Application of adipose-derived stem cells in treatment of neurodegenerative diseases: A review
2022-09-19FangFangLiuHaoFeiFanQingManLiFengGuoXiNanYiHaiYingZhang
Fang-Fang Liu, Hao-Fei Fan, Qing-Man Li, Feng Guo, Xi-Nan Yi, Hai-Ying Zhang
Hainan Key Laboratory for Research and Transformation of Tropical Brain Science, Science Research Center of Hainan Medical University,Department of Anatomy, Hainan Medical College, Haikou 571199, China
Keywords:Neurodegenerative diseases ADSCs AD PD
Neurodegenerative disease is a disease that involves age. It is characterized by loss of neurons, leading to a gradual decline in brain function. The clinical symptoms are cognitive decline or loss of motor function. Affected by the aging of the population,the quality of life of patients has seriously declined, which has increased the burden on medical systems around the world[1]. AD is a neurodegenerative disease related to age and cognitive deficits.Other diseases of this type mainly affect the motor system, including PD, multiple sclerosis (MS) and spinocerebellar ataxia[2].ADSCs have proliferation and multi-differentiation potential in vitro. After induction and differentiation, ADSCs can express neuronal star markers (Nestin, MAP2, β-tubulin III) and glial cell star markers (GFAP, NG2, p75 NGF Receptor)[3]. The ADSCs implanted in the human body have no adverse side effects such as tumorigenicity, chromosomal abnormalities or immune rejection[4].ADSCs is a potential source of cells and has attracted many attentions in recent years. In this review, we mainly summarize the research progress of ADSCs in neurodegenerative diseases,including AD, stroke, PD, etc., in order to provide reference for the clinical application of stem cell therapy.
1. Biological characteristics of ADSCs
ADSCs is a kind of cells that are convenient to obtain materials,sufficient sources, easy to digest, simple to separate and incubate,and do not involve ethical safety issues. They are used to treat central nervous system diseases (CNS), such as AD, HD, and PD[5].ADSCs have strong self-reproduction ability, fast proliferation and renewal, multi-directional differentiation, genetic stability and other characteristics[6]. So far, many experimental evidences about ADSCs have shown that, under appropriate conditions, ADSCs can not only selectively differentiate into mesenchymal cell lines in vitro, but can also be induced into endoderm and ectoderm cell lines[7]. The regeneration characteristics of ADSCs include:secretion of repairing growth factors, multi-lineage differentiation ability, activation of immune cells, and repair of damaged areas[8].ADSCs can be differentiated into bone, fat and cartilage, with immunosuppressive function[9]. Therefore, ADSCs have potential application value in the treatment of CNS diseases in tissue repair and regeneration.
2. Paracrine function of ADSCs
ADSCs secrete different types of factors, enzymes, hormones,etc. (Table 1). The expression of ADSCs protein is affected by the local internal environment, and the paracrine function of ADSCs has practical value in tissue regeneration applications[10].VEGF, HGF and TgF-β can promote vascular wall formation and wound healing, potentially promoting the growth of new tissues[10-12]. Factors such as prostaglandin E2 and IL-10 have immunosuppressive effects, which can reduce the activation of dendritic cells and helper T cells, thereby reducing inflammation and the formation of granular tissue[13]. GM-CSF, IL-6, IL-7 and TgF are pro-inflammatory cytokines secreted and released by ADSCs,which can attract macrophages and help remove cell debris[14-18].Studies have shown that Leptin secreted by ADSCs in co-culture can accelerate endothelial cell migration, vascular wall formation, and tissue angiogenesis [19]. In addition, the secretion factors of ADSCs cultured in vitro have also been shown to reduce cell apoptosis,cell fibrosis and cell hypertrophy[10-12]. In animal models, ADSCs intervention has a certain protective effect on kidney injury, stroke,myocardial infarction, and peripheral nerve damage[20].
3. Multi-line differentiation function of ADSCs
A large number of studies have shown that ADSCs are similar to MSCs and have the ability to differentiate into a variety of cells from mesenchymal (fat, bone, cartilage, muscle, nerve) and nonmesenchymal (blood vessels), indicating that adipose tissue does contain pluripotent cells[11]. In particular, in terms of muscle differentiation, there is evidence that ADSCs have the ability to differentiate into contractile cells with characteristics of striated muscle cells or cardiomyocytes[20].
After ADSCs were cultured in RPMI for 2 weeks, 20%~30% of the cells became larger and their morphology changed. Similarly,after three weeks of exposure to the conditioned medium of rat cardiomyocytes, ADSCs expressed cardiomyocyte markers,including sarcomere α-actin, cardiac troponin I, and connexin-43 (CX-43); ADSCs are morphologically differentiated into ventricular-like, atrial-like, and pacemaker-like cells, which express CX-43 spontaneously, and are accompanied by pulse-triggered action potentials[20]. In addition, differentiated cells express cardiac transcription factor NKX 2.5, cardiac transcription regulator GATA 4 and myocyte promoting factor MEF-2C, cardiac structural protein,atrial natriuretic peptide, myosin light chain-2 ventricular and atrium expression, and bone markers Myosin and smooth muscle actin are not expressed, but they express myosin heavy chain, light chain-2 ventricles and atria, and atrial natriuretic peptide[27-28]. Other studies have shown that ADSCs are directly transplanted as a monolayer cell sheet to the heart of infarcted mice, and it is found that the graft gradually grows to form a thick layer containing new blood vessels,undifferentiated cells and cardiomyocytes[25].
In addition, ADSCs can also play an important role in immune regulation and damaged tissue repair. ADSCs inhibit the proliferation of activated lymphocytes through cell-cell binding and paracrine signals[13,29]. In vivo, ADSCs amplification showed immunosuppressive properties in mice, reducing graftversus-host disease, colitis, and arthritis[29]. In an intraperitoneal injection of ADSCs Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin A plus lipopolysaccharide-induced fatal shock in mice, ADSCs significantly reduced the severity of histopathological inflammation and improved the survival rate [20]. In another study, using ADSCs to treat severe sepsis model mice, it was found that the degree of infiltration ofinflammatory cells in different target organs was reduced, and the level of serum inflammatory mediators was reduced[30].
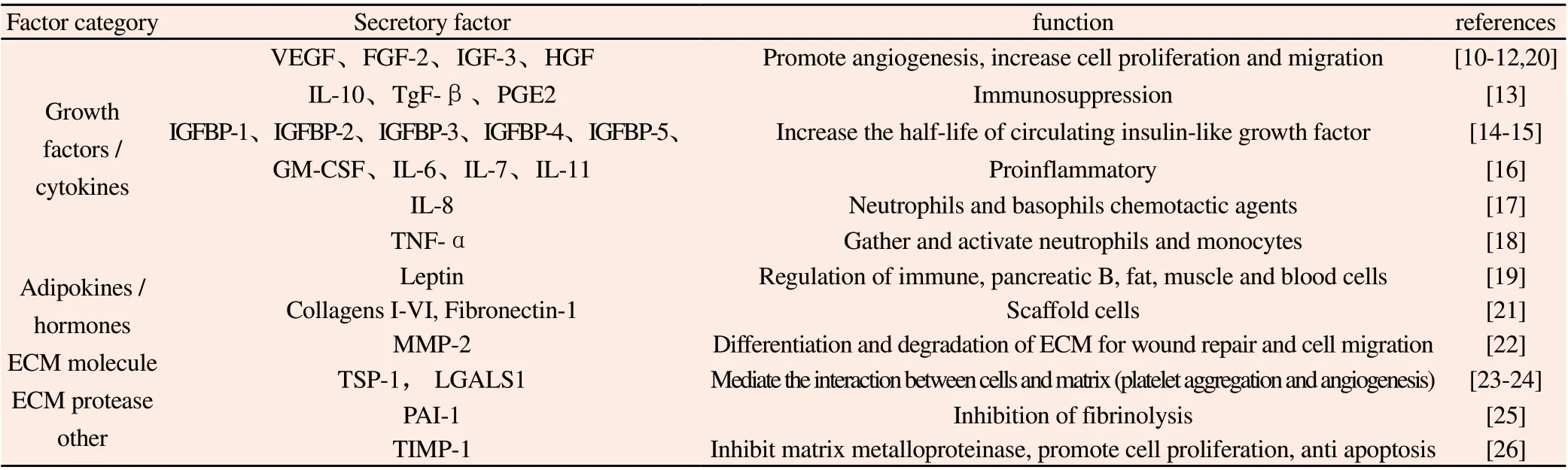
Table 1 secretory factors of ADSCs related to regeneration
4. The effect of ADSCs on neurodegenerative diseases.
ADSCs are stem cells screened out by adipose tissue gradient centrifugation. They are popular research objects for their pluripotency and ability to differentiate into multiple tissue types,and have similar immunomodulatory properties to MSCs from other sources[9]. Due to its biological characteristics, ADSCs can be considered for cell therapy and nerve regeneration.
4.1 The effect of ADSCs on AD
New strategies for stem cell therapy to treat AD are worthy of in-depth study. AD is a disease characterized by cerebral cortex atrophy, amyloid plaque deposition, and cognitive decline. There are currently no effective drugs and methods for the treatment of AD[2].Studies have reported that in human ADSCs (hADSCs) intervention in AD mouse model Tg2576 transgenic (Tg) mice, it was found that the learning and memory functions of Tg mice were significantly improved, Aβ deposition was reduced, and neuropathological symptoms were effectively alleviated[31-32]. In addition, in the brains of Tg mice transplanted with ADSCs, the proliferation ability of endogenous neural stem cells increased, the state of synapses and dendrites became better, and the expression of IL-10 and VEGF in Tg mouse tissues was up-regulated[32]. In 2013, Tuo[33] and other studies found that transplantation of ADSCs into the brain can activate microglia and improve neuropathological defects in AD mice. Transplantation of ADSCs can reduce Aβ deposition in the brain cavity of APP/PS1 mice and restore learning and memory.After transplantation of ADSCs, the microglia of the hippocampus and cortex were activated. The expression levels of pro-inflammatory factors were decreased, and the expression levels of antibody degrading enzymes and Neprilysin were increased. In 2020, Ma X[34] and other studies confirmed that extracellular vesicles (ADSCsduced EVS, EVS) derived from ADSCs can attenuate neuronal damage in AD mice, promote nerve regeneration, and strengthen memory function; the possible mechanism is After ADSCs are administered through the nasal cavity, EVS quickly and effectively reaches the brain and mainly accumulates in the CNS. It has a strong protective effect on neuronal toxicity induced by Aβ oligomers or glutamate, and effectively improves APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Nerve damage in the whole brain area significantly increases the number of new neurons and inhibits memory impairment in APP/PS1 mice;at the same time, EVS also reduces the deposition of Aβ and the activation of microglia to a certain extent. Therefore, ADSCs have great potential application value for the treatment of AD, and provide new treatment options for neuroprotection, nerve regeneration and slowing the decline of AD cognitive function.
4.2 The effect of ADSCs transplantation on stroke
Stroke is a neurological deficit syndrome caused by the rupture or blockage of cerebral blood vessels and blood circulation in the brain,which causes a series of corresponding neurological dysfunctions in the brain. Lack of effective treatment[35]. Studies have shown that in a rat model of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO),intravenous injection of autologous ADSCs found that the range of cerebral infarction, apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammatory response were inhibited, and neurological function was gradually restored[36]. In 2011, Yang[37] et al. studied the effect of rat ADSCs transplantation to treat cerebral ischemia in rats, with a high degree of brain function recovery and reduced cerebral hemisphere atrophy.They also found that ADSCs isolated from rat adipose tissue can express Nestin after induction and differentiation. , MAP2 and GFAP and other factors. In 2014, Du[38] et al. injected ADSCs intravenously in MCAO rat model, which resulted in ischemic brain injury and reduced infarct volume. In 2019, Gong[39] and other studies found that the protective effect of intravenous transplantation of hADSCs on cerebral ischemic injury in rats may be improved by stimulating the expression of neuroprotective IL-6 and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). . Many studies have proved the positive protective effect of ADSCs on cerebrovascular injury[40], so ADSCs is an effective method for the treatment of stroke.
4.3 ADSCs and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
ALS is a neuron disease caused by injury of the spinal cord, upper motor cortex, and lower brainstem motor neurons. Clinically, it often manifests as muscle weakness, fasciculation, and bulbar palsy.There is still no effective means for this disease[41], and ADSCs are considered to be a potentially useful drug in the treatment of this type of disease, including ALS. Studies have shown that ADSCs can differentiate into neuronal cells, can regulate the phenotype of ALS cells, reduce the accumulation of superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1),reduce the level of intracellular SOD1, and protect mitochondrial function[42]. After intravenous injection of ADSCs in ALS model mice, the expression levels of neurotrophic factors (such as BDNF,IGF and VEGF) in the spinal cord increased, apoptosis decreased,and glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor and basic fibroblast growth factor were significantly up-regulated , Indicating that ADSCs may play a role in neuroprotection and symptom relief[2]. ADSCs treated Tg mice (SOD1-G93A mutant) and found that the number of lumbar motor neurons in the mice increased, and the levels of GDNF and BFGF increased[43]. A recent study by Epperly[44] et al. suggested that transplantation of ADSCs in Tg mice can exert neuroprotection by producing cell/growth factors.
4.4 ADSCs and Huntington's disease (HD)
Huntington’s disease is a rare hereditary disease caused by an autosomal dominant mutation, which results in the abnormal amplification of three nucleotides (CAG) in the Huntington gene,loss of spinal neurons, and delayed neurodegenerative disease of basal ganglia. It is characterized by deficits in muscle coordination,cognitive decline, and mental disorders[45]. The clinical treatment of Huntington's disease includes drugs and adjuvant treatments, which can only relieve the symptoms and cannot achieve a complete cure.Studies have shown that when ADSCs are transplanted into YAC128 Huntington's disease transgenic mice, the paracrine protective factors can prevent cell apoptosis and improve behavioral defects in animal models[46]. Therefore, ADSCs may slow down the disease progression of HD animal models and may become a potential treatment for HD.
4.5 ADSCss and Parkinson's disease (PD)
PD is caused by the degeneration of dopamine neurons produced in the dense part of the substantia nigra. Its hallmark features are the accumulation of α-synuclein, loss of dopaminergic neurons,damage to the connecting pathways between the basal ganglia,cerebellum and cortex, and low excitability in the areas of the motor and premotor cortex[47]. Studies have shown that ADSCs conditioned medium can block 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-induced neurotoxicity and free radical generation in rat midbrain and cerebellum neurons [48], and can directly reduce H2O2-induced nerves Yuan died[49]. Studies have shown that implantation of ADSCs into 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)unilaterally damaged PD rhesus monkey model can protect damaged neurons and replace apoptosis. The role of apoptotic neurons[50].
4.6 ADSCs and Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
SCI is caused by continuous injury of the spinal cord, resulting in loss of function of damaged neurons[51]. The induced ADSCs were transplanted to the SCI injury, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) type myelin sheath was formed on the CNS axon.Immediately after spinal cord injury, mixing ADSCs extract(ADSCs-E) and Matrigel directly into the spinal cord can also reduce apoptosis, astrocyte proliferation and reduce myelination[52].ADSCs can be used as seed cells for the treatment of SCI.Chondroitinase ABC (ChABC) can differentiate chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan in the glial scar formed after spinal cord injury, so that stem cells can penetrate the scar and accelerate the recovery of nerve performance[53] . In 2016, Wu[53] and other studies showed that ChABC-ADSCs constructed by lentiviral vector transfection can stably express ChABC, and the expression of ChABC significantly enhances the migration ability of ADSCs. In 2020, Menezes[54]and other studies found that after balloon compression injury in rats, injection of human adipose tissue-derived stromal stem cells(hADSCs) or their culture medium can induce angiogenesis around the injury site and promote spinal cord injury tissue repair.
4.7 ADSCs and multiple sclerosis (MS)
MS is a type of inflammatory disease of the cerebrospinal cord[55].The study found that the use of ADSCs and interstitial blood vessel scores in the animal model of the disease showed that experimental autoimmune encephalitis (EAE) demyelination and pathological features were reduced, EAE was improved, and ADSC significantly improved motor function and relief Inflammation occurs[56].
5. Prospect
At present, ADSCs therapy has broad application prospects,especially in the treatment of cognitive dysfunction such as AD,stroke, and PD. Using the proliferation and multi-differentiation ability of ADSCs to induce differentiation into nerve cells, immune cells, cardiomyocytes, etc., applied to neurodegenerative diseases may be a potentially effective treatment method. However, the molecular mechanism of ADSCs intervention in the treatment of neurological diseases such as AD and stroke is not yet clear. How to ensure the high-efficiency secretion of protective factors after its induction is worthy of further study. In short, ADSCs may be an effective means to treat neurodegenerative diseases such as AD.
Author's contribution
Fangfang Liu is the main author of the review, completing the collection, analysis of relevant literature and writing of the first draft of the paper; Haofei Fan, Qingman Li, Feng Guo participate in the analysis and collation,Xinan-Yi is the project designer, Haiying Zhang is the project leader, guiding the writing of the paper. All authors read and agree to the final text.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Physiological and pharmacological functions of G protein coupled receptor 124: A review
- Clinical efficacy of Chinese herbal compound in the treatment of infertility with kidney deficiency: A meta-analysis
- Analysis of hyperuricemia in physical examination population of a hospital in Haikou
- Berberine protects diabetic nephropathy rats by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress
- Effect of TSG on tau phosphorylation via GSK-3β pathway
- Effect of Simiao Yongan Decoction on atherosclerotic carotid plaque in ApoE-/- mice via antagonizing Ox-LDL lipid metabolism pathway
