A Systematic Review of Economic Evaluation of CDK4/6 Inhibitors in HR+/HER2-Advanced Breast Cancer
2022-12-30WangFangZhangFangLiXueDongLi
Wang Fang,Zhang Fang,Li Xue,Dong Li
(1.School of Business Administration,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang 110016,China;2.ZTE Foundation,Shenzhen 518055,China;3.Health Development Research Center of the National Health Commission,Beijing 100044,China)
Abstract Objective To review the domestic and foreign economic studies on CDK4/6 inhibitors in first-line or secondline treatment of HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer,and to analyze the main methodologies and research results.Methods Systematic literature review was used to search PubMed,EMBASE,Cochrane Library,CNKI,CBM,and Wanfang database.The incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was taken as the main outcome index,and all pharmacoeconomic evaluations with CDK4/6 inhibitors as intervention measures were included,such as Palbociclib,Ribociclib,and Abemaciclib.According to the Quality of Health Economic Studies Instrument,the quality of the included articles was evaluated,and then the included literature was analyzed.Results and Conclusion A total of 16 pharmacoeconomic evaluation studies were included,mainly from the perspective of national healthcare systems or third-party payers.Only 2 studies focused on second-line treatment,and the remaining treatment levels were first-line treatment.In terms of model structure,7 studies adopted the Markov model,6 studies adopted the PSM model,and 3 studies adopted the DES model.The basic analysis results showed that CDK4/6 inhibitor combined with endocrine regimen was not economical compared with endocrine alone regimen when the threshold was the conventional willingness to pay (WTP) value of each country.The uncertainty analysis included deterministic sensitivity analysis and probability sensitivity analysis.The included studies are all Cost-Utility Analysis with high-quality evaluation,which can provide evidence support for health-related decision-makers in decision-making.It can also provide methodological reference for the economic evaluation of other targeted drugs.
Keywords: CDK4/6 inhibitor;breast cancer;cost-effectiveness analysis;systematic literature review
Breast cancer is one of the common malignant tumors that threaten women’s health,and its incidence ranks first among female malignant tumors in the world.The prognosis of advanced breast cancer is often poor.The 5-year survival rate is only about 20%,and the median overall survival time is about 2-3 years[1].HR+/HER2-breast cancer accounts for 70% of all breast cancer types[2].In addition,the complexity of HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer makes treatment difficult,so HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer has caused a heavy burden on patients.Traditional endocrine therapy (ET) for patients with HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer mainly includes aromatase inhibitors (AI) and Fulvestrant,but endocrine therapy often leads to drug resistance.It is also the main cause of tumor recurrence or progression in these patients.
The advent of targeted CDK4/6 inhibitors Palbociclib,Ribociclib,and Abemaciclib has brought new hope to these patients,and the results of phase III clinical trials have demonstrated that compared with endocrine monotherapies in both the first-line and second-line treatment,CDK4/6 inhibitors combined with endocrine regiments significantly increase the clinical benefit of patients.MONARCH 3[3],a phase III clinical trial of Abemaciclib,showed that during initial endocrine therapy in patients with HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer,the progressive free survival (PFS) was prolonged from 14.76 months to 28.18 months by adding Abemaciclib compared with Letrozole alone.In addition,the MONARCH 2[4,5]clinical trial showed that in patients with advanced HR+/HER2-breast cancer who progressed after endocrine therapy,the addition of Abemaciclib increased PFS from 9.3 months to 16.4 months compared with Fulvestrant alone.Besides,the overall survival (OS) was increased from 37.3 months to 46.7 months.Based on the significant benefits of clinical trials,FDA has approved these three CDK4/6 inhibitors in combination with Nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitors (NSAI) for initial endocrine therapy of HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer,or in combination with Fulvestrant in patients with advanced HR+/HER2-breast cancer who have progressed after prior endocrine therapy.
However,the high price of CDK4/6 inhibitors has caused a greater economic burden on both the patients and the healthcare system.In order to cope with the ever-increasing pressure of medical insurance funds,value-based pricing is playing an increasingly important role.Different nations also require new drugs to use the results of cost-effectiveness analysis on the basis of clinical effects as important evidence for decision-making during medical insurance access.Therefore,many scholars have evaluated the economics of CDK4/6 inhibitors in the treatment of HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer patients from different countries.This study will systematically review the economic evaluation of literature,using a structured form to extract data from the included literature,analyzing the basic characteristics,research design,economic evaluation results,and uncertainty.Then we can provide an evidence support for followup related health decisions as well as a methodological reference for the pharmacoeconomic evaluation of other targeted drugs.
1 Method
1.1 Literature search
Chinese databases such as CNKI,CBM,Wanfang,and some English databases like PubMed,EMBASE,and Cochrane Library were systematically searched.The search time is from the establishment of the database to June 2021.The search method is a combination of medical subject terms and free words,and the search subject terms include “Breast Neoplasm” “CDK4/6 inhibitor” “Abemaciclib”“Palbociclib” “Ribociclib” and “Cost Benefit Analysis”.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
(1) Population were women with HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer;(2) The interventions were CDK4/6 inhibitor combined regimen,including Abemaciclib or Palbociclib or Ribociclib combined regimen;(3) The research types included cost-utility analysis (CUA),cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA),cost-benefit analysis (CBA) and cost minimization analysis (CMA).
1.3 Exclusion criteria
(1) The research objects were men with earlystage breast cancer or triple-negative breast cancer patients;(2) The economic literature of the health outcome index was not QALY or LY;(3) Literature of intervention did not include CDK4/6 inhibitors;(4)The research type was partial economic evaluation,such as cost analysis,effect analysis and budget impact analysis;(5) News reports,expert opinions,critical literature and abstracts were not included;(6)Repeated publications were not covered.
1.4 Data extraction
According to the above inclusion and exclusion criteria,two professional researchers independently conducted literature screening and determined the final included literature.Then,according to the preestablished data extraction table,if there was any doubt or disagreement during literature screening and data extraction,a third researcher would assist in resolving the disagreement,and the decision would be made through meeting discussion.
1.5 Quality assessment
The quality of the included literatures was evaluated according to Quality of Health Economic Studies Instrument (QHES)[6].QHES consists of 16 evaluation items,which had answers like “yes” or“no” according to whether the literature met each item,and the scores of all the items that answer“yes” were accumulated to obtain the quality score of the reviewed literature.The total QHES score was 100,with 0 to 24 indicating very poor research quality.Scores of 25 to 49 indicated low research quality.Scores of 50 to 74 indicated medium research quality.And the scores of 75 to 100 indicated high research quality.Two researchers scored at the same time,and made the decision by discussion in case of disagreement.
2 Results
2.1 Literature search results
A total of 119 related articles were retrieved,and 84 articles remained after deduplication.Then 41 articles were excluded by reading the titles and abstracts.The full text of the remaining 43 papers were read and 27 papers were excluded according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria.Finally,a total of 16 papers were obtained.The flow chart of the specific inclusion and exclusion of articles was shown in Fig.1.

Fig.1 Flow chart of inclusion and exclusion of economic evaluation literature of CDK4/6 inhibitors
2.2 Literature inclusion and Quality assessment results
The 16 studies were all model-based cost-utility analyses,including 6 from the perspective of the United States,2 from Canada,1 from Switzerland,1 from the United Kingdom,1 from Singapore,1 from China,1 from Spain,1 from Brazil,and the other two were analyzed from both the Chinese perspective and the American perspective.According to the 16 evaluation items of QHES,the quality evaluation scores of the included documents were all greater than 75 points.The study objectives,perspectives and model structure were described in detail,sensitivity analysis of model uncertainties was performed,and study limitations were explained.In addition,these studies were based on the results of phase III clinical trials,which was a common research method of anticancer drug economics.The 16 included articles were considered to be of high quality.
2.3 Treatment level and treatment plan
2.3.1 Treatment level
Among the included articles,except Zhang,et al.[7]and Mamiya,et al.[8],who compared the costeffectiveness of Palbociclib combined with Fulvestrant versus Fulvestrant alone in the second-line treatment of HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer,the treatment levels of the rest of the articles all aimed at first-line(Table 1).
2.3.2 Treatment plan
In this study,the endocrine single-agent regimen for first-line treatment of postmenopausal patients with HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer referred to Letrozole or Anastrozle,and the combined regimen referred to Abemaciclib or Palbociclib or Ribociclib
with Letrozole or Anastrozle.The endocrine single-agent regimen for second-line treatment of postmenopausal patients with HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer referred to Fulvestrant,and the combined regimen referred to Abemaciclib or Palbociclib or Ribociclib with Fulvestrant.The endocrine regimen for first-line treatment of premenopausal patients with HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer referred to Goserelin+NSAI/tamoxifen,and the combined regimen referred to Ribociclib+Goserelin+NSAI/tamoxifen.Among the 16 studies,4 were the comparison of Palbociclib combined regimen and Ribociclib combined regimen,and the rest were the economic evaluation of the comparison of Palbociclib/Ribociclib combined endocrine regimen and endocrine single-agent regimen.At present,no fulltext economic evaluation of Abemaciclib combined regimen has been published.
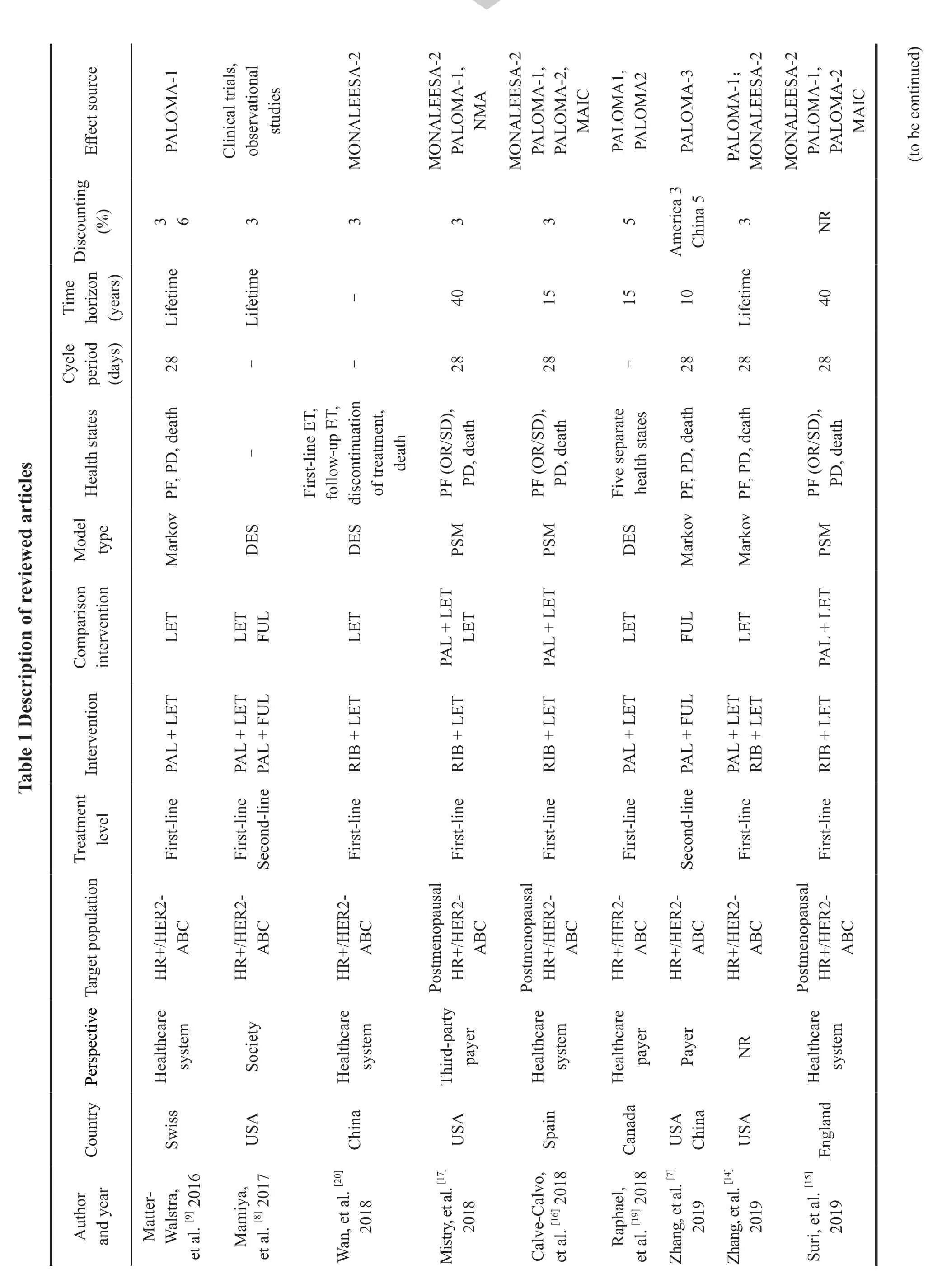
2.4 Model structure
All the included articles were model-based research designs,of which seven adopted Markov model,six adopted partition survival model (PSM),and the discrete event simulation (DES) model was used in three studies.
Matter-Walstra,et al.[9],Zhang,et al.[7],Huang,et al.[10],Le,et al.[11],Stellato,et al.[12],Yang,et al.[13]and Zhang,et al.[14]adopted Markov model.These regimens were all evaluated for the economics between Palbociclib or Ribociclib combined with endocrine and endocrine regimens alone.Among them,Yang,et al.[13]compared the cost-effectiveness of Ribociclib combined with Fulvestrant and Fulvestrant monotherapy for first-line treatment of postmenopausal women with HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer.Then they divided the model into four health states: progression-free (PF),first progressive disease (1st PD),second progressive disease (2nd PD),and death.The remaining six studies divided the model into three health states: PF,PD and death.The probability of metastasis among different states was calculated by the KM survival curves of progressionfree survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) of the corresponding clinical trials.
Suri,et al.[15],Galve-Calvo,et al.[16],Mistry,et al.[17],and Buehler,et al.[18]used the Partition survival model to analyze the cost-effectiveness between Palbociclib combination regimen and Ribociclib combination regimen.The Partition survival model of breast cancer was constructed in line with other tumor survival analysis models methods.The patient’s survival status was divided into three health statuses: PF(OR/SD),PD and death.Then,the progression-free survival curve and the overall survival curve were used to directly estimate the patient’s state occupancy over time.Unlike the Markov model,which needs to calculate the transition probability between different health states,the PSM model directly estimates the proportion of surviving patients through the area under the OS curve,and the proportion of surviving and progress-free patients were estimated through the area under the PFS curve.The proportion of patients who survived but progressed through the difference between OS and PFS were also calculated.Then the simulation of the total costs and total effects of intervention and control regimens was completed within the time horizon.
In addition,Raphael,et al.[19],Mamiya,et al.[8],Wan,et al.[20]adopted discrete event simulations model to compare the economics between Palbociclib or Ribociclib combined with endocrine and endocrine alone.Discrete event simulations model is also called time-to-event model,which is different from traditional Markov model and PSM,because Markov model and PSM divide time into increments of fixed duration and time.However,the time in DES is continuous.In DES model,the disease history of simulated individuals is modelled to occur as a sequence of discrete events where the time between events may be fixed or selected randomly from appropriate time-to-event distributions[19].
2.5 Cost and resource usage
One of the included literatures was from the perspective of society,while the other literature was from the perspective of medical and health payers,including the healthcare systems of various countries and third-party payers.In cost identification,all the 16 articles only considered direct medical costs,including drug costs,laboratory and imaging monitoring costs,follow-up costs,severe adverse reaction management costs,follow-up costs,best supportive care costs,and end-of-life costs.The direct medical cost is basically the same in all countries,but the specific cost is slightly different according to the characteristics of various countries’ medical and health systems.For example,in the United States and the United Kingdom,the best supportive care and end-of-life cost are generally included,while in China,it is generally not considered.
In terms of adverse events,all 16 studies only considered adverse events above grade 3,but different studies had certain differences in the inclusion of specific adverse events.For example,when comparing the economics between Palbociclib combined with endocrine and endocrine alone,Zhang,et al.[7]only considered neutropenia and anemia with an incidence greater than 5% and a difference rate of greater than 4% between the two groups.Walstra,et al.[9]only considered the impact of severe neutropenia on the cost.When comparing the economics between Ribociclib combined with endocrine and endocrine alone,Loke,et al.[21]included neutropenia,febrile neutropenia,hepatic dysfunction,and QT interval prolongation.While Yang,et al.[13]included neutropenia,leukopenia,infection,hepatobiliary toxicity,and prolonged QT interval.
Evidence showed that although the three CDK4/6 inhibitors did not have significant differences in clinical efficacy,they had certain differences in adverse drug reactions[22].Among them,the hematologic adverse events,such as neutropenia and anemia,were higher with Palbociclib and Ribociclib.Meanwhile,the incidence of gastrointestinal adverse events such as diarrhea of Abemaciclib was higher,and Ribociclib might also have the risk of prolonging the QT interval[23].Therefore,the economic evaluation of CDK4/6 inhibitors should consider all adverse events that have a significant impact on patient costs and health-related quality of life based on different study designs.
2.6 Utility
The health utility value data in the included literature came from published literature.Among them,the health status in PSM and Markov model was generally divided into progression-free,progressive disease and death state.The utility values of progression-free,progressive disease state were all derived from the published literature,and the utility value in the death state was 0.The health status in the DES model was divided according to the endocrine treatment period,the chemotherapy period and the end-of-life treatment period,and the corresponding utility value was assigned according to the published literature.There were 10 articles that considered the disutility value caused by adverse drug reactions,and 7 of them clearly explained the disutility value caused by severe neutropenia.
2.7 Economic evaluation results
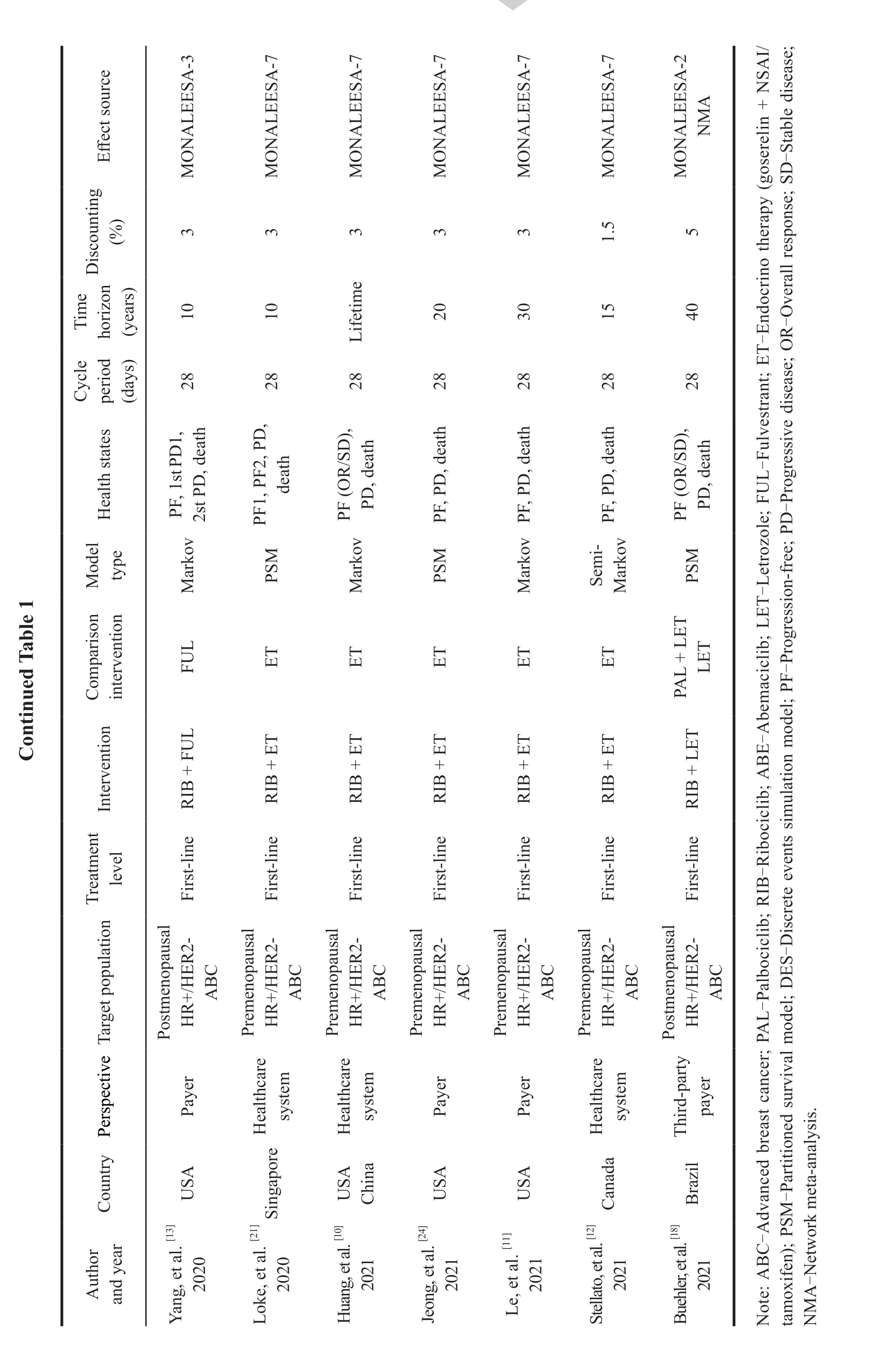
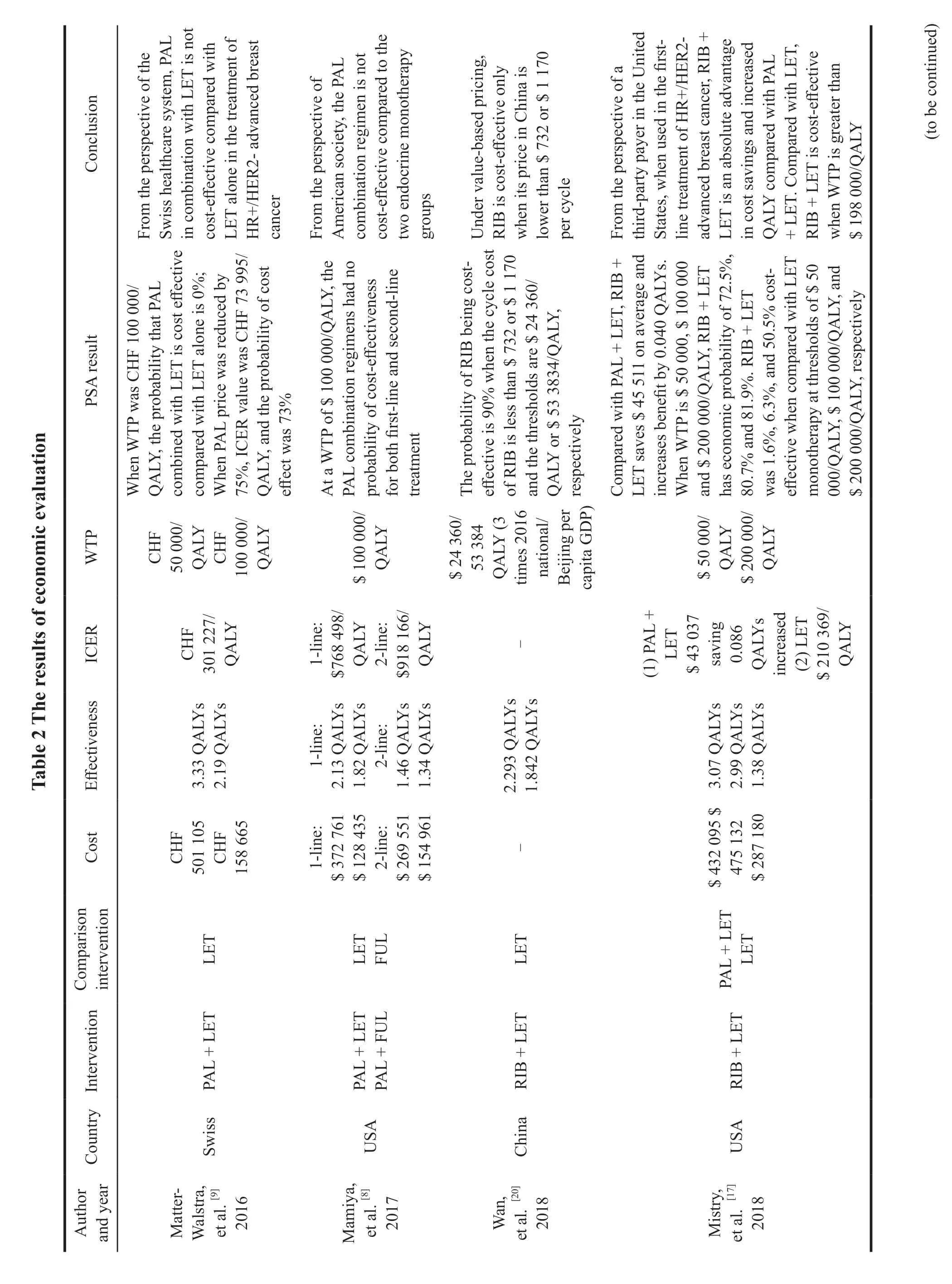
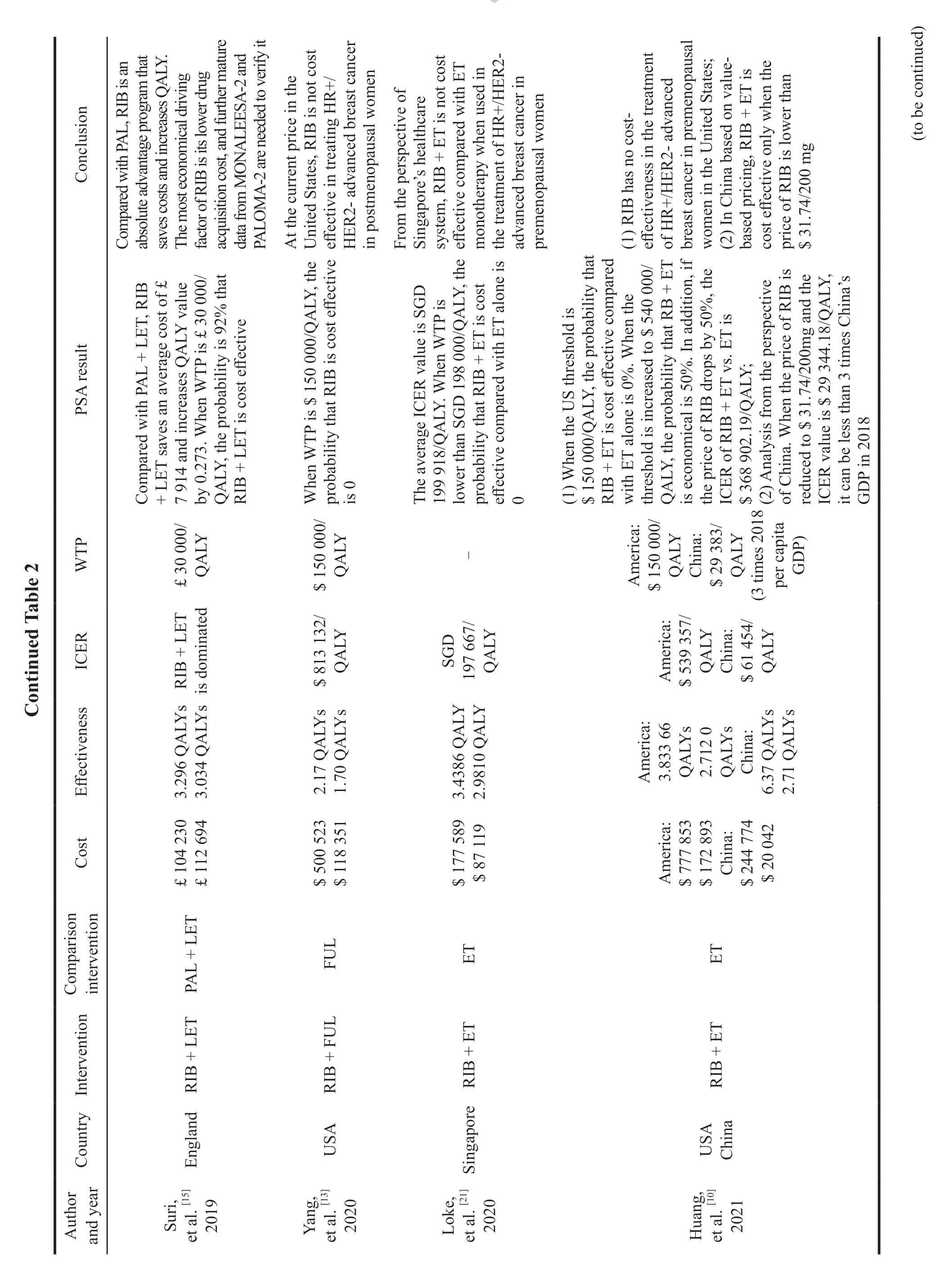
2.7.1 Palbociclib
Four articles[8,9,14,19]compared the costeffectiveness of Palbociclib combined with Letrozole versus letrozole alone in the first-line treatment of HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer from the perspective of payers in Switzerland,Canada,and the United States,respectively.The results showed that Palbociclib combined with Letrozole was not cost-effective.Two articles[7,8]analyzed from the perspectives of China and the United States that Palbociclib combined with Fulvestrant was not costeffective compared with Fulvestrant in the secondline treatment of HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer.Among them,Mamiya,et al.[8]compared the economics of the combination of Palbociclib in the first-line and second-line treatment of HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer from the perspective of American society.The results showed that ICER value of Palbociclib combined with Letrozole was $768 498/QALY compared with letrozole in first-line treatment.The ICER value was $ 918 166/QALY when compared Palbociclib combined with Fulvestrant in the second-line therapy,and neither was cost-effective at the US threshold of $100 000/QALY (Table 2).
2.7.2 Ribociclib
Seven articles[7,10,12,14,20,21,24]compared the economics between Ribociclib combined with endocrine and endocrine therapy in patients with HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer from the perspectives of China,Canada,Singapore,and the United States,respectively.The results showed that Ribociclib combined regimen was not cost-effective under conventional WTP in all countries.Only one paper written by Le,et al.[11],from the perspective of the United States,considered that compared with endocrine regimen,Ribociclib combined regimen was economical when WTP was $ 150 000/QALY,and the ICER value was $ 124 513/QALY.
In addition,four articles compared the economics between Ribociclib combined with Letrozole and Palbociclib combined with Letrozole,and three of them[15,17,18]analyzed from the perspectives of Britain,the United States and Brazil respectively,which showed that Ribociclib combined regimen was an absolute advantage scheme because both saved costs and increased benefits.An article[16]from the perspective of Spain showed that compared with Palbociclib combined regimen,the total cost increased by 439.86 euros and the total benefit increased by 0.437 QALYs of Ribociclib combined regimen in the 15 years,and the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio was € 1 543.62/QALY.When the WTP used in Spain was € 20 000-€ 30 000/QALY,the probability of cost-effectiveness of Ribociclib combined regimen compared with Palbociclib combined regimen was 99.85% (Table 2).
2.7.3 Abemaciclib
No full-text literature has been published for the economic evaluation of Abemaciclib,but two abstracted studies were retrieved to analyze the economics of Abemaciclib combined with Letrozole,in which Schroeder,et al.[25]studied from the perspective of Brazilian health system that compared with letrozole alone.Abemaciclib in combination with letrozole in first-line treatment of HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer had an incremental costeffectiveness ratio of $ 81 530/QALY,which was not economical at the Brazilian threshold of $ 35 000/QALY.Vekov,et al.[26]compared the economics of the three CDK4/6 inhibitors in first-line treatment from the perspective of a third party in Bulgaria,and the results showed that Abemaciclib combination was an absolute advantage with cost saving and increased clinical benefits compared with Palbociclib combination and Ribociclib combination (Table 2).
2.8 Sensitivity analysis
Uncertainty analysis was carried out in all studies,14 of which carried out one-way sensitivity,and 16 articles carried out probability sensitivity analysis.The results of one-way sensitivity showed that the main factors affecting the results were: the utility value of PF/PD healthy state,the drug price of each CDK4/6 inhibitor,and the OS/PFS hazard ratio (HR) between different drug regimen.The oneway sensitivity results were consistent with the basic analysis results within the set parameter variation range.In the probability sensitivity analysis,these studies used Monte Carlo simulation to conduct 1 000-10 000 samplings,and the model was run 1 000-10 000 times with the parameters simultaneously varied with a specific pattern of distribution[20].Results obtained from probability sensitivity analysis were consistent with the basic analysis,which further illustrated the stability of the basic analysis results.
3 Conclusion and discussion
This study systematically reviews domestic and foreign economic research on the use of CDK4/6 inhibitors for first-line or second-line treatment of HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer.The included literature was evaluated through the Quality of Health Economic Studies Instrument.The quality evaluation scores of 16 articles were all greater than 75 points,which were considered to be of high quality.16 documents are all cost-utility analysis,and Markov model,PSM and DES model are used for the model structure.Besides,each research is based on randomized controlled trials to design the model structure.In terms of cost measurement,only direct medical costs are considered,which is related to the research perspective.The literature review shows that there are 7 studies from the perspective of the healthcare system,7 studies from the perspective of the payer,1 study from the social perspective,and 1 study has no research perspective.In addition,health outcomes are measured by life years (LY) and quality-adjusted life years (QALY),and the outcome indicator is mainly ICER.By comparing the research results ICER with the thresholds commonly used in various countries,we can see whether the intervention measures are economical.Although there is no unified or clear standard for cost-effectiveness threshold in all countries,the review shows that within the WTP values commonly used in all countries,neither Palbociclib combination regimen nor Ribociclib combination regimen is cost-effective compared with endocrine regimen alone.Compared with Palbociclib,the economic results display that the combination of Ribociclib is more cost-effective.


It can be seen from the treatment regimen that most economic evaluation adopted the comparison between CDK4/6 inhibitor combined with endocrine regimen and endocrine regimen alone.As the cost of combined drugs is pure increment,the combined regimen is often not cost-effective.Although the results of the included literature show that CDK4/6 inhibitors are not cost-effective in each country’s system,the United States,the United Kingdom,Canada,and other countries have included CDK4/6 inhibitors in the list of medical insurance reimbursement.Analyzing the reasons,we take England as an example,the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE),through patient access scheme (PAS),the combination of Palbociclib/Ribociclib/ Abemaciclib with letrozole is cost-effective compared with letrozole alone in firstline treatment of HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer under confidential price discount agreements,which is therefore recommended for NHS reimbursement.When the CDK4/6 inhibitor combination regimen is used in the second-line treatment of patients with HR+/HER2-advanced breast cancer,in the economic evaluation of the selection of control drugs regimen,in addition to Fulvestrant,Tamoxifen,Exemestane and Exemestane +Everolimus are also selected.It is believed that the combination of Palbociclib/Ribociclib/Abemaciclib with Fulvestrant is economical,but there is a great uncertainty.In order to benefit cancer patients in time,they are recommended to the Cancer Drug Funds (CDF),and then,based on further evidence improvement,Ribociclib/Abemaciclib combined with Fulvestrant is recommended to the NHS for reimbursement through the PAS.It also suggests that in the pharmacoeconomic evaluation of combination anticancer drugs,we should consider the particularity of the combination drugs in selecting the control schemes.In addition to the traditional model,multicriteria decision analysis can also be applied in the study design to include more stakeholders,which can make the decision more comprehensive.When applying the results of economic evaluation to health decision-making,we should explore innovative payment methods,such as learning from the way of setting up cancer fund in the UK,so that cancer drugs with better clinical efficacy can benefit the majority of patients.
杂志排行
亚洲社会药学杂志的其它文章
- Research on the Development of Drug Regulatory Science in China
- Study on the Changes of FDA Finished Pharmaceuticals Warning Letters between 2011 and 2021
- Interviews on the Cooperation between Hainan and Macaoin the TCM Industry to Promote Hainan’s TCM Industry
- Co-integration Analysis of the Relationship between New Product Output and R&D Investment in China’s Pharmaceutical Industry
- A Case Analysis of the lnfluencing Factors of Job Satisfaction of Licensed Pharmacists in Retail Pharmacies Based on SEM-Taking R Retail Pharmacy for an Example
- Research on the Extraction Techniques of Ginseng Based on Patent Analysis
