Clinical observation of acupuncture and moxibustion for functional dyspepsia due to Yang deficiency of the spleen and stomach
2022-12-28Yan刘燕ZHANGShaozhan张少战NGYashuang丁雅霜OUYANGLing欧阳玲Qiong刘琼
LⅠU Yan (刘燕), ZHANG Shaozhan (张少战), DⅠNG Yashuang (丁雅霜), OUYANG Ling (欧阳玲), LⅠU Qiong (刘琼)
1 Chenggong Hospital Affiliated to Xiamen University, Xiamen 361003, China
2 Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, China
Abstract
Keywords: Acupuncture-moxibustion Therapy; Acupuncture Therapy; Electroacupuncture; Thermal Box Moxibustion;Dyspepsia; Quality of Life; Yang Deficiency of the Spleen and Stomach Pattern
Functional dyspepsia (FD) is a multifactorial disorder characterized by symptoms in the gastroduodenal region. According to statistics, the incidence of FD is 40% in European countries, 5%-30% in Asian countries,and 11%-23% in China[1-2]. FD is easy to recur and lingering unhealed, seriously affecting patients’ life and work. The pathogenesis of FD is not very clear, and it is related to factors such as gastrointestinal motility abnormalities, psychological factors, brain-gut axis dysfunction, and intestinal flora imbalance[3-4]. Among them, gastrointestinal motility disorder is considered to be the main cause of FD[5]. Therefore, the clinical symptoms of FD can be improved by regulating the gastrointestinal motility of patients. Acupuncturemoxibustion treatment of FD has been extensively carried out in clinical studies, with a definite curative effect and low recurrence rate[6-7]. Baixiao moxibustion is a new type of moxibustion based on the theory of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) moxibustion. It is safe, effective, comfortable, and convenient. However,the clinical efficacy and mechanism of this method for the differentiation treatment of FD are still unclear. In this study, Baixiao moxibustion plus electroacupuncture(EA) was applied in the treatment of FD due to Yang deficiency of the spleen and stomach, so as to observe its clinical efficacy and effect on gastrointestinal movement.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
The diagnostic criteria in Western medicine of FD referred to the diagnostic criteria in Rome Ⅳ[8].According to the related literature[9], criteria for TCM syndrome differentiation of Yang deficiency of the spleen and stomach in this study were established.
Primary manifestations: Dull pain or stuffiness in the stomach, preferring warmth and pressing.
Secondary manifestations: Vomiting water;decreased food intake or poor appetite, fatigue, cold limbs, and loose stools.
Tongue and pulse manifestations: A pale tongue with white coating. The pulse is thready and weak.
Those who had 2 main manifestations, plus any 2 of the secondary manifestations, together with the tongue and pulse manifestations, could be diagnosed.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
Those who met the diagnostic criteria of FD; aged 20 to 65 years old; gender unlimited; no organic lesions showed by gastroscopy in the past 1 month, with negativeHelicobacter pyloritest; agreed to participate in this clinical trial and signed informed consent.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Patients with a history of abdominal surgery or other gastrointestinal diseases; those with severe primary diseases, psychosis, and mental disorders and were unable to cooperate; women during pregnancy or lactation; those who had taken gastric prokinetic drugs in the past 1 week; those who were allergic to mosapride or refused acupuncture-moxibustion treatment; those who were participating in other clinical studies.
1.4 Statistical methods
All data were statistically analyzed by the SPSS version 21.0 statistical software. Counting data were expressed as cases or rates and analyzed by Chi-square test. Measurement data in normal distribution were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (±s);one-way analysis of variance was used for betweengroup comparisons, and the least significant difference(LSD) test was used for comparisons between the two groups., pairedt-test was applied to intra-group comparisons. Measurement data in non-normal distribution were expressed as median (interquartile)[M (IQR)], and Kruskal-WallisH-test was applied.Kruskal-WallisH-test was also used for the comparisons of ranked data.P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
1.5 General data
All patients with FD due to Yang deficiency of the spleen and stomach were enrolled from Chenggong Hospital Affiliated to Xiamen University, between May 2020 and May 2021. The study protocol was reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Chenggong Hospital Affiliated to Xiamen University (Approval No.73JYY202069416). According to the previous pre-trial,n1=n2=n3 was designed, with bilateralα=0.05 and 1-β=0.8. The sample size of each group was calculated by PASS version 11 software to be 24 cases, and a total of 72 cases were needed for three groups. With an estimated dropout rate of 20%, a total of 90 cases were needed for inclusion. All cases were divided into an acupuncture-moxibustion group, an EA group, and a mosapride group using the method of random number table, with 30 cases in each group. There were no statistically significant differences in the general data of gender, age, and disease duration among the three groups, indicating that the three groups were comparable (P>0.05). See Table 1.
Table 1 Comparison of general data among the three groups
2 Treatment Methods
2.1 Mosapride group
Mosapride citrate dispersible tablets (Batch No.200412, specification: 5 mg/tablet, Lunan Better Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., China) were taken orally before meals, 5 mg/time, 3 times/d.
2.2 EA group
Points: Guanyuan (CV4), bilateral Neiguan (PC6),Tianshu (ST25), Zusanli (ST36), and Sanyinjiao (SP6).
Methods:The patient took a supine position. After routine disinfection, the Hwato brand disposable sterile acupuncture needles of 0.30 mm in diameter and 25-50 mm in length (Suzhou Medical Appliance Factory,China) were used for the acupuncture treatment. Even reinforcing-reducing manipulation was performed after Qi arrival (Deqi). Then the handles of the needles were connected [on the same side, Neiguan (PC6) and Tianshu (ST25) as a group, Zusanli (ST36) and Sanyinjiao(SP6) as a group] to a Hwato brand SDZ-Ⅱ EA apparatus, with a sparse-dense wave at 2 Hz/100 Hz.The intensity was set according to the patient’s tolerance, and the time was set as 30 min. The treatment was performed once a day.
2.3 Acupuncture-moxibustion group
On the basis of the treatment in the EA group,moxibustion therapy was added.
Points: Zhongwan (CV12), Xiawan (CV10), and Shenque (CV8).
Methods:BX-A002 Baixiao moxibustion device was applied and pasted on the points with medical adhesive tapes for moxibustion. Then the moxibustion tube cover was pulled out, and the moxibustion cone was put into the moxibustion cover and ignited, and then the moxibustion tube cover was buckled on the moxibustion tube. The size of the air inlet was adjusted by rotating the moxibustion tube, so as to make the moxibustion temperature appropriate (generally about 42 ℃)[10]. The treatment was performed 30 min per time, once a day.
All three groups took 10 d as a treatment course and 2 courses in total, with a 2-day interval between 2 treatment courses. The curative efficacy was observed after 2 treatment courses.
3 Observation of Curative Efficacy
3.1 Observation items
The following observation items were measured before and after treatment.
3.1.1 Primary observation items
Gastrointestinal motility indicators: Lactulose hydrogen breath test was used to detect oral-colon transit time (OCTT). And enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to measure the serum glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) level. The specific operation was completed according to the kit.
3.1.2 Secondary observation items
TCM symptom score: According to theExperts Consensus on Traditional Chinese Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment of Functional Dyspepsia (2017)[9]and theGuiding Principles for Clinical Study of New Chinese Medicines[11], the TCM symptom score was evaluated.Primary symptoms were scored 0, 2, 4, and 6 points as the degree of none, mild, moderate, and severe.Secondary symptoms were scored 0, 1, 2, and 3 points as the degree of none, mild, moderate, and severe.Tongue and pulse manifestations were not scored. The total score of primary and secondary symptoms was calculated and taken as the TCM symptom score. The higher the score, the more severe the clinical symptoms of the patients.
Quality of life score: Functional digestive disorder quality of life questionnaire (FDDQL)[12]was used to evaluate the quality of life of patients, including daily activities, anxiety, diet, sleep, discomfort, disease treatment, disease control, and stress. The higher the FDDQL score, the better the quality of life.
3.2 Criteria of clinical curative efficacy
According to theExperts Consensus on Traditional Chinese Medicine Diagnosis and Treatment of Functional Dyspepsia (2017)[9]and theGuiding Principles for Clinical Study of New Chinese Medicines[11],the criteria of curative efficacy in this study were developed. The clinical efficacy was evaluated after the end of the treatment course.
Clinically cured: Symptoms and signs disappeared or basically disappeared, and the TCM symptom score decreased by ≥95.0%.
Markedly effective: Symptoms and signs were significantly improved, and TCM symptom score decreased by ≥70.0% but <95.0%.
Effective: Symptoms and signs were improved, and TCM symptom score decreased by ≥30.0% but <70.0%.
Invalid: No significant improvement was found in symptoms or signs, or even got worsened, with the TCM symptom score reduction less than <30.0%.
3.3 Treatment results
3.3.1 Comparison of the clinical efficacy
The total effective rate was 96.7% in the acupuncturemoxibustion group, 86.7% in the EA group, and 73.3% in the mosapride group. The differences among the three groups were statistically significant (χ2=18.307,P<0.01). The total effective rate of the acupuncturemoxibustion group and the EA group was higher than that of the mosapride group, and the total effective rate of the acupuncture-moxibustion group was higher than that of the EA group (P<0.05). See Table 2.
3.3.2 Comparison of the TCM symptom and FDDQL scores Before treatment, there were no statistical differences in the TCM symptom score or FDDQL score among the three groups (P>0.05). After treatment, the TCM symptom score in all three groups decreased, the OCTT of the patients in all three groups decreased, and the FDDQL score increased; the intra-group differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). After treatment,the change after treatment in the TCM symptom score in the acupuncture-moxibustion group and the EA group was more significant than that in the mosapride group, and the change in the acupuncture-moxibustion group was more significant than that in the EA group.The change after treatment in the FDDQL score in the acupuncture-moxibustion group and the EA group was greater than that in the mosapride group, and the change in the acupuncture-moxibustion group was larger than that in the EA group. The inter-group differences were all statistically significant (P<0.05). See Table 3.

Table 2 Comparison of the clinical efficacy among the three groups Unit: case
Table 3 Comparison of TCM symptom and FDDQL scores among the three groups ( ±s) Unit: point

Table 3 Comparison of TCM symptom and FDDQL scores among the three groups ( ±s) Unit: point
Note: TCM=Traditional Chinese medicine; FDDQL=Functional digestive disorder quality of life questionnaire; BT=Before treatment;AT=After treatment; D-value=Difference value between before and after treatment; compared with the same group before treatment,1) P<0.05; compared with the mosapride group, 2) P<0.05; compared with the electroacupuncture group, 3) P<0.05.
Group n TCM symptom score FDDQL score BT AT D-value BT AT D-value Acupuncture-moxibustion 30 14.6±3.2 3.1±1.61) -11.5±2.92)3) 47.5±13.7 78.9±17.11) 31.4±12.22)3)Electroacupuncture 30 14.3±2.9 5.4±1.91) -8.9±2.52) 46.1±12.4 69.6±15.81) 23.5±11.92)Mosapride 30 13.9±2.6 7.2±2.31) -6.7±2.2 46.3±12.8 60.5±15.21) 14.2±11.3
3.3.3 Comparison of OCTT and serum GLP-1 level
Before treatment, there were no statistical differences in the OCTT or the serum GLP-1 level among the three groups (P>0.05). After treatment, the OCTT in the three groups decreased, and the serum GLP-1 level increased, and the intra-group differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). After treatment, the change after treatment in the OCTT in the acupuncturemoxibustion group and the EA group was more significant than that in the mosapride group, and the change in the acupuncture-moxibustion group was more significant than that in the EA group. The change in the serum GLP-1 level in the acupuncturemoxibustion group and the EA group was greater than that in the mosapride group, and the change in the acupuncture-moxibustion group was larger than that in the EA group (P<0.05). See Table 4.
Table 4 Comparison of OCTT and serum GLP-1 level among the three groups before and after treatment ( ±s)
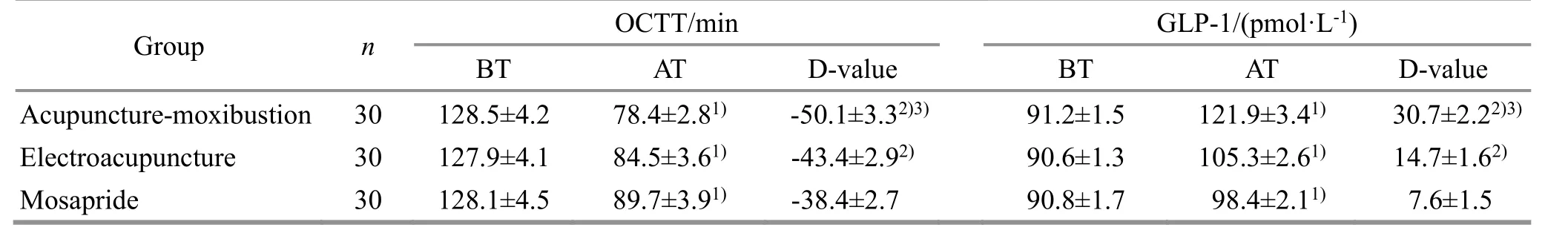
Table 4 Comparison of OCTT and serum GLP-1 level among the three groups before and after treatment ( ±s)
Note: OCTT=Oral-colon transit time; GLP-1=Glucagon-like peptide-1; BT=Before treatment; AT=After treatment; D-value=Difference value between before and after treatment; compared with the same group before treatment, 1) P<0.05; compared with the mosapride group, 2)P<0.05; compared with the electroacupuncture group, 3) P<0.05.
Group n OCTT/min GLP-1/(pmol·L-1)BT AT D-value BT AT D-value Acupuncture-moxibustion 30 128.5±4.2 78.4±2.81) -50.1±3.32)3) 91.2±1.5 121.9±3.41) 30.7±2.22)3)Electroacupuncture 30 127.9±4.1 84.5±3.61) -43.4±2.92) 90.6±1.3 105.3±2.61) 14.7±1.62)Mosapride 30 128.1±4.5 89.7±3.91) -38.4±2.7 90.8±1.7 98.4±2.11) 7.6±1.5
4 Discussion
According to the clinical symptoms, FD can be classified into the category of “gastric stuffiness” in TCM.Deficiency cold of the spleen and stomach is the key pathogenesis of gastric stuffiness, and Yang deficiency of the spleen and stomach is a common syndrome of FD,accounting for about 11%[13]. Therefore, it should be paid attention to the spleen and stomach Yang Qi in the treatment of FD[14]. Moxibustion has a warm effect and is an important therapy to treat gastric stuffiness caused by deficiency cold.
In this study, Baixiao moxibustion was used, as it can be directly fixed at the point area on the body surface,avoiding hand-held operation, and without body position limitation. The moxa cone is burned in a closed box, the heat is concentrated, and the temperature is easy to control. And there is no leaking flame and no ash fall, which can reduce or avoid burns[15-16]. In this study, Zhongwan (CV12), Xiawan (CV10), and Shenque(CV8) were selected for moxibustion. Zhongwan (CV12)is the Front-Mu Point of the stomach and the Influential Point of Fu-organs in the Eight Influential Points, with the effect of harmonizing the stomach and strengthening the spleen. Xiawan (CV10) is the crossing point of the Conception Vessel and the Spleen Meridian.It can invigorate the spleen and harmonize the stomach,regulate Qi and resolve bloating. Shenque (CV8) is an important tonifying point, and moxibustion at it can invigorate and reinforce Yang Qi and regulate the intestine. The combination of the three points can invigorate and reinforce Yang Qi, invigorate the spleen and harmonize the stomach, and regulate Qi and resolve bloating. In the prescription for EA, Neiguan(PC6) is one of the Confluent Points of the Eight Extraordinary Meridians. It can harmonize the stomach and down-regulate Qi, regulate Qi, and alleviate pain.Tianshu (ST25) is the Front-Mu Point of the large intestine, with the effect of regulating intestine and stomach, resolving masses, and eliminating stagnation.Guanyuan (CV4) can invigorate and reinforce Yuan-Primordial Qi, and tonify the spleen and stomach.Zusanli (ST36) can invigorate the spleen and harmonize the stomach, dry and transform the spleen dampness,serving as the key point for all kinds of gastrointestinal disorders. Sanyinjiao (SP6) can invigorate the spleen and stomach, and regulate Qi and blood. The combination of the above points achieves the effect of regulating gastrointestinal function. Moxibustion combined with EA can synergistically play the effect of warming the middle Jiao (energizer) and strengthening the spleen,harmonizing the stomach and resolving bloating.
The results of this study showed that moxibustion plus EA could reduce the TCM symptom score and increase the FDDQL score, and the total effective rate was 96.7%, indicating that this method can improve the clinical symptoms and the patient’s quality of life, fully reflecting the advantages of acupuncture combined with moxibustion in the treatment of FD[15].
Modern medicine believes that the occurrence of FD is multifactorial, among which gastrointestinal motility disorder is one of the recognized pathogenesis of FD,and has received more and more attention, including abnormal gastric electrical activity, impaired receptive relaxation, and delayed gastric emptying[3,17]. In this study, we further observed the effect of moxibustion combined with EA on OCTT and the serum GLP-1 level.Of them, OCTT is one of the important indicators for the clinical evaluation of gastrointestinal peristalsis function.Prolonged OCTT indicates that gastrointestinal peristalsis is slow, while conversely, gastrointestinal peristalsis is faster. Studies have pointed out that patients with FD have prolonged OCTT compared with healthy people[18-19], indicating that they have insufficient gastrointestinal motility. GLP-1 is a hormone secreted by intestinal L cells. It can inhibit glucagon secretion under physiological conditions, delay gastric emptying, and reduce food intake. The relevant report[20]pointed out that the serum GLP-1 level in FD patients was lower than that in healthy people,accompanied by OCTT prolongation, indicating that FD patients have decreased serum GLP-1 levels and prolonged OCTT at the same time. Therefore, it can be speculated that the hypo-function of gastrointestinal motility caused by the decrease of serum GLP-1 level may be one of the pathogenesis of FD. In this study,after 2 treatment courses of moxibustion plus EA, the OCTT of the patients decreased, and the serum GLP-1 level increased, and the improvements were superior to those of EA or mosapride alone, indicating that moxibustion plus EA can enhance the gastrointestinal peristalsis by increasing the serum GLP-1 level,therefore further improving the clinical symptoms of the patients with FD.
In summary, acupuncture-moxibustion is effective in treating FD due to Yang deficiency of the spleen and stomach. It may regulate gastrointestinal motility by increasing the serum GLP-1 level and improve clinical symptoms and patients’ quality of life. It is an effective treatment method and worthy of clinical reference.However, the sample size of this study was small and should be increased in the future to further explore the mechanism of action.
Conflict of Interest
There is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Project of Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (湖南省自然科学基金项目, No. 2022JJ40301); Fund Project of Hunan Province Education Office (湖南省教育厅科学研究项目, No. 21B0369); Scientific Fund Project of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine (湖南中医药大学科研基金项目, No. 2021XJJJ013).
Statement of Informed Consent
Ⅰnformed consent was obtained from all individual participants.
Received: 6 October 2021/Accepted: 29 December 2021
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Efficacy of electroacupuncture for patients with dry eye syndromes: a randomized controlled trial
- Clinical observation of Tiao Shen Tong Du Tuina in promoting neuropsychological development of premature infants
- Clinical observation of acupuncture combined with sitting-position knee-adjustment manipulations for patellofemoral arthritis
- Clinical study of acupuncture combined with medication for the elderly with Alzheimer disease
- Effects of herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion on the expression of thyroid autophagy-related factors LC3B and Beclin-1 in rats with autoimmune thyroiditis
- Effects of Tuina on serum creatine kinase and skeletal muscle mitochondria in delayed onset muscle soreness model rats
