Enlightenment from Development Experience of World-Class Universities in Foreign Inland Regions
2022-11-12YangGui
Yang Gui
Sichuan University
Abstract: Only a few world-class universities are in inland regions. The development of inland universities is restricted by many factors, which is especially true in the construction of universities of the Double First Class initiative in China’s western inland regions.① In October 2015, the State Council of the People’s Republic of China issued the Overall Plan for Coordinately Advancing the Construction of World First-Class Universities and First-Class Disciplines (also the “Double-First Class” initiative), announcing the construction of world-class universities in China. According to the list jointly released by the Ministry of Education (MOE), the Ministry of Finance (MOF), and the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC)in 2017, 42 universities and colleges will be developed into world-class educational institutions, about one-third of which are located in western China. To learn more about how this situation evolved, we conducted research focused on world-class inland universities in foreign countries to sort out their experiences during their development. Through literature reviews and online surveys, we found that the development of such universities is restricted by the economic and social environment of the cities and regions in which they are located. Further, these universities are good at seizing historic development opportunities to actively advance internal reform and fully integrate into regional economic and social development. As a result,they have made great contributions to talent training and scientific research. They have also enhanced their strength and international influence in the process of coordinated development with their region.Therefore, we suggest universities in western China draw on such experience to grow into double first class universities. Specifically, they should closely follow major national and regional strategies and comprehensively integrate into regional economic and social construction to seek opportunities by taking full advantage of local development. They should also continuously deepen institutional and systematic restructuring to unleash their vitality and potential in education management and development and focus on major projects to expand influence in their regions.
Keywords: inland, world-class universities, development experience, universities in western China
Introduction
The majority of the world-class universities are located in coastal regions or capital cities that are densely populated with convenient transportation, favorable environments, and booming economies. Very few well-known universities are in non-coastal regions and noncapital cities across the world.①According to the 2022 QS World University Rankings, among the top 200 universities, only 30 are located in the non-coastal and non-capital regions (including universities in the Great Lakes region of the US).To bolster support for China’s goal of becoming an innovative country, it is of great importance to build a group of world-class universities in western China.In this process, we should draw on the development experience of world-class universities in foreign inland regions.
Currently, there is a growing body of literature concerning the development experience of world-class universities. Many papers (see Figure 1), with such keywords as “university” and“experience and enlightenment” in the disciplines of higher education, normally introduce the initiatives and experience of one or more foreign universities by examining certain aspects of their development, such as innovation and entrepreneurship education (Bai, 2012; Zheng et al., 2014), undergraduate education (Li, 2021; Chen et al., 2022), postgraduate education (Zhao et al., 2021), teachers’ development (Liu et al., 2011), general education (Qu, 2005), teaching reform (Liu et al., 2007; Qiu et al., 2021), discipline construction (Luo et al., 2006; Bao et al.,2017; Chen et al., 2021), and internationalization (Zhou, 2013). For the overall research into universities, the main focus is on strategic planning (Li, 2008; Wei et al., 2009; Liu, 2011).There is also foreign literature concerning research into general education (Ye et al., 2022),teaching reform (Henderson et al., 2011), entrepreneurship education, and industrial integration(Debackere et al., 2005; Geuna et al., 2006; Veugelers et al., 2005; D’Este et al., 2007). Studies on the development of non-developed countries (such as Inés et al., 2022) were also conducted.Studies on inland universities are about teaching (Trede, 2010), employment (Xu et al., 2016),and more. In general, domestic research is mainly concentrated in prestigious universities in the US, the UK, Singapore, Australia, and other well-developed countries. Foreign studies are mainly about developed countries introducing their own practices. Universities mentioned in most of the above studies boast obvious regional advantages. Therefore, their experience is of little referential value for the development of the geographically disadvantaged universities in western China.

Figure 1 Distribution of Chinese papers searched with keywords of “universities” and “experience and enlightenment” on the CNKI(China National Knowledge Infrastructure) platform in the disciplines of higher education (by year)
In China, compared with the coastal region, the western region faces four major challenges in building world-class universities. (a) Lack of funds. The western region lags behind the coastal region in terms of dedicated funds from the provincial and municipal governments.Compounded by a smaller economic aggregate and a lower development level, the western region receives less educational support for building world-class universities. (b) Lack of highend talent. In the western region, it is rather difficult to retain and attract top-level talent.Moreover, there is also a serious problem of brain drain. (c) Lack of supporting conditions,especially infrastructure, to support major scientific research. Among the cities selected to build world-class universities in the western region, only six are on the list of China’s top 100 cities in terms of GDP. Owing to an undeveloped economy and inadequate industrial development,such cities cannot provide a favorable environment for the development of universities, let alone infrastructure to support significant international research. (d) Geographical restrictions and conservative thinking. Geographically, the western region does not have the advantages of carrying out opening-up and international cooperation and exchanges.
Therefore, it is urgent to study the development routes concerning the universities in the western regions. There is still a certain amount of literature on inland universities (more details will be presented in the following passages) that can roughly outline the development status of these universities (although it may not be the whole story). Therefore, in this paper,we discuss the development experience of some world-class inland universities in foreign countries by examining secondary literature and relevant Internet-sourced information on the development of such universities, in the hope of providing references for the construction of world-class universities in western China.
Cases of Building World-Class Universities in Foreign Inland Regions
Universities in Munich, Germany
In 2021, the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München (LMU), both located in inland Europe, ranked 50th and 64th in the QS World University Rankings, respectively. The development of universities in Munich is attributed to the following reasons.
Strong industrial strength of Munich.
The Munich High-tech Industrial Park is a research and development center for electronics,microelectronics, and electromechanics in Germany. Known as the “Bavarian Silicon Valley,”the Park focuses on developing laser technology, nanotechnology, and other industrial sectors.Munich, as one of the two largest industrial centers in the country, quickly overtook Berlin as Germany’s new industrial and technological center after World War II. In the 1960s, Germany attached great importance to science and technology enterprises, focusing on developing their civil electromechanical industry. After the economic crisis of the 1970s, the electronics sector along the Munich Corridor created an economic miracle.①Sun Jin. Munich: An Oasis in the European Urban Forest [N]. Shenzhen Special Economic Zone News, 2014-01-14 (A06).
Top scientific research clusters.
In Munich, there formed a local, regional collaborative innovation network around TUM and LMU. From 2006 to 2017, TUM and LMU, together with other institutes, carried out a series of interdisciplinary research projects through cooperation with six clusters in Munich,such as the Center for Integrated Protein Science Munich (CIPSM), Cluster of Excellence Cognition for Technical Systems (CoTeSys), and Munich Cluster for Systems Neurology(SyNergy), since the launch of the German Excellence Initiative. They have made great contributions to the scientific and technological development in Munich and greatly enhanced the innovation capability and popularity of TUM and LMU. Since 2019, four Clusters of Excellence②The four Clusters of Excellence mainly target sustainable energy supply (interdisciplinary development with nanoscience), quantum science, astrophysics,biophysics, and neurology.have been established and promoted in Munich to study interdisciplinary issues by means of interdisciplinary exchanges and cooperation, enabling both universities to achieve their first success in the Cluster of Excellence strategy. In addition, the two universities also established a research alliance focusing on renewables and climate change, starting a new trend in collaborative research among world-class universities in the region (Qie, 2021).
In-depth integration into local industry development.
In Munich, universities have established close relationships with various large, small,and medium-sized enterprises. They not only transfer talent to enterprises but also carry out cooperation with them in technology R&D. LMU has established a special Business Partners Team to support cooperation projects between university professors and businesses and to help businesses identify research areas with great significance.
Government policy support.
In terms of high-tech development, the German government set up 96 joint research associations at the end of the 20th century to facilitate the application of research findings throughout the industry. It was clearly stipulated that government-funded universities must cooperate with enterprises to accelerate scientific and technological development. The government also adopted a range of measures to promote regional economic innovation and development, bolster the development of world-class universities and research institutes,and advance industrial cooperation to accelerate the R&D and application of cutting-edge technologies. Germany has paid more attention to technology R&D in recent years. The federal government invested more than EUR 15.8 billion in technology R&D in 2018 and planned to spend 3.5 percent of its GDP on R&D every year through 2025.
Characteristic regional collaborative innovation network.
The formation of the characteristic regional collaborative innovation network in Munich is driven by many factors. First, Munich is abundant in scientific and educational resources,including 16 universities and more than 70 institutes. The Munich High-tech Industrial Park is often referred to as the “Silicon Valley of Europe.” In addition, there is also a mature intermediary service system in the region. Second, Munich is the hub of leading industries oriented toward technology and research. Third, with its unique regional culture, Munich can provide comprehensive cultural services, such as outstanding theaters, museums, galleries,symphony performances, and football games, attracting a large pool of high-end talent to settle there. Finally, entrepreneurship is another feature in the academic circle of Munich. In 2007, LMU established the “Entrepreneurship Center,” which has nurtured more than 150 start-ups. The president of the university said that it has been a goal of the university to “teach each student how to start a company.”①How does Munich, Germany’s Silicon Valley, attract start-ups and tech giants? [EB/OL]. 2021-08-23 [2021-11-08]. Available from: https://www.163.com/dy/article/GI3D4PGF0511DV4H.html.
World-Class Universities in Switzerland
Located in inland Europe, Switzerland covers an area of only 41,000 kilometers(roughly equal to that of China’s Hainan province), and its economy heavily depends on exports (Liang et al., 2018). However, this country has ranked first in the world in terms of innovation capability for nine consecutive years.②The data comes from the Global Innovation Index 2019 issued by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO).It also takes the lead in patent applications,patent returns, and high-tech product manufacturing, with extremely high efficiency in the commercialization of scientific and technological achievements (INSEAD, 2018). The Swiss universities have long performed well in overall strength (see Table 1).
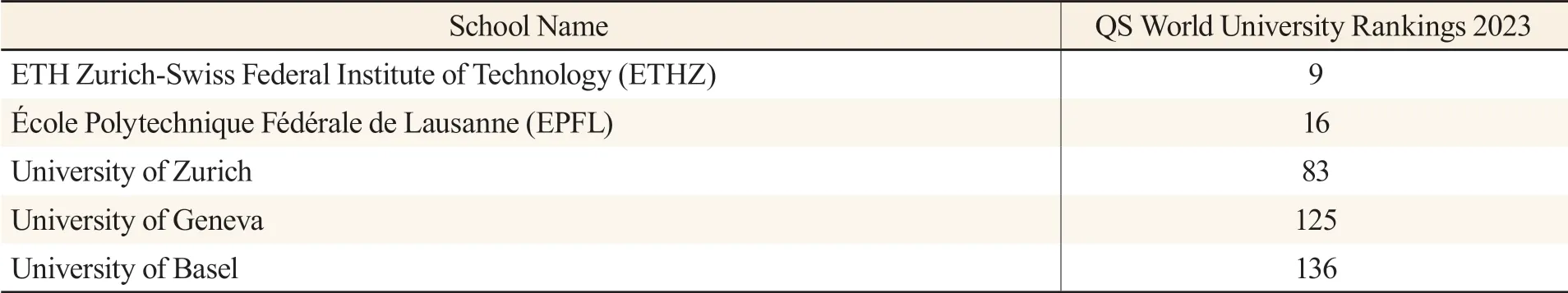
Table 1 Rankings of Some Swiss Universities in 2022
As a historically neutral country, Switzerland has attracted top-level talent from all over the world and accumulated sufficient funds for development. Meanwhile, many factors, such as the social atmosphere of honoring contracts, proven vocational education systems, and applicationoriented scientific research, have all contributed to a good environment for scientific and technological innovation (Guo, 2019). The Swiss government highly values knowledge innovation and research. The public and private expenditures on education and R&D of the country account for five percent and three percent of GDP, respectively, each year (Guo, 2019). In the late 1990s,Switzerland began to carry out higher education reform, increasing higher education funding and promoting mutual cooperation among higher educational institutions. The outstanding performance of Swiss universities can also be attributed to the following aspects.
Building a scientific governance system.
Swiss universities enjoy a high degree of autonomy and are less restricted in terms of funds utilization and personnel appointments and promotions. For example, they have the right to decide the pay rates of their senior faculty and provide them with more flexible promotion systems. In terms of academic governance, universities in Switzerland also exercise a high degree of autonomy in adding, abolishing, and designing degree programs, selecting teaching languages, and establishing internal quality assurance mechanisms, among others. In addition, the opinions of university professors are fully respected in assessing the quality and performance of higher education. At present, many universities have formed reliable systems for the evaluation of teaching quality and academic achievements based on peer reviews.
Gathering the world’s top talent.
Universities in Switzerland are attracting and gathering the world’s top talent by making full use of their advantages, such as the flexible salary systems, scientific evaluation mechanisms, and a relaxing academic atmosphere, in addition to the national influence of Switzerland. Home to global talent, Switzerland has ranked first in the list of countries attractive to the world’s top talent for seven consecutive years.
Advocating internationalization in running schools.
Switzerland advocates diversity in languages, culture, and economy. It has four official languages (German, French, Italian, and Romansh), and more than 20 percent of its population holds foreign passports (Liang et al., 2018). The universities there have long ranked high among the global universities in terms of internationalization level. According to statistics,ETHZ had a total of 9,100 staff in 2016, of whom 55.9 percent have international backgrounds.
Universities in Siberia, Russia
In 2021, Novosibirsk State University (NSU), located deep in the Eurasian continent, stood at 246th in the QS World University Rankings①Tomsk State University is another famous university in Siberia that is ranked 272nd in the QS World University Rankings. Due to the lack of relevant information, we only introduced Novosibirsk State University in this paper.and the third among Russian universities. The development of NSU is attributed to the following reasons.
Fully integrating into major national strategies and actively building the Novosibirsk Scientific Center.
The NSU, established in 1958 as part of the Siberian Branch of the Former Soviet Academy of Sciences, made great contributions to the construction of the Novosibirsk Scientific Center. After World War II, the establishment of the Novosibirsk Scientific Center created a relatively relaxed research environment for scientists, gathering outstanding scientists from all over the country. In pursuit of integrated development of scientific research and education, Novosibirsk Scientific Center has been focusing on comprehensive interdisciplinary research in basic sciences. By taking multiple measures, it has accelerated the application of scientific research findings to the national economy. Novosibirsk Scientific Center, relying on its strong scientific research strength, ranked among the top ten scientific centers in the world in the 20th century, making it “a miracle of Siberia in the 20th century.”
Attaching great importance to the cultivation of students’ scientific research capability.
The NSU implements the principle that higher education institutions should regularly carry out exchanges with research institutions and that every student must participate in scientific research. All the students in the NSU must participate in the research practice of the institutes of the Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences, and the various workshops and academic conferences, to cultivate practical abilities, learn about the latest scientific research achievements, and understand the latest major theories. Students receive a traditional education for the first three years, followed by 3-year internships at various institutes. At the same time,many outstanding scientists have been invited to teach part-time at the university. Most of the department heads and lecturers of the main courses are members and corresponding members of the Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS).
Advocating internationalization in running schools.
The university has established an advanced platform for scientific research and innovation.It attaches great importance to the selection of outstanding students in mathematics, natural science, and informatics, according to well-proven selection and training systems. Many of its graduates work in world-class universities and research centers. Furthermore, it has an efficient management team that is competent for the current reforms. All these have laid a solid foundation for the NSU to edge into the list of world-class universities. These competitive advantages can not only attract excellent domestic and overseas students to accelerate NSU’s internationalization but also attract investment from economic sectors and social business associations, which plays an important role in attracting off-budget funds.
Universities in the Midwest of the US
Universities in the Midwest of the US performed well in the QS World University Rankings in 2021 (see Table 2). For reference, only the rankings of universities in Arizona,Utah, Michigan, and Pittsburgh are shown here.
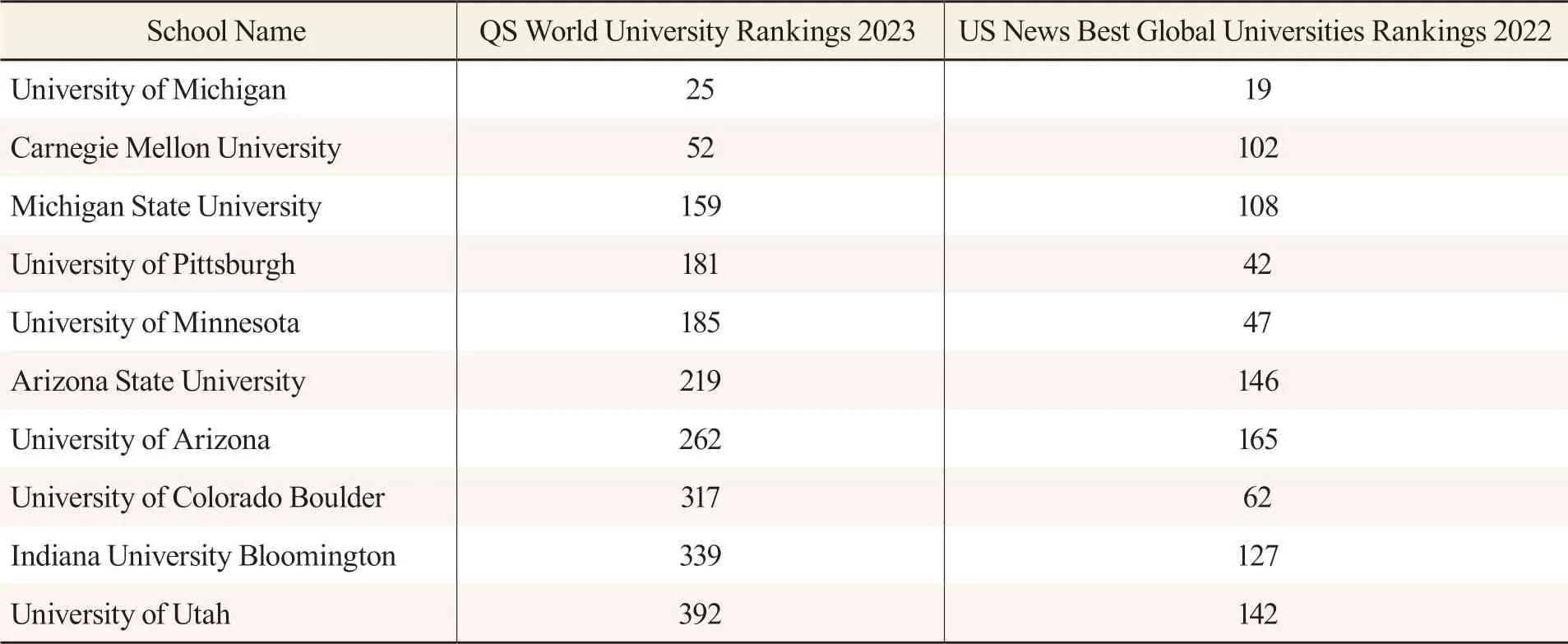
Table 2 Rankings of Some Universities in the Midwest of the US in 2022
Examples of universities in Arizona.
The development of universities in Arizona is attributed to the development of the industrial clusters there. In the late 1980s and early 1990s, Arizona suffered a severe economic recession. In 1992, Arizona promoted the recovery and transformation of the local economy by implementing a strategy of building industrial clusters, making it one of the fastest-growing regions in the US in the following decades. The development of industrial clusters in Arizona benefited from its scientific strategy design and a dual-driven development model featuring“technology-intensive SMEs + enterprise networks” (Lu et al., 2015). Arizona has introduced a tax system characterized by lower tax rates, fewer tax categories, and simpler procedures,to lower the operating costs of enterprises. A variety of tax credit programs have also been launched to support the development and expansion of enterprises. The region has also made efforts to improve the labor market to provide high-quality labor resources for enterprises. In addition, Arizona is one of the few regions in the US that provides federal project navigation to encourage enterprises to build strategic partnerships with each other and with the government.It provides free consulting and assistance for technology-based enterprises that are planning to move in and expand business there (Ni, 2015).
The University of Arizona, founded in 1885, is one of the top research-oriented universities in the US, with strong comprehensive strength. The university is reputed as one of the “Public Ivy League” universities due to its remarkable scientific research capabilities in natural sciences, such as astronomy, geology, geography, and excellent performance in humanities,such as anthropology, sociology, and philosophy. It is also a member of the Association of American Universities (AAU). Here are some measures adopted by the University of Arizona in its development.
Emphasizing development planning of the school. The University of Arizona never settles for less than the best for Arizona, using Engagement, Innovation and Partnership to create Synergies that will transform the modern research university for the 22nd century. In terms of innovation, the university put forward the following measures. (a) Promote core strengths to address grand challenges. The university is committed to strengthening its competitive edges in the medical field by deepening cooperation between its Mel and Enid Zuckerman College of Public Health and related clinical research institutes. (b) Expand opportunities for interdisciplinary collaboration. (c) Recruiting top talent and training excellent teachers.The university is making every effort to increase the retention rate of excellent teachers and reduce differential treatment between assistant professors. (d) Hire, nurture and retain a diverse, outstanding faculty. (e) Attract, educate and engage first-rate doctoral students. (f)Improve support for the development of major proposals and new initiatives. The university is striving to create world-class information infrastructure and research programs and engage more researchers in key areas. (g) Diversify external research support and expand strategic external partnerships. The university is attracting funds and investments from entrepreneurship programs for universities in Arizona and strengthening support for the construction of research infrastructure. In terms of Synergies, the university has expanded opportunities for interdisciplinary collaboration. It has also invested in building an interdisciplinary research center to address the current issues with international resources, thus strengthening international exchanges and domestic influence. Further, it has adjusted information technology to meet requirements in teaching, scientific research, and management (Zhang, 2015).
Commercializing scientific research findings for regional economic development. The University of Arizona, focusing on research and cooperation in six competitive industries,including biology, environmental technology, aerospace, information technology, optics, and composite materials, is exploring a development channel that combines the efforts of enterprises and universities based on the needs of industrial innovation. The university has established the Tech Launch Arizona (TLA) to promote the commercialization of scientific research findings(Lu et al., 2015). Led by the University of Arizona, a diversified knowledge transformation mechanism has been formed in southern Arizona, and several intermediaries for knowledge transformation and development have also been created in this region (Ni, 2015).
Arizona State University (ASU) was founded in 1885. Although not edged into the list of research-oriented universities until 1958, the university witnessed rapid growth in research strength. In the absence of a medical college and agricultural college, its expenditure on research exceeded USD 200 million in 2010 and surpassed USD 400 million in 2014. For this reason, it was classified as a “high-level research-oriented university” according to the Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education. Here are some measures adopted by Arizona State University in its development.
Forging ahead with reform. Since 2008, Arizona State University has initiated a series of reforms aimed at building a “New American University (ASU).” The goals of the New American University are: to demonstrate leadership in enabling academic excellence and accessibility at scale; establish national standing in academic quality and impact of colleges and schools in every field; establish ASU as the leading global center for interdisciplinary research, discovery and development by 2027; and enhance our local impact and social embeddedness (Yang et al., 2016).
Serving economic and social development through scientific research. ASU has maintained strong momentum in the number of patents applied for, thanks to the Arizona Technology Enterprise (AzTE), its institution dedicated to commercializing research findings.ASU’s strategies for the commercialization of research findings can be outlined as follows.The general idea is to pay attention to consolidating and developing competitive knowledge clusters. For promoting innovation projects, the Group Problem-Solving method is adopted to produce the final products, construct innovation laboratories, and establish specialized hightech incubation institutions (Lu et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2016).
During the almost ten years from 2003 to 2012, the number of research projects for which the university has received federation funds increased by 162 percent, far higher than the average increase of 15 similar public universities (Hu, 2017).
Examples of Universities in Utah.
In the 1990s, Utah started education reforms by promoting the industrialization of science and technology, developing infrastructure, supporting high-tech enterprises, and developing the economy through education and science and technology. Such reforms have created a“Utah Miracle,” with economic growth ranking top in the US. In the valley between Salt Lake City, its capital, and Provo (40 miles away), rose a high-tech industrial town-World Software Industry Valley, that rivals Silicon Valley. In less than ten years, the region has recovered and embarked on a path of prosperity (Sun, 1996).
The University of Utah, founded in 1850, is one of the most famous and honored public universities in western US. Regarded as the birthplace of computer graphics, it is esteemed as the “Mecca of Computer Graphics.” As one of the birthplaces of the Internet, it is also the university with the most developed wireless network in the US. The development of the University of Utah mainly benefits from the following management behaviors.
Seizing the historic opportunity in local reform and development. First, Utah took the lead in educational reforms. It increased investments in education and research to cultivate competitive and creative high-tech talent. Second, it vigorously promoted the industrialization of science and technology. Against the background of the global information technology revolution, Utah launched a “Centers of Excellence program,” aiming to promote the development of future industries. The state selected and focused on developing three hightech industries, including software, medical devices, and biological engineering, that feature low investment, high efficiency, and small transportation volume. By creating a high-tech economic development pattern led by software and information industries, Utah has changed its economic structure that used to be underpinned by military, mining, and tourism. The university has fully grasped the historic opportunity and achieved win-win cooperation with the local government in economic reform. Its research center has incubated Adobe which has produced well-known software, such as Acrobat and Photoshop. Its medical school has made great contributions to the US and even the world, especially in the research of cancer and ophthalmology. In addition, it has developed advantageous disciplines, such as chemistry,biology, architecture, civil engineering, and materials.
Valuing the commercialization of scientific and technological achievements. All scientific achievements of the university are managed by the Commercialization Office. Driven by the“commercialization engine” (Tang et al., 2019), risks are reduced in the early stage or in the R&D stage of scientific and technological achievements so that those with high commercial value can obtain certain financial support and become commercialized. At the same time, an engine fund is set up to provide phased financial support in the commercialization of scientific and technological achievements.
Vigorously building the university research park. In the late 1960s, the university was unable to provide any investment for the establishment of a research park other than an undeveloped space on a rugged hillside next to the campus. However, the school authorities managed to ingeniously secure the cooperation between the government and the developer in building the research park through a realistic and attractive business plan. Upon completion, the research park, located in the midwest of the US with relatively poor natural conditions, became one of the most successful university research parks in the US, behind only the research parks of Stanford University and the University of North Carolina (Li, 1999). The University of Utah is the top research university in the nation when it comes to commercializing technology innovations, according to the Milken Institute’s 2017 ranking of Best Universities for Technology Transfer. The ranking is based on the University Technology Transfer and Commercialization Index, which uses four key indicators of technology transfer success,measured on a four-year average (2012-2015): patents issued, licenses granted, licensing income and start-ups formed. The University of Utah was propelled to the No. 1 position due to licensing income and start-ups, which received the highest weights in the overall index..
Examples of Universities in Pittsburgh.
Pittsburgh, known as the “Steel City,” was mired in recession because of economic crisis,resource exhaustion, and the advent of the era of science and technology. However, it finally achieved “the Pittsburgh Renaissance” in the 1980s by temporarily sacrificing economic growth and gradually restricting the steel industry while promoting the integration of high-tech industries, universities, and research institutes. It took a little more than 30 years for the city to complete the transformation and create the well-established “Pittsburgh Model” (Lin et al., 2020).There are two famous universities in Pittsburgh: the University of Pittsburgh and Carnegie Mellon University. The development of these universities is mainly attributed to the following measures.
Facilitating urban transformation. In 1985, against the backdrop of economic transformation, the Pittsburgh government and Carnegie Mellon University jointly formulated the “Strategy 21: Pittsburgh/Allegheny economic development strategy to begin the 21st century: a proposal to the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania,” trying to cope with the problem of depending on a single industrial sector by developing a diversified economy. In the 1990s,the local government vigorously developed service industries, such as education and tourism.During this period, the University of Pittsburgh and Carnegie Mellon University became the main driving force for the development of Pittsburgh and served as an incubator of high-tech industries and an important window to showcase the local culture. In 2006, the new mayor announced the plan for the “Pittsburgh’s Third Renaissance ,” focusing on developing the healthcare and education industries. On the one hand, based on its rich mineral resources, the city achieved mechanization and technicalization and increased the added value of products through deep processing. On the other hand, a group of high-tech headquarters began to gather in Pittsburgh. In particular, the employment rate in the healthcare industry saw significant growth, accounting for more than 10 percent of the total, which greatly promoted the development of medical tourism and related industries. In smart transportation, Pittsburgh also encouraged the exploration of autonomous driving, making the city a pilot testing base for new technologies. Today, Pittsburgh has become a smart city backed by education and healthcare, and the two universities there have also witnessed great development.
Vigorously developing medical science and accelerating the commercialization of medical achievements. In 1982, Pittsburgh, responding to the call of the times, established the Pittsburgh Technology Center to promote university-enterprise cooperation and encourage the University of Pittsburgh and Carnegie Mellon University to commercialize new technological findings (Li, 2017). The University of Pittsburgh Medical Center was a good example with particularly prominent performance. After the 1980s, the Medical Center gradually evolved into a commercial complex aimed at the integrated development of academic research and the healthcare industry. In 1998, it became an independent medical industrial group that has a medical school for developing new technologies and a hospital for offering medical services worldwide. The Medical Center takes the commercialization of research findings as its highest priority. In the mid-1980s, it invested USD 5 million in medical technology research, especially in psychiatry. It also integrated the latest research findings in neurology and epidemiology and accelerated the commercialization of such findings, making it a leading medical institution in the US, and the Medical School of the university is now renowned nationwide. In addition,the Medical Center is committed to medical research to maintain its leading position in the industry. With external funds and its own profits, the Medical Center takes steps to promote its development, including timely updating of its diagnosis and treatment facilities, introducing top talent, rewarding scientific and technological innovation, and providing research funds for visiting scholars. Meanwhile, it encourages the Medical School to carry out interdisciplinary research and promote the collaborative innovation of subordinate institutions. Thanks to the leading position of the Medical Center in the field, Pittsburgh became known as the “Organ Transplantation Capital of the World” in the 1980s (Li, 2017). By 2005, the Medical Center had managed more than 20 hospitals of different types, more than 400 outpatient clinics, 14 chronic disease centers, and other related facilities. Its business also expanded to Asian and European countries, such as Ireland, Italy, and Qatar.
Formulating scientific development strategies. Carnegie Mellon University is among the top four universities in the US for its computer research, and it is most well known for its development strategy. During its development, the university grasped the historic opportunity to highlight its competitive edges and do the right thing. In the late 1960s and early 1970s, the school authorities believed that information technology would play a most critical and decisive role in the next phase of science and technology development. With insufficient resources, funds, and a small scale, the university concentrated on developing computer science and engineering. Driven by computer science, public management related to information management also witnessed rapid development. Meanwhile, software and hardware were also developed to supply the needs of using computers to control many of the machines used in research. As a result, the university achieved unprecedented development in such fields as computers, robotics, software engineering,and information technology management. Achievements have also been made in some innovative science and technology fields. Since then, the university has achieved leapfrog development in its evolution from an ordinary regional university to a world-renowned research-oriented university(Liu et al., 2017). From the 1970s to the 1980s, the university, guided by the law of comparative advantage, gave full play to its existing advantages to make them stronger instead of seeking a leading position in all fields, which coincides with the saying that a wise man knows what should be done and what should not. The faculties of the university, yet to be expanded, all strove for a leading position in their respective fields. In the 1990s, the university put its strategic focus on improving undergraduate education and invested substantial funds to improve teaching methods and the learning and life quality of students outside the classroom. Carnegie Mellon University ranked among the top four universities with the most significant improvement in education quality between 1988 and 1998, according to the research of the Institute of Higher Education in California. As noted by George Keller, a prominent American educator, the greatest miracle in the past two hundred years in higher education has been the rise of Stanford University and Carnegie Mellon University.
Emphasizing interdisciplinary cooperation. As early as the period from 1939 to 1940, Robert E. Doherty, the then President of Carnegie Mellon University, led the development of the worldfamous “Carnegie Plan,” a philosophy in which students were taught to apply fundamental knowledge to solve practical problems and were required to learn about and appreciate academic disciplines outside their primary area of study. The plan required all students of science and engineering select courses (one-fourth of their total courses) concerning humanities and social sciences to improve their knowledge structure. Many faculties at Carnegie Mellon University were set up based on interdisciplinary cooperation. For example, the Heinz College of Information Systems and Public Policy, now a world-class teaching and research center, gathered excellent teachers from the College of Engineering, College of Public Administration, and Tepper School of Business through an interdisciplinary appointment system to engage in teaching and research on technology policy. Currently, the university boasts a total of 22 interdisciplinary programs designed to enable students to acquire multidisciplinary skills. In addition, it has also launched some inter-university interdisciplinary collaboration programs, such as the Medical Scientist Training Program (MSTP), a cooperative program jointly initiated by Carnegie Mellon University and the Medical School of the University of Pittsburgh (Liu et al., 2017).
Examples of Universities in Michigan.
Michigan, dominated by manufacturing and agriculture, is one of the most important automobile production bases in the US and the world and one of the important agriculturebased states in the US. Michigan produces 22 percent of the nation’s cars, with half of the world’s 150 largest auto parts suppliers and 175 R&D institutes settled there. There are more than 65,000 professionals engaged in vehicle research, prototype development and design, and product development. Meanwhile, efforts are being made there to develop high-tech industries,such as life sciences, information technology, and advanced manufacturing. There are two famous universities in Michigan: the University of Michigan and Michigan State University.Here are some measures adopted by these universities in their development.
Establishing a university alliance to promote the commercialization of academic research findings. In 2006, Michigan State University established the University Research Corridor(URC), together with Wayne State University and the University of Michigan, to promote collaborative development, reserve talent, attract investment, encourage the registration of businesses, and create jobs. The URC, supported by USD 1.3 billion of federal funds per year, has helped strengthen partnerships among universities, communities, and states, and made great contributions to the local economy. Meanwhile, the university has promoted its outstanding scientific research achievements to the market. Its water purification technology and thermoelectric technology have bolstered the development of the local new economy. In addition, Michigan State University has set up hospitals and physical therapy centers by joining hands with local communities. This makes it the only university in the US that owns three hospitals, and one of the national research centers for Parkinson’s disease, breast cancer, and environmental issues. With exquisite medical skills, attentive medical care services, advanced medical education, the university has not only safeguarded residents’ health but also boosted local economic development and enhanced its mission of advancing innovative education.
Carrying out interdisciplinary research. The University of Michigan has dismantled the tradition that a faculty member is only affiliated with a primary department and introduced a variety of joint appointment systems. The joint appointments may occur in a variety of forms, including: (a) A continuing tenure system joint appointment; (b) Some are split almost equally between academic units; others are for a small fraction of time in one academic unit,an almost equal split between academic units; (c) A small fraction of time in one academic unit with another unit(s) as the majority shareholder; (d) For a specified period of time subject to renewal (or with no option for renewal); (e) An appointment between an academic unit and an administrative unit; (f) An appointment on an adjunct or clinical basis without pay. Fixedterm faculty and academic staff also may be involved in joint appointments. More importantly,each school or department can recruit teachers under the joint appointment system with no limitation on staff numbers, but they need to specify their research purpose, practical significance, and the future prospects of the proposed application field (Lin et al., 2019).
Further exploring its advantageous fields based on regional development. From its founding in 1855 to the 1960s, the Michigan State University has undergone major changes in its name, from Agricultural College of the State of Michigan, State Agricultural College,Michigan Agricultural College, Michigan State College of Agriculture and Applied Science,and Michigan State University of Agriculture and Applied Science, to the current name,Michigan State University, with agricultural science as its traditional field. Michigan is one of the important agricultural states in the US. As agriculture is an essential part of Michigan’s economy, the university has historically focused on this field. At present, the university has become an important driver of the state’s new economic development relying on its competitive disciplines, such as biological research technology, teacher education,automation engineering, and food safety research, as well as its water purification technology related to agriculture, thermoelectric technology, renewable energy technology, water biochip technology, and portable pathogen detection devices.
Development Experience of World-Class Universities in Foreign Inland Areas
After reviewing the development experience of world-class universities in foreign inland areas, we found that the development of such universities is restricted by the economic and social environment of the cities and regions where they are located. Further, these universities are especially at seizing historic development opportunities to actively advance internal reform and fully integrate them into regional economic and social development. As a result, they have made great contributions to talent training and scientific research and have enhanced their strength and international influence in the process of coordinated development with the region.
Location Plays a Vital Role in the Development of Inland Universities
Based on our observations of the development of world-class inland universities around the world, the development of a world-class university is based on the natural conditions of the region where it is located and largely dependent on the economic and social development of the region. On one hand, these universities are relatively restricted by their inland locations.On the other hand, these universities are in either regional centers, resource-abundant regions,regions with main traffic arteries, or regions supported by strong industries. The cities or regions where world-class universities are located always boast favorable geographical advantages in the inland areas. Due to a lack of distinguished higher educational resources,these universities are especially influential to the local development.
National Administration Support and Local Policy Support Are Particularly Important for the Development of Inland Universities
The development of a university is inseparable from the development of the city or region where it is located. To this end, national administration support and local policy support play a particularly important role in the development of inland universities. National and local administration affects educational investments and staff turnover. Local governments with great resolutions will actively create a good environment for social and economic development,thus bringing about the rapid development of local universities. The support of the state and government, especially by offering educational funds, is particularly essential for building world-class universities in inland areas.
Proactively Advancing Reform Adds Weight to the Building of Inland Universities
As communities for academic research and development, universities have two basic functions,i.e., knowledge creation and knowledge dissemination. Problems and demands stimulated the creation of knowledge. All world-class universities develop by gathering talent and expertise to solve problems. Different disciplines are formed to solve different problems. Hence discipline clusters are developed that bring about new growth points and renewal of different disciplines.Through such reforms, and by following the natural laws of development, these world-class inland universities have gained competitive edges despite their unfavorable locations compared with those in coastal areas. The bonus of these reforms not only effectively boost more local support,but also they swiftly and accurately the benefit local economic and social development. They have achieved great success in their development by identifying breakthrough points, often during times of disadvantageous economic conditions.
Deep Integration into Regional Industrial Development Lays the Foundation for the Development of Inland Universities
The development of all world-class universities is closely related to regional industries.Culture and knowledge are generated from social and industrial development practices, and ultimately realize their value in social and industrial development practices, thus stimulating and maintaining the development of academic communities. With the aim of solving problems in development, world-class universities have established communication channels between intellectual groups and social industries. Some have even established university industrial parks to serve business incubation. The relatively smaller input capacity drives inland regions to allocate their limited resources into areas that are in great need. Inland universities can only gain more support from outside by serving the industries that are beneficial to local economy and the people's livelihood. These inland world-class universities are closely related to the growth of urban industries. For example, they realize self-development while serving the urban industries. However, with narrower space for self-development by serving the urban industries,they can only stand out by integrating deeply into the regional industrial development.
Academic Independence and School Governance Are the Basic Missions of Universities
The development of the Swiss universities shows that academic autonomy contributes to the development of universities, while the experience of Russia demonstrates that government centralization does too. In addition, the experience of the US proves that university planning based on academic autonomy also plays a positive role in promoting the development of universities. For inland universities with limited resources, it will be necessary for them to make a rational plan that identifies industries where they will have a comparative advantage before committing to their limited resources. It is especially important for inland universities to improve their governance capability, make full use of their limited resources, and seize historic opportunities. They should aim at future developmental trends and strengthen their advantages to open new areas.
In addition, education investments in countries such as the UK, France, and Germany,invariably come from the governments, while in the US, it mainly comes from private investors. The diversified and high-quality private investments supported the characteristic development of American universities, which is the proven experience of the US in building world-class universities (Geng, 2010). The practices of the various countries and universities we studied show that actively expanding sources of educational investment is the key to the development of universities.
Enlightenment for Western China in Building World-Class Universities
Based on the development experience of world-class universities in foreign inland areas, it is notable that successful inland universities have comprehensively integrated into the regional economic and social development by closely following major national and regional strategies.By seeking opportunities in local development, they have continuously deepened institutional and systematic restructuring to unleash their vitality and potential in school management and development. In addition, they focus on major projects to promote the transformation from“expanding the scale by quantity” to “achieving development by quality.”
Inland Universities in China Should Seize the Present Historic Opportunity for Regional Economic and Social Development
At present, China is in a stage of rapid development. The 14th Five-Year Plan highlights the“four regions” and “five major strategies.” China’s regional development strategy includes the overall strategies for “four regions.” That is, ushering in a new stage in large-scale development in the western region, promoting breakthroughs in the revitalization of northeast China,accelerating the rise of the central region, and encouraging the eastern region to accelerate modernization. The five major strategies are formulated for the coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, the development of the Yangtze Economic Belt and the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, integrated development in the Yangtze River Delta, and ecological protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River basin.These strategies have created various opportunities for the development of inland universities in China. These universities should fully grasp the historic opportunities by actively taking part in, and sharing responsibility, for the coordinated development in their regions. Only when their science and technology contribute to the construction of the inland areas, and even the whole country, can they lay a solid foundation for growing into world-class universities.
Inland Governments Should Step up Investments in Education and Resolutely Carry out Reform and Development
The inherent disadvantages of inland areas in geographical locations during their development can be compensated by policy support and reforms. However, this requires the local government to have clear thinking and strong abilities to plan for and boost the local economic and social development. The local government should commit any limited resources to industries with comparative advantages to achieve differential development in the process of regional economic and social development. Universities should make full use of their own advantages, take the initiative in the local economic and social development, and lead and promote local development.
Inland Universities Should Continue to Modernize Their Governance System and Capability and Strengthen Their Top-Level Designs
To better serve the regional economic and social development, inland universities should carry out internal reforms. In the new era of rapid changes, we should keep an open mind in developing and expanding universities. First, we need to reform the academic evaluation mechanisms in universities to measure the academic achievements of engineering sciences by application of industrial engineering technology and medical sciences by clinical treatments to introduce a classified evaluation system in lieu of the current one-size-fits-all approach. Second,we need to integrate and change the discipline systems in universities. We should restructure the university discipline systems by “targeting the global science frontiers, serving the main economic battlefield, striving to fulfill the significant needs of the country and benefiting people’s lives and health” and by focusing on tackling problems. We should not only promote interdisciplinary development but also expand and lead the development of disciplines. When the time and conditions are ripe, we need to accelerate the commercialization of scientific and technological achievements and create university industrial parks to promote the development of local industries while conducting scientific research. Meanwhile, we need to vigorously improve the governance ability and quality of universities and make responsible development plans for universities to chart a course for reform and pool their strengths for development and integration into the commerce of their region. Universities need to make full use of the limited resources when managing schools. School planning plays a very important role in the construction of American universities, especially its world-class universities. This certainly is closely related to the idea of helping to fund universities through private investments and social donations. All universities need to make rational future-oriented development plans, sharpen their advantages, and expand by taking targeted measures and setting priorities to grow into world-class universities and build and manage their brands.
Conclusions
To provide references for the construction of world-class universities in western China,we examined secondary literature and relevant Internet-sourced information about the development of world-class inland universities and summarized their development experience.We found that these universities are good at seizing historic development opportunities to actively advance internal reform and fully integrate into regional economic and social development. As a result, they have enhanced their strengths and international influence in the process of coordinated development within the region. Although these universal successful experiences are not unique to inland universities, it is worthwhile to learn from the common development routes these wellknown universities presented. Based on limited literature, this paper may be incomprehensive and biased in summarizing and introducing the successful development experience of each university. Therefore, we provided limited enlightenment on the construction of world-class universities in western China. Since the situation varies from university to university, there is no universal approach to their development. There is still a long way to go, and further research is needed before the universities find a path that suits their own needs.
杂志排行
Contemporary Social Sciences的其它文章
- Research on the Influence Degree and Effect of Support on Innovation Incentives for R&D Personnel in Micro and Small Enterprises: An Empirical Study based on the China Micro and Small Enterprise Survey (CMES)
- Rural Road Investment and Economic Growth
- Research on the Development of Rural Tourism in the Context of Comprehensively Promoting Rural Revitalization: A Social-System-Based Approach
- On the Development of Modern Tourism in Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture, Sichuan Province
- A Study of Sanxingdui Museum’s Building of International Communication Capacity
- Erasable/Inerasable L1 Transfer in Interlanguage Phonology: An Optimality Theory Analysis of /aʊn/and Sentence Stress in Chinese Learners of English
