煤矸石堆积区土壤重金属潜在危害评价及污染特征
2022-11-03顾霖骏申艳军王念秦宋世杰聂文杰
顾霖骏 申艳军 王念秦 宋世杰 聂文杰




摘 要:煤矸石長期堆积是中国部分煤矿区特别是北方矿区表层土壤遭受重金属污染的重要成因。为掌握中国煤矸石长期堆积区表层土壤中重金属元素的潜在环境危害性及污染性特征,采用数理统计分析方法,研究中国煤炭主产区煤矸石重金属含量的地域分布特征;通过重金属潜在危害评价方法,评价煤矸石源重金属元素在表层土壤中的迁移性及毒性,明确煤矸石中对环境潜在危害性突出的重金属元素;结合煤矸石堆积地域分布特征,利用重金属生物有效性原理,分析了这些污染元素在矿区表层土壤中的空间分布及形态分布特征。结果表明:中国煤矸石中Cr,Pb,Zn含量明显高于其余常见重金属元素,且西部煤矸石重金属含量较东部、中部更高;煤矸石中Cd,Zn,Pb对土壤潜在污染程度在中等以上,各重金属元素对环境的潜在危害程度E排序为:Cd>Pb>Cu>Zn>As>Cr;煤矸石堆积区表层土壤中,Cd的迁移性及其形态分布受外源干扰程度总体高于Pb;东、西部的Cd与东部的Pb对机体处于高暴露风险水平。研究成果可为中国煤矸石堆积区土壤重金属污染针对性防治及修复工作提供较好借鉴。
关键词:煤矸石;潜在危害评价;数理统计分析;重金属污染特征;重金属形态中图分类号:TD 167
文献标志码:A
文章编号:1672-9315(2022)05-0942-08
DOI:10.13800/j.cnki.xakjdxxb.2022.0513开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID):
Pollution characteristics and potential risk accessment of heavy metals in soil of coal gangue accumulation areas
GU Linjun,SHEN Yanjun,WANG Nianqin,SONG Shijie,NIE Wenjie
(1.College of Geology and Environment,Xi’an University of Science and Technology,Xi’an 710054,China;2.Geological Research Institute for Coal Green Mining,Xi’an University of Science and Technology,Xi’an 710054,China;3.Shaanxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Geological Support for Coal Green Exploitation,Xi’an University of Science and Technology,Xi’an 710054,China)
Abstract:The long-term accumulation of coal gangue is an important cause of heavy metal pollution in the surface soil of some mining areas in China,especially in the northern mining areas.To grasp the potential environmental hazards and pollution characteristics of heavy metal elements in the surface soil of the long-term coal gangue accumulation areas in China,mathematical statistics,heavy metal pollution evaluation and heavy metal speciation analysis methods were comprehensively used.The contents of heavy metals in coal gangue in the main coal producing areas of China were analyzed.According to the geographical distribution characteristics of coal gangue,the mobility and toxicity of common heavy metal elements in coal gangue in the surface soil were evaluated,and the heavy metal elements with outstanding potential harm to the environment in coal gangue were identified.Spatial distribution and morphological distribution characteristics of polluting elements in the surface soil of the mining area were examined.The results show that the content of Cr,Pb and Zn in Chinese coal gangue is significantly higher than that in other common heavy metal elements,and the content of heavy metals in coal gangue in the western China is generally higher than that in the eastern and central China.In coal gangues in China,the potential pollution degree of Cd,Zn,and Pb to soil is above the medium level,and the potential hazardous degree(E)of various heavy metal elements to the environment are ranked as follows:Cd>Pb>Cu>Zn>As>Cr.In the surface soil of coal gangue accumulation areas in China,the mobility of Cd and the degree of external interference to its speciation are generally higher than those of Pb.In addition,Cd in the eastern and western China and Pb in the eastern China have a higher exposure risk to the organism.The research results can provide a good reference for the targeted prevention and remediation of soil heavy metal pollution in coal gangue accumulation areas in China.
Key words:coal gangue;potential risk assessment;mathematical statistics method;characteristics of heavy metal pollution;heavy metal speciation
0 引 言煤矸石是中国生产及堆存规模第一的工业固体废弃物,年排放量约占原煤产量的10%~15%,累计积存量高达50~60亿t。在“双碳”战略背景下,煤矸石资源化利用产业得到长足发展,但存在技术、产业更新滞后,盈利困难等不足,如何有序降低煤矸石堆存量、实现大宗量循环利用仍是煤炭行业绿色低碳转型面临的重要痛点。煤矸石长期堆积形成高势能泥流型污染源,内部重金属持续释放,经运移扩散损毁水土环境,呈现隐蔽、持久、不可逆等污染特征。煤矸石长期堆积是中国部分煤矿区,特别是北方矿区表层土壤遭受重金属污染的重要成因,也是粮食主产区耕地生态红线安全的重要威胁。中国学者高度重视煤矸石堆积区土壤重金属污染问题。王兴明等采用微核试验方法对淮南北部矿区矸石山附近土壤重金属作了生态毒性评价;马骅等分析了不同PH值降水条件对矸石堆重金属浸出率的影响;丛鑫等对煤矸石堆附近土壤重金属作了潜在生态风险评价,认为Ni的生态损害性最为显著;王萍等研究了贵州省中西部矿区矸石堆存造成耕地污染问题,通过土壤重金属释放试验明确了造成污染的首要元素为Cd,在农田稻米中具有显著富集性;王延东等采用土壤基本理化指标测试手段及RAC评价方法,研究了矸石山重金属在临近最多风向土壤中的赋存特征与生态风险性。围绕煤矸石源重金属污染问题的研究重点聚焦重金属含量分布、运移规律及环境风险评价方面,但在中国地域分区格局上,对煤矸石源重金属的潜在生态风险及污染特征研究相对较少。采用数理统计方法分析不同煤炭主产区煤矸石重金属含量的地域性分布特征,通过重金属潜在危害评价方法,评估煤矸石重金属对环境的潜在污染程度,明确其中具有显著生态损害效应的种类,利用生物有效性原理,剖析这些污染元素在煤矸石堆积区表层土壤中的空间分布及形态分布特征。
1 中国煤矸石重金属元素潜在危害评价明确不同煤炭主产区潜在环境危害显著的煤矸石重金属元素,对于煤矸石源土壤重金属污染针对性防治至关重要。
1.1 煤矸石重金属含量分区统计步骤
微量元素中Cd,Pb,Cr,Hg与类金属As毒性高,Zn,Cu,Ni等元素毒性次之,优先选择毒性中等以上的元素;将半数以上取样点未测得元素含量的重金属元素去除。将取样点按东、中、西部进行分区,对各取样点煤矸石中6种常见重金属含量进行分区统计(表1)。
1.2 煤矸石重金属含量地域性分布特征中国煤矸石中Cr,Pb,Zn含量明显高于其余常见重金属含量(表1)。从煤矸石重金属含量的地域分布角度看,东部煤矸石富集Zn,中部煤矸石富集Zn,Cr,西部煤矸石富集Cr,西部煤矸石中各重金属平均含量较东部、中部更高(图1(a))。将样本总体平均值/中国土壤背景值称为潜在富集指数C,用于表征在中国土壤环境背景下,若煤矸石中重金属全部释放对土壤造成的污染程度。参照单因子污染指数法对污染系数的分级标准,中国煤矸石常见重金属元素中,对土壤潜在污染程度严重(C≥3)的有Cd(21.44)和Zn(7.08),潜在污染程度中等(2≤C<3)的是Pb(2.70),其他重金属元素对土壤潜在污染程度均在轻度以下(C<2)。
1.3 煤矸石重金属元素潜在危害性评价金属毒性系数T可表征水体对重金属敏感程度及重金属对机体亲和性,引入该指标用于综合评价土壤重金属元素的迁移性及毒性水平。将C与T的乘积记为E,用来表示煤矸石样品中某一重金属元素对土壤环境的潜在危害程度。E计算结果如图1(b)所示,中国煤矸石中各重金属元素对环境的潜在危害性排序为:Cd>Pb>Cu>Zn>As>Cr。
2 中国煤矸石堆积区土壤重金属污染特征Cd,Pb浓度超标是导致中国耕地减产的常见原因,考虑到矸石堆中这2种元素对临近土壤的潜在危害程度较高,掌握中国煤矸石堆积区表层土壤中Cd,Pb的污染特征对矿区生态恢复而言具有突出意义,有必要剖析两者在矿区表层土壤中的空间分布及形态分布特征。
2.1 土壤重金属含量空间分布特征重金属主要通过风力搬运、径流冲刷进行迁移,运移过程中重金属浓度与到煤矸石堆积中心的水平距离L呈负相关。影响因素包括:①土壤吸附作用,土壤胶体及离子对重金属吸附能力总体受到土壤物相组成及理化性质的控制,偏移现象与不同空间地理位置土质差异存在关联性;②风化迁移作用,风化煤矸石形成大量飘尘,随风力迁移沉降地表,造成重金属最大浓度位置沿最大风向发生偏移;③地形高差作用,煤矸石山为高势能泥流型堆积体,在水力冲蚀作用下重金属溶出,通过地下水、径流向下游迁移,并在沿途低洼地形中易大量沉积,出现重金属聚集现象。煤矸石中重金属进入土壤后,主要受黏土胶体吸附积聚于表层,0~40 cm為地面矿业活动造成表层土壤重金属累积的主要影响深度,土深范围内重金属浓度与土壤深度呈负相关性。40 cm以下重金属浓度变化规律各异,与重金属迁移转化性质密切相关,若40 cm深度内重金属可迁移态含量占比大幅增加,重金属将向土壤深层(>40 cm)大量富集。高硫煤矸石淋溶水呈酸性,入渗土壤后促使Cd等碱性金属向弱酸提取态转化,向下迁移扩散能力加强,进入40~60 cm深度后,因土壤含水率和有机质大幅减少,重金属迁移性降至最低,产生富集现象。在煤矸石堆积区表层土壤中重金属富集深度主要为0~40 cm,但在酸性水入渗、矿业废水灌溉等因素作用下将突破40 cm。
2.2 土壤重金属形态分布特征在对土壤中重金属形态进行分级方面,目前国际上尚无统一标准,实际测试中常用萃取方法,主要包括BCR法和Tessier法。以上述萃取方法为样本选取标准,对中国部分典型煤矸石堆积区土壤中Cd,Pb化学形态分布情况进行了统计(表2)。
需要指出:①土壤取樣深度主要为0~20 cm;②土样重金属形态测试采用ICP-OES或ICP-MS方法;③BCR法和Tessier法在重金属形态划分上的对应关系为,S对应F和F,S对应F,S对应F,S对应F,故统计数据可统一用BCR法表示。
从表2可以看出,在中国煤矸石堆积区表层土壤中Cd,Pb主要以S形态存在,平均含量都接近40%,S平均含量都超过20%,但比较S(该形态迁移性最强)对应的平均含量,Cd要比Pb大,说明表层土壤中Cd迁移性总体比Pb大。Cd各形态变异系数排序为S(83%)>S(47%)>S(37%)>S(36%),Pb的相应排序为S(80%)>S(65%)>S(53%)>S(46%),均介于10%到100%之间,两者形态含量分布属于中等强度变异。变异系数间接反映表层土壤中重金属分布的均匀程度,亦或是受到外源干扰的强烈程度,除S外其余形态变异系数Pb均高于Cd,说明中国煤矸石堆积区表层土壤中Cd的形态分布受外源干扰程度总体高于Pb。
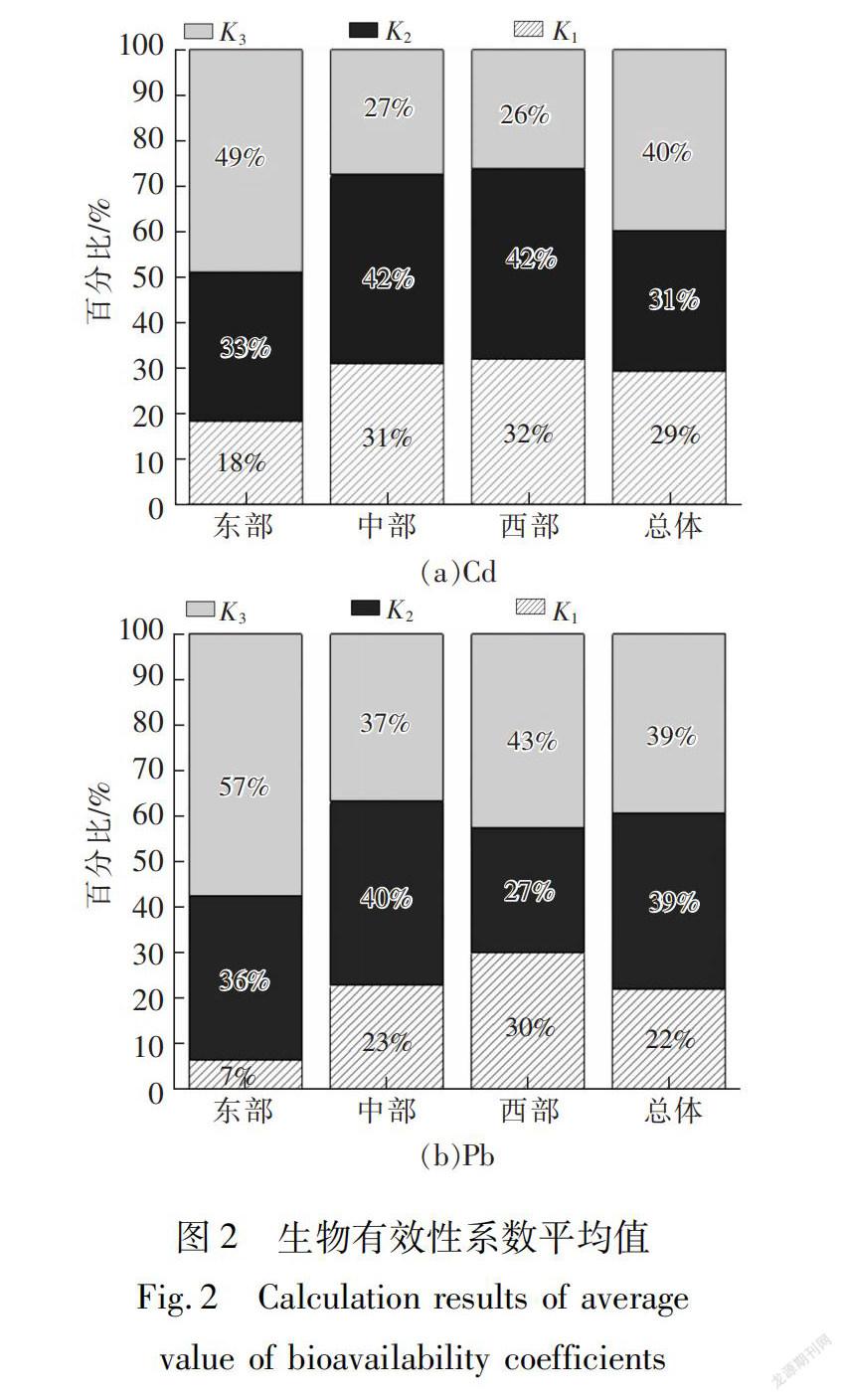
2.3 土壤重金属生物有效性特征生物有效性是评价重金属生物毒性的直接依据。BCR法4种形态的可给性规律为:S形态的重金属均易被生物体吸收利用;S,S形态的重金属需要经过一定条件转化后才能被生物体吸收利用,生态毒性中等;S形态的重金属长期稳定赋存于沉积物中,难以被生物吸收,生态毒性最小。对重金属生物有效性水平进行分级,用C(i=1~4)表示对应S形态重金属含量占总量的百分比,引入系数K(C)、K(C+C),K(C)分别表示易利用、可利用、难利用3个等级。以此为分级标准,对表2中各煤矿矸石堆积区表层土壤中Cd,Pb作生物有效性分析(图2)。
中国不同煤矸石堆积区表层土壤中,重金属的生物有效性存在显著区域性差异。在东部,Cd,Pb均存在K>K>K的规律,表现为生物难利用性;在中部,Cd,Pb均表现为生物可利用性;在西部,Cd,Pb分别表现为生物可利用性和生物难利用性。将重金属对生物体暴露风险划分为高(K<0.3)、中(0.3≤K<0.7)、低(K≥0.7)3个等级,基于这一分级标准可判断东部和西部的Cd及东部的Pb对机体处于高暴露风险水平。总体上,中国煤矸石堆积区表层土壤中,Cd,Pb表现为生物难利用性,对机体处于中等暴露风险水平。
3 结 论
1)中国煤炭主产区煤矸石中主要重金属含量存在显著的空间分布差异性特征,煤矸石中Cr,Pb,Zn含量明显高于其余常见重金属元素,东部煤矸石富集Zn,中部煤矸石富集Zn和Cr,西部煤矸石富集Cr,西部煤矸石中重金属含量总体较东、中部更高。2)煤矸石中Cd,Zn,Pb 3种潜在环境危害性突出的重金属元素对土壤潜在污染程度在中等以上,煤矸石中常见重金属元素对土壤环境潜在危害程度E大小排序为Cd>Pb>Cu>Zn>As>Cr。3)煤矸石堆积区表层土壤中重金属含量呈现水平偏移、竖向局部富集的分布特征。土壤剖面水平方向上重金属含量最大值相对堆积中心发生偏移,主要影响因素包括土壤吸附、风化迁移和地形高差。4)煤矸石堆积区表层土壤中Cd,Pb的生物有效性存在明显的区域性分布差异,比较重金属的迁移性及形态分布特征所受外源干扰程度大小。
参考文献(References):
[1]邱继生,杨占鲁,关虓,等.煤矸石陶粒混凝土微观孔结构特征及抗压强度[J].西安科技大学学报,2020,40(1):110-117.
QIU Jisheng,YANG Zhanlu,GUAN Xiao,et al.Microscopic pore structure and compressive strength of coal gangue ceramsite concrete[J].Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology,2020,40(1):110-117.
[2]邱继生,王民煌,关虓,等.钢纤维煤矸石混凝土冻融后本构关系试验研究[J].西安科技大学学报,2018,38(5):743-750.QIU Jisheng,WANG Minhuang,GUAN Xiao,et al.Experimental study on constitutive relationship after freeze-thaw of steel fiber gangue concrete[J].Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology,2018,38(5):743-750.
[3]TANG Q,LI L,ZHANG S,et al.Characterization of heavy metals in coal gangue-reclaimed soils from a coal mining area[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration,2018(MAR.5),186:1-11.
[4]王興明,张瑞良,王运敏,等.淮南某煤矿邻近农田土壤中重金属的生态风险研究[J].生态环境学报,2016,25(5):877-884.WANG Xingming,ZHANG Ruiliang,WANG Yunmin,et al.Eco-toxicity effect of heavy metals in cropland soils collected from the vicinity of a coal mine in Huainan[J].Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2016,25(5):877-884.
[5]马骅,任明强,赵宾.煤矸石毒性浸出及周边土壤环境影响分析[J].能源环境保护,2017,31(3):55-57,25.MA Hua,REN Mingqiang,ZHAO Bin.Analysis of coal gangue leaching toxicity and influence on surrounding soil environment[J].Earth and Environment,2017,31(3):55-57,25.
[6]丛鑫,雷旭涛,付玲,等.海州煤矿矸石山周边土壤重金属污染特征及生态风险评价[J].地球与环境,2017,45(3):329-335.CONG Xin,LEI Xutao,FU Ling,et al.Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soils around the gangue heap of Haizhou coal mine,China[J].Earth and Environment,2017,45(3):329-335.
[7]王萍,刘静,朱健,等.贵州省煤矿区污染农田重金属累积与迁移对生态环境的影响[J].湖北农业科学,2019,58(21):68-72.WANG Ping,LIU Jing,ZHU Jian,et al.Influence of accumulation and migration of heavy metals in polluted farmland on ecological environment in coal mining area of Guizhou province[J].Hubei Agricultural Sciences,2019,58(21):68-72.
[8]王延东,李晓光,黎佳茜,等.煤矸石堆存区周边土壤重金属污染特征及风险评价[J].硅酸盐通报,2021,40(10):3464-3471,3478.WANG Yandong,LI Xiaoguang,LI Jiaxi,et al.Heavy metal pollution characteristics and risk evaluation of soil around coal gangue stockpile area[J].Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2021,40(10):3464-3471,3478.
[9]李雪.不同影响因素下热区稻菜轮作土壤镉形态分布及其生物有效性的研究[D].海口:海南大学,2018.LI Xue.Study on the form distribution and bioavailability of cadmium in rice-vegetable rotation soil in tropical area under different factors[D].Haikou:Hainan University,2018.
[10]罗成科,毕江涛,肖国举,等.宁东基地不同工业园区周边土壤重金属污染特征及其评价[J].生态环境学报,2017,26(7):1221-1227.LUO Chengke,BI Jiangtao,XIAO Guoju,et al.Pollution characteristics and assessment of heavy metals in soil of different industry zones of Ningdong base in Ningxia,China[J].Ecology and Environmental Sciences,2017,26(7):1221-1227.
[11]代晓璐.煤矸石有益元素利用及有害元素污染分析[J].西部探矿工程,2019,31(2):151-153.Dai Xiaolu.Utilization of beneficial elements and pollution analysis of harmful elements in coal gangue[J].West-China Exploration Engineering,2019,31(2):151-153.
[12]PENG B,Li X,ZHAO W,et al.Study on the release characteristics of chlorine in coal gangue under leaching conditions of different pH values[J].Fuel,2018,217(APR.1):427-433.
[13]安茂国.兖州煤田煤矸石中敏感性元素动态淋滤特征及环境效应评价[J].山东国土资源,2019,35(7):51-57.AN Maoguo.Dynamic leaching characteristics and environmental effects assessment of sensitive elements in coal gangue of Yanzhou coalfield[J].Shandong Land and Resources,2019,35(7):51-57.
[14]XU D J,SHI L Q,QU X Y,et al.Leaching behavior of heavy metals from coal gangue under the impact of site Ordovician limestone karst water from Shandong closed coal mines,North China[J].Energy & Fuels,2019,33(10),10016-10028.
[15]HUA C Y,ZHOU G Z,YIN X,et al.Assessment of heavy metal in coal gangue:distribution,leaching characteristic and potential ecological risk[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2018(32):32321-32331.
[16]张敬凯,王春红,姚文博,等.煤矸石在动态淋溶条件下重金属的溶出特性[J].煤炭技术,2018,37(12):323-325.ZHANG Jingkai,WANG Chunhong,YAO Wenbo,et al.Charactertics of heavy metal element dissolution of coal gangue under dynamic leaching condition[J].Coal Technology,2018,37(12):323-325.
[17]秦可敏.大同矿区煤中有害微量元素的赋存特征及其环境效应[D].徐州:中国矿业大学,2019.QIN Kemin.Occurrence characteristics of hazardous trace elements in coal and their environmental effects in Datong mining area[D].Xuzhou:China University of Mining and Technology,2019.
[18]芦根玲,张博,王毅斌,等.屯兰矿煤矸石综合治理模式研究[J].现代矿业,2020,36(6):209-212.LU Genling,ZHANG Bo,WANG Yibin,et al.Study on coal gangue comprehensive treatment mode of Tunlan mine[J].Modern Mining,2020,36(6):209-212.
[19]骈炜,张敬凯,王金喜,等.矿区煤矸石淋溶对周边地下水环境污染分析[J].河北工程大学学报(自然科学版),2016,33(3):80-84,108.PIAN Wei,ZHANG Jingkai,WANG Jinxi,et al.Environmental pollution of surrounding groundwater from coal gangue leaching in mining area[J].Journal of Hebei University of Engineering(Natural Science Edition),2016,33(3):80-84,108.
[20]QI W,HUANG Y,HE H,et al.Potential pollution of groundwater by dissolution and release of contaminants due to using gangue for backfilling[J].Mine Water and the Environment,2019,38(2):281-293.
[21]劉旭.淮南潘集采煤沉陷区重金属分布赋存及生物累积特征研究[D].合肥:安徽大学,2019.LIU Xu.Chemical forms and bioaccumulation characteristics of heavy metals in subsidence area of Panji coal mining in Huainan,Anhui province,China[D].Hefei:Anhui University,2019.
[22]王旭东.皖北矿区固体废弃物堆积地微量元素环境地球化学研究[D].合肥:中国科学技术大学,2019.WANG Xudong.Environmental geochemistry of trace element in solid waste dumping area of Wanbei coalfield[D].Hefei:University of Science and Technology of Chinan,2019.
[23]王丽艳,刘光正,王小东,等.江西省主要产煤区煤矸石堆特性研究[J].南方林业科学,2015,43(3):43-46.WANG Liyan,LIU Guangzheng,WANG Xiaodong,et al.Research on characteristics of coal gangue piles in main coal-produced region of Jiangxi province[J].South China Forestry Science,2015,43(3):43-46.
[24]廖四海,杜勇立,刘振华,等.煤矸石堆放地周围土壤中重金属的污染特性及评价[J].环境工程,2014,32(8):118-120,126.LIAO Sihai,DU Yongli,LIU Zhenhua,et al.The pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in gangue piling site to surrounding soil[J].Environmental Engineering,2014,32(8):118-120,126.
[25]LI W P,SUN Y Q,YAO M,et al.Release activity and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals incoal gangue of Hancheng,China[J].International Journal of Energy and Power Engineering,2015,4(5):304-310.
[26]徐畅,张恩,师卓璇,等.甘肃阿干煤矸石的矿物组成与演变[J].矿物岩石,2018,38(2):114-119.XU Chang,ZHANG En,SHI Zhuoxuan,et al.Mineralogical composition and evolution of gangue in Agan area of Gansu province[J].Mineralogy and Petrology,2018,38(2):114-119.
[27]高琦.鄂尔多斯矿区煤矸石特征研究及综合利用策略[D].南京:东南大学,2019.GAO Qi.Study on characteristic and comprehensive utilization strategy of coal gangue in Ordos mining area[D].Nanjing:Dongnan University,2019.
[28]YANG L,SONG J,BAI X,et al.Leaching behavior and potential environmental effects of trace elements in coal gangue of an open-cast coal mine area,inner Mongolia,China[J].Minerals,2016,6(2):50.
[29]周辰昕,李小倩,周建伟.广西合山煤矸石重金属的淋溶实验及环境效应[J].水文地质工程地质,2014,41(3):135-141.ZHOU Chenxin,LI Xiaoqian,ZHOU Jianwei.Leaching experiment and environmental effect of heavy metals of coal gangue in Heshan mining area,Guangxi province[J].Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2014,41(3):135-141.
[30]孙亚乔,段磊,王晓娟,等.煤矸石酸性水释放对土壤重金属化学行为的影响[J].水土保持学报,2016,30(1):300-304,314.SUN Yaqiao,Duan Lei,Wang Xiaojuan,et al.Acid water of coal gangue piles on chemical behavior of heavy metals in soil[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2016,30(1):300-304,314.
[31]陈莉薇,陈海英,武君,等.利用Tessier五步法和改进BCR法分析铜尾矿中Cu、Pb、Zn赋存形态的对比研究[J].安全与环境学报,2020,20(2):735-740.CHEN Liwei CHEN Haiying WU Jun,et al.Comparative study on speciation of Cu,Pb and Zn from mining tailings via Tessier 5-step sequential extraction and improved BCR method[J].Journal of Safety and Environment,2020,20(2):735-740.
[32]LI H,JI H.Chemical speciation,vertical profile and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in soils from coal-mine brownfield,Beijing,China[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration,2017,183(DEC.):22-32.
[33]秦胜,田莉雅,张剑.兖州矿区矸石山与周围土壤中微量元素形态分析[J].中国煤炭,2010,36(10):125-127,140.QIN Sheng,TIAN Liya,ZHANG Jian.Speciation analysis of trace elements in the waste piles and surrounding soil in Yanzhou mine field[J].China Coal,2010,36(10):125-127,140.
[34]劉玥,乔栋,牛宏,等.煤矿周边土壤重金属形态特征及迁移转化规律[J].中国煤炭,2016,42(3):115-120.LIU Yue,QIAO Dong,NIU Hong,et al.Morphological characteristics and migration and transformation rule of heavy metals in soil around the coal mine[J].China Coal,2016,42(3):115-120.
[35]庞少鹏.煤矿区土壤-作物系统重金属生物有效性研究[D].焦作:河南理工大学,2015.PANG Shaopeng.The bioavailability of heavy metals in soil-crop system in coal-mining region[D].Jiaozuo:Henan Polytechnic University,2015.
[36]张锂.黄土高原地区煤矿土壤重金属污染调查研究及生态风险评价[D].兰州:西北师范大学,2007.ZHANG Li.Investigation on heavy metal contamination in soils and risk assessment of eco-environment Honggu coal-mining area of Lanzhou,Loess Plateau in northwest China[D].Lanzhou:Northwest Normal University,2007.
[37]吴先亮,黄先飞,李朝婵,等.黔西煤矿区土壤重金属污染水平及其形态[J].水土保持研究,2018,25(6):335-341.WU Xianliang,HUANG Xianfei,LI Chaochan,et al.Soil heavy metal pollution degrees and metal chemical forms around the coal mining area in western Guizhou[J].Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2018,25(6):335-341.
