COVID-19 incidence and local ozone level:is there any association?
2022-10-30
Dear Editor,
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a new coronavirus respiratory infection.This new emerging infection disease has already caused more than 30,000,000 infected cases worldwide since its f irst appearance in late 2019.The eff ect of underlying metrological background on the incidence of the COVID-19 is an interesting issue but little is known on this issue.1In fact,the eff ect of environmental gas on the respiratory infection is an important issue in public health.2Focusing on local environmental gas in atmosphere,the association with local COVID-19 incidence has never been assessed.
We analyzed the data to assess the relationship between COVID-19 incidence and local ozone level in a tropical country which is the second country of the world getting aff ected by the new emerging COVID-19.The primary data on incidence of COVID-19 was derived from local Public Health Ministry and the primary data of local ozone was derived from Department of Pollution Control of Thailand.The studied area in the present study is the area covering 13 provinces (Payao,Phare,Uttaradit,Pitsanuloke,Pichit,Nongbualumpu,Chaiyaphum,Mahasarakham,Roiet,Yasothorn,Sakonnakorn,Beungkarn and Kalaasin) in rural northern and northeastern region areas of Thailand which is not a destination for international tourists.In the present study,only data on non-local transmission COVID-19 cases were used for further analysis.The data were collected between March and June 2020,when the COVID-19 outbreak started in the studied area following its f irst appearance in China.According to the study,the scatterplot shows the relationship between COVID-19 incidence and ozone level(Figure 1).There was no signif icant correlation (r= 0.076,P= 0.805) between COVID-19 incidence and local ozone level in the studied area.
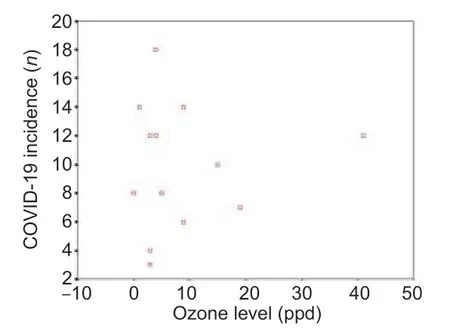
Figure 1:Relationship between coronavirus disease 2019 (COVlD-19)incidence and local ozone level.
The association between ozone and COVID-19 is still poorly understood.The positive eff ect of ozone therapy on the COVID-19 infection has been reported.3The cytoprotection of ozone may attribute to the therapeutic eff ect of ozone on COVID-19 infection.3,4In the present report,we assessed the interrelationship between environmental ozone level and COVID-19 incidence.Interestingly,there was no association between them.In some areas with high ozone level still have high incidence (number) of COVID-19 cases.This might not support that environmental ozone background can have protective eff ect against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection.This preliminary observation may provide evidence for further investigations on this issue.
Beuy Joob*,Viroj Wiwanitkit
Medical Academic Center,Bangkok Thailand (Joob B)
Department of Community Medicine,Dr DY Patil University,Pune,India (Wiwanitkit V)
*Correspondence to:Beuy Joob,MD,beuyjoob@hotmail.com.
orcid:0000-0002-5281-0369 (Beuy Joob)
doi:10.4103/2045-9912.326005
How to cite this article:Joob B,Wiwanitkit V.COVID-19 incidence and local ozone level:is there any association? Med Gas Res 2022;12(2):72.
Copyright license agreement:The Copyright License Agreement has been signed by both authors before publication.
Plagiarism check:Checked twice by iThenticate.
Peer review:Externally peer reviewed.
Open access statement:This is an open access journal,and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License,which allows others to remix,tweak,and build upon the work non-commercially,as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
杂志排行
Medical Gas Research的其它文章
- Potential therapeutic effect of oxygen-ozone in controlling of COVID-19 disease
- Perioperative melatonin in COVID-19 patients:benefits beyond sedation and analgesia
- Effects of Iranian Polyherbal Syrup (Zufa syrup)on oxygen saturation and clinical symptoms in suspected patients with COVID-19:a triple-blinded,randomized,placebo-controlled trial
- Ozone gas applied through nebulizatıon as adjuvant treatment for lung respiratory dıseases due to COVID-19 infectıons:a prospective randomized trial
- Prediction of diagnosis and prognosis of COVID-19 disease by blood gas parameters using decision trees machine learning model:a retrospective observational study
- Acute asthma exacerbation after SARS-CoV-2 vaccine(Sinovac®):a case report
