Exploration to the Application of In-person + On-line Blending Teaching Method to College English Teaching in Translation Based on Group Discussion
2023-01-16ZhangRui
Zhang Rui
School of Foreign Languages, Changchun University of Technology, Changchun, China
Email: 359892845@qq.com
[Abstract] Covid-19 Pandemic raged the whole year in 2020 and continued to 2021, which has been sweeping every field and bringing changes in almost all aspects. Under this circumstance, In-person + On-line Blending Teaching Method is introduced to College English Teaching. Translating in College English Teaching is more difficult compared to other modules so this article studies the application of the method to translation teaching With the help of Catti skills and materials, adopting the study model of group discussion, this author comes to the conclusion that the In-person + On-line Blending Teaching Method has its place in translation teaching.
[Keywords] College English; In-person + On-line Blending Teaching Method; Translation Teaching; Catti
With the development of science and technology and globalization, College English Teaching is always on the road to reform and to meet the changes in every field because the status of English as a tool of world language is on the rise. The rampage of Covid-19 pandemic has almost changed everything in the world, such as people’s living style, people’s working style and people’s entertainment. Education is with no exception wrapped in the list of changing, so College English Teaching is forced to step onto the road to reform again. With Covid-19 pandemic being under control in China, and with the sparse occurrence of some cases now and then, schools and universities have to adopt blending teaching mode, that is, the application of in-person teaching + on-line blending teaching method. Under this circumstance, English teachers squeeze their brain and come up with different ideas and means to improve English teaching.
English teaching, with the lowering of craze for English and the reducing of teaching hour, is still a fundamental course in almost every university and college. How to solve this teaching problem within the social situation and how to improve students’achievements in the pandemic air? Different teachers devoted themselves to their teaching with excellent strategies and methods. Our group put in-person teaching + on-line blending teaching method into practice, for example, in listening, speaking, reading and writing, especially translating. Translation is a cross-cultural linguistic activity, and its process is a cognitive activity, which is based on the translator’s understanding of the meaning of the original text, and different people have different understandings, comprehension and translation are subject to the translator’s experience and cognitive ability. Translation is not a simple process of decoding the source language and encoding the target language, but a double cognitive process. NIDA’s (Gentzler, 2007) equivalence of form and function, Newmark’s (Gentzler, 2007) equivalence of meaning and communication, Nord’s (Gentzler, 2007) equivalence of text and function, Jokobson’s (Gentzler, 2007) imitation and functional equivalence all construct a two-dimensional spatial equivalence for translation. Translation theory mainly deals with the concept, nature, standard, process, method, type and evaluation of translation, the conditions of translators, training rules, the similarities and differences between Chinese and foreign languages, culture and stylistics. In the past, translation teaching was only for English majors, while non-English majors only dabbled in it or were not included in the teaching requirements at all. In 2004, the General Office of the Ministry of Education has issued the notice of “College English curriculum requirements (for trial implementation)” (2004) (hereinafter referred to as“Curriculum requirements”). In the course requirements, the requirements for translation competence in the three levels of college English teaching are clearly put forward. Subsequently, the reform of college English teaching was carried out in full swing in colleges and universities all over the country. In 2005, the Ministry of Education also announced the “National College English Test 4&6 reform program (trial)” in the new program to add a new Chinese-English questions. All these put forward new requirements for translation teaching for non-English majors. Under these conditions, Cet-4 and CET-6 have been reformed accordingly, and the Reformed Cet-4 was implemented in January 2007. Six years later, the website of the National College English Test (CET4) (Wang, 2015) announced that“Starting from December 2013, the CET4 and CET6 examination committee will make partial adjustments to the structure of CET4 and CET6 papers and the types of test questions.” Among them, “The types of test questions in the translation section will be changed from single-sentence Chinese-English translation to paragraph Chinese-English translation. The translation involves the history, culture, economy and social development of China. The length of four levels is 140-160 characters, and the length of six levels is 180-200 characters. The translation portion of the score increased from 5% to 15%, indicating an increase in its importance throughout the examination. As one of the most influential examinations in China, the reform of CET-4 and CET-6 has attracted a lot of attention and aroused a lot of heated discussions. The majority of candidates generally reflect that the reform of the translation examination has increased the difficulty, increasing the pressure to prepare for the examination. Wen Qiufang, director of China Foreign Language Education Research Center, proposed that the starting point of the reform is to optimize the input, pay attention to the output, and improve the quality of college English teaching. The topic of translation involves China’s history, society, culture, economy and so on, to introduce China’s situation abroad, is also to strengthen the idea of export. The rating was based on sentence by sentence, 50% letter and 50% letter. With the rapid development of internationalization and society in our country, the partial adjustment of translation test questions puts forward new requirements to college foreign language teaching and new tasks and challenges to the cultivation of foreign language talents. Lian Xiaohui, associate professor of the Department of Foreign Languages at the Henan University of Finance and Economics, said the reform signals that students should put more emphasis on practical use of English and enhance the role of foreign languages as a means of communication. This reform, from the question type can be seen that in the future, more emphasis will be placed on language proficiency tests, this is not by rote memorization, simple memorization of vocabulary and phrases can achieve good results, improve the level of English. The tide of globalization makes the Earth become a global village, cross-cultural communication becomes a universal reality, and communication with people from different cultural backgrounds and orientations becomes inevitable. In order to adapt to the new situation, Cet-4 and Cet-6 (Xiao, 2015), as the main means of assessing whether the English ability of college students in our country can meet the teaching requirements, must be reformed accordingly, whether people of different cultural groups can coexist well depends on whether we can communicate effectively and reach mutual understanding step by step. How to express the history, society, culture and economy of China well in foreign countries depends on English learners’overall improvement of English level, formation and development of sensitivity and flexibility to cultural differences. At the same time, in the process of Chinese-English translation, we should follow the English expression methods and use certain translation skills to express information reasonably. However, the improvement of the translation requirements of Cet-4 and Cet-6 can, to a certain extent, urge students to master practical translation skills and familiarize themselves with English expressions of Chinese society and culture. In this context, it is of great practical significance to study the challenge of translation examination reform to college English teaching and its countermeasures. Due to the influence of tradition and test baton, teachers pay more attention to explain the basic knowledge of language in reading, focusing on the training of students’language ability at sentence level, such as the understanding of language points, grammatical structure, phrase collocation, idiomatic usage and complex, difficult sentences, etc.. Due to the restriction of class hours, teaching materials and teachers, translation teaching has many shortcomings. Listening, speaking, reading and writing occupy a large proportion in the overall arrangement of college English courses: one class hour is set aside for listening in four English classes every week, and the other three classes are used for intensive reading and extensive reading, and the translation of the treatment is more than enough. A written survey of translation teaching in a college English teaching seminar shows that no translation course is offered in English courses for non-English majors in the first and second grades, translation is integrated into the teaching process of intensive reading. As for the content of the textbooks, the basic translation theories are seldom mentioned in the textbooks of college English, and the content of translation is limited to the Chinese-English translation and the English-Chinese translation exercises in each unit, many teachers only read the answers to the Chinese-English translation exercises and the English-Chinese translation exercises, and many times even the answers are omitted. Students do not understand the importance and difficulty of translation, many students think that “as long as you know English words, or a dictionary in hand, translation will not be a problem”, the traditional emphasis on reading comprehension at the textual level and the excessive encouragement of guessing also make the students careless and uninterested in understanding the exact meaning of the language, the ability to translate is naturally unsatisfactory. At present, many foreign language materials are needed to be translated and countless Chinese original books are needed to be translated into different languages so as to spread Chinese culture. This phenomenon puts those who have passed CET-4 or CET-6 at a loss, because they are not trained to reach that high in translation, which shows that there are some problems in translation teaching. Translation teaching can not keep up with the speed and demand of economic development, so reform is imperative. The “China Accreditation Test for Translators and Interpreters” (Catti) (Chinese Translators Journal, 2007) , a national Accreditation Test for Translators and Interpreters that is planned and administered by the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security of the People’s Republic of China, China International Publishing Group, to meet the needs of the Socialist market economy, to strengthen the development of our foreign language translation professionals, and to assess the level and capability of translation professionals in a scientific, objective and fair manner, to better serve our country’s opening to the outside world and international exchanges and cooperation, in accordance with the spirit of establishing the National Vocational Qualification Certificate system, a unified, society-oriented, and most authoritative professional qualification (level) in translation shall be carried out throughout the country; it shall be a recognition of the candidates’ability and level of bilingual translation in interpretation or translation. Cet-3 is an entry-level test for professional translation, which has great influence and authority in the whole country. The objectives and requirements of the translation practice examination in the “Syllabus for tem-3” state that “Candidates should have the basic skills and abilities for bilingual translation, be able to use general translation strategies and techniques for bilingual translation, and translate fluently and accurately without obvious grammatical errors, mistranslations and omissions.” It is worth mentioning that, taking Catti translation practice as an example, this paper makes an analysis of the present situation of translation teaching for non-English majors and the translation questions in the new type of CET-4, it is of great significance to explore new approaches to translation teaching for non-English majors.
The 3-year pandemic has been changing a lot of things from almost every aspect, for example, our life style and our teaching style. The traditional in-person classroom teaching was interrupted and the on-line teaching found its way into our campus teaching. In-person + On-line Blending Teaching Method becomes a must and a new teaching method. To test its validity and the output of this method, our task group conducts a two-semester empirical study of the experimental and control classes, integrating the theory and practice of Catti’s three-level translation practice into English translation teaching, and carrying out a series of reforms and innovations in translation teaching in the experimental classes, the control class also follows the original teaching plan and steps. During the empirical research, we make comparison with the data collected from our study, solve problems appeared in and after class and gradually summarize strategies and suggestions to improve students’translation ability. The steps are as follows:
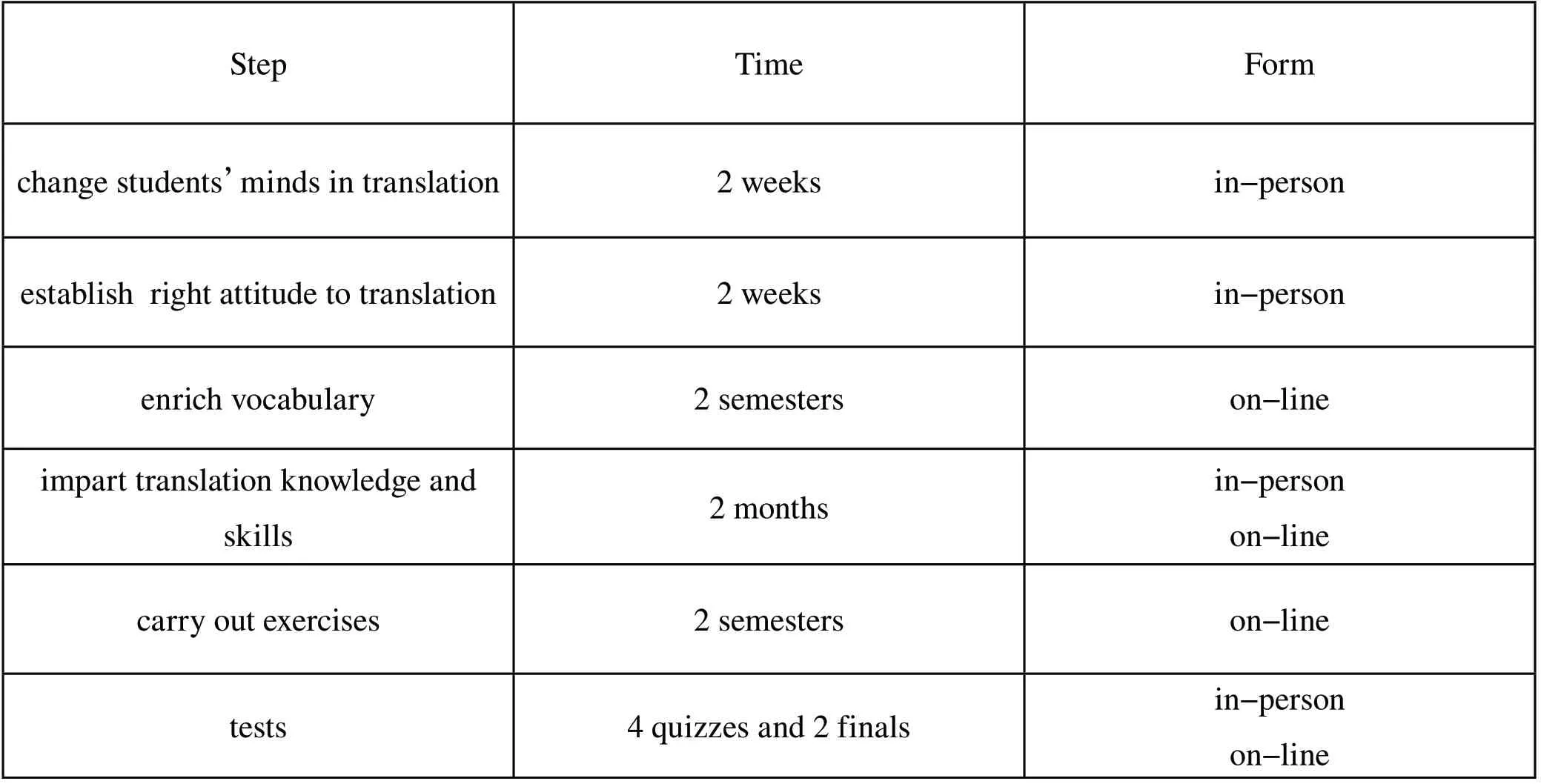
Table 1 Steps of Implementation
Just as the above table described, the empirical study was carried out following the steps of implementation because our task group believes that mindset changing decides action, that is, we English teachers must use our heads to change students’minds in learning translation, and that is why we give priority to mind changing. In students’minds, translation is of no importance in the percentage of the final paper and in the percentage of the CET-4 and CET-6 as well. With the neglecting of translation in the mind, no one can learn it well, not to speak of mastering it. Establishing right attitude to translation has its own significance in English learning and College English teaching. These two steps were implemented in in-person class because when teacher-student is performing faceto-face study, they can experience eye contact which can give trust and affection to each other. The third step falls on “enriching vocabulary”because our group unanimously agrees that the necessary vocabulary is a prerequisite for good translation. As far as the current situation of non-English majors’translation ability is concerned, teachers have the responsibility to consciously help students to suck in new words as possible as they can. Word- input is not an immediate task to be completed within a short time so the time allocation of this part occupies much more time. What we do in in-person class or on-line class is to provide more skills and methods in remembering more words. As to “impart translation knowledge and skills”, we put theories into practice. Practice makes perfect! It is a universal rule applying to almost every field. We all agree that the most time-consuming and difficult part is “carrying out exercises”. What kind of materials are the appropriate? How do we control the difficulty of the material? We should put more factors into consideration. While doing the research and giving lessons, we draw some conclusions and earn some experience, which is the reason why we choose corpus from Catti’s three-level translation practice because Catti (Liu, 2012) has an all-round practice in translation. To implement this step, we had divided students into several discussion groups so that students could be trained some skills not only in translation, but also in other daily life, for instance, team work, communication and so on. For we do not have adequate time to carry out translation exercises, students are required to complete their assignments done by all group members after class. Language sense of translation is another skill students must grasp? How to cultivate the skill? Students are expected to compare and read bilingual input to the texts of different subjects and genres to increase and grasp the skill. During the course of approaching perfect translation, we pay attention to training students to get optimized language input information, so that students can enhance their sensitivity to English and Chinese language through the increasingly perfect foreign language learning environment in school, through multimedia network and social practice, etc. , to enrich the bilingual expression of various concepts and things.
Test is an essential evaluation of this method. Over two-semester time, we gave students 4 quizzes and 2 finals altogether. The following tables show us the consequence of implementing in-person +on-line blending teaching method.
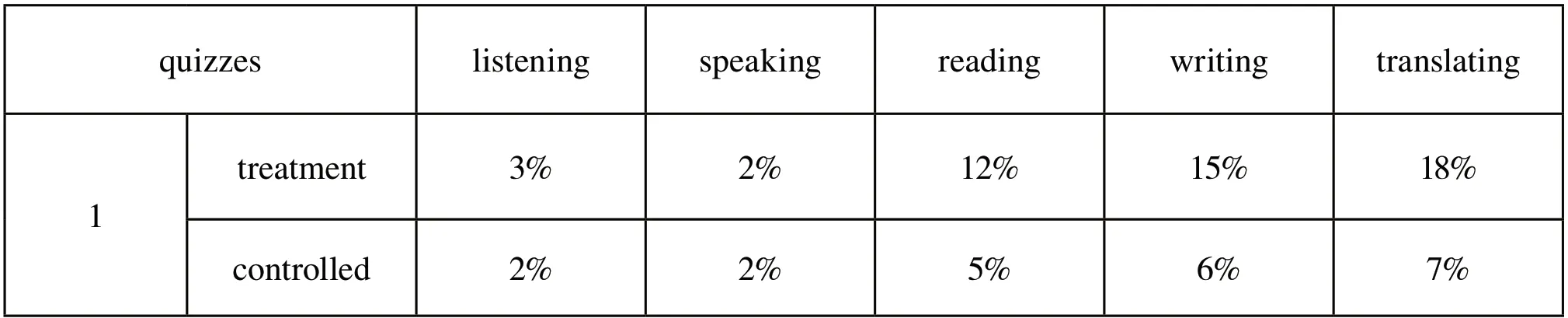
Table 2 Results of 4 quizzes (%)
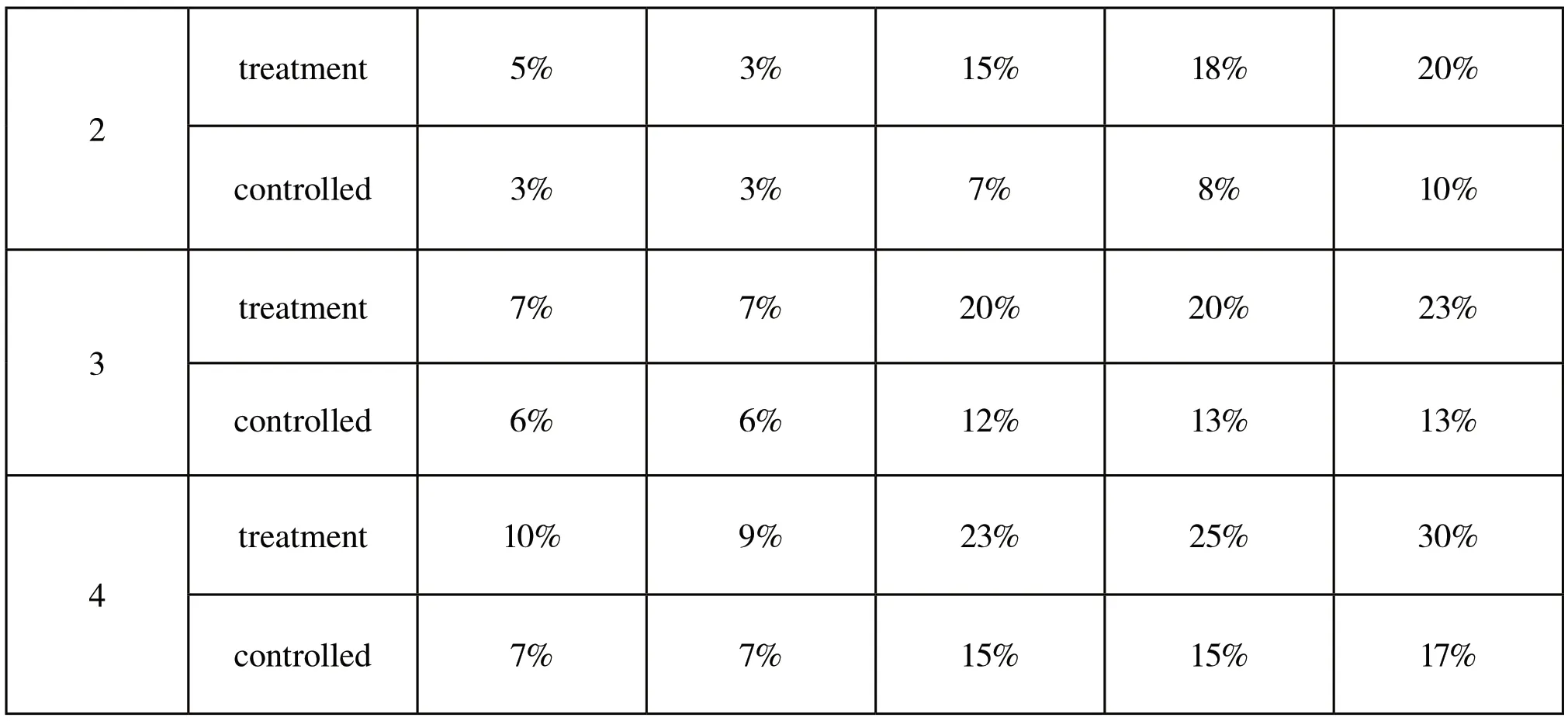
treatment 5% 3% 15% 18% 20%2 controlled 3% 3% 7% 8% 10%treatment 7% 7% 20% 20% 23%3 controlled 6% 6% 12% 13% 13%treatment 10% 9% 23% 25% 30%4 controlled 7% 7% 15% 15% 17%
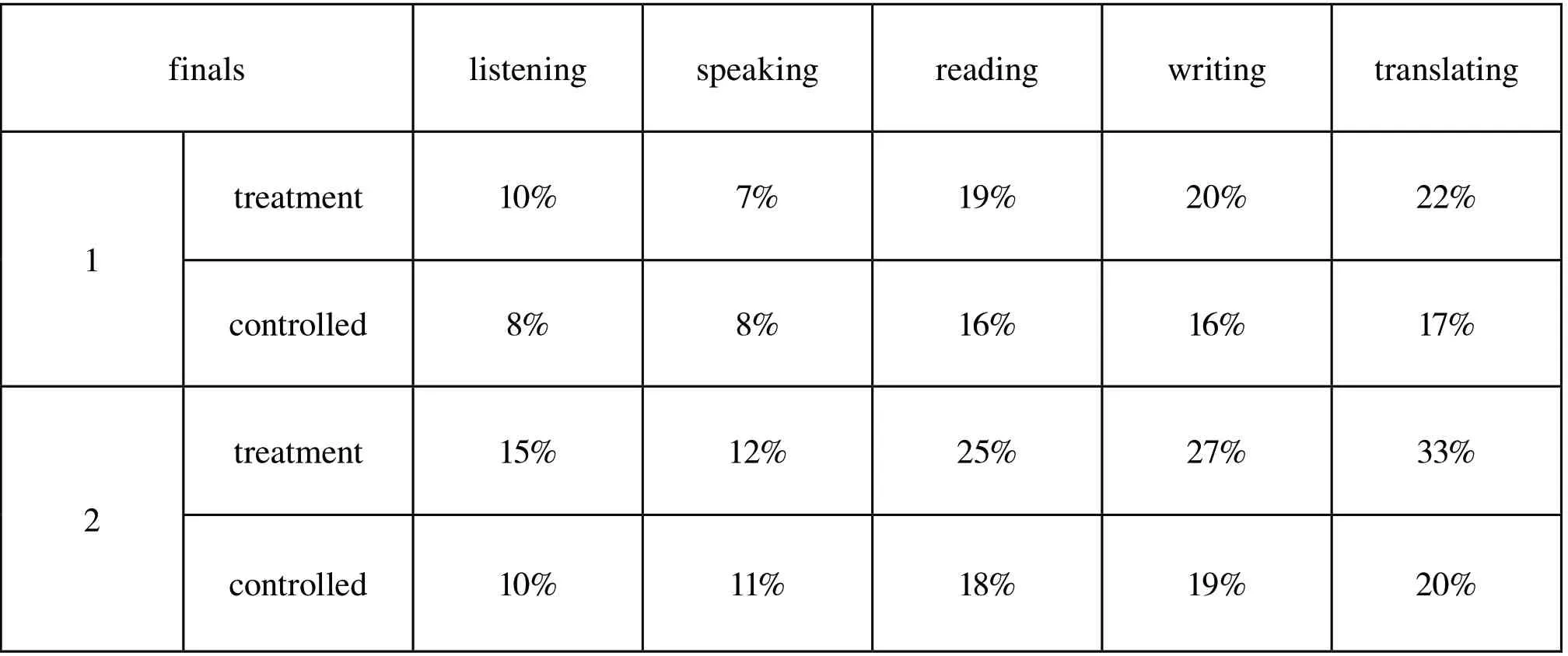
Table 3 Results of finals (%)
The above simple tables depicts the results of this research and it tells us that the study of “Application of In-person + On-line Blending Teaching Method to College English Teaching in Translation Based on Group Discussion” is workable to a large extent. For decades, College English, as a basic course in colleges and universities, has always been a basic course of teaching. In order to adapt to the reform of new questions in CET-4 and CET-6, meet the needs of pandemic situation and improve students’practical English application ability, teachers have been trying various teaching methods and means in teaching. Therefore, facing the current situation and the present teaching conditions, we borrowed the skills, the contents and the means of the national relevant English certificate examination (Catti) in the teaching practice of college English projects for reference, so as to improve students’learning effect and English achievement, to enhance students’practical English ability and level. Based on group discussion after class and taken group discussion as a unit, integrated Catti translation practice into translation teaching, this comparative study concludes that this method can improve the improvement of students’translation level and other English skills, especially reading. Although this study has its limit, our group would devote ourselves to College English Teaching.
杂志排行
Proceedings of Northeast Asia International Symposium on Linguistics,Literature and Teaching的其它文章
- A Comparative Study of the Phonology and Phonetics of Chinese and German Vowels
- Deconstructive Analysis of New Media Communication from Translanguaging Perspective
- A Probing into What Extent Listening Comprehension Ability Influences on Chinese English Learners
- Exploring Linguistic Landscape of the Qianzhou Ancient Town in Xiangxi through Ecological Linguistics
- Teaching Practice and Research of Scientific and Technical French Translation Based on Production-Oriented Approach
- A NEW“5W+1”COMMUNICATION MODEL TO TRANSLATE CHINESE KEYWORDS TO ENHANCE INTERNATIONAL COMMUNICATION
