Not just a sponge:novel functions of circRNAs in cholangiocarcinoma
2022-12-03JieHanLiHaoLinBaoZiYueHuangZiXinLiangNingLinChunJieNiYiXu
Jie-Han Li ,Hao-Lin Bao ,Zi-Yue Huang ,Zi-Xin Liang ,Ning Lin ,Chun-Jie Ni ,Yi Xu,2,,,5*
1Department of Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery,Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University,Harbin 150001,China.2Department of Pathology,School of Clinical Medicine,Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine,The University of Hong Kong,Hong Kong 999077,China.3Key Laboratory of Functional and Clinical Translational Medicine,Fujian Province University,Xiamen Medical College,Xiamen 361000,China.4Jiangsu Province Engineering Research Center of Tumor Targeted Nano Diagnostic and Therapeutic Materials,Yancheng Teachers University,Yancheng 224000,China.5Key Laboratory of Myocardial Ischemia,Ministry of Education,Harbin Medical University,Harbin 150001,China.
Abstract Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is one of the most common and highly malignant tumors,and its incidence and mortality rates are increasing yearly.Circular RNAs (circRNAs),a class of closed-loop non-coding RNAs formed by reverse splicing of exons or introns,play an essential regulatory role in CCA and have been a hot topic of medical research in recent years.In addition,about 80% of current research reports focus on the ability of circRNAs to sponge miRNAs in CCA.However,as research continues,circRNAs are more than just a sponge in CCA;they can also alter protein subcellular localization,encode proteins and affect other cells via extracellular vesicles(EVs).Interestingly,circRNAs not only serve as novel players in CCA pathogenesis but also as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for CCA.
Keywords: cholangiocarcinoma;circular RNA;miRNA sponge;extracellular vesicles
Introduction
Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) is a highly heterogeneous and aggressive malignant tumor of the hepatobiliary system,and its incidence is rising.As a malignant tumor mainly originating from bile duct epithelial cells,CCA is classified into three different tumor types according to its anatomical location: intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma(iCCA),perihilar cholangiocarcinoma (pCCA)and distal cholangiocarcinoma (dCCA) [1].Early surgical resection of the tumor is still the only option to cure CCA effectively.However,early diagnosis is difficult due to the complex etiology and insidious onset of CCA.Most CCA patients are diagnosed at a late stage and miss the best time for surgery.Even if there is an opportunity for radical resection,the postoperative recurrence rate is often high,and the prognosis is poor,with a 5-year survival rate of only 25%-35% [2].Therefore,studying the molecular pathogenesis of CCA and finding reliable biomarkers and effective therapeutic targets have become urgent practical clinical problems.
CircRNAs:an emerging functional non-coding RNA
CircRNAs (circRNAs) were first discovered by humans in 1976 in viruses [3].For many years afterward,circRNAs did not attract much attention until they were shown to exist in large numbers in living organisms.In recent years,circRNAs have become an emerging functional non-coding RNA as their functions are gradually elucidated.CircRNAs are a class of circular non-coding RNAs without 5' and 3'end-tail structures and are hundreds to thousands of nucleotides in length [4].Compared with linear RNA,the most significant difference of circRNA is that the 3' end of its molecule is linked to the 5' end to form a closed-loop structure.This unique natural closed-loop structure also gives circRNA high stability,specificity,and conservation properties [5].There is growing evidence that circRNAs possess biological functions such as competitively binding miRNAs,regulating gene expression,interacting with RNA-binding proteins,and encoding proteins or functional peptides that play an essential role in cancer progression.
As a sponge
The competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) mechanism was first proposed by Salmena et al.[6],revealed that circRNAs can competitively bind miRNAs and regulate the expression of miRNA target genes.CircHMGCS1-016 was reported to bind directly to miR-1236-3p and negatively regulate miR-1236-3p expression in iCCA cells.Furthermore,the downregulation of miR-1236-3p promoted increased expression of CD73 and GAL-8,thereby reshaping the tumor immune microenvironment and promoting iCCA invasion [7].Interestingly,considering the critical role of CD73 and GAL-8 in the tumor immune microenvironment (TME),cirHMGCS1-016 could be a regulator of the TME through its effect on CD73 and GAL-8 protein expression.Xu et al.[8] confirmed that circ-LAMP1 sponged miR-556-5p and miR-567 and downregulated their expression in CCA cells.circ-LAMP1 overexpression significantly accelerated the growth and metastasis of CCA cells,but transfection of miR-556-5p and miR-567 mimics into CCA cells resulted in malignant behaviors that were both inhibited.In another study,circ-CCAC1 was confirmed to up-regulate YY1 expression by competitively binding miR-514a-5p and further activating GAMLG expression to promote tumorigenesis and metastasis of CCA [9].Thus,it can be seen that the sponging effect on miRNA is currently the most crucial function of circRNA.Through this mechanism,we can better determine the metastasis of CCA and use the circRNA-miRNA-mRNA axis as a new therapeutic target to guide clinical medication.In addition,we summarized circRNAs as regulatory pathways of ceRNAs in CCA in recent years,as shown in Table 1.
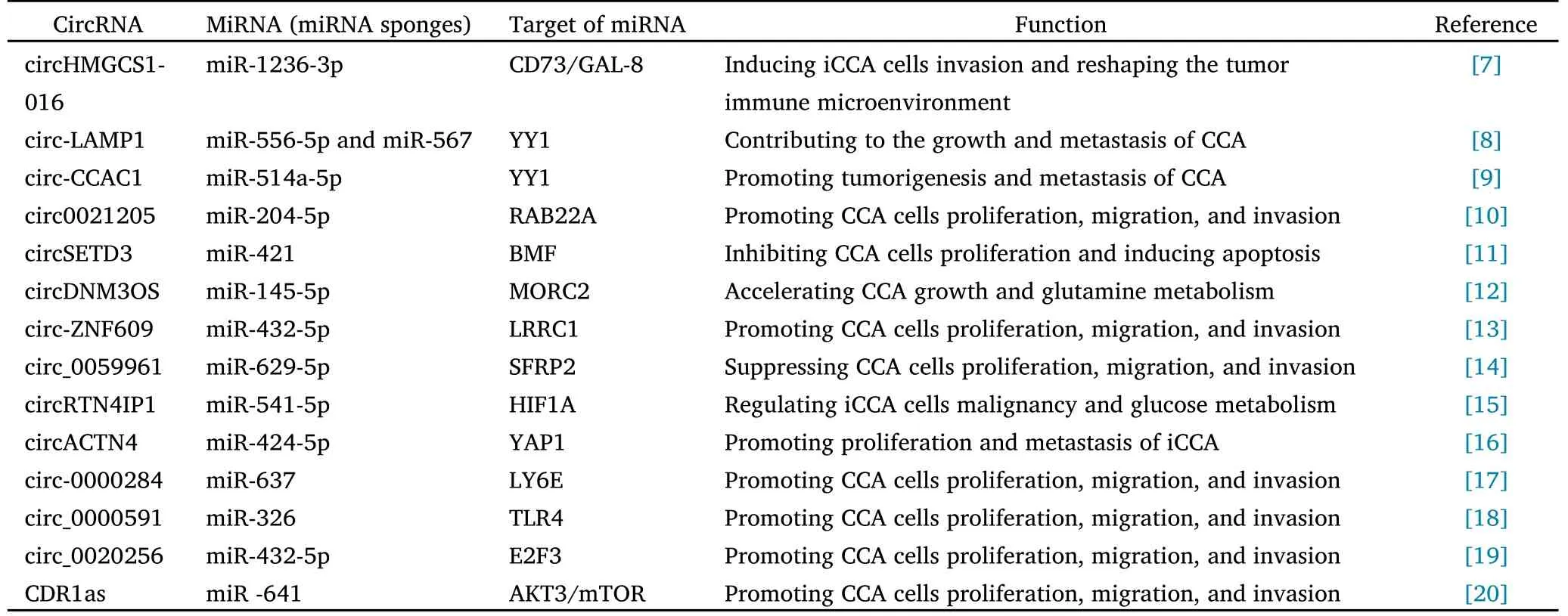
Table 1 CeRNA regulatory network
Not just a sponge in CCA
With the rapid development of biotechnology,such as high molecular throughput sequencing in recent years,the mystery of circRNAs in CCA has been unveiled layer by layer.However,about 80% of published reports have focused on circRNAs regulating the expression of oncogenes and oncogenes by regulating mRNA translation and degradation through sponging miRNAs.As researchers continue to explore the biological functions of circRNAs,we would like to point out that circRNAs are more than simply sponges of miRNAs in CCA.
Changing the subcellular location of proteins
Increasing evidence suggests that circRNAs can serve as dynamic scaffolds for assembling other components and binding or sequestering proteins,among others,to specific subcellular locations[21].It has been reported that circACTN4 is upregulated in iCCA,and its overexpression promotes the proliferation and invasion of iCCA.Mechanistically,circACTN4 can recruit the promoter region of the transcription factor Y-box binding protein 1 (YBX1) to Frizzled-7(FZD7) to initiate transcription of FZD7,thereby activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [16].Therefore,this study demonstrates that circACTN4 can act as a scaffold to localize the transcription factor YBX1 into the nucleus,thereby promoting the transcription of FZD7.This also means circACTN4 can regulate CCA progression in a complex transcriptional regulatory system.
RNA binding proteins (RBPs) bind to RNA during its metabolism and are involved in several processes regulated by RNA.Studies have shown that circRNAs can bind directly to RBPs to form RNA-protein complexes,which can regulate RBPs or affect their functions [22].Xu et al.[9] confirmed that circ-CCAC1 in CCA enters endothelial cells via exosomes by strongly binding to EZH2,thus sequestering EZH2 in the cytoplasm.Interestingly,EZH2 can enter the nucleus to bind to the SH3GL2 promoter and induce H3K27 trimethylation,thereby inhibiting SH3GL2 expression.Notably,because circ-CCAC1 restricts the nuclear localization of EZH2,SH3GL2 expression is increased in the absence of EZH2-mediated promoter H3K27 trimethylation.Eventually,the increased expression of SH3GL2 inhibited the expression of the intercellular linker proteins ZO-1 and Occludin,thereby increasing cell permeability.From this,we can conclude that the binding of circRNA to the protein will affect the localization of the protein,causing it to stay in the cytoplasm and thus inhibiting its activity as a transcription factor.
Coding proteins
CircRNA was originally defined as a unique class of endogenous non-coding RNAs.However,as circRNAs' functions continue to tap,increasing evidence suggests that circulating RNAs may not be a true class of non-coding RNAs and are translatable under certain special conditions.For example,Legnini et al.[23] found that polyribosomes on the circZNF609 molecule translate proteins in mouse myogenic cells in a non-traditional manner driven by internal ribosome entry sites (IRES).Both internal ribosome entry site (IRES) and N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modifications reported so far can drive the translation of circRNA.In eukaryotic cells,IRES-containing circRNAs can bind directly to ribosomes and translate into short peptides in vivo or in vitro,independent of the 5'cap structure[24].Li et al.[25] found that cGGNBP2 was detected to have a highly conserved open reading frame (ORF) and IRES with the potential to encode 184aa-protein.In addition,this study demonstrated that cGGNBP2 could translate a protein consisting of 184 amino acids(cGGNBP2-184aa) driven by IRES.cGGNBP2-184aa interacted with STAT3,and cGGNBP2-184aa directly interacted with STAT3 to activate the JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway,which ultimately promoted iCCA cell proliferation and metastasis.CircRNAs can translate proteins in a 5′ endcap-independent manner,a finding that blurs the boundary between coding and non-coding RNAs and provides us with a new perspective to investigate the mechanism of circRNAs in CCA.However,unfortunately,there are few relevant reports on the progress of circRNAs encoding proteins regulating CCA.
EV-circRNAs:a new player in CCA progression
Extracellular vesicles(EVs)are membranous vesicles secreted by cells,ranging from 40 nm to 1,000 nm in diameter,containing mainly exosomes,microvesicles,and apoptotic vesicles [26].Initially,the release of EVs was once thought to be only a way for cells to transport excretory substances outward,and for a long time,EVs did not attract much attention.In recent years,EVs have been found to carry critical signaling molecules,such as non-coding RNA,DNA fragments,and proteins.In addition,they are also important mediators of intercellular communication and participate in normal physiological processes and pathological progression [27].The study of the mechanism of action of EV-circRNAs in CCA is still in its infancy,but several reports have described the role of EV-circRNAs as novel players in the progression of CCA.Circ_0020256 has been reported to be highly expressed in tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs)-derived exosomes.Importantly,circ_0020256 can be delivered to CCA tumor cells via exosomes from TAMs to enhance the biological activity of CCA cells by regulating the expression of the transcription factor E2F3 through sponging miR-432-5p [19].In addition,the oncogenic factor circ-0000284 could be transferred directly from CCA cells to surrounding normal cells via exosomes,evoking the malignant phenotype of CCA cells through cellular communication,thus exhibiting a pro-carcinogenic effect on surrounding normal cells [17].Xu et al.[9] demonstrated that circ-CCAC1 was highly expressed in CCA cells in exosomes.Interestingly,circ-CCAC1 can promote the metastasis of CAA cells by translocating to endothelial cells via exosomes,disrupting the vascular endothelial barrier,inducing angiogenesis,and increasing the permeability of the endothelial monolayer.The mechanism of EV-circRNAs involved in CCA progression is shown in Figure 1.Therefore,we can conclude that Evs,as a bridge between cells communicating with each other,can participate in cell multiple signaling between cells,thus regulating the progression of CCA.

Figure 1 Mechanisms by which circRNAs regulate CCA progression via Evs.(A) Circ-CCAC1 was delivered to endothelial monolayers by CCA cell-derived Evs,which increased the expression of SH3GL2 to inhibit the expression of the intercellular linker proteins ZO-1 and Occludin by binding to EZH2,ultimately increasing cell permeability;(B)Circ_0020256 was delivered to CCA cells by Evs secreted by TAMs,which upregulated the expression of the transcription factor E2F3 through sponging miR-432-5p,thus enhancing the biological activity of CCA cells;(C)Circ-0000284 was delivered to normal cells by Evs secreted by CCA cells,which upregulated the expression of transLY6E through sponging miR-637,thereby promoting the progression of CCA.SH3GL2,Src homology 3 (SH3) domain GRB2-like 2;ZO-1,Zona occludens 1;TAMs,tumor-associated macrophages;E2F3,recombinant E2F transcription factor 3;LY6E,lymphocyte antigen 6E.
Clinical values
CircRNAs are abundant,stable,and differentially expressed in saliva,urine,blood,bile,and exosomes.Notably,circRNAs' unique structure and stable nature make them ideal candidates as biomarkers for CCA.Jiang et al.[28] studied the expression of circRNA Cdr1as in cancer and paracancerous tissues of 54 patients with cholangiocarcinoma and found that circRNA Cdr1as expression was significantly upregulated in tumor tissues and was closely associated with lymph node infiltration,advanced TNM,and postoperative recurrence.Multifactorial regression showed that Cdr1as could be used as a novel independent prognostic biomarker for CCA patients (sensitivity=83.3%,specificity=58.3%).Due to the broad applicability of biliary drainage in patients with obstructive jaundice,we can quickly obtain bile from CCA patients in the clinical setting,which facilitates specimen collection and storage.In addition,EV-circRNAs derived from CCA can be easily detected in bile and serum,which has a promising development in diagnosing and treating CCA.For example,Xu et al.[9]found that circ-CCAC1 expression was upregulated in bile and serum-derived Evs from CCA patients,and their AUCs were 0.857 and 0.759,respectively.The diagnostic value of serum Evs was almost equal to that of serum CA19-9 (AUC=0.757).At the same time,bile Evs had superior diagnostic performance to CA19-9.In addition,this study demonstrated a correlation between circ-CCAC1 expression and poor prognosis/high postoperative recurrence rate of iCCA.It was an independent prognostic marker for iCCA.
For the treatment of CCA,circRNA has also shown some clinical value.It was found that upregulation of circHMGCS1-016 expression impeded the response of iCCA to anti-PD1 therapy,and targeting circHMGCS1-016 may be a practical approach to restore the sensitivity of iCCA to anti-PD1 therapy [7].The promotional effect of circ-SMARCA5 on chemotherapy sensitivity makes it a promising biomarker for monitoring iCCA progression and prognosis [29].Furthermore,exogenous overexpression of cNFIB enhances the antitumor effect of trametinib (MEK inhibitor),which also implies its potential to combat iCCA metastasis[30].
Conclusion and future perspectives
CCA,as the second most malignant tumor in the hepatobiliary system,has been a complex problem for clinicians due to its difficult early diagnosis,high malignancy,and poor prognosis.circRNAs are RNAs that form a covalently closed continuous loop with limited ability to translate proteins.As researchers continue to focus on circRNAs,most studies have confirmed that circRNAs can act as post-transcriptional regulators,regulating the expression of their target genes through sponging miRNAs and thus regulating the progression of CCA.However,circRNAs are more than simply sponges of miRNAs in CCA.In the past few years,circRNAs have been given additional functions,including altering their subcellular localization by recruiting or sequestering proteins,encoding proteins,and affecting other cells through the transport of Evs.
Compared with linear RNA molecules,circRNAs are insensitive to nucleases.This stable natural structure gives circRNAs a clear advantage in developing and applying circRNAs as biomarkers and effective therapeutic targets for CCA.The current mechanism of circRNAs in CCA is mainly a sponge for miRNAs,so we can use the circRNA-miRNA-mRNA axis as a new therapeutic target for guiding clinical drug use.Secondly,the clinical value of circRNAs and their encoded proteins as novel tumor markers or potential therapeutic targets for CCA is enormous.In the future,we can determine whether we can achieve therapeutic disease by artificially designing circRNAs with coding ability to encode specific proteins.Therefore,accelerating the exploration of the biological functions of circRNAs and their encoded proteins will also be a future research direction.In addition,nanoparticles are currently used as translational vectors for gene therapy.Evs,as stable transport carriers to transport therapeutic drugs into recipient tissues or cells for therapeutic purposes,are also a hot spot for future research.
Despite the great promise of circRNAs in diagnosing and treating CCA,some questions deserve deeper consideration.For example,the mechanisms regulating the spatial localization of circRNAs have not been investigated.Other mechanisms by which circRNAs translate proteins or functional peptides and their regulatory factors.Whether circRNAs that exert cancer-promoting or tumor-inhibiting effects through the ceRNA mechanism also act by encoding proteins or functional peptides.Although significant progress has been made in the study of the functions of circRNAs in CCA,there are still many unknown functions of circRNAs to be further investigated.It is believed that as we explore further research on circRNAs,these unknown functions will be further uncovered,thus providing new ideas and strategies for diagnosing and treating CCA.
杂志排行
Clinical Research Communications的其它文章
- POEMS syndrome characterized by peripheral neuropathy as the first symptom: a rare case report
- Effectiveness of hip upslip correction method on ambulation and back pain in patients with lumbar discopathy:a case report
- Effect of Xingnao-Jianshen granules in treating AIS patients: study protocol for a non-randomized controlled intervention trial
- Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of Shenkang injection combined with Western medicine in the treatment of chronic glomerulonephritis
- A study of ultrasonography for the treatment of Qingre Liangxue decoction on blood-heat psoriasis
