Regulatory effects of evodiamine on glucose metabolism-related factors in CT26 colorectal carcinoma-bearing mice
2022-12-31JiangYueYuKuiChenRuoQinZhaoLiQunWangChaoGongShenZhouHuangYunJuanZhengPeiWenZhuXinRanSongFangHuaWu
Jiang-Yue Yu,Kui Chen,Ruo-Qin Zhao,Li-Qun Wang,Chao Gong,Shen-Zhou Huang,Yun-Juan Zheng,Pei-Wen Zhu,Xin-Ran Song,Fang-Hua Wu*
1General Surgery,Fujian Medical University Affiliated Fuzhou First Hospital,Fuzhou 350009,China.2College of Forestry,Shanxi Agricultural University,Jinzhong 030801,China.3School of Bioengineering,Tianjin Modern Vocational Technology College,Tianjin 300350,China.
Abstract Objective:To investigate the therapeutic effect of evodiamine(EVO)on the expression of hexokinase(HK),lactate dehydrogenase A(LDHA),and pyruvate kinase M(PKM),key enzymes of glycolysis,in the tumor-bearing mice after modeling mouse colon cancer cells(CT26).Methods:A tumor-bearing mouse model was generated by administering axillary injection of CT26 and intraperitoneally injecting different doses of EVO.The therapeutic effects of EVO on CT26 tumor-bearing mice were evaluated by measuring the thymus and spleen indices,tumor volume,tumor suppression rate,and other related indicators in the tumor tissues of mice in each group after the administration of EVO,in addition,histopathological changes in the tumor tissues of the mice in the groups were studied by hematoxylin and eosin staining.The expression levels of HK,LDHA,and PKM in the tumor tissues of each group of mice were measured by performing Western blot to investigate the mechanism of EVO treatment in CT26 tumor-bearing mice.Results:EVO inhibited the growth of tumors in CT26-bearing mice and enhanced their splenic and thymic indices.Western blot results showed that EVO reduced the expression levels of HK,LDHA,and PKM proteins in the tumor tissues of CT26 tumor-bearing mice.Conclusion:EVO has a therapeutic effect on CT26 tumor-bearing mice,and its mechanism of action may be related to the low expression of key enzymes HK,LDHA and PKM of glycolysis in tumor tissues.
Keywords:evodiamine;mouse colon cancer cells;tumor-bearing mice;glycolysis;hexokinase;lactate dehydrogenase A;pyruvate kinase M
Introduction
Colon cancer is a common malignancy of the digestive system.It mainly occurs at the junction of the rectum and sigmoid colon and is mostly seen in people aged 40–50 years.Owing to the changes in living habits and diet in recent years,the incidence rate of this disease has increased and poses a great threat to the patients[1].Colon cancer now ranks fourth and fifth in terms of incidence and mortality rates,respectively[2].The pathogenesis of colon cancer involves multiple steps and mechanisms.Similar to most malignancies,the pathogenesis of colon cancer is still unclear;however,it is thought to be caused by a combination of environmental factors and genetic factors[3].Although traditional treatments(e.g.,surgery,radiotherapy,and chemotherapy)have certain therapeutic effects against colon cancer,chemotherapy can damage the normal cells;further,recurrence and metastasis of cancer cells reduces the survival rate of patients and causes a series of other problems[4].Moreover,antitumor chemotherapeutic drugs have severe toxic side effects and are susceptible to drug resistance upon its long-term use[5,6].Therefore,it is crucial to develop antitumor drugs with less side effects and good efficacy.Studies have shown that the metabolism of tumor cells is different from normal cells,and regulating tumor cell metabolism can help in the development of antitumor drugs[7].
Traditional Chinese medicine(TCM)is advantageous as it has multiple pathways of action,multiple targets,few toxic side effects,and it can treat tumors.In recent years,clinical and basic studies have been conducted on the treatment of tumors using TCM.Immunological TCM polysaccharides have been widely used in clinical adjuvant therapy as they can modulate the immune function of the body and have remarkable antitumor activity and low toxic side effects[8,9].Few studies found that Bletilla striata polysaccharide inhibited tumor growth in mouse colon cancer cells(CT26)tumor-bearing mice,which may be related to the enhancement of antitumor immunity and activation of TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway in tumor-bearing mice[10].The immune response and improvement in gut microbiota structure in CT26 tumor-bearing mice can be regulated byDendrobium catenatumpolysaccharide that may be involved in inhibiting proliferation and angiogenesis of tumor cells and promoting angiogenesis[11].Wogonin can downregulate the expression of glycolytic enzymes hexokinase(HK)II,pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase I,and lactate dehydrogenase A(LDHA)in colon cancer cells HCT116 and inhibit glycolysis,thereby exerting antitumor effects[12].
Evodiamine(EVO)is a tryptamine indole alkaloid extracted from Tetradium ruticarpum,which belongs to the familyRutaceae,with a relative molecular mass of 303.36,a molecular molecular formula of C19H17N3O,and a melting point of 278°C.EVO is yellow flaky crystal with several pharmacological effects,including anti-inflammatory,antihypertensive,analgesic,and anti-allergic effects[13].Additionally,EVO can exhibit anticancer activity and act as an antitumor agent by inducing tumor cell apoptosis and inhibiting the cell cycle and migration[14].Previous studies suggested that EVO interferes with tumor-specific glucose metabolism and fatty acid metabolism.The effects of EVO on tumor cell blockade,inhibition of proliferation,and induction of mitotic catastrophe apoptosis have also been reported[15].
Tumor cells have different metabolic behavior than the normal cells,and reprogrammed sugar metabolism is a common metabolic feature of tumor cells.Studies have shown that the key enzymes of glycolysis,HK,LDHA,and pyruvate kinase M(PKM)type,are crucial for the rapid proliferation of tumor cells.HK phosphorylates glucose entering the cell to glucose-6-phosphate,which is the first reaction in the glycolytic pathway[16].LDHA converts pyruvate to lactate and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide(NAD+)[17].Tumor cells can also form lactate that is catalyzed by LDHA even under adequate oxygen conditions,thereby increasing the rate of lactate production by glycolysis[18].This mode of aerobic glycolysis is important for the proliferation of tumor cells.The PKM gene encodes for two isoforms,PKM1 and PKM2.PKM2 is expressed in embryonic tissues,most normal tissues in adults,and in rapidly proliferating cells,and is hence an important marker for tumor cells[19,20].In recent years,regulation of cellular glucose metabolism for inhibition of tumor cell growth has become a research hotspot in the field of tumor cell biology and metabolism.Therefore,modulating cellular glucose metabolism could be an important way to treat colon cancer.In this study,CT26 were injected in the axillae of mice and treated with EVO.First,we investigated the therapeutic effect of EVO on CT26 tumor-bearing mice.Second,we studied the effect of EVO on the expression of glycolytic key enzymes,HK,LDHA,and PKM,in CT26 to investigate the mechanism of action of EVO in treating colon cancer.
Method
Animals and materials
Generation of CT26 model and grouping for axillary inoculation in mice.Fifty 8-week-old healthy male C57 BL/6 mice weighing 20±2 g were purchased from Beijing HFK Bioscience Co.Ltd(manufacturer license:SCXK).The housing environment was maintained at 25±2°C,with relative humidity of 50±15% and light and dark cycle of 12 h;the animals had ad libitum access to food and water.The experiment was approved by the First Hospital of Fujian Medical University.Ethics number:House ethics202110014.
After acclimatizing the mice for 1 week,they were randomly divided into model group,oxaliplatin group,EVO high-dose group,EVO medium-dose group,and EVO low-dose group(n=10).Mice were given axillary inoculations at a concentration of 1×107cell mL-1CT26 0.2 mL.Model group mice were administered intraperitoneal injection of saline 0.2 mL per day after model generation.Mice in the oxaliplatin group were administered intraperitoneal injection of oxaliplatin(7.5 mg/kg)on days 1,5,9,and 13 after model generation.Mice in the EVO high-dose group were administered intraperitoneal injection of EVO injection(10 mg/kg)per day after model generation for 14 days.Mice in the EVO medium-dose group were administered intraperitoneal injection of EVO injection(5 mg/kg)per day after model generation for 14 days.Mice in the EVO low-dose group mice were administered intraperitoneal injection of EVO injection(2.5 mg/kg)per day after model generation for 14 days(Figure 1).

Figure 1 Model making and administration regimen.EVO,evodiamine;CT26,mouse colon cancer cells.
Drugs and reagents
EVO(catalog no:B21315)was purchased from Shanghai Yuanye Biotechnology Co,Ltd.Oxaliplatin(catalog no:H20203216)was purchased from Qilu Pharmaceutical Co,Ltd.HK(catalog no.22029-1-AP),LDHA(Item No.66287-1-Ig),and PKM(Item No.10078-2-AP)were purchased from Proteintech.
Experimental instruments
CO2incubator(Thermo Corporation),ultra-clean bench(Suzhou Ruitong Purification Technology Co,Ltd.),TDL-5A centrifuge(Shanghai Feiqiaer Analytical Instruments Co,Ltd.),electrophoresis instrument(Beijing Junyi Electrophoresis Co,Ltd.),and shaker(Tianjin Honor Instruments Co,Ltd.)were used in the study.
Preparation of tissue samples
After 2 hours of administration on day 21,blood was collected from the orbital plexus,and the mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation.Tumor,spleen,and thymus tissues were obtained.When the tumor and organs were collected,the organs were gently rinsed in saline to remove residual blood,and the excess water was gently blotted using an absorbent paper.The tissues and organs were weighed,and these data were used to calculate the thymus index,spleen index,and tumor suppression rate according to the following formula.
Thymus index=Thymus weight(mg)/Body weight(g)
Splenic index=Spleen count(mg)/Body weight(g)
Tumor suppression rate=(Mean tumor weight of negative control group-Mean tumor weight of experimental group)/Mean tumor weight of negative control group×100
In addition,hematoxylin and eosin(HE)staining was performed on tumor tissues to observe the histopathological changes of tumors in each group of mice.
Pathological staining
We used 4% paraformaldehyde-fixed tumor tissues to make paraffin sections.Changes in tumor histopathology were observed under light microscopy after staining with HE.The films were quantified[21].
Western blot analysis of protein levels
The expression levels of HK,LDHA,and PKM were quantified in tumor cells using Western blot method.Radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer lysis buffer was added to the extracted mouse tumor tissues,which were then homogenized and centrifuged.Next,total protein was extracted and quantified using the bicinchoninic acid protein assay kit.The proteins were resolved using electrophoresis,transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride membrane,blocked using 5%skimmed milk powder for 2 h at room temperature,and removed.After removal,different rabbit antimouse primary antibodies,HK(dilution ratio,1:5000),LDHA(dilution ratio,1:2000),PKM(dilution ratio,1:2000),and β-actin(dilution ratio,1:10000)were added and incubated overnight at 4°C.After washing the membrane,secondary antibody(goat antirabbit IgG;dilution ratio,1:20000)was added,incubated for 2 h at room temperature,and the membrane was washed with TBS+Tween.Next,Enhanced chemiluminescence reagent was added for the detection of proteins.The electrophoretic strip images were scanned to quantify protein expression levels,using β-actin as the internal reference.ImageJ software was used to calculate the mean optical density values.
Statistical processing
The experimental results were analyzed using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences Statistics 20.0 software.Quantitative data were expressed as¯x±s using t-test.One-way analysis of variance method was used to compare the means among multiple groups.A difference withP<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Effects of EVO on tumor suppression rate,thymus index,and spleen index
As shown inFigure 2,the model group had the largest tumor volume,and all treatment groups developed an inhibitory effect against the tumor.Compared to the model group,the positive control(oxaliplatin)(P<0.01)and EVO high-dose groups(P<0.01)had the most significant tumor inhibitory effect.
From the data mentioned inTable 1,we can conclude that the positive control(oxaliplatin)group exhibited the most significant tumor suppression activity.The tumor suppression rate was different for tumors treated with different doses of EVO intervention,among which the EVO high-dose group exhibited the highest efficacy in suppressing the tumor.In addition,the thymus and spleen indexes rebounded in the treatment group compared to the model group,among which the positive control(oxaliplatin)group(P<0.01)and the EVO high-dose group(P<0.01)had the most significant effect.
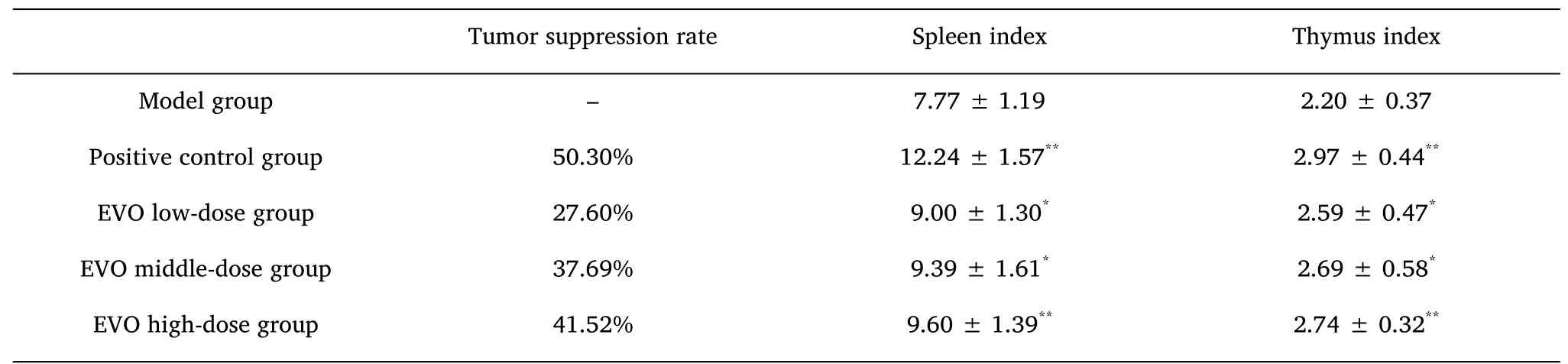
Table 1 The tumor suppression rate,thymus index and spleen index of mice in each group
Effect of EVO on histopathological manifestation of tumors in mice
The HE staining results showed that the tumor cells in the model group were neatly arranged,without edema or rupture,and tightly spaced.Tumor cells showed different degrees of changes after drug administration.The changes included disorganized arrangement of tumor cells,increased cell spacing,presence of many vacuole-like degeneration,and necrosis of tumor cells(Figure 3a).
HE staining scores were the highest in the model group and low in all treatment groups,with the most significant efficacy in the oxaliplatin(P<0.01)and EVO high-dose groups(P<0.01)(Figure 3b).
Effect of EVO on the levels of key glycolytic enzymes HK,PKM,and LDHA in tumor tissues
The levels of HK,LDHA,and PKM were detected using Western blot technique.It was found that all treatment groups showed different degrees of improvement.The levels of HK,LDHA,and PKM were lower in the treatment groups than in the model group.Among the treatment groups,HK,LDHA,and PKM levels in tumor tissues were significantly low in the positive control(oxaliplatin)and EVO high-dose groups(Figure 4a).
The Western blot quantification results showed that the expression levels of HK,LDHA,and PKM were lower in the treatment groups than the model group(Figure 4b).

Figure 2 The tumor volumes in each group.EVO of effect on Inhibition rate,spleen index and thymus index of colon cancer mice(n=10,¯x±s).EVO,evodiamine.
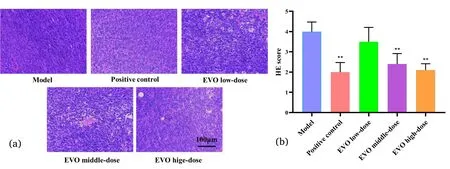
Figure 3 HE staining of the tumor tissue.(a)HE staining of tumor tissue;(b)HE staining score of tumor tissue.*,compare with Model group P<0.05;**,compare with Model group P<0.01.HE,hematoxylin and eosin;EVO,evodiamine.
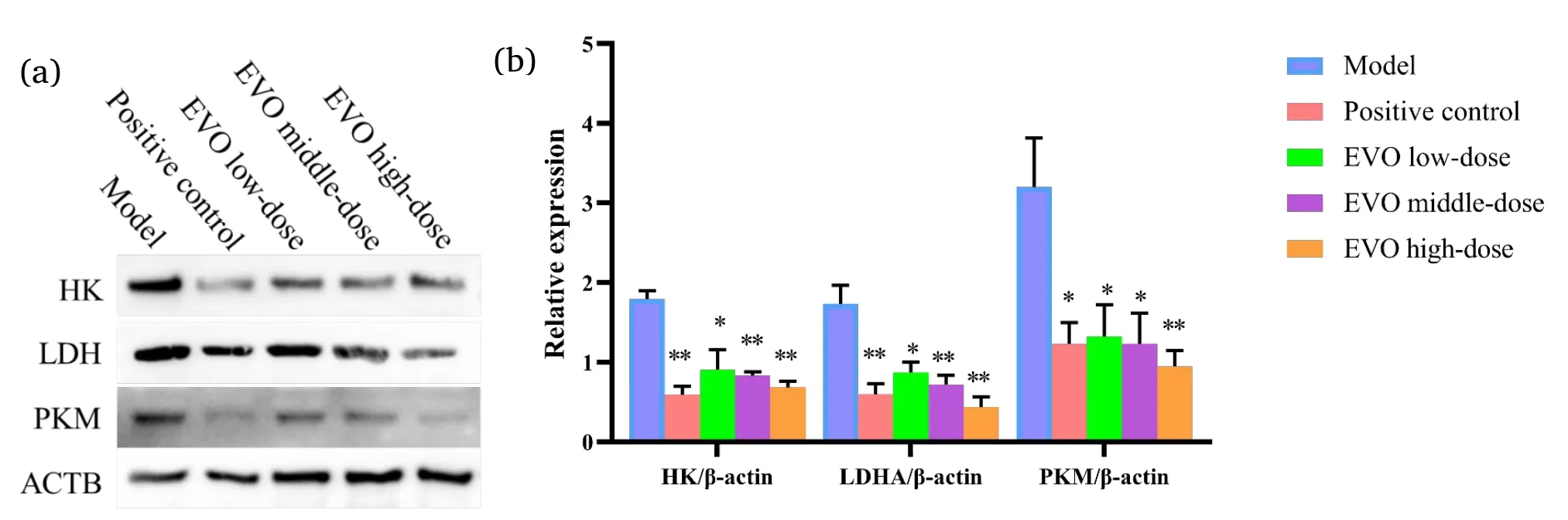
Figure 4 Protein expression of tumor tissue HK,LDHA,and PKM.(a)Western blot plots of tumor tissues HK,LDHA,and PKM protein;(b)quantification analysis of Western blot plots of tumor tissue HK,LDHA,and PKM proteins.*,compare with Model group P<0.05;**,compare with Model group P<0.01.EVO,evodiamine;HK,hexokinase;LDHA,lactate dehydrogenase A;PKM,pyruvate kinase M;ACTB,β-actin.
Discussion
Colon cancer is caused internally by the deficiency of positive qi and externally due to the external invasion of toxins.Deficiency in positive qi leads to weakening of peripheral defenses,making the body susceptible to toxin invasions.In case of the deficiency of positive qi and abundance of toxin,toxins stay in the gut and cause this disease.In the early stage,damp-heat and stasis toxins are common;in the later stage,positive qi and blood deficiency,liver and kidney yin deficiency,and spleen and kidney yang deficiency are common[22].According to TCM,colon cancer is caused by root vacuity and tip repletion,with dampness,heat,toxicity,and stagnation as the symptoms of deficiency of positive qi[23].Colon cancer has an insidious onset and many patients do not show apparent symptoms until the middle or later stage of cancer.Most manifestations of the middle-and late-stages colon cancer are“positive qi deficiency and excessive toxins”so clinical treatment is often targeted at recovering the deficiency and dispelling the heat.Among them,spleen(qi)deficiency is the common basic symptom of“positive qi deficiency”in middle-to-late stages of colon cancer,and it is the most widely distributed symptom in colon cancer cases[24,25].
In this study,a tumor-bearing mouse model was generated by administering axillary injection of CT26,and the appearance of a significant mass in the axilla of the mice was considered as successful model generation.Our results showed that the tumor growth was more remarkably inhibited and reduced in the treatment group than the model group.The pathological results showed that the tumor tissue structure was clear and the cells were closely arranged in the model group mice.These results were consistent with the pathological manifestations of the tumors,and EVO intervention significantly inhibited the tumor growth in CT26 tumor-bearing mice.These observations confirm the therapeutic effect of EVO on tumors.
Both tumor metastasis and cachexia are important causes of death in tumor patients.Aerobic glycolysis is one of the characteristics of abnormal metabolism in tumor cells[26].Although aerobic glycolysis is less efficient in terms of energy production,it has few reaction steps and therefore it can generate more adenosine triphosphate molecules per unit of time.More importantly,the carbon-based intermediates generated during glycolysis can be used as raw materials for tumor cells to synthesize biomolecules and facilitate tumor cell division and proliferation.In addition,the end product of glycolysis,lactic acid,can lower the pH of the tumor microenvironment,which may weaken the neutralizing effect of immune cells on tumor cells and favor immune evasion by tumor cells[27].The first step in glucose metabolism is catalyzed by HK.Among the HK isomers,HK1 and HK2 are mitochondria-associated,high-affinity HKs that combine oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis[28].On the one hand,this reaction maintains a concentration gradient of glucose inside and outside the cell,allowing continuous intake of glucose into the cell.On the other hand,this reaction provides a common substrate for glucose to enter other metabolic pathways[29].LDHA also has an important impact on the tumor microenvironment and tumor progression and metastasis[30].An increase in LDHA activity also simultaneously increases lactate production,thereby increasing lactate levels in the extracellular environment and leading to a rearrangement of the extracellular matrix.This promotes the aggressive proliferation of tumor cells[31].The four PK isoforms in mammalian cells are mainly encoded by two genes,pyruvate kinase isozymes R/L and PKM.Protein Kinase is the indicator rate-limiting enzyme in the last step of glycolysis and is responsible for the conversion of phosphoenolpyruvate and adenosine diphosphate in the cytoplasm to pyruvate and adenosine triphosphate to promote tumor growth[32,33].This enzyme plays a crucial role in the progression of several types of tumors.One isoform of PKM,PKM2,is highly expressed in tumor cells and is therefore used as a predictive marker for cancers[34,35].Aerobic glycolysis is essential for the proliferation and metastasis of tumor cells,and regulation of tumor cell glycolysis may become a new target for antitumor therapy[36].The results of this study showed that EVO reduced the expression levels of HK,LDHA,and PKM in tumor cells,indicating that EVO may alleviate the disease progression of cancer by regulating glycolysis in tumor cells.
In summary,EVO slowed down the glycolytic response in tumor tissues of CT26-bearing mice,and its mechanism of action was related to the reduction of HK,LDHA,and PKM protein expression levels in tumor tissues and amelioration of further cancer development.
杂志排行
Precision Medicine Research的其它文章
- Combining PD1 inhibitor,PARP inhibitor and antiangiogenic medication for lung squamous cell carcinoma with liver metastasis:a case report
- The therapeutic mechanism of Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide on T2DM rats based on the Nrf2 signaling pathway
- Network pharmacology study of drug pair Tubeimu-Zhebeimu in the treatment of breast cancer
