In-vitro and in-vivo pharmacological screening of Iris albicans
2022-11-17DawoodKamalRoohullahFazleRabbiAttiqaNazMuhammadBilal
Dawood Kamal,Roohullah,Fazle Rabbi,Attiqa Naz,Muhammad Bilal
Dawood Kamal,Roohullah,Fazle Rabbi,Attiqa Naz,Muhammad Bilal,Department of Pharmacy,Abasyn University Peshawar,Peshawar,25000,Khyber Pakhtunkhwa,Pakistan
Abstract OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the anti-oxidant,enzyme inhibition,anti-pyretic,anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic activities of Iris albicans.METHODS: Anti-oxidant assay was evaluated using DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) radical scavenging and ABTS (2,2′-azino-bis-3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) inhibitory protocol while enzyme inhibitory assay was evaluated by lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitory protocol respectively.Antipyretic,anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic potential was evaluated using brewer’s yeast induced pyrexia,carrageenan induced paw edema and streptozocin induced diabetes protocols respectively.Serum biochemical parameters were monitored for the period of study.RESULTS: The anti-oxidant activity of chloroform fraction of Iris albicans showed the highest scavenging potential against DPPH and ABTS while the maximum inhibitory action recorded against lipo-oxygenase and cyclooxygenase-2 enzymes was shown by n-hexane and chloroform fractions respectively.The anti-pyretic potential of the crude methanolic extract showed dose dependent activity in reducing pyrexia,thereby when the dose was increased the anti-pyretic effect was also enhanced.The anti-inflammatory action of the crude methanolic extract administered at the dose of 300 mg/kg was significant at 1 h after its administration,which was found maintained up to 5 h.Similarly the anti-diabetic effect of the crude methanolic extract administered at the dose of 200 and 300 mg/kg was noted highly significant at day 6 and was found well maintained throughout the study time period up to 10 days.Significant (P < 0.001)improvement appeared in hemoglobin,protein,cholesterol,triglycerides,urea,creatinine,HDL and LDL of extract treated diabetic mice.CONCLUSION: From this data it could be concluded that Iris albicans have significant anti-oxidant,enzyme inhibition,ant-pyretic,anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic potential.
Keywords: antioxidants;anti-inflammatory agent;antipyretics;hypoglycemic agents;Iris Albicans
1.INTRODUCTION
The emphasis on the use of medicinal plants had been placed on the treatment rather than prevention of diseases.However,there exists in the literature considerable report in recent times on research work on the use of medicinal plants and their constituents in disease prevention.1Traditional Medicine as the sum total of all knowledge and practices,whether explainable or not,used in diagnosis,prevention and treatment of physical,mental,or social imbalance and relying exclusively on practical experience and observation handed down from generation to generation,whether verbally or in writing.Over 90% of traditional medicine recipes/ remedies contain medicinal plants.Medicinal plants have been implicated with preventive measures in disease control strategies.However,it must be noted that only a very thin divide exists between treatment and prevention in some cases.2
Currently,a focus on integrated medicine provides plenty of plants and plant constituent choices for treatment of sickness.3,4Not only in modern medicine,but also the use of plants,aromatherapy,crude drugs,and several other therapies have been adopted in homes and hospitals.Those natural drugs and therapy are useful for preventive medicines too.Medicinal plants are a good source to develop new medicine and to treat ailments.The possibility of medicinal plants is a hope continually for human live.5
Iris albicans is indigenous to Arabia and Yemen.It is frequently planted in many parts of the Mediterranean area.It grows in or near cultivated areas and cemeteries.A literature survey showed that biological and phytochemical investigations on Iris albicans were carried out showing its antimicrobial,anti-mutagenic and cytotoxic activities.6,7The anti-cholinesterase activities of the fresh rhizomes and dried flowering aerial parts extracts of Iris albicans were also studied.8Phyto-chemical investigation of Iris albicans leaves afforded known compounds e.g.flavonoids,isoflavonoids,xanthones etc.9The aim of the current study was to evaluate the enzyme inhibition,anti-oxidant,anti-inflammatory,anti-pyretic and anti-diabetic activities of Iris albicans throughin-vitroandin-vivoprotocols.
2.MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1.Plant material collection
The Iris albicans whole plant was collected from the areas of Bajaur and Mohmand in the province of Khyber Pukhtunkhwa Pakistan.The collected sample specimen was submitted for identification in botany department of Peshawar University.The research associate Mr.Wail Muhammad (botanist) identified the specimen as Iris albicans.The herbarium of Botany department assigned a voucher No.20151 (PUP) to the identified Iris albicans.
2.2.Extraction and fractionation
The dust and mud from the parts were removed and then turned into small pieces weighing 6.43 kg.The collected parts were dried under shade at room temperature for 30 d,reducing weigh to 4.57 kg.The dried material was then crushed into powder with the help of a grinder.The net weight obtained after crushing was 3.35 kg and thereafter this powder was brought for extraction and fractionation purpose.Methanol (20 L) was used to soak powder (3.35 kg)for 3 weeks at room temperature.The contents were then filtered after soaking (3 weeks).The obtained filtrate was concentrated using Rotary evaporator at 40 ℃ and at the end dried crude extract (480 g) was obtained.10The obtained crude extract (480 g) was mixed with distilled water (2.5 L) and soaked (24 h).The process of preparation of fractions of the dried crude extract (methanolic) was then carried out in the order of increasing polarity i.e.n-hexane,chloroform,ethyl acetate,water (Less polar to high polar).It was then extracted successively with n-hexane (3 × 2.5 L),dichloromethane (DCM) (3 × 2.5 L),ethyl acetate (3× 2.5 L),and n-butanol (3 × 2.5 L) to obtain the respect.11
2.3.Experimental animals
Swiss albino mice were used for the carrying out ofin vivopharmacological activities.These mice were kept according to standard protocols.12
2.4.In-vitro pharmacological screening
Crude extract and its fractions of Iris albicans were evaluated for its various pharmacological activities as per following detailed procedures.
2.5.Antioxidant activity
DPPH radical scavenging assay: to determine the antioxidant potential of Iris albicans,various plant samples were evaluated against stable radical DPPH (1,1 diphenyle-2-picryhydazyl).Various concentrations of the extract were prepared and then added 2% DPPH (2 mL).The ascorbic Acid (vitamin C) was used as positive control.The maximum absorbance will be determined at 517 nm at specified interval as per protocol.
ABTS inhibitory potential: the inhibitory potential(antioxidant) of different fractions of Iris albicans were subjected to evaluation against 2,2-azinobis [3-ethylbenzthiazoline]-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS).The test were done on the base of the antioxidant′ s capability to inhibit ABTS radical cations,resulting decrease in absorbance at 734 nm,using ascorbic acid as positive control.14
2.6.Enzyme inhibition assay
Lipoxygenase inhibitory activity: test samples of various concentrations of plant extract were prepared i.e.125,250,500 and 1000 μg/mL.Enzyme solution having the concentration of 10000 U/mL was prepared.The linoleic acid and buffer phosphate (pH 6.3) of 80 and 50 mM(substrate solution) was prepared.Reaction mixture(2 mL) was formulated by adding equivalent quantities of enzyme,buffer and substrate.Various concentrations of fractions samples along with control (positive) of 0.2 mL volume were added to the reaction mixture.The rate of reaction of samples and positive control were evaluated without inhibitor.Using UV-visible spectrophotometer,the percent enzyme potential was ascertained at 234 nm.Absorbance of test samples were checked for comparison with control and percent inhibition were determined by using Zileuton as positive control.15
Cyclooxygenase-2 assay: solution with concentration of 300 U/mL of cyclo-oxygenase -2 enzymes was prepared.For the activation 10 μL of enzyme,solutions were kept on ice for 5 min with cofactor solution (50 μL)containing 0.24 mM TMPD (N,N,N,N-tetra methyl-pphenylene diamine di-hydrochloride),0.9 mM glutathione and 1 mM hematin in Tris HCl buffer (0.1 M)with 8.0 pH,60 μL of the enzyme solution and test samples of 20 μL,having different concentrations were reserved for five min at room temperature.The response was shown by adding 30 mM arachidonic acid (20 μL).After incubation (5 min),UV-visible spectrophotometer was used for calculating the absorbance at 570 nm.COX-2 percent inhibition was determined from absorbance value per unit time.Celecoxib was used as positive control during this study.16In vivopharmacological activities: evaluation ofin vivopharmacological activities of methanolic extract of Iris albicans and its subsequent fractions were carried out as per following procedures in detail.
2.7.Antipyretic activity
Pyrexia Induction using Brewer’s Yeast: Iris albicans hypothermal activity was scrutinized by using mice of either sex (22-30 g),distributed five (05) in each group.Mice were allowed free Access to water and kept fasted overnight.Normal saline (10 mL/kg,body weight) were administered as negative control to group I.Paracetamol(150 mg/kg body weight) was given as standard drug to group Ⅱ.Groups Ⅲ to V received 100,200 and 300 crude extract prior to induction of pyrexia.Using digital thermometer,normal temperature of all the mice was noted and the pyrexia was induced by administering 20%suspension (aqueous) of brewer’s yeast (10 mL/kg body weight) subcutaneously in all the mice.All the animals were free to water (drinking) and after lapse of 24 h,the rectal temperature was recorded in mouse (each) in the group and the above doses were injected in to the corresponding groups.17The rise in temperature by more than 0.5℃ confirmed induction of pyrexia in all the animals.Then the drug was administered in the above stated doses in the animal group and change in rectal temperature after administration of the drug was again noted periodically after 30,60 and 90 min.Percent reduction in pyrexia was calculated with the help of below formula;
% Reduction=100-B-Cn/ B -A × 100
Where,A=normal rectal temperature,B=rectal temperature after 24 h and Cn=rectal temperature after 30,60 and 90 min.
2.8.Anti-inflammatory activity
Carrageenan induced Paw Edema: mice of either sex weighing between 22 to 30 g were used for carrying out the anti-inflammatory activity.For this purpose five groups were made consisting of five (05) animals in each group.18Normal saline 10 mLviaintra-peritoneal route per kg body weight was injected to group I.Similarly Aspirin (150 mg/ kg body weight,i.p) to group Ⅱ,while sample extract was administered in doses (100,200 and 300 mg/kg) to groups Ⅲ-V respectively.In hind paw(right) of albino mice (each),1% carrageenan (0.05 mL)was subcutaneously injected after 30 min of the above administration.Immediately after injecting carrageenan and then after 30,60 and 90 min,the edema was calculated by Plethysmometer (LE 7500 plan lab S.L).Edema (average) treated drug was compared with control and potential % inhibition of edema was calculated by using below mentioned formula.
% inhibtion=X-Y/Y × 100
Where X=paw edema of control and Y=paw edema of tested group
2.9.Anti-diabetic activity
Streptozocin induced diabetes: mice were divided in to 06 groups (n=6 in each group).Group I served as control (normal),group Ⅱ as disease control,group Ⅲ as standard control (metformin 25 mg/kg,i.p),while groupⅣ-Ⅵ were administered with 100,200 and 300 mg per kg of crude extract.19Mice were fasted for 16 h and prior to the streptozocin administration (50 mg/kg,i.p.),baseline blood glucose levels were noted.After lapse of 72 h of STZ administration,blood glucose levels were again measured and the animals exhibiting > 270 mg/dL blood glucose levels were selected in the study.On the same day,treatment to the respective groups was started with dosing of the saline,standard drug (metformin 25 mg/kg,i.p.),crude extract in doses of 100,200 and 300 mg/kg (i.p) for consecutive 10 d with measuring the impact of treatment on blood glucose levels on daily basis.
2.10.Biochemical analysis
Sugar level was measured by collecting the blood from mice tail using Accu-Chek Active test strips in Accu-Chek Active test meter.Hemoglobin,Total protein,Total cholesterol,triglycerides,serum urea,creatinine,HDL and LDL were assayed using the reported protocol.20,21
2.11.Statistical analysis
Anti-pyretic and anti-inflammatory activities were analyzed by Graph Pad Prism (Version 5.0.San Diego,CA,USA) using one way analysis of variance (ANOVA)followed by Dennett’s post hoc analysis.Anti-diabetic activity was analyzed by using two way ANOVA,followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison assessment.Each parameter mean ± standard error of mean were calculated while significance level was kept atP <0.05.
3.RESULTS
3.1.In vitro pharmacological screening
DPPH scavenging assay: results of plant samples tested against the free radical DPPH are shown in the Table 1.The highest scavenging potential is shown by the chloroform fraction at various doses followed by ethyl acetate fraction,methanolic extract,aqueous fraction and n-hexane fraction with IC50 values of 139,150,750,1050 and 1370 μg/mL respectively,while the scavenging potential of the standard ascorbic acid was highest with IC50 value of 13 μg/mL respectively.
ABTS Scavenging assay: results of ABTS free radical scavenging effect are presented with their IC50 values in the Table 1.Chloroform exhibited highest ABTS free radical scavenging activity followed by ethyl acetate fraction,methanolic extract,n-hexane fraction and aqueous fraction with IC50 values of 330,410,525,1060 and 1240 μg/mL respectively.Ascorbic acid used as standard showed IC50 value of < 0.1 μg/mL.
3.2.Enzyme inhibition assay
Lipoxygenase inhibition assay: lipoxygenase inhibitorypotential of methanolic extract and its fractions are presented in Table 1.n-hexane fraction exhibited high inhibitory activity followed by with methanolic extract,chloroform fraction,ethyl acetate fraction and aqueous fraction with IC50 value of 675,830,960,1280 and 2176 μg/mL respectively.The inhibition by Zileuton used as standard exhibit IC50 value of 2 μg/mL.

Table 1 Antioxidant and enzyme inhibition assay of various fractions of Iris albicans
Cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibition assay: in cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitory assay,chloroform fraction exhibited highest potential showing IC50 of 240 μg/mL as shown in Table 2.Similarly the inhibitory effects of ethyl acetate,aqueous,n-hexane and methanolic fractions are present in Table 1.Celecoxib showed highly significant result as standard with IC50 value of 32 μg/mL.
3.3.In-vivo pharmacological screening
3.3.1.Antipyretic activity
Brewer′s yeast induced pyrexia: results of all the administered test doses of crude extract of Iris albicans is depicted in Figure 1 showing antipyretic potential of tested sample.The yeast administration induced rise in rectal temperature of mice,which was strongly subsided by the administered doses of 200 mg and 300 mg/kg at intervals of 30,60 and 90 min.The test dose at 100 mg showed significant change at 30 and 60 min after administration however it was highly significant at 90 min.Effective response in pyrexia reduction was observed by paracetamol during study period of 30,60 and 90 min respectively.
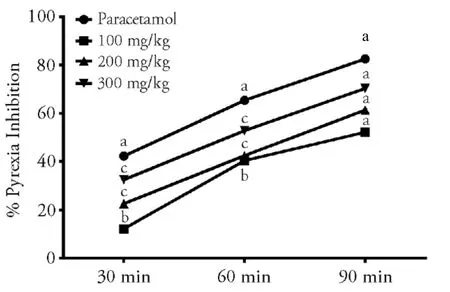
Figure 1 Anti-pyretic activity of Iris albicans crude extract using brewer’s yeast induced pyrexia model
3.3.2.Anti-inflammatory activity
Carrageenan induced Pawedema: The anti-inflammatory potential of crude extract of Iris albicans at the administered doses intra peritoneal of 100,200 and 300 mg/kg is mentioned in Table 2.The extract of iris albicans at the test dose of 100 mg/kg remained nonsignificant at 1,3 and 5 h respectively,however at the dose of 200 mg in the first hour it was significant at (P <0.05),while it was highly significant after 3rd and 5th hour at (P <0.0001) after the administration of carrageenan.The anti-inflammatory potential at 300 mg/kgof test dose was found highly significant throughout the experiment at (P <0.0001) with inhibitory effect of 34.24%,47.61% and 56.36% respectively which was greater than the anti-inflammatory effect of Aspirin 150 mg/kg (Figure 2).

Figure 2 Percent inhibition potential of edema induced by Carrageenan

Table 2 Effect of crude extracts of Iris albicans administered intra peritoneal at 100,200 and 300 mg/kg in paw edema induced by Carrageenan
3.3.3.Anti-diabetic activity
Streptozocin induced diabetes: results of anti-diabetic effect of Iris albicans crude extract are presented in Table 3 and Figure 3.It is evident from the results that Streptozocin significantly (more than 3-4 folds) raised the blood glucose level of mice.Mice were administered the doses as per prescribed protocol.Significant results were observed on day 6 and onwards on treatment with extract (in any dose) in a dose dependent manner comparable to standard drug.Potent anti-diabetic potential was observed in case of 300 mg/kg,followed by 200 mg/kg respectively.

Figure 3 Effect of crude extract of Iris albicans in streptozocin induced diabetes
3.3.4.Biochemical parameters
Biochemical results demonstrated that standard drug,extract treated groups showed results by significantly reducing (P< 0.001) levels of glycosylated hemoglobin,total proteins,total cholesterol,triglycerides,serum urea,creatinine,HDL and LDL respectively (Table 4).

Table 3 Potential Effect of Iris albicans100 mg,200 mg and 300 mg/kg intra peritoneal in streptozocin induced diabetes

Table 4 Effect of treatments on biochemical parameters of diabetes in STZ-induced mice
4.DISCUSSION
The plant crude methanolic extract as well as the fractions showed more pronounced effects.Plants with antioxidant activities are getting more popularity day by day because they possess those agents which detoxify thetoxic effects of the free radicals.22The antioxidant effect of the plant has been studied in the same project and promising results have been observed.This plant being a strong antioxidant may also contain phenolic compounds.Iris albicans may also be responsible for the antienzymatic activity.Plethora of reports is available which mention the enzyme inhibitory potential of plants which may be due to the presence of anti-oxidants constituents.Lipoxygenase inhibition was shown by n-hexane and methanol fractions of Iris albicans.As we know,lipoxygenase is a non-heme iron containing dioxygenase extensively dispersed in nature.Lipoxygenases enzymes convert linoleic,arachidonic and other polyunsaturated fatty acid into biologically active metabolites that are involved in immune and inflammatory responses.In human,lipoxygenase genes have been identified and due the diversity of lipoxygenase genes,the role of lipoxygenase is complex in the development and succession of cancer.Furthermore,lipoxygenase different profiles were observed between studies on experimentally induce animal tumor models and on human tumor.23
In order to analyze the possible mechanisms and the specificity of the herbal extract in inhibiting COX-2 enzyme,in vitroCOX-2 anti-inflammatory activity was studied by COX catalyzed prostaglandin biosynthesis assay.Study showed that chloroform fraction showed significant results.The effective percentage inhibition of COX-2 enzyme contributes scope for elucidation of active ingredients involved in anti-inflammatory response.This study establishes an empirical evidence for the folkloric claims reporting the anti-inflammatory activity of plant extract.Two major symptoms of the body against inflammation are pain and enhanced body temperature.Like NSAIDs,usually an anti-inflammatory agent also exerts action against analgesia and pyrexia.24
Pre-treatment with Iris albicans extract significantly alleviated the carrageenan elicited paw edema after 3 and 5 h at dose of 200 and 300 mg/kg (P <0.001).It shows that there might be various secondary metabolites,exhibiting slow onset of action and long duration of action.The development of edema after carrageenan injection (sub-plantar) in mice is attributed to kinins,histamine,serotonins and prostaglandins release.25
The crude extract of Iris albicans was screened for antipyretic activity as well.Crude extract showed reduction in body temperature significantly after 60 min at a dose of 200 and 300 mg/kg (P <0.001) respectively.This antipyretic effect persisted till 90 min.Pyrexia reduction occurs through action of extract on PGE2 in hypothalamus.Crude extract might possess secondary metabolites responsible for prostaglandin inhibition.26
Crude extract of Iris albicans contains outstanding antidiabetic potential as well.The Crude extract showed profound effect in lowering the blood glucose level which may be the action of flavonoids containing antioxidant constituents.27The tested crude extract revealed a promising hypoglycemic effect in the diabetic mice after treatment for 10 d when compared to the normal control and standards control groups.This provides a strong scientific approach to the plant to be used against diabetes.Further detailed designed study in this regards,involving phytochemistry and pharmacology may determine its concocted foundation.
Kidney damage is the main concern in severe diabetic patients as well as in severe STZ-induced diabetes.Glomeruli destruction causes significant increases in creatinine and blood which leads to chronic renal failure.Both creatinine and urea are kidney function markers,indicating that the extracts were not nephrotoxic.28Similarly hyperglycemia is associated with dyslipidemia while under normal circumstances insulin activates the enzyme lipoprotein lipase which hydrolyses triacylglycerols.29Dyslipidemia is characterized by increase in triacylglycerol and total cholesterol while decrease in HDL-cholesterol.This serum lipid profile(abnormal) progresses towards normal after therapy with crude extracts.Phytochemical constituents may be the main cause of significantly increase LDL receptor mRNA levels,which,in a result,increase LDL hepatic uptake and degradation,causing a decrease in level of serum LDL.30Hence it can be concluded that crude extract have significant effect owing to its ability to reduce level of blood glucose,total protein,total cholesterol,creatinine,urea and triglyceride and increase HDL level.
In conclusion,from the results of the present investigation it can be concluded that Iris albicans possess antioxidant,lipo-oxygenase inhibitory,antiinflammatory mediated by COX-2,antipyretic and antidiabetic activities.
杂志排行
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Flavonoids from traditional Chinese herbs for diabetes in rats: a network Meta-analysis
- Detailed approach toward the anti-hyperglycemic potential of Sterculia diversifolia G.Don against alloxan-induced in vivo hyperglycemia model
- Efficacy of Bushen Culuan decoction (补肾促卵方) on ovarian follicle and follicular granulosa cells in mice with premature ovarian insufficiency induced by tripterygium wilfordii polyglycoside
- Efficacy of Wumei Baijiang prescription (乌梅败酱方) on regulatory T cells/ helper T cells Immune balance in mice with ulcerative colitis
- Shenweifang-containing serum inhibits transforming growth factorβ1-induced myofibroblast differentiation in normal rat kidney interstitial fibroblast cells
- Therapeutic effects of salidroside vs pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate against severe acute pancreatitis in rats
