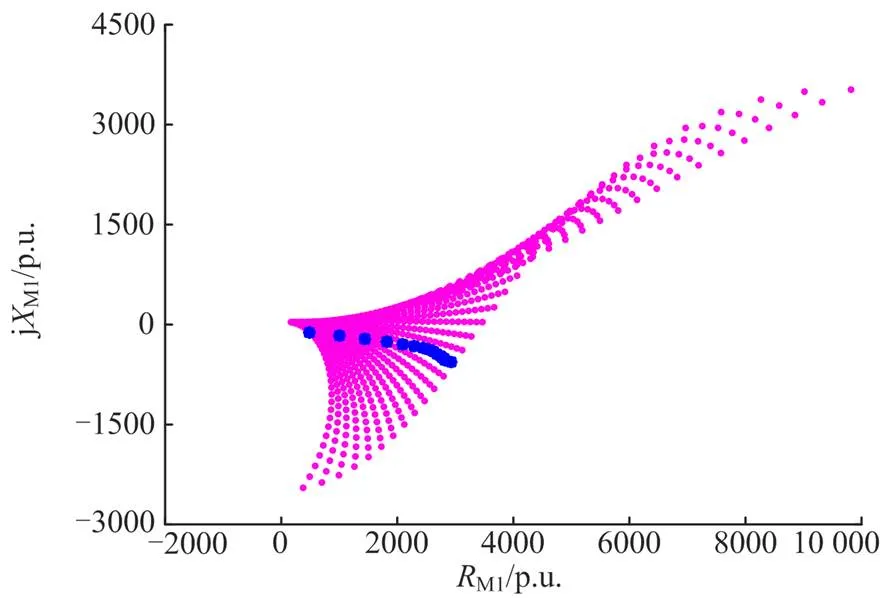
图5 正序阻抗波动验证图
4.2 正序故障分量方向元件动作性能
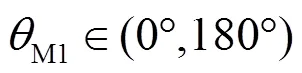

图6 正序故障分量方向元件动作性能图
4.3 新型参数识别方向元件性能
4.3.1正方向故障

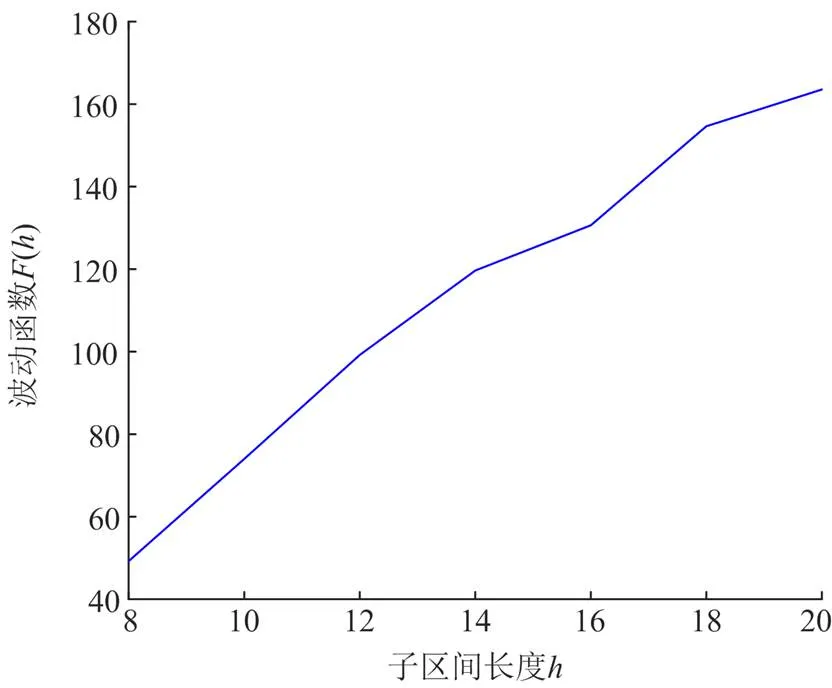
图7 M侧正方向故障F(h)结果
4.3.2反方向故障

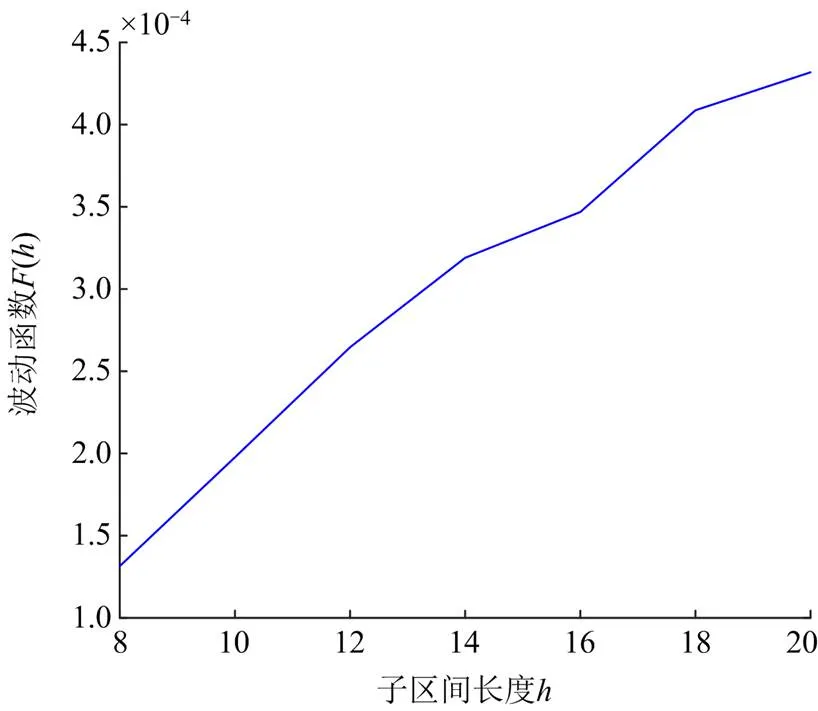
图8 M侧反方向故障F(h)结果
4.3.3系统振荡对新型参数识别方向元件的影响
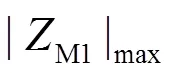
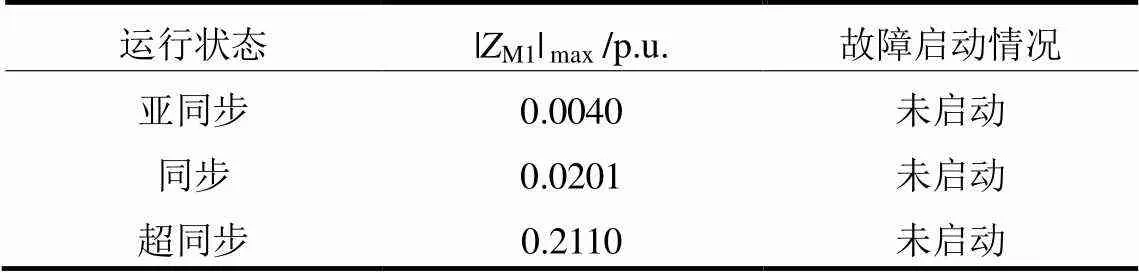
表3 系统振荡下的元件性能
由表3可知,新型参数识别方向元件在风电场不同运行状态下不受系统振荡影响。
4.3.4异常数据对新型参数识别方向元件的影响
异常数据干扰分为数据缺失与虚假脉冲,以f2处发生ABG故障为例,设置M侧电压、电流信号每5 ms出现一次数据缺失或虚假脉冲,对应仿真结果如表4、表5所示。其中220 kV线路最大过渡电阻为100 Ω,故以最大过渡电阻验证异常数据影响下的新型参数识别方向元件性能。
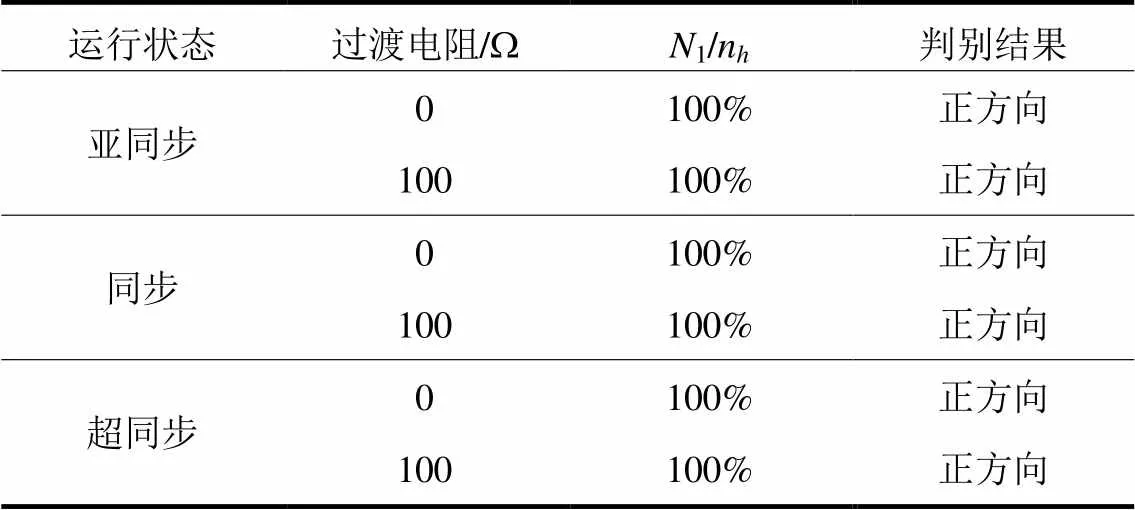
表4 数据缺失下的元件性能
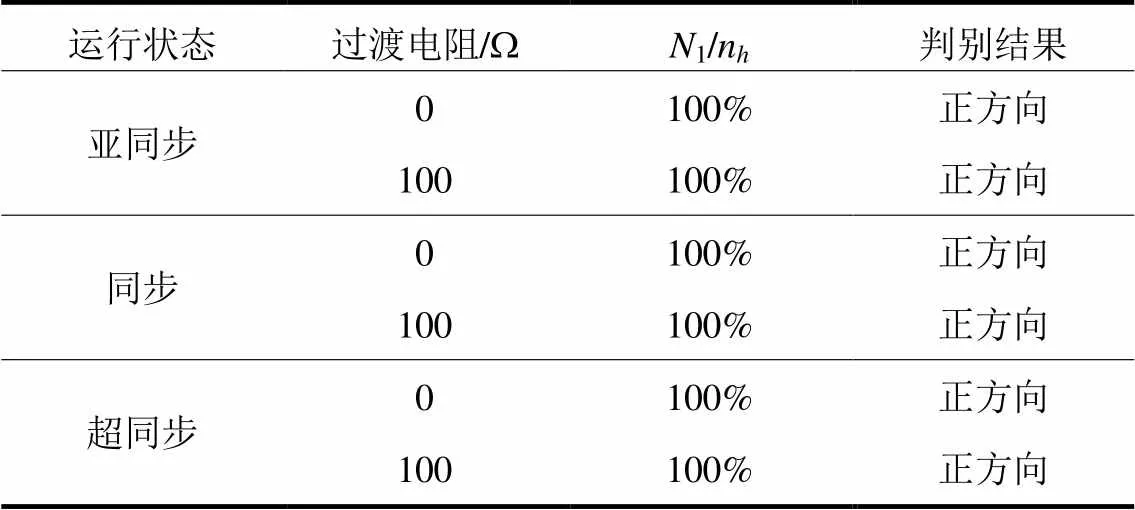
表5 虚假脉冲下的元件性能
由表4、表5可知,新型参数识别方向元件对不同运行状态、不同过渡电阻下的异常数据适应性较强。
5 结论
本文利用M侧背侧正序阻抗波动特征,结合正序故障分量方向元件判别原理,对正序故障分量方向元件适应范围分析,提出基于正序阻抗幅值波动差异的新型参数识别方向元件,得到以下结论:
2) 基于正序阻抗幅值波动差异的新型参数识别方向元件能可靠、灵敏地判别故障方向,继承了故障分量方向元件优点,同时受异常数据影响较小,完全适用于在风电接入的弱馈系统中。
附录A
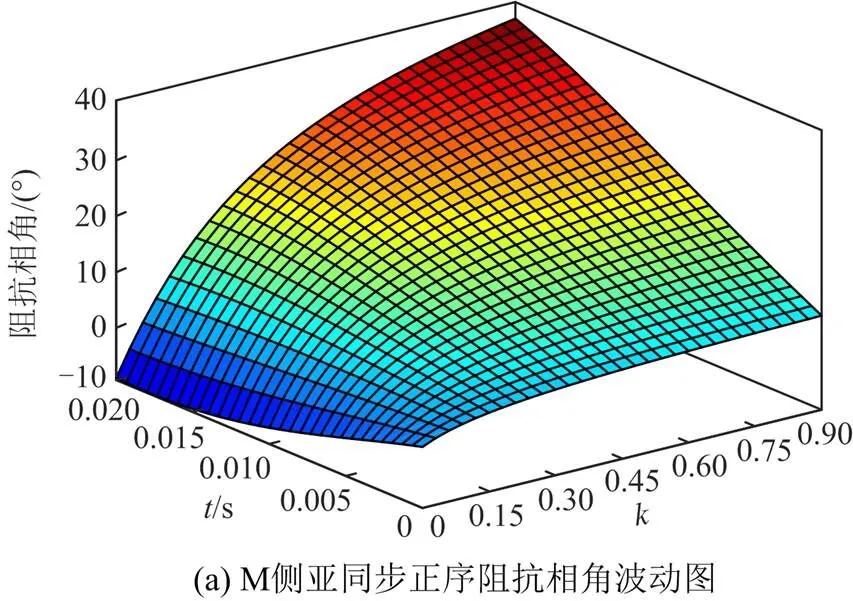
图A1 M侧亚同步正序阻抗波动图
Fig. A1 M-side sub-synchronous positive sequence impedance fluctuation
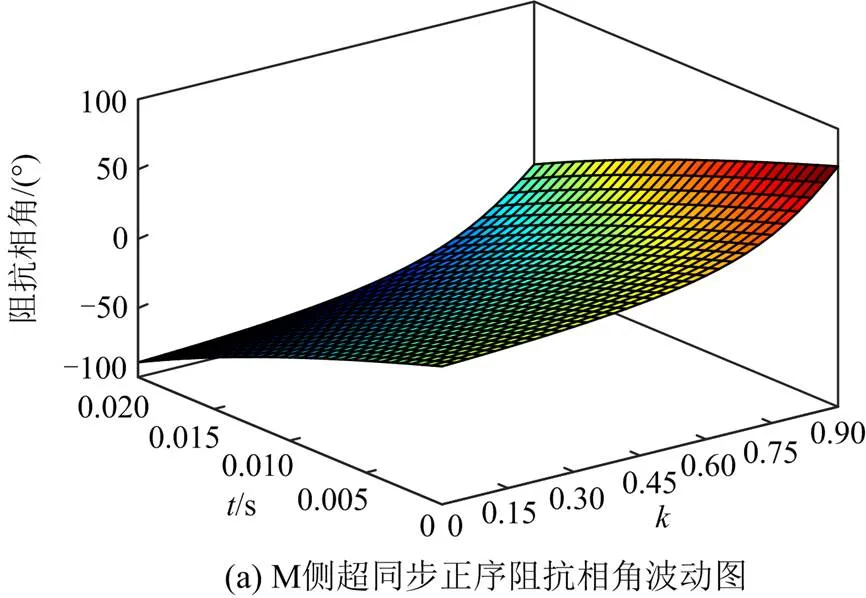
图A2 M侧超同步正序阻抗波动图
Fig. A2 M-side super-synchronous positive sequence impedance fluctuation
[1] 张太升, 韩伟, 杨霖, 等. 基于波形相关分析的双馈风电场送出线时域距离保护[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(14): 82-88.
ZHANG Taisheng, HAN Wei, YANG Lin, et al. Time- domain distance protection for transmission lines of doubly-fed wind farms based on waveform correlation analysis[J].Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(14): 82-88.
[2] 于淼, 汤亚芳, 黄亦欣, 等. 双馈风机控制方式对继电保护影响的研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48(2): 180-187.
YU Miao, TANG Yafang, HUANG Yixin, et al. Research on the influence of control mode of DFIG on relay protection[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48(2): 180-187.
[3] 马健, 樊艳芳, 李锋, 等. 适用于集群风电场送出线的选相元件研究[J]. 可再生能源, 2020, 38(9): 1217-1225.
MA Jian, FAN Yanfang, LI Feng, et al. Research on fault phase selection method for cluster wind farm outgoing line[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2020, 38(9): 1217-1225.
[4] SONG Guobing, WANG Chenqing, WANG Ting, et al. A phase selection method for wind power integration system using phase voltage waveform correlation[C] // 2018 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), August 5-10, 2018, Portland, OR, USA.
[5] 文劲宇, 周博, 魏利屾. 中国未来电力系统储电网初探[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2022, 50(7): 1-10.
WEN Jinyu, ZHOU Bo, WEI Lishen. Preliminary study on an energy storage grid for future power system in China[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2022, 50(7): 1-10.
[6] TAO Renfeng, LI Fengting, CHEN Weiwei, et al. Research on the protection coordination of permanent magnet synchronous generator based wind farms with low voltage ride through capability[J]. Protection and Control of Modern Power Systems, 2017, 2(3): 311-319.
[7] 王春又, 孙士云, 毛肖, 等. 适应于双馈风电场送出线的时域距离纵联方向保护[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(13): 82-94.
WANG Chunyou, SUN Shiyun, MAO Xiao, et al. Longitudinal direction protection of time domain distance applicable to the outgoing line of a double-fed wind farm[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(13): 82-94.
[8] 黄涛, 陆于平, 蔡超. DFIG等效序突变量阻抗相角特征对故障分量方向元件的影响分析[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2016, 36(14): 3929-3940.
HUANG Tao, LU Yuping, CAI Chao. Analysis of phase angle characteristics of DFIG equivalent sequence superimposed impedances and its impact on fault components based direction relay[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2016, 36(14): 3929-3940.
[9] 饶鸿江. 风电场站送出线路纵联保护及故障测距新方法研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2021.
[10] 焦在强. 大规模风电接入的继电保护问题综述[J]. 电网技术, 2012, 36(7): 195-201.
JIAO Zaiqiang. A survey on relay protection for grid- connection of large-scale wind farm[J]. Power System Technology, 2012, 36(7): 195-201.
[11] 罗美玲. 双馈式风电机组群的短路电流特性及其对线路保护的影响研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2015.
LUO Meiling.Research on characteristics of DFIG-based wind farm short circuit current and its influence on line protection[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2015.
[12] 宋国兵, 常鹏, 侯俊杰, 等. 故障分量方向元件在交直流多端馈入系统中的适应性分析[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2021, 45(9): 136-145.
SONG Guobing, CHANG Peng, HOU Junjie, et al. Adaptability analysis of fault component directional element in AD/DC multi-terminal infeed system[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2021, 45(9): 136-145.
[13] 杨启帆, 刘益青, 朱一鸣, 等. 适用于DFIG并网线路的改进负序方向元件[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43(10): 118-126, 149.
YANG Qifan, LIU Yiqing, ZHU Yiming, et al. Improved negative sequence directional element for transmission line connecting DFIG[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43(10): 118-126, 149.
[14] 钟显, 樊艳芳, 王一波. 双馈集群汇集站主变及送出线路继电保护研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2016, 44(5): 47-54.
ZHONG Xian, FAN Yanfang, WANG Yibo.Research of transformer and outgoing line protection of collection station where cluster of double-fed wind farms put in[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2016, 44(5): 47-54.
[15] 滕予非, 行武, 张宏图, 等. 风力发电系统短路故障特征分析及对保护的影响[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2015, 43(19): 29-36.
TENG Yufei, XING Wu, ZHANG Hongtu, et al.Analysis of characteristics of short circuit fault of wind power system and the impact on the protection[J].Power System Protection and Control, 2015, 43(19): 29-36.
[16] 王晨清, 宋国兵, 汤海雁, 等. 选相及方向元件在风电接入系统中的适应性分析[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2016, 40(1): 89-95.
WANG Chenqing, SONG Guobing, TANG Haiyan, et al. Adaptability analysis of phase selectors and directional relays in power systems integrated with wind farms[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2016, 40(1): 89-95.
[17] 杨欢红, 李庆博, 盛福, 等. 双馈风电场的弱馈性及风电接入对突变量保护元件的影响[J]. 上海电力学院学报, 2016, 32(2): 103-108, 114.
YANG Huanhong, LI Qingbo, SHENG Fu, et al. Weak feed of doubly-fed wind farm and its impact on fault component protection[J].Journal of Shanghai University of Electric Power, 2016, 32(2): 103-108, 114.
[18] 陈童. 含分散式双馈风力发电机的配电线路保护研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2020.
CHEN Tong. Research on distribution line protection with distributed DFIG[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2020.
[19] 陈玉, 文明浩, 胡列翔, 等. 双馈风机风电场联络线出口故障方向判别[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报, 2020, 32(2): 1-6.
CHEN Yu, WEN Minghao, HU Liexiang, et al. Fault direction identification for outgoing line of DFIG-based wind farm[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2020, 32(2): 1-6.
[20] 李彦宾, 贾科, 毕天姝, 等. 逆变型电源对故障分量方向元件的影响机理研究[J]. 电网技术, 2017, 41(10): 3230-3236.
LI Yanbin, JIA Ke, BI Tianshu, et al. Influence mechanism of inverter-interfaced renewable energy generators on fault component based directional relay[J]. Power System Technology, 2017, 41(10): 3230-3236.
[21]谭爱国, 吴颖颖, 王传启, 等. 基于保障低压穿越能力的风电机组撬棒自适应投切策略研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(18): 98-109.
TAN Aiguo, WU Yingying, WANG Chuanqi, et al. Adaptive switching strategy for a wind turbine crowbar based on the guarantee of low voltage ride-through capability[J].Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(18): 98-109.
[22] 黄涛. 风电接入对继电保护影响机理及充分式保护新方案研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2017.
HUANG Tao.Study on impact mechanism of wind power integration on protective relaying and new sufficient criterion protection schemes[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2017.
Novel parameter identification directional element based on impedance amplitude fluctuation difference
NIU Weimin1, FAN Yanfang1, ZHANG Xinyu2, MA Jian2
(1. School of Electrical Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830046, China; 2.State Grid Xinjiang Electric Power Co., Ltd. Electric Power Research Institute, Urumqi 830011, China)
There is a problem in that the fault component directional element is not suitable for grid-connected large-scale DFIG. Thus a novel parameter identification directional element based on the difference of positive sequence impedance amplitude fluctuation is proposed. First, this paper quantifies the positive sequence impedance fluctuation of a wind farm, analyzes the impact of impedance fluctuation and obtains the rejection boundary of the positive sequence fault component directional element on the wind farm outgoing line. Second, based on the Prony algorithm combined with a band-pass filter, the power frequency is extracted, and the characteristics of the positive sequence impedance amplitude change of the forward and reverse faults on the wind power side of the outgoing line are analyzed. Finally, detrended fluctuation analysis (DFA) is introduced to calculate the fluctuation function, and a novel parameter identification directional element action criterion is constructed to realize the fault direction identification. The simulation results show that the proposed parameter identification directional element is unaffected by the operating conditions of the wind farm, fault types and system oscillations. When the transition resistance reaches 100W, it can still correctly determine the fault direction, has strong anti-interference performance, and is suitable for weak feeder power systems with wind power access.
doubly-fed wind farm; fault component directional element; impedance fluctuation; DFA; fluctuation function; parameter identification
10.19783/j.cnki.pspc.220750
国家自然科学基金项目资助(51877185);新疆维吾尔自治区高校科研重点项目资助(XJEDU2021I009)
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51877185).
2022-05-18;
2022-07-21
牛伟民(1997—),男,硕士,研究方向为电力系统保护与控制;E-mail: nwmxju@126.com
樊艳芳(1971—),女,通信作者,教授,博士生导师,研究方向为电力系统保护与控制。E-mail: 410849062@ qq.com
(编辑 姜新丽)
