Characteristics of Implicit Customer Needs in Product Design and Methods for Their Identification
2023-01-31HUANGHuaDENGYimin
HUANG Hua, DENG Yimin
(Faculty of Mechanical Engineering & Mechanics, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, China)
Abstract:The identification of customer needs is one of the important first-step works for product design. Contrary to explicit ones, the implicit customer needs are less obvious, thus relying on the designers to discover. Up till now, there still lacks a rational or systematic method on the identification of implicit customer needs. Designers have to rely on their own intuition and personal experience to do the work, hindering the product design and development further on. Therefore, it is necessary to study the implicit customer needs and their identification methods. To this end, this paper first studies the characteristics of implicit needs, and clarifies the relationship between implicit needs and explicit needs. Based on this, the concept of customer needs life cycle is put forward. After that, two methods for the identification of implicit needs are proposed, including an active approach and a passive approach. For the active approach, it is suggested to exploit the functional characteristics of the product and the products in the same series or categories, for which a direct acquisition method and an evaluation data mining method are proposed, and a treadmill design case is studied. For the passive approach, it is suggested to exploit the scenario elements of product usage, for which a scenario elements questionnaire method and a scenario adaptation problem method are proposed, and a spinning bike design case is studied. The two design cases have demonstrated the process of customer needs identification and also verified the applicability of the proposed methods.
Keywords: implicit customer needs; needs identification; functional characteristics; scenario elements
1 Introduction
The rapid economic development has greatly shorten the time to market of new products. One of the factors on the success of the new products in the marketplace is whether they can meet the customer needs to the fullest extent. At present,the ways to obtain customer needs are generally through questionnaire survey answered by the customers directly. The customer needs obtained in this way are generally referred to as explicit needs. For this type of customer needs,there have been quite many researches being conducted,which are commonly based on the QFD model and the Kano model[1-2].
Contrary to the explicit needs,the so-called implicit needs are much more difficult to obtain. Zi defined implicit needs and based on which made a classification of them,but the basis for the classification is not clearly expounded[3]. Masaki advocated that implicit needs should be made clear and also explained their importance,but did not provide the corresponding methods[4]. Van et al. shed light on the non-linear effect of online market factors as predictors of customer needs through data mining techniques[5]. Archak et al. studied data mining technology for product customer evaluation information,and further analyzed customer preferences for product features[6]. As can be seen,the current researches on the methods for customer needs identification were relatively simple,as they did not make distinction between customer needs of various characteristics,and most of them were actually using relevant technical means to extract explicit product information and made summaries from statistical analysis results on the extracted information. For products that have entered marketplace not long enough,these methods tend to fail due to the problem of lack of information. To tackle this problem,it is necessary to study for a systematic method that is capable of transforming the implicit needs into explicit ones in a more formalized way so that they can be easily identified.
Based on the concept of implicit needs put forward by Masaki[4],this paper firstly makes a clarification at the conceptual differences of various types of implicit needs,and also studies the lifecycle characteristics of the customer needs. After that,the methods to identify the implicit needs,including an active approach and a passive approach,are proposed for different types of implicit needs,so as to tackle the limitations of existing methods as aforementioned,before concluding.
2 Characteristics of implicit needs
2.1 Classification of implicit needs
Before working on the characteristics of implicit needs,let′s take a look at the explicit needs first. The explicit needs may be referred to as the needs that human designers can recognize by themselves,or obtain directly from the known information or from the customers,such as the those on the shape,color,size,materials,etc.,as well as the functions of the product as required by the customers.
On the contrary,the implicit needs correspond to the needs that human designers cannot identify directly,nor is it possible to be provided by the customers directly. In other word,the implicit needs are actually linked with the unconscious requirements by the designers,only that they did not realize at the moment the product is being designed.
In fact,the daily activities that humans engage in can be categorized as being conscious or unconscious,where the unconscious activities often take a greater part. Therefore,it is very important to obtain the implicit needs,as it is very likely that they might account for a greater part of the total amount of customer needs.
Due to the varied human cognitions of customer needs,we can classify the customer needs into three categories:
①Implicit needs:the customer needs at which the customers have no understanding at all[7];
②Semi-implicit needs:the customer needs at which the customers do not have a clear understanding but may have some vague or initial understanding;
③Explicit needs:the customer needs at which the customers have a very clear understanding or the needs are clearly identifiable to either the designers or the customers.
The semi-implicit customer needs can be further detailed as of either structural semi-implicit or technical semi-implicit. The structural semi-implicit needs refer to the needs that the customers themselves only have vague understanding or even no understanding at all,whereas on the contrary the company that is engaged in the production of the products is very much aware of them. For example,in the earlier stages of electronic product development process,there lacks the customer needs on avoiding radiation because at the time,the customers have no knowledge of radiation coming out of electronic products,although the company developing and producing them is very much knowledgeable of it. On the other hand,the technical semi-implicit needs means that the customers have a clear understanding of the needs,but the company is quite ignorant due to various technical reasons. For example,even though the customers have been longing for electric vehicles for quite long time already,the companies involved in the production of transportation vehicles are seen as ignorant of this kind of customer need,due to the technical obstacles in their development of such vehicles. Figure 1 illustrates such a two-dimensional classification scheme of customer needs.
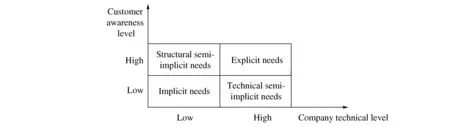
Figure 1 Two-dimensional classification of customer needs
2.2 Life cycle characteristics of customer needs
The life cycle of a product[8]is often accompanied by the iterative changes of certain customer needs,which constitute the life cycle of customer needs. The life cycle of customer needs can be understood as the change of customer needs from implicit to explicit,and then from explicit to implicit,and so on and so forth. It is different from the life cycle of the product itself,which is related to new technologies,competing products[9]and/or substitutes of the products. Even though the life cycle of customer needs is also related to technology,but in essence it depends on the changes of product usage scenario,meaning that it is the product usage scenario change that drives the change of customer needs. As such,it is necessary to study product usage scenarios,should we want to have a better understanding of the characteristics of customer needs that would help us to develop the methodologies on their identification.
The development or transformation of implicit needs to explicit needs can be divided into two stages. The first stage is the transformation from implicit to semi-implicit,including structural semi-implicit and technical semi-implicit. This type of transformation depends mainly on the development of technology and/or the development of cognitive understanding level of the customers. The development of the first stage is illustrated in Figure 2.

Figure 2 First-stage development
The second stage of development is the transformation from semi-implicit needs to explicit needs. The hallmark of this stage is that both the cognitive understanding level and the technical level have reached a certain height at the same time. That is to say,not only can a customer need be recognized by the customers,but also it can be realized with the available technologies at the same time. The second stage of development is shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3 Second-stage development
Further on,the transformation of explicit needs to implicit needs is relatively simple,which is generally due to the changes occurred in the usage scenario of the product. To save space,it is not to be expounded.
3 Active identification of implicit needs
To facilitate product design and development,it is obvious that implicit customer needs should be identified,so that they can become observable by the designers. Due to the special relationship between implicit needs and explicit needs,namely the life cycle characteristics of the customer needs,this identification may be assisted by exploiting the existing explicit needs and the product usage scenario,with which the implicit needs may be transformed into explicit needs. To this end,this paper proposes two methods to help transforming the implicit needs into explicit ones,including an active approach and a passive approach. By active,we mean that the process of identification is based on the analysis of the functional characteristics of the product,whereas passive identification means the implicit customer needs are forced to become manifested due to scenarios change,as will be elaborated further in the following sections.
As mentioned above,customer needs are constantly changing with technological progress and usage scenarios change. Individually,changes in customer needs are often random and unpredictable;yet collectively,the overall trend of changes can be analyzed,often following a certain route of trend. The most intuitive manifestation of customer needs change is the change of product functions and performances exhibited over the past few years. In this regard,patents can be exploited to investigate the change of customers needs relevant to product functions,performances,as well as appearances. Therefore,the general trend of future product development can be reasonably predicted by analyzing and summarizing the change of product functions and performances,together with their relevant patents. Besides,the data to be investigated should not be limited to the particular product that is being designed-all relevant products that are in the same category or same series should be studied as well,so as to get a better understanding of the tread of product change. Below are the steps proposed for this identification process:
1)Collect information about the product and those in the same category or same series.
2)Extract functional characteristics information of the products.
3)Obtain the structural composition of the products.
4)Upgrade or optimize the product structure according to the functional characteristics and formulate new customer needs.
This identification process can be carried out by two methods. One is to obtain and summarize the functional characteristics information directly,and the other is to obtain the product functional characteristics information by collecting the customer evaluation information of the product and then obtaining the functional characteristics information from this evaluation information. The first method is relatively simple,and it is in effect a common feature extraction method,but is more time consuming. The second method involves data mining of evaluation information,which is technically more complex,but its data processing efficiency is relatively much higher,and the obtained data is more objective.
The two methods are applicable to different occasions,with the first method being more suitable for products with relatively simple and obvious functional characteristics. The second method,on the other hand,is suitable for products that are more complex and with availability of a large amount of evaluation data. To apply the second method,a search software system called Archie[10]may be employed. This software can purposefully search through a large amount of data,which is regarded as the implementation of initial crawler technology. Other software systems that can also be exploited include the Igloog system[11],which is the first real data capture system. The Lidicraw[12],which improved the data mining efficiency. As well as a web crawler based on the Hadoop distributed system[13],which improved the ability of data capture,and so on so forth.
3.1 Extract functional characteristics directly
As said before,the functional characteristics of a specific product alone are normally hard to reflect the trend of changes in customer needs. This can be offset by exploiting the products that are of the same category or same series. In this paper,we use the term product family to indicate these products. By taking into account the information of product family,the steps to obtain product functional characteristics are as follows:
1)Build up a product family.
2)Extract functional characteristics of the products at each stage of the past development history.
3)Identify the differences in the functional characteristics.
To illustrate how the above steps can be executed,let′s take a product of fitness equipment,i.e. the treadmill,as a case study. Treadmills used for keeping fit purpose originated in the early 20th century and were designed by inventors in the United States. Its principle is that the internal combustion engine drives the running belt to move. In the following century,treadmills had been improved from mechanical drive to electric drive for convenience and comfort,and the auxiliary functions had become more and more abundant.
To apply the above steps,a product family of the treadmill should be built first. For this purpose,treadmill brands were screened to obtain those brands that have been in the market with a long development time. After that,the series of chosen treadmills brands are categorized into various development stages. Assume that four brands are chosen from within China,including those of Wanqingnian,Qiaoshan,Huixiang and Bailiheng[14]. According to the functional changes of the treadmill products,the development of treadmills in China is divided into three stages,and a product family of four brands of treadmills is formed.
The next step is to obtain the functional characteristics of the product family. This can be done by studying the three development stages identified during the first step. In the first stage,the products from 2006 to 2010 are shown in Table 1. In the second stage,the products from 2011 to 2014 are shown in Table 2. In the third stage,the products from 2015 to 2020 are shown in Table 3.
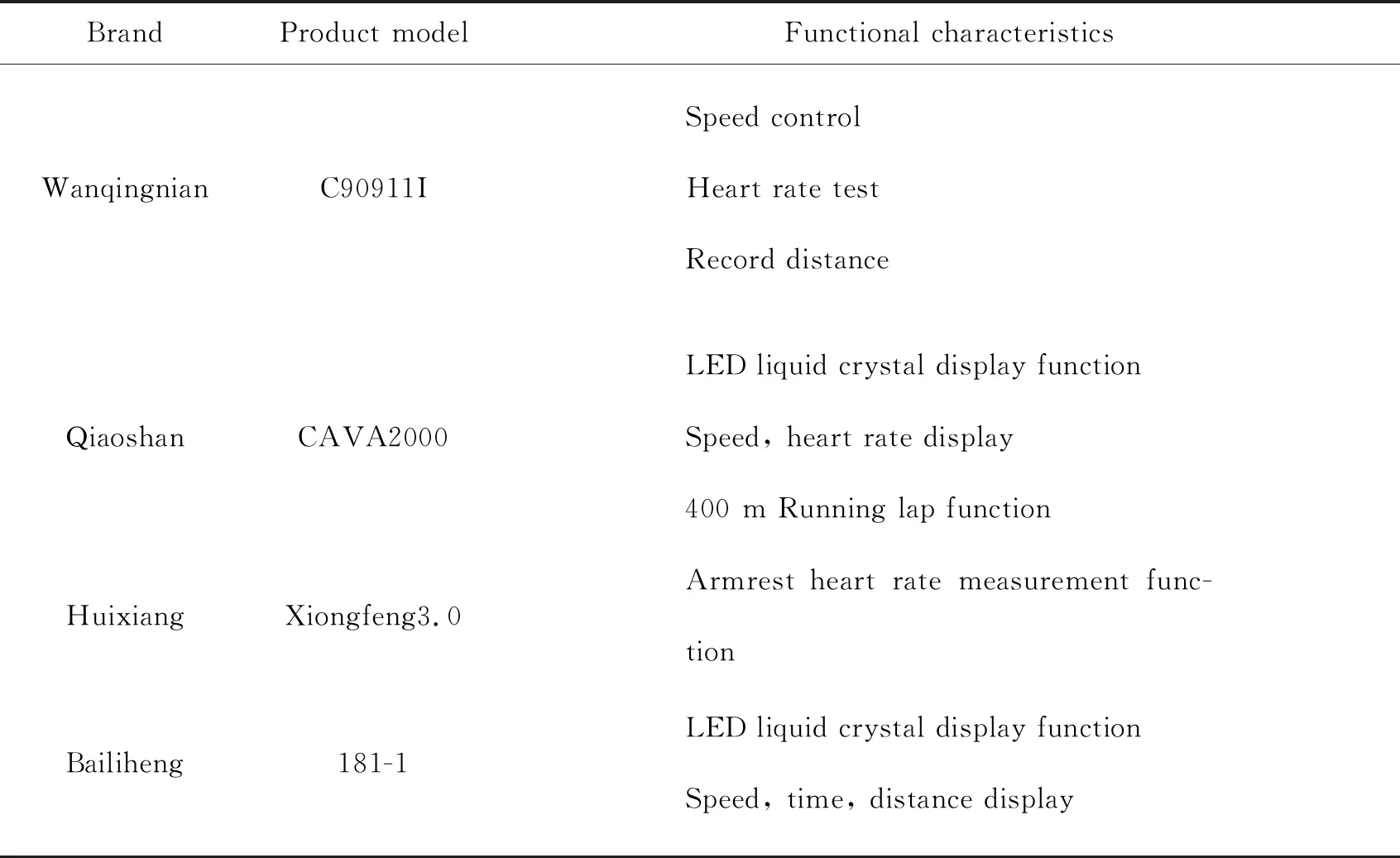
Table 1 Functional characteristics of first stage treadmills
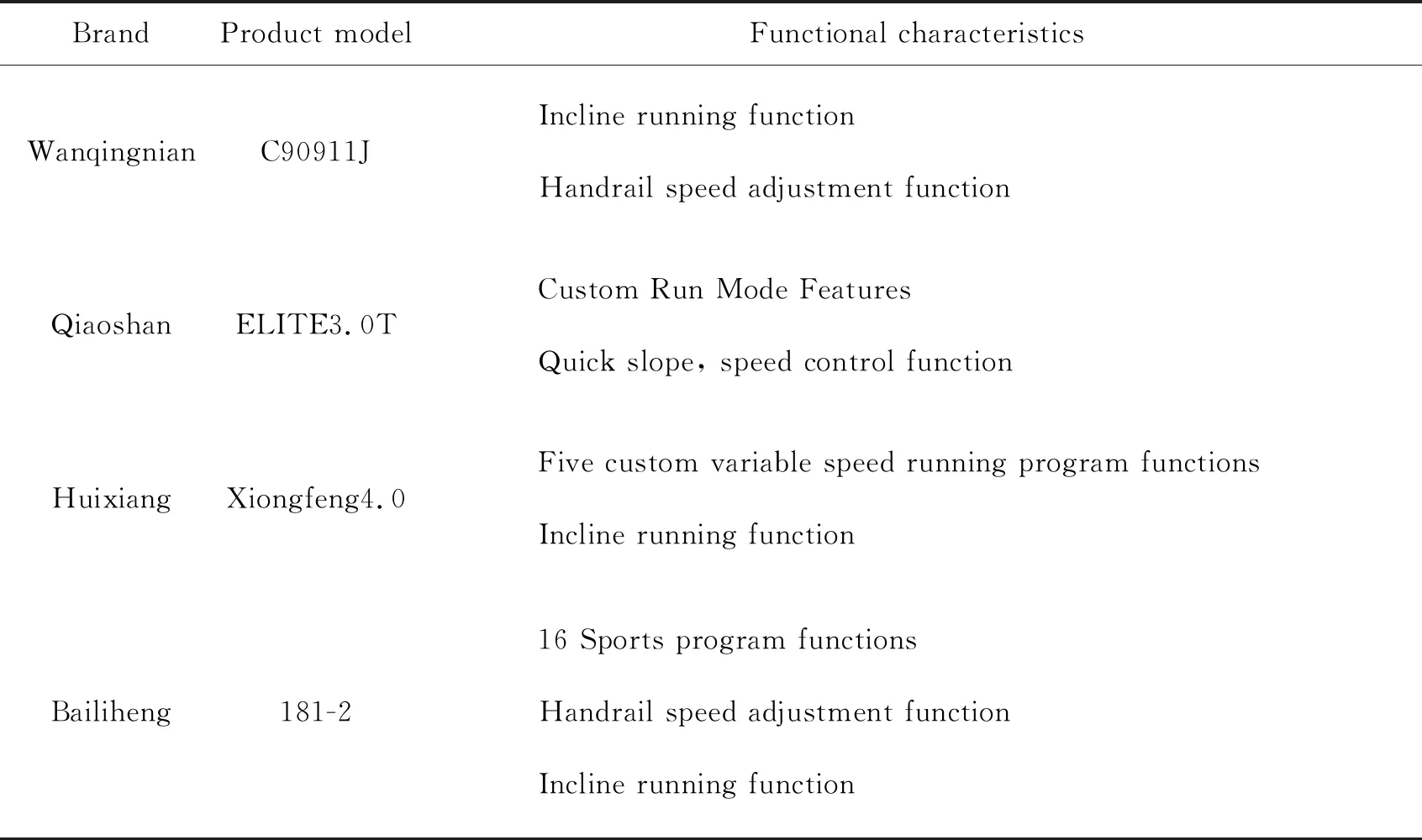
Table 2 Functional characteristics of second stage treadmills

Table 3 Functional characteristics of third stage treadmills
The third step is to identify the differences in the obtained functional characteristics. By taking a comprehensive analysis of the data listed in Tables 1-Tables 3,the functional characteristics can be summarized,as shown in Table 4.
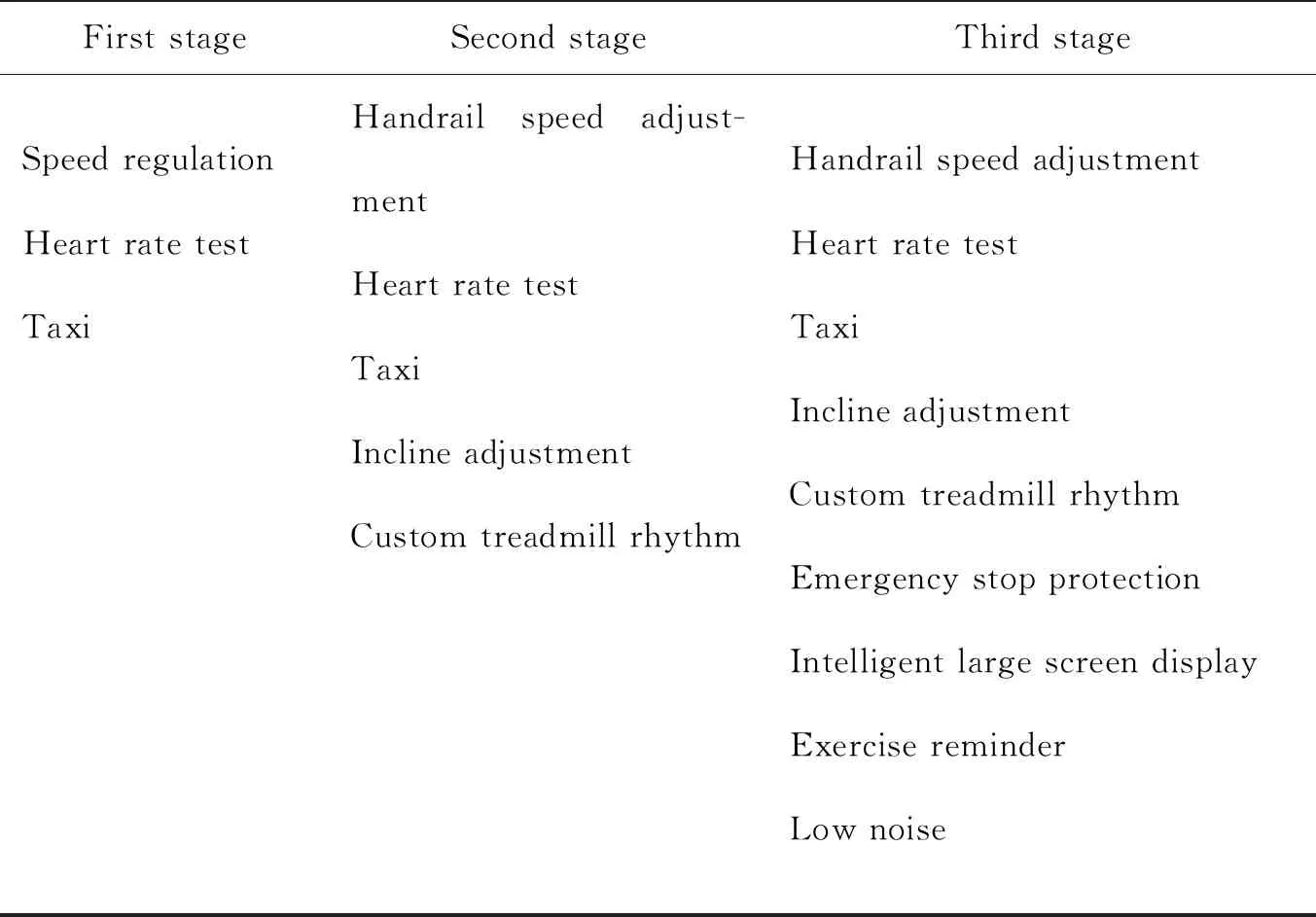
Table 4 Three-stage treadmill functional characteristics
As can be seen,during the period of 2006-2010,the treadmills could mainly deliver the basic functions such as speed adjustment and heart rate test. During the period of 2011-2014,apart from the basic functions the treadmills were upgraded towards accomplishing slope adjustment and automatic speed regulation. Compared with the basic functions,these additional functional characteristics are of a higher level,in that they make the products be more convenient to use. Further on,during 2015-2020,the functions of the treadmill were developing in the direction of optimized human experience of product operation,with intelligent interactive system and high-quality audios being some of the exemplar characteristics.
3.2 Extract functional characteristics from evaluation data
This corresponds to the second method in identifying the trend of customer needs change,as aforementioned. To implement this method,the following steps can be taken:
1)Collect customer evaluation data.
2)Preliminary processing of data.
3)Extract functional characteristics.
For the first step,the main sources of evaluation data include those from online shopping platforms,websites advertising or recommending products,etc. At present,two of the most popular online shopping websites are JD.com and Tmall.com,where JD.com is more professional in selling electrical and electronic products,while Tmall.com is more professional for general daily necessities. Since the product studied i.e. the treadmill belongs to the category of electrical products,so JD.com may be used as the data source,including both the regular evaluation and supplementary evaluation from customers. The regular evaluations refer to the evaluations about product quality,product delivery and after-sales service upon the accomplishment of product delivery,and the supplementary evaluation refers to the customer′s further evaluation after the product has been used for a certain period of time. For the purpose of extracting functional characteristics information,the supplementary evaluation data should be preferred as they often provide a higher degree of credibility.
The second step is data processing. Since the format of the evaluation texts given by the customers is not uniformed,and the language habits of each customer are also different,it is necessary to perform some kind of preliminary data processing on the evaluation texts. In this paper,the text information is processed by the relevant string processing tools,with which those meaningless words are removed,such as the subjects,objects and modal particles,etc.,and the adjectives and verbs that describe the product are retained for further processing. For example,the original evaluation text of“I can easily move this treadmill”shall be processed with only“easy move”being retained.
The third step is to extract functional characteristics. After preliminary processing,the text containing evaluating semantics such as adjectives and verbs need shall be extracted and classified. During this process,repeated words and phrases should be counted to record the number of customer favors on certain characteristics. Table 5 shows the results of processing on treadmill products using these three steps.
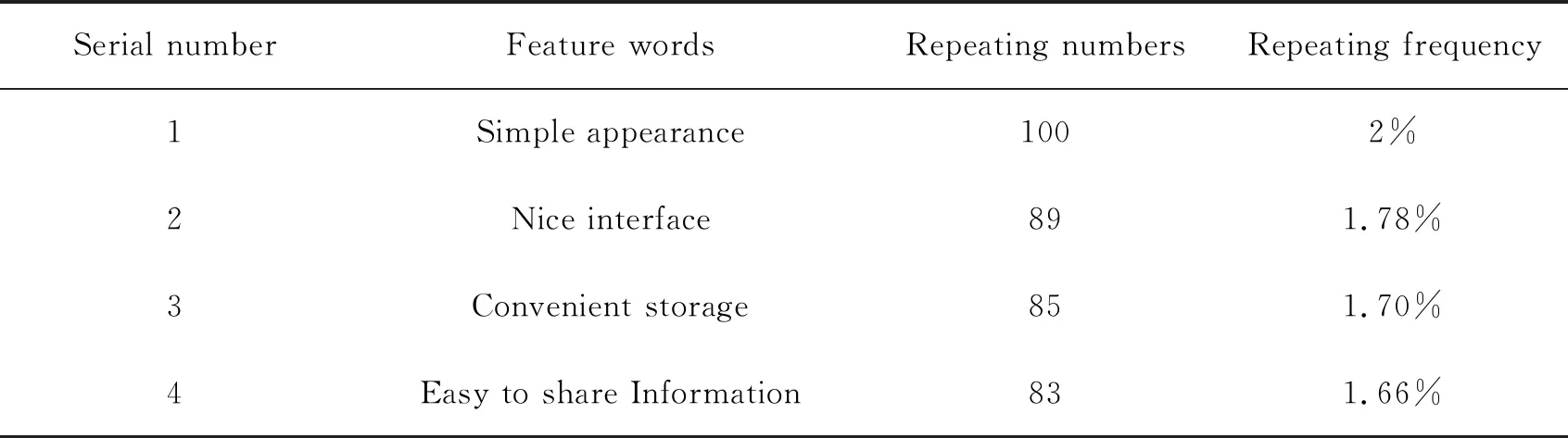
Table 5 Treadmill evaluation word statistics
3.3 Formulate new customer needs
The product functional characteristics obtained by the above step should be further exploited in order to formulate the expected customer needs. For the convenience of description,the following content will be based on the functional characteristics obtained from using the first method. From the above description,it is known that the trend of customer needs change for treadmills has evolved from improving basic functions to enhancing user experience,for which the intelligent interaction has made the fastest progress,including intelligent exercise reminder,and intelligent large screen design,etc. This development trend can be used as a guide for product upgrading and optimization,where product structure may be exploited in formulation of new customer needs. This is because that the changed structural components of the new product are capable of making it explicit the new customer needs. For the treadmill example,Figure 4 shows the links between the functional characteristics and the product structure,whereS1,S2, …,S5represent the most basic structural components of the product,which will be exploited in identifying new customer needs to be elaborated below.
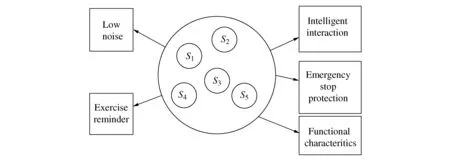
Figure 4 The links between structural components and functional characteristics of treadmills
The treadmill product is mainly composed of a running belt,a frame,a drive motor and an interactive control system. Corresponding to these structural components,the new customer needs can be formulated or identified by studying the trend of development change for each of the aforementioned functional characteristics. For example,the intelligent interaction characteristic of treadmills shown in Figure 4 can be further explored from the perspective of enhancing intelligence. Since voice recognition technology and IntelliSense technology are some of the means on enhancing product intelligence,and intelligent interaction characteristic is linked with the product structure of interactive control system,we can consider formulating new customer needs on using voice recognition technology and IntelliSense technology for interactive control system,as listed in Table 6.
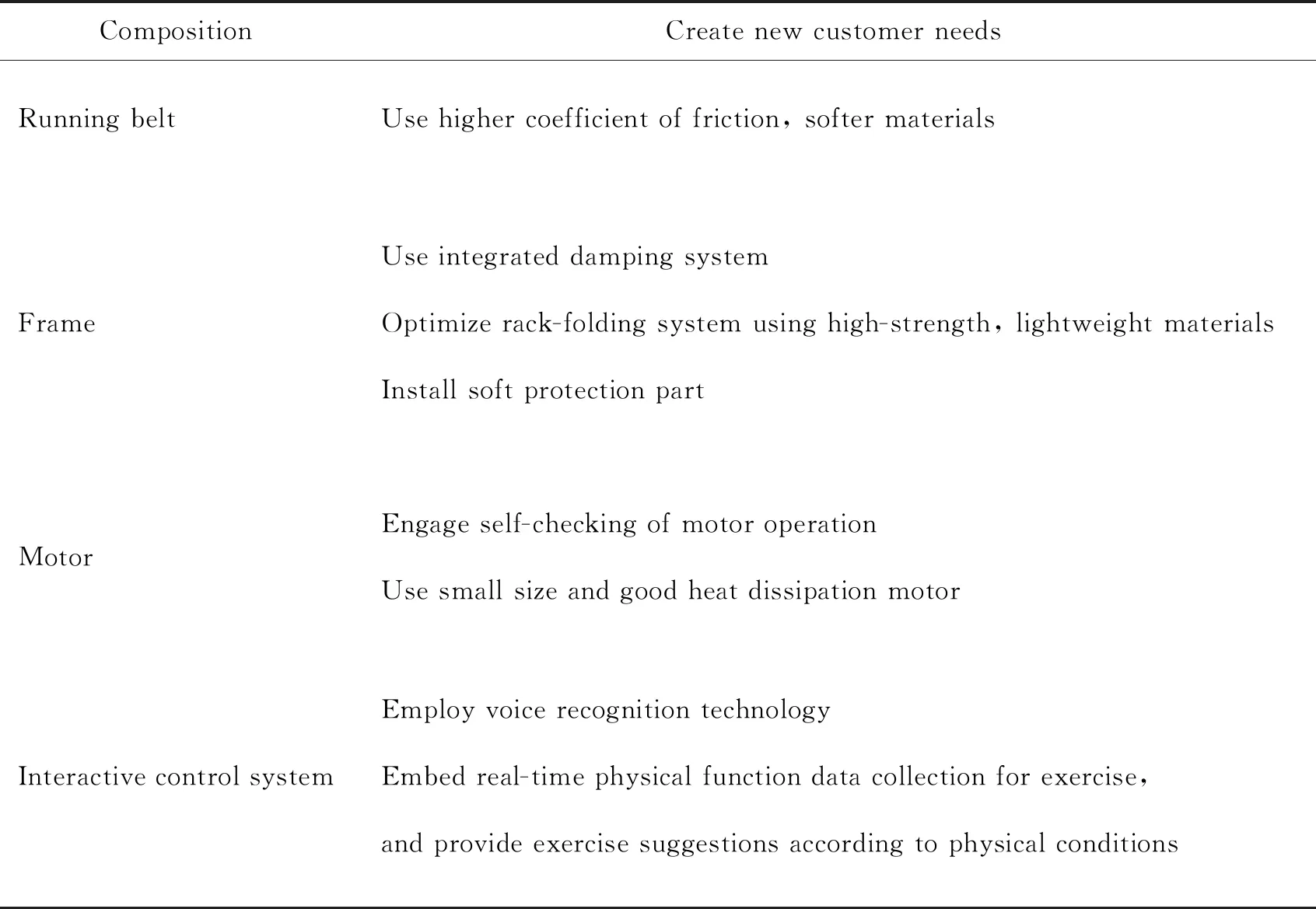
Table 6 Identified new customer needs for treadmill products
Another way to formulate new customer needs is to broaden the existing requirements on the relevant functional characteristics. For example,the“emergency stop protection”shown in Figure 4 is a welcome functional characteristic which should be retained. For identifying new customer needs,not only can we consider including new technology in enhancing product safety for the corresponding structural components,we may also consider incorporating safety protection designs for other relevant parts of the treadmill structure. The new customer needs formed as are listed in Table 6.
4 Passive identification of implicit needs
Sometimes it is difficult to identify the implicit customer needs by applying the above active identification approach,especially for the products that are relatively new in the marketplace thus having less historical development information. For this type of problem,it is suggested to exploit the product usage scenario,as product usage scenario is closely linked with customer needs. In this way,the customer needs are sought out in a passive way,as they are made known via a third media,i.e. the usage scenario. The following steps are proposed to carry out such a scenario-based identification process:
1)Identify new usage scenario;
2)Identify the elements of the scenario;
3)Obtain the structural composition of the product;
4)Formulate new customer needs by upgrading or optimizing the product structure according to the scenario elements.
Among these steps,identification of the scenario elements is more or less the crux of the entire process. Changes of usage scenario will have a great impact on the customers′experience of using the product. Beside,different customers may have different usage scenarios for a same product. Based on the research about scenario perception[15-17],this paper classifies scenario into two categories,with each consisting of many scenario elements. The first type of scenario is closely related to human feelings,for which a solution to obtain scenario elements is proposed based on the five senses of human feeling,including view,smell,hear,taste and touch. For those scenarios that have little to do with human feelings,i.e. the second type of scenarios,we propose to obtain scenario elements by studying the problems incurred by the new scenario. Figure 5 illustrates the two approaches.
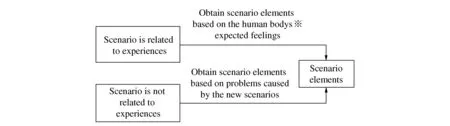
Figure 5 Identification of the scenario elements
4.1 Obtain scenario elements based on questionnaire survey
To obtain the scenario elements by exploiting human feelings about the usage scenario,it is necessary to obtain the customers′feeling data first. To this end,a survey questionnaire is designed,as shown in Table 7. The process of conducting this survey is shown in Figure 6.

Table 7 Product usage scenario elements questionnaire
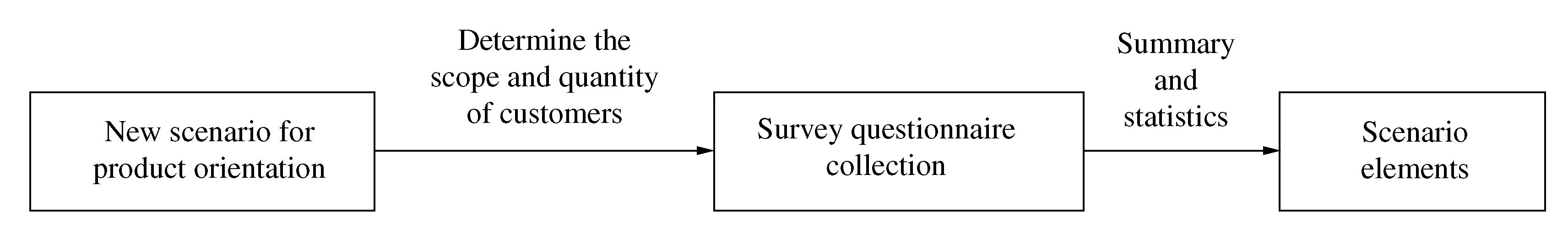
Figure 6 Scenario element acquisition process
The results of the survey are then further processed by counting the number of choices for each of customer feedbacks,and then select the scenario elements that are favored by most customers. Whenever there is a tie between the numbers of customer favors,for example,when the number of customer favors on sitting and that on standing are very close and both numbers are very large,we may consider developing two products that are suitable for sitting and standing respectively. In other word,two separate scenario elements may be both retained,with each one used for a specific product.
To demonstrate how this method can be applied,let′s take the design of a spinning bike as an example,which is assumed to be used both in office environment and at home. Unlike the aforementioned treadmill product,this product is relatively new,with little historical data available,hence is more suitable to employ the passive approach in identification of implicit customer needs. Firstly,100 customers were asked to complete the scenario element survey questionnaire. Then,the survey results are summarized,as shown in Table 8.
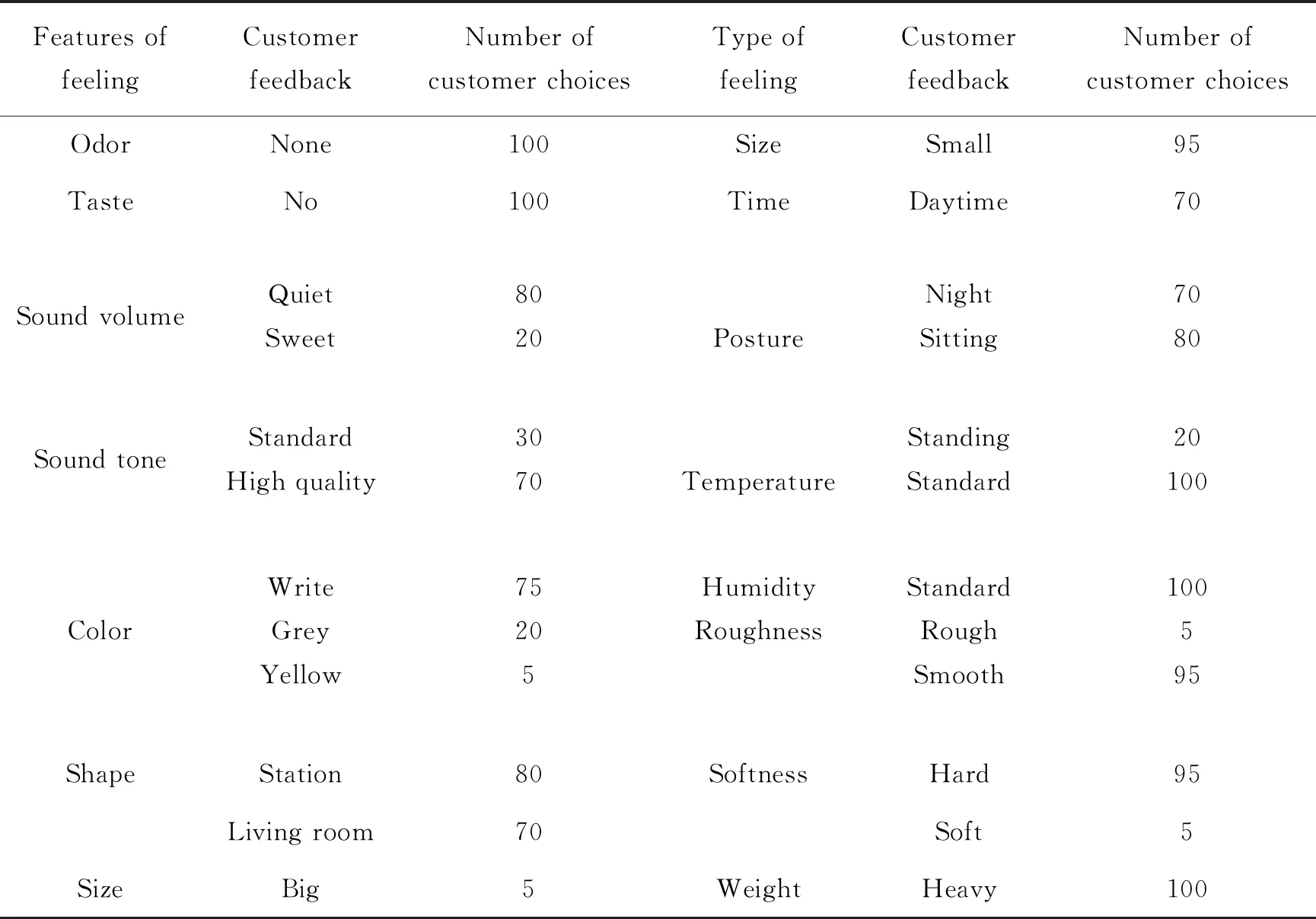
Table 8 Summary of survey data on spinning bike scenario elements
Next,the scenario elements with a large number of customer choices are selected from Table 8,including silence for sound volume,high quality for sound tone,gray for color,small space for product size,sitting for posture,smoothness for roughness,and firmness for softness. Obviously,these scenario elements are more expected by customers than others,therefore they will greatly improve the customer satisfaction should they be considered in the design.
4.2 Obtain scenario elements based on problems caused by the new scenario
Products facing new working scenario may have problems of poor adaptability. However,if this kind of problems do not have repercussions on the user experience,it will not be possible for them to be addressed by the scenario elements survey questionnaire. At present,there is no direct and effective method to tackle this problem. This paper gives two suggestions. One suggestion is to explore the scenario elements by checking whether the safety and durability of product in the new scenario meet the specified criteria and whether the basic functions are accomplished. Another suggestion is that additional scenario elements can be discovered based on the feedbacks from users in the later stage of product use. Figure 7 illustrates this dual-route approach.
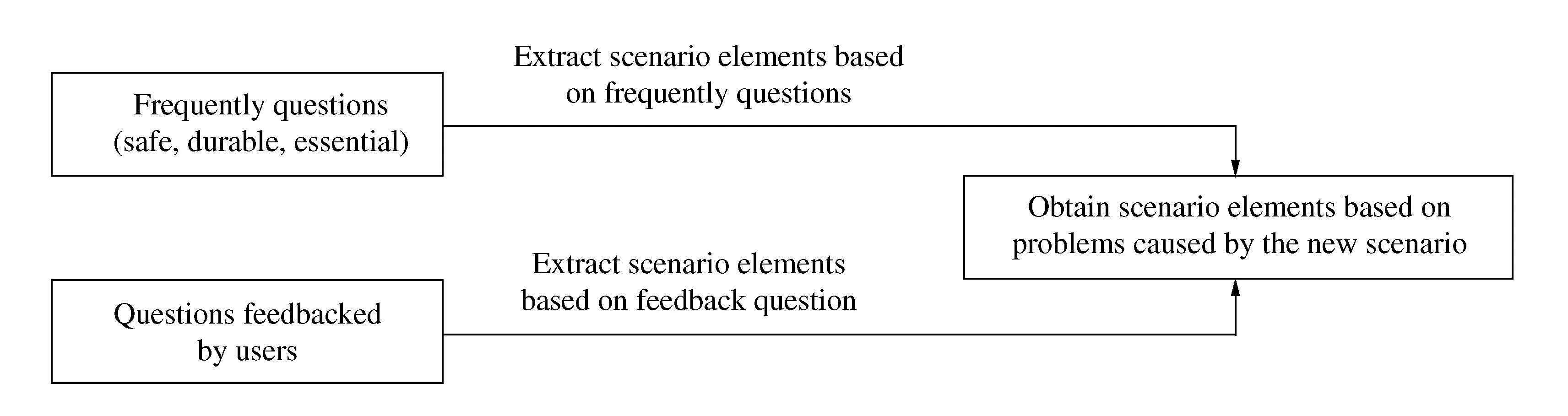
Figure 7 Scenario element acquisition process
4.3 Formulate new customer needs
After the identification of customer-favored scenario elements,new customer needs can then be formulated by taking into account the product structure. For the spinning bike design case,we can conceive a product structure that caters to the those scenario elements like quietness,high-quality speakers,cool-colored appearance,small size,easy handling,anti-skidding,as well as shock resistance. Figure 8 shows the link between these customer-favored scenario elements and the corresponding structural elements.
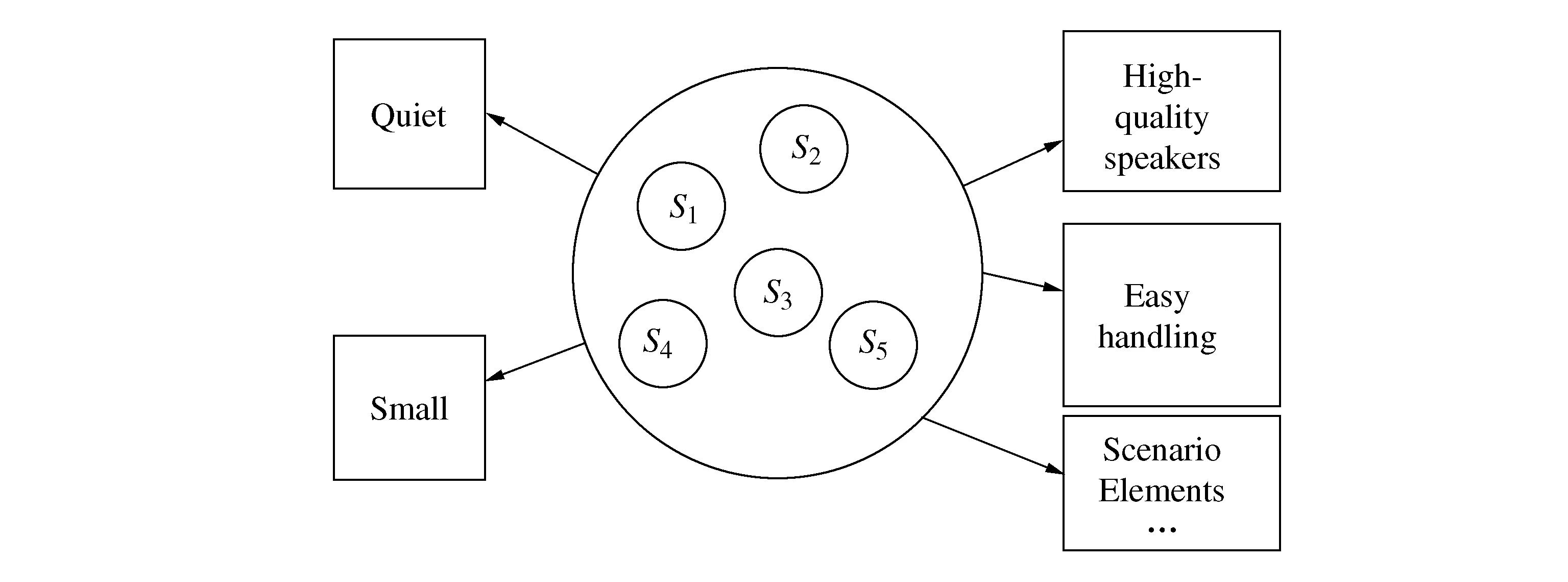
Figure 8 The link between scenario elements and product structure for spinning bike design
The spinning bike is mainly composed of flywheel,pedal,seat,frame and braking system. The composition of the product can be refined or optimized that caters to the above scenario elements,during which the relevant new customer needs can be identified,as shown in Table 9.
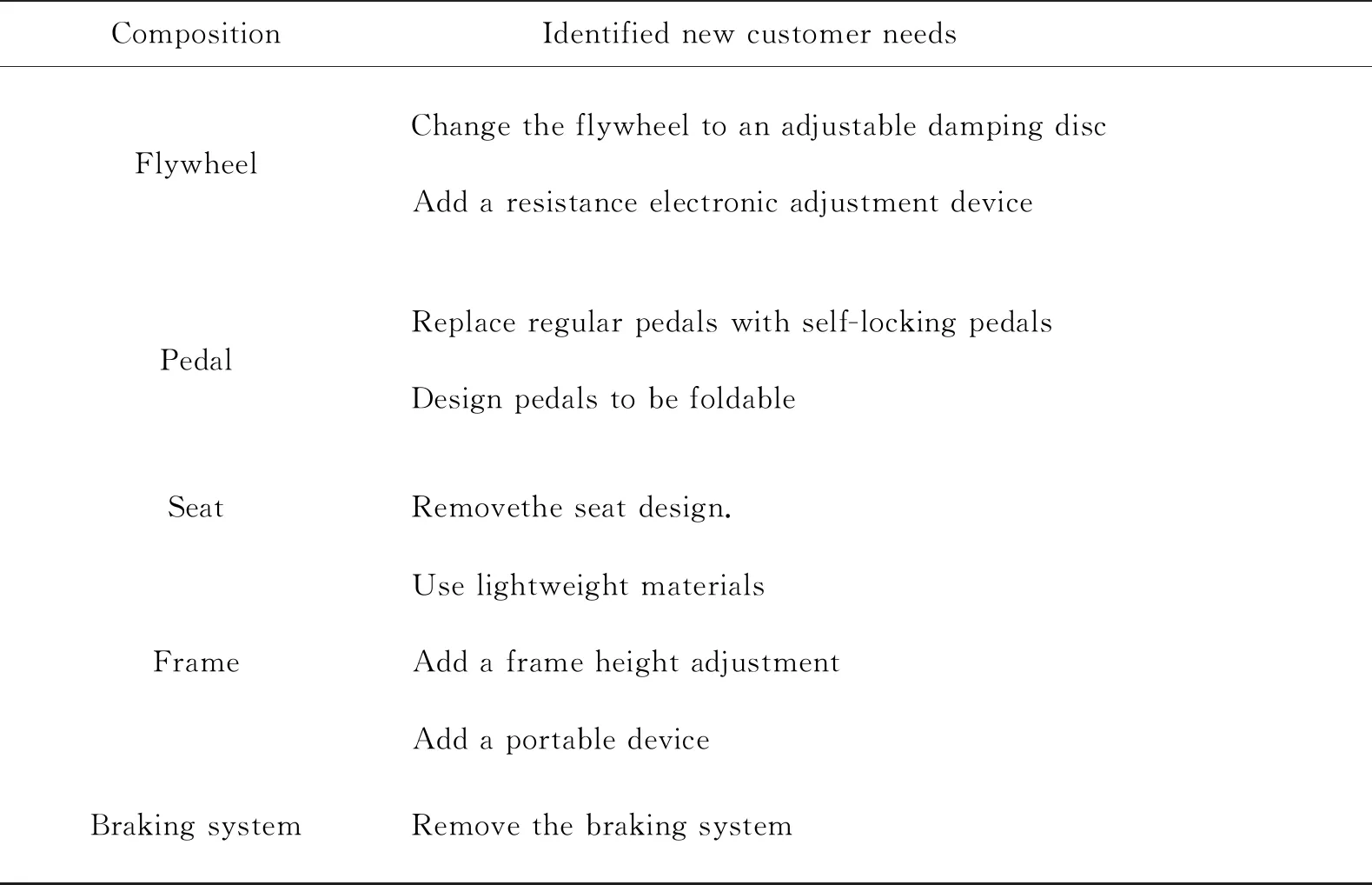
Table 9 New customer needs for spinning bike design case
According to the new customer needs identified,the spinning bike can be redesigned. Figure 9 shows one example of the new design.
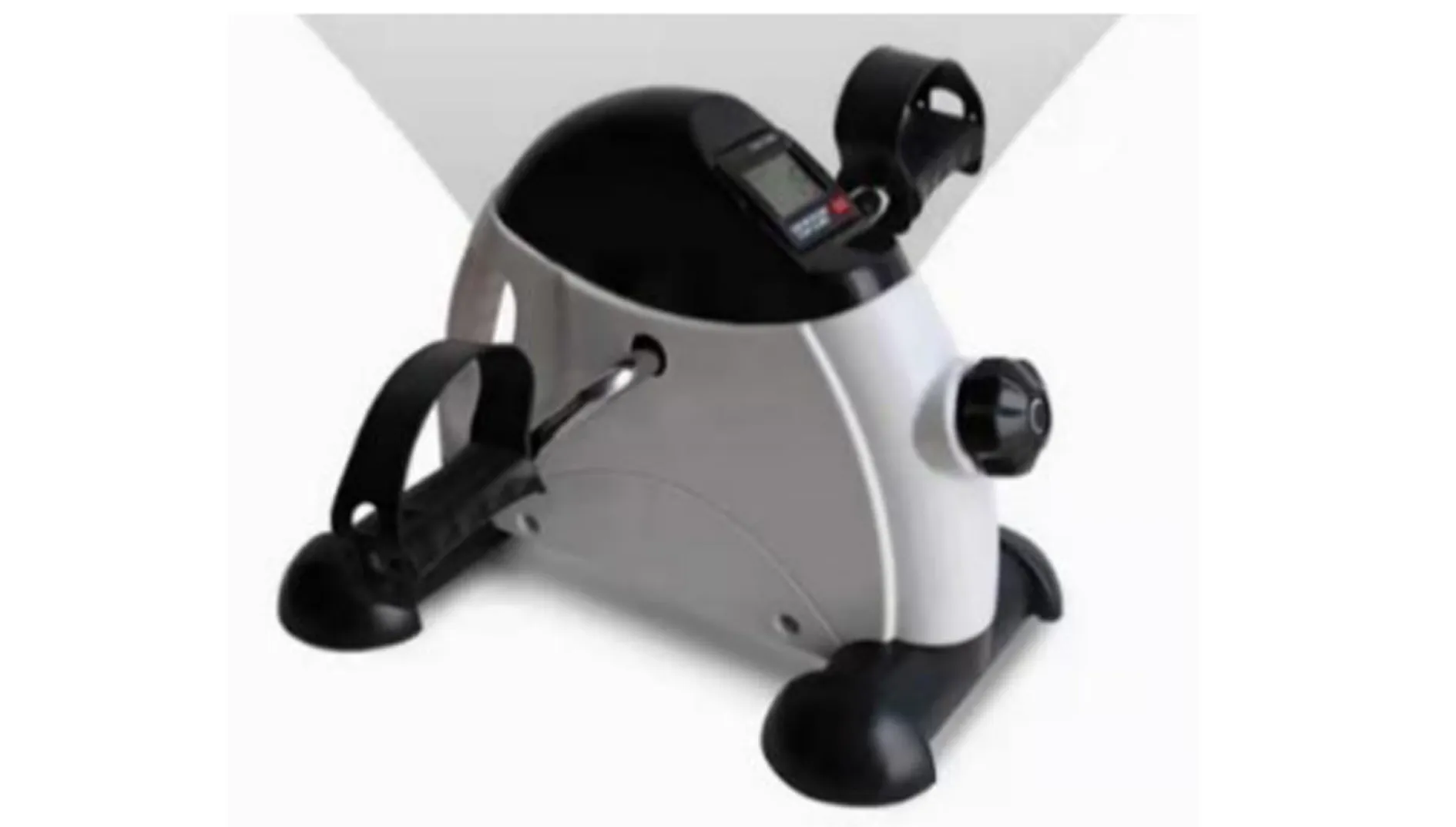

Figure 9 Design concept of a new spinning bike
As can be seen,the two approaches for identification of implicit needs are similar in the procedural structure. The active approach is by identifying the functional characteristics of product family through either analysis of product development history,or data mining of customer evaluation,and then to combine the functional characteristics with the product structure so that the new customer needs are formulated. The passive approach,on the other hand,is by identifying the customer-favored scenario elements obtained through questionnaire survey,or from analysis of scenario adaptation problems,and then to combine them with the product structure to formulate new customer needs. Figure 10 illustrate the procedural structures of the two approaches.

Figure 10 Procedural structures for identification of customer needs
5 Conclusion
The above sections expounded on the concept and characteristics of the implicit customer needs,and proposed two approaches for their identification. The two approaches are applicable to different kind of products,where products with obvious trends of change in their development process can take the active approach and those lacking such information can be treated with the passive approach. For the former,two ways of functional characteristics acquisition can be employed,including direct analysis of product development history data and data mining of various customer evaluations. The identification process was elaborated and also demonstrated by the case of treadmill design. For the latter,which is suitable for those products that are relatively new in the marketplace,two ways of scenario elements acquisition can be employed,including the questionnaire survey method and the method on analysis of scenario adaptation problems. The case of spinning bike design was used to demonstrate this identification process. Finally,the identified new customer needs were applied to the design of the products by combining the functional characteristics or scenario elements with the product structure,with a design concept for the spinning bike being presented. Further research will be conducted on studying more practical design cases,so as to refine the two identification procedures to enable more implicit customer needs be discovered.
