Effect of TSG on tau phosphorylation via GSK-3β pathway
2022-09-19WanYingMengChaoYuLiuXiaoYanXiaYanBingLiZhenZhongLiXiaoYingZhuYanHuaLiaoZhongShiHuang
Wan-Ying Meng, Chao-Yu Liu, Xiao-Yan Xia, Yan-Bing Li, Zhen-Zhong Li, Xiao-Ying Zhu, Yan-Hua Liao, Zhong-Shi Huang✉
1. College of Pharmacy, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, China
2. College of Basic Medicine, Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise 533000, China
3. College of Pharmacy, Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise 533000, China
4. College of Clinical Medicine, Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise 533000, China
Keywords:Tetrahydroxy stilbene glycoside Alzheimer's disease GSK-3β PI3K PKC PKB PKA
1. Introduction
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a degenerative disease of the central nervous system occurring in the elderly. The pathological manifestations include senile plaques (SP), neurofibrillary tangles(NFTs), progressive synaptic damage and neuron loss. According to the World Alzheimer's Disease Report 2019 [1], more than 55 million people worldwide were living with dementia in 2019, and this number is expected to increase to 152 million by 2050. The important role of GSK-3β protein kinase in the field of medical biology has been verified in domestic and foreign literature[2-4],and has been widely studied as a therapeutic target in cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. TSG is one of the effective chemical constituents of Fallopia multiflora and its main component, TSG,have a good effect on improving models of central neurodegenerative diseases (Parkinson's disease, vascular dementia, senile dementia,etc.)[5-6], and the mechanism of its improvement has been found to be related to some biological signaling pathways[7-8]. In previous experiments, GSK-3β was found to be elevated in the brain tissue of animal models of dementia. In addition, the learning and memory ability of dementia animals were improving and the expression level of GSK-3β were decreasing after the intervention of TSG,so we were speculated that TSG could regulate the expression level of GSK-3β to intervene in the process of Tau protein phosphorylation[9]. Therefore, this study mainly focused on GSK-3β factor, and further explored the mechanism of TSG intervening in Tau phosphorylation through GSK-3β pathway by observing GSK-3β associated signal pathways and influencing factors. In this study, we used the 24-month old rat model and Aβ25-35to establish a dementia model. In domestic and foreign studies, Elderly rats are rarely used in the study. This study provides a research basis for the development of effective and low-toxicity anti-dementia drugs and the establishment of a new effective dementia model.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
2.1.1 Animals
Male SD rats (weight 680-720g, 24 months old) were supplied by Changsha Tianqin Biotechnology Co. LTD (Qualified number:SCXK2019-0014). Bred in YouJiang Medical College for Nationalities SPF animal laboratory. The experiment was carried out with the approval of the Ethics Committee of YouJiang Medical College for Nationalities (Approval No. 2020101501).
2.1.2 Drugs and reagents
TSG(Chengdu Keloma Biotechnology Co., LTD, Batch No.CHB180810); Aβ25-35(SIGMA, Batch No. 118M4892V);Xylazine hydrochloride(Jilin Province Huamu Animal Health Products Co. LTD, Batch No. 190913); HE test kit(Solarbio, Batch No.:20200508); BCA test kit (Biyuntian Biotechnology Co., LTD,Batch No. 070618181227); DAB(Beijing Zhongshan Jinqiao Biotechnology Co., LTD, Batch No. 2010A1125); Universal two-step immunohistochemistry kit(Beijing Zhongshan Jinqiao Biotechnology Co., LTD, Batch No. 2009B1118); TRIZOL(ThermoScientific);Extremely sensitive chemiluminescence reagent(Affinity, Batch No.1927b02); 10% Polyacrylamide Gel Rapid preparation Kit(Shanghai Yase Biotechnology Co., LTD, Batch No. 03512300); Rabbit antimouse PI3K polyclonal antibody(Affinity, Batch No. 26k7234);Rabbit anti-mouse GSK-3β polyclonal antibody(Affinity, Batch No. 24c3033); Rabbit anti-mouse PKA polyclonal antibody(Affinity,Batch No. 15j0929); Rabbit anti-mouse tau polyclonal antibody(Affinity, Batch No. 18s9967); Rabbit anti-mouse P-tau polyclonal antibody(Affinity, Batch No. 75f5235); IgG(Proteintech,Batch No. 20000174); Rabbit anti-mouse PKC polyclonal antibody(Affinity, Batch No. 17e3745); Rabbit anti-mouse PKB polyclonal antibody(Affinity, Batch No.:34d5362); Rabbit antimouse GAPDH polyclonal antibody(Affinity, Batch No. 62u0922).
2.1.3 InstrumentZH-B/S Mouse brain stereotaxometer(Anhui Zhenghua Biological Instrument Equipment Co., LTD); ZH-KES micro-injection pump(Anhui Zhenghua Biological Instrument Equipment Co.,LTD); HistoCore PEARL automatic programmable dehydrator;EG1150C automatic embedding machine(LEICA); SpactraMax i3x multimode Reader(Molecular Devices); Neofuge15R high speed freezing centrifuge; Tanon-5200 multi automatic chemiluminescence image analyzer; LightCycler96 real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction system.
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Establish an animal modelSD rats were weighed and anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of xylazine hydrochloride (8mg·kg-1). The rats were fixed in the middle of the two slides with the fixator and ear rod, and the nasal ring pressure was pressed tightly. The shaving skin on the top of the head of rats was disinfected with 75% alcohol. Made a 3cm incision along the sagittal suture with surgical blade, dissection of the subcutaneous fascia to expose the parietal bone, remove fascia and muscle from the skull surface with forceps. Using rat anterior halogen as the origin, the hippocampal region (posterior fontanelle 3.5mm, lateral midline 2.0mm) was selected according to the stereotaxic map of rat brain.Use a dental drill to drill holes on both sides, micro-injector is vertically inserted into 2.7mm.The Aβ25-35was incubation at 37℃ for 1 week, 5μg·μL-1Aβ25-35solution was slowly injected into both ventricles at a rate of 0.2μL·min-1with a volume of 1μL. After the injection, the needle was left for 5 min to avoid drug spillover [10-12].
2.2.2 Screening of animal models of dementia
Fifteen young rats aged 3 months were used as training subjects.On day 1, the rats were used to swim freely for 4 times, 2 min each.From the second day, the water maze experiment was conducted four times a day in different water entry directions, and the escape latency was recorded. Those who failed to find the end point within 2 minutes were calculated as 2 minutes. After the end of the experiment for 4 days, the average escape latency of young rats was obtained. A certain number of elderly rats in the blank group, the sham operation group and the elderly rats injected with Aβ25-35were also selected. The operation method was the same as before, and the average escape latency of each elderly rat was recorded.
The mean escape incubation period of young rats plus one times standard deviation was taken as the lower standard, the mean escape incubation period of young rats plus two times standard deviation was taken as the upper standard. Use this way to rule out born with dementia’s rats and which rats failure to build up dementia model.Totally, we got 6 elderly rats in blank group, 6 elderly rats in sham operation group, and 24 elderly rats with dementia model were selected for subsequent experimental operations[13-14].
2.2.3 Animal grouping and administration
Thirty-six male SD rats aged 24 months were randomly divided into normal group, sham operation group, model group, TSG lowdose group, TSG medium-dose group and TSG high-dose group,with 6 rats in each group. After Aβ25-35hippocampal modeling,Morris water maze screening, the normal group, sham operation group, model group (normal saline, 30 mL·kg-1), TSG low-dose,medium-dose and high-dose groups (TSG, 0.033, 0.1, 0.3 g·kg-1)[9], each group was given orally once a day. Continuous 4 weeks [15].
2.2.4 Hematoxylin-eosin staining
Each group rats were anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection of toluene thiazide at 8 mg·kg-1. The skull was opened with orthopedic forceps to expose the rat brain tissue, and the left and right hippocampal tissues were removed with forceps. The left brain tissue with hippocampus was fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 24 h and embedded in paraffin. The section thickness was set to 4μm and the slices were baked at 70℃ for 2h. Paraffin sections were routinely dewaxed and placed in distilled water. The sections were stained with hematoxylin dye for 3min, and the excess dye was gently washed with a washing bottle. The sections were differentiated in alcohol hydrochloride for 2-3s. After washing, the sections were stained in 1% eosin aqueous solution for 40s, and then washed. Gradient alcohol dehydration, sealing. The pathological morphological changes of hippocampal CA1 region were observed under light microscope, and the image J software was used to conduct automatic cell counting operation for the selected observation region.
2.2.5. Real-time PCR
Used Real-time PCR to detect the mRNA expressions of GSK-3β, PKA, PI3K, PKC and PKB in the hippocampus of rats.The brain tissue was exposed with orthopedic forceps, and both sides of the hippocampus were taken. The right hippocampus of rats was operated according to the instructions of the Trizol kit, and total RNA in the hippocampus was extracted.Used the ultraviolet detector to concentration and purity of RNA.When the OD260/OD280was in the range of 1.7-2.0 can be used for reverse transcription.Used the cDNA reverse transcription kit, let the RNA transform cDNA.Primer sequence synthesis was completed by Wuhan Jinkailui Bioengineering Co., LTD. GAPDH as internal reference, used the 2-ΔΔCtto calculate the Relative expression of mRNA.Primer sequences are shown in Table 1

Table 1 Primers sequence of PCR
2.2.6 Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry was used to detect the expression of PKC and PKA proteins in hippocampal and cerebral cortex of rats. Prefrozen paraffin blocks were sectioned with thickness of 4μm and baked at 70℃ for 2h. After conventional dewaxing, paraffin sections were dyed in distilled water. The sections were placed into boiling citric acid antigen repair solution and repaired for 2 min. Each section was added with one drop or 50μ L 3% hydrogen peroxide and incubated at room temperature for 10 min to block the peroxidase activity. Sections were added with 50μL PKC (diluted at 1:100) and 50μL PKA (diluted at 1:150), and incubated at 4℃ overnight. Each section was added with 50μL secondary antibody in the universal immunohistochemical kit, and incubated at room temperature for 15 min. DAB reagent was used for color rendering, and the reaction was observed under microscope. The reaction was terminated at appropriate time, washed with distilled water, after mild redyeing with hematoxylin for 30s, rinse with running water. Gradient alcohol dehydration, xylene transparent, neutral gum sealing, microscopy observation of hippocampal CA1 protein expression level.Image Pro Plus software was used to analyze the immunohistochemical sections, and the ratio of the positive expression optical density value of the observation area to the area of the observation area was the average optical density value, which was used as the expression form of the relative expression of PKA and PKC proteins for data analysis.
2.2.7 Western blotThe expression of GSK-3β, P-Tau, Tau, PI3K and PKB proteins in brain tissues was detected by Western blot. The right hippocampus of rats was added to the prepared protein lysate (RIPA lysate:PMSF) in proportion (150uL protein lysate per 20mg tissue).Phosphatase inhibitor =100: 1: 1) ice lysis for 30min; After the cracking, the supernatant in the tube was collected by a high-speed refrigerated centrifuge of 12 000 g at 4℃ for 5min. The total protein concentration was determined according to the instructions of the BCA protein concentration determination Kit, and then diluted with 4x protein loading buffer solution, and denaturated in water bath at 100℃ for 10min. The modified total protein was subjected to gel electrophoresis, 10% SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis for 80V,30 min. Then 120V, 60min. The membrane transfer conditions were 300mA, 60min, 25℃. Use a quick sealing liquid shaker to seal for 15min at room temperature. The corresponding NC films were placed in GSK-3β, P-Tau, Tau, PI3K and PKB (1:1500), respectively, and incubated overnight at 4℃. After primary antibody incubation, it was washed 3 times in TBST buffer solution,5min each time. The second antibody (1: 6000) was incubated at room temperature for 2h and washed 3 times in TBST buffer,5min each. Develop according to ECL instruction. Automatic chemiluminescence image analyzer was used to analyze and scan the band density. The ratio of gray values of GSK-3β, PI3K and PKB bands to the gray values of internal reference bands was used as the relative expression level of the target protein. The gray values of Tau were used as the reference, and the ratio of p-Tau/Tau gray values was used as the relative expression level of P-Tau protein.
2.2.8 Statistical methodSPSS21.0 statistical software was used for analysis, and the results were expressed as±s. One-way ANOVA was used for comparison between multiple groups, and LSD test was used for comparison between groups with homogeneity of variance. Tamhane's T2test was used for comparison when variance was not uniform, and P<0.05 indicated statistically significant differences.
3. Results
3.1 Effect on pathological morphology of rat brain
Under the microscope can observe that pyramidal cells and neurons in the hippocampus of rats in the normal group and the sham operation group were arranged closely and orderly, and there were a large number of neurons and nerve cells, with uniform coloring,clear nucleoli, light red tissue slices, and cell apoptosis was rare. The morphological states of the two groups were similar. Compared with normal group and sham group, hippocampal nerve cells in model group were disordered, scattered, not compact, cell boundary was not clear, apoptosis level increased, and the number of nerve cells and neurons in cortex and hippocampus decreased significantly.Compared with model group, TSG low-dose, medium-dose and high-dose groups could enhance the number of nerve cells in cerebral cortex and hippocampal area of rats to a certain extent, and improve the level of apoptosis to varying degrees. See Table 2 and Figure 1.
Table 2 Effects of TSG on the number of nerve cells in hippocampus and cerebral cortex of rats(±s, n=3)
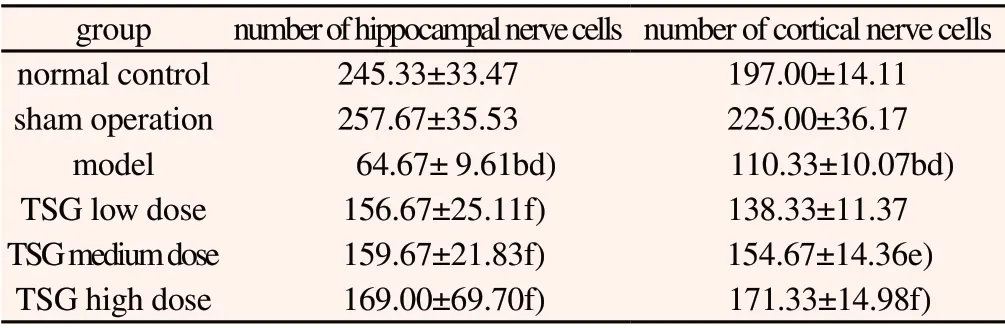
Table 2 Effects of TSG on the number of nerve cells in hippocampus and cerebral cortex of rats(±s, n=3)
group number of hippocampal nerve cells number of cortical nerve cells normal control 245.33±33.47 197.00±14.11 sham operation 257.67±35.53 225.00±36.17 model 64.67± 9.61bd) 110.33±10.07bd)TSG low dose 156.67±25.11f) 138.33±11.37 TSG medium dose 159.67±21.83f) 154.67±14.36e)TSG high dose 169.00±69.70f) 171.33±14.98f)

Figure 1 Effects of TSG on the morphology of nerve cells in hippocampus and cortex of rats
3.2 Effects on mRNA expression levels of GSK-3β, PI3K,PKB, PKA and PKC in rat brain tissue
Compared with normal group and sham operation group, the expression of PI3K, PKB, PKC mRNA in model group the expression level showed a downward trend(P<0.05, P<0.01),GSK-3β, PKA mRNA the expression level showed aupregulation(P<0.05); Compared with blank control group, the expression of GSK-3β, PI3K, PKB, PKA, PKC mRNA in shamoperated group was simillar with blank control group, was close to one, and there was no significant difference between the two;Compared with model group, the mRNA expression of GSK-3β decreased in TSG groups(P<0.05), The expression of PKA mRNA in TSG low-dose group showed a downward trend(P<0.05),The mRNA expression levels of PI3K and PKC in TSG groups were significantly increased(P<0.01), The mRNA expression of PKB in TSG medium-dose group and high dose group was significantly increased(P<0.01). See Table 3 and Figure 2.
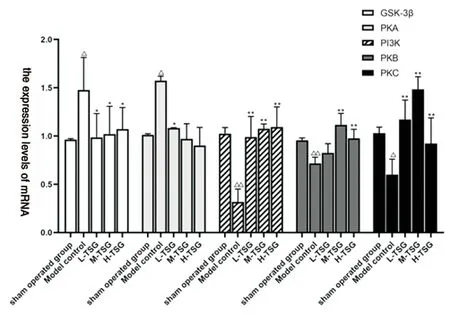
Figure 2 Effect of TSG on mRNA expression levels of PKA, PP2A and GSK-3β in rat brain tissue(±s, n=3)
3.2 Effects on PKC protein expression in hippocampus and cortex of rat brain
Compared with normal group, the positive expression of PKC in hippocampus and cortex was similar in sham operation group without significant difference; the expression of PKC protein in hippocampus and cortex of model group was significantly decreased(P<0.01);Compared with sham operation group, the expression of PKC protein in hippocampus and cortex of model group was negative, and the positive expression level was significantly decreased(P<0.01);Compared with the model group, the positive expression of PKC protein in cortical area was significantly increased in TSG groups(P<0.01), the positive expression of PKC protein in the hippocampus was significantly increased at medium and high doses of TSG, and the expression of PKC protein was also increased in the low doses of TSG, but there was no statistical significance. See Table 4 and Figure 3.

Figure 3 Effects of TSG on PKC protein expression in hippocampus and cortex of rats(IHC, Bar=20 μm)
3.3 Effects on PKA protein expression in hippocampus and cortex of rat brain
Compared with normal control group and sham operation group,the positive expression of PKA protein in hippocampus and cortex was high in model group(P<0.05); The blank control group was compared with sham operation group, PKA expression was low in both cortical and hippocampal regions(P<0.05), the mean optical density values are similar; Compared with model group, in TSG medium and high dose groups could see the PKA protein downregulate in hippocampus(P<0.05), TSG dose groups have a certain degree of down-regulation of cortical PKA protein(P<0.05). See Table 4 and Figure 4.
Table 3 Effects of TSG on mRNA expression levels of GSK-3β, PKA, PI3K, PKB and PKC in rat brain tissue(±s, n=3)

Table 3 Effects of TSG on mRNA expression levels of GSK-3β, PKA, PI3K, PKB and PKC in rat brain tissue(±s, n=3)
Note: The mRNA expression levels of all indexes in the normal group were 1.Compared with normal group a)P<0.05, b)P<0.01; Compared with sham operation group c)P<0.05, d)P<0.01; Compared with model group e)P<0.05, f)P<0.01(Table 2, 3, 4, 5 as same).
group GSK-3β PKA PI3K PKB PKC model 1.477±0.337ac) 1.573±0.047ac) 0.317±0.134bd) 0.716±0.065bd) 0.601±0.159ad)sham operation 0.964±0.010 1.013±0.010 1.025±0.064 0.955±0.024 1.030±0.062 TSG low dose 0.987±0.246e) 1.084±0.003e) 0.991±0.212f) 0.825±0.095 1.171±0.202f)TSG medium dose 1.021±0.288e) 0.970±0.187 1.076±0.050f) 1.116±0.119f) 1.485±0.130f)TSG high dose 1.071±0.225e) 0.903±0.187 1.093±0.210f) 0.976±0.094f) 0.922±0.266f)
Table 4 Effects of TSG on PKC protein positive cells in hippocampus and cerebral cortex of rats(±s, n=3)
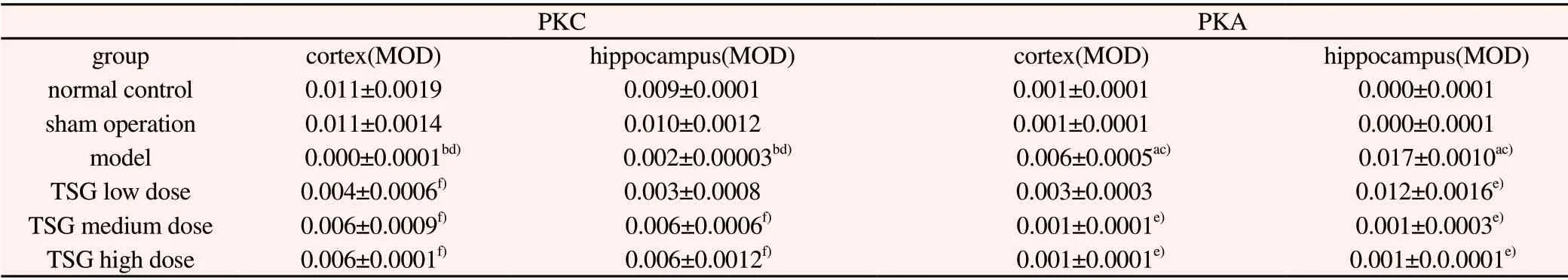
Table 4 Effects of TSG on PKC protein positive cells in hippocampus and cerebral cortex of rats(±s, n=3)
PKC PKA group cortex(MOD) hippocampus(MOD) cortex(MOD) hippocampus(MOD)normal control 0.011±0.0019 0.009±0.0001 0.001±0.0001 0.000±0.0001 sham operation 0.011±0.0014 0.010±0.0012 0.001±0.0001 0.000±0.0001 model 0.000±0.0001bd) 0.002±0.00003bd) 0.006±0.0005ac) 0.017±0.0010ac)TSG low dose 0.004±0.0006f) 0.003±0.0008 0.003±0.0003 0.012±0.0016e)TSG medium dose 0.006±0.0009f) 0.006±0.0006f) 0.001±0.0001e) 0.001±0.0003e)TSG high dose 0.006±0.0001f) 0.006±0.0012f) 0.001±0.0001e) 0.001±0.0.0001e)

Figure 4 Effects of TSG on PKA protein expression in hippocampus and cortex of rats(IHC, Bar=20 μm)
3.4 Effects on GSK-3β, P-Tau, PI3K and PKB protein expression in rat brain tissue
Compared with normal group and sham operation group, the relative expression levels of GSK-3β and P-Tau protein in hippocampus of model group were up-regulated(P<0.05, P<0.01),the protein expression levels of PI3K and PKB were significantly decreased(P<0.05, P<0.01); Compared with normal controls,The relative expression levels of GSK-3β, P-Tau, PI3K and PKB proteins in the hippocampus of sham operation group were similar, there was no statistical difference between the two groups;Compared with model group, TSG groups increased PI3K and PKB proteins in hippocampal region of brain at different levels(P<0.05,P<0.01), TSG groups showed a down-regulation trend to GSK-3β protein in hippocampus of rats(P<0.01), the relative expression of P-Tau protein was decreased in TSG medium-dose group(P<0.05).See Table 5 and Figure 5.

Figure 5 Gel electrophoresis of GSK-3β, P-Tau, Tau, PI3K and PKB in rat hippocampus
4. Discussion
Tau protein is a neuronal microtubule-binding protein. Normally,the levels of Tau protein phosphorylation/dephosphorylation are balanced in the human body, but in the brain of an AD patient, Tau protein is over-phosphorylated and loses the ability to combine with microtubules. NFT formed by aggregation is deposited in the brain,which leads to degeneration of neurons and apoptosis of neurons[16-17].GSK-3β is a serine/threonine kinase that not only regulates glycogen synthase activity, but also has been widely studied as a therapeutic target in cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. GSK-3β can aggravate the inflammatory response of the nervous system,increase the production of amyloid beta, and reduce the synthesis of acetylcholine in AD patients, resulting in the loss of neurons, which is closely related to the phosphorylation of Tau protein, apoptosis and memory impairment of patients[18].This study mainly studied the mechanism of TSG' s intervention on Tau phosphorylation through GSK-3β pathway, and explored its possible mechanism by detecting GSK-3β related factors PI3K, PKB, PKC and PKA.
A large number of amyloid plaques can be observed in pathological sections of patients with Alzheimer's disease, its main component is Aβ protein. Aβ protein is A short peptide of approximately 40-48 amino acids in length, it is produced by shearing amyloid precursor protein by secretase, the molecular weight is about 4kD. Modeling drug Aβ25-35is a fragment of Aβ protein hydrolyzed in vitro and does not exist in vivo, it has strong neurotoxicity, can lead to increase cell free radical damage, have direct cytotoxic effects, synaptic changes, neuron death, etc.In this study, 24-month old SD rats were injected with Aβ25-35into the hippocampus to induce dementia model, Filtered through Morris Water Maze, this molding method has a high success rate, but the resistance of old rats was poor and need a certain amount of nursing time after the operation. From the result of Hematoxylin-eosin staining we can see that, compared with the model group, the nerve cells in the hippocampus and cortex of TSG group were arranged more closely, the number of nerve cells was more, and the level of neuronal apoptosis was decreased.However, compared with the normal group, the number of pyramidal cells and neurons in model group was less, and the color was lighter,and the arrangement was relatively loose and chaotic. It can be seen that TSG has a certain protective effect on nerve cells in the brain.
Table 5 Effects of TSG on GSK-3β, P-Tau, PI3K and PKB protein expression in rat brain tissue(±s, n=3)

Table 5 Effects of TSG on GSK-3β, P-Tau, PI3K and PKB protein expression in rat brain tissue(±s, n=3)
group PI3K/GAPDH PKB/GAPDH GSK-3β/GAPDH P-tau/Tau normal control 0.823±0.057 1.316±0.357 0.875±0.023 0.743±0.041 sham operation 0.878±0.077 1.127±0.311 0.834±0.062 0.750±0.070 model 0.648±0.075ad) 0.414±0.095bd) 1.275±0.107bd) 1.067±0.085ac)TSG low dose 0.938±0.033f) 0.943±0.234e) 0.924±0.068f) 0.880±0.280 TSG medium dose 1.048±0.104f) 1.025±0.205e) 0.870±0.067f) 0.760±0.166e)TSG high dose 0.975±0.076f) 1.113±0.290f) 0.778±0.113f) 0.845±0.167
Tau protein phosphorylation is regulated by both protein kinase and protein esterase activities. In recent years, GSK-3β has been identified as the main protein kinase that induces abnormal phosphorylation of Tau, It increased inflammation in the nervous system, increased the formation of Aβ amyloid plaques, it also reduces the accumulation of acetylcholine transmitters in the brain of dementia patients, these can cause severe nerve damage[19-20]. It also can be observed in this experiment, increased GSK-3β expression was observed in the dementia induced model. After treatment with TSG, the gene level and protein level of GSK-3β decreased to a certain extent. GSK-3β can be regulated by multiple pathway factors, and PI3K-Akt is an upstream regulatory pathway of GSK-3β. In recent years, many literatures have reported that this signaling pathway is closely associated with Alzheimer's disease[21-23], it is speculated that the drug can activate the expression of GSK-3β by inhibiting the PI3K-Akt pathway, and GSK-3β is involved in the process of Tau phosphorylation, aggravating the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease. In this study, the mRNA expression and protein expression of GSK-3β, PI3K and PKB were determined by RTtime PCR and Western Blot. It was found from the experimental results that the high expression of GSK-3β in the model group was accompanied by low expression of PI3K and PKB, and the relative expression of P-Tau protein showed an increasing trend. After TSG administration, the expression level of GSK-3β decreased, PI3K and PKB showed an increasing trend, and the expression level of P-Tau decreased, indicating that the phosphorylation level of Tau decreased.
PKC plays a key role in memory formation, studies showed that[24-25], there was a regulatory relationship between GSK-3β and PKC, metformin has the effect of improving cognitive dysfunction in SAMP8 mice, which has the potential of treating Alzheimer's disease. It was found that metformin can reduce the expression of GSK-3β and P-Tau, and increase the expression of PKC, the mechanism may be that metformin can increase the expression of PKC, thereby inhibiting the overactivation of GSK-3β and decreasing the phosphorylation level of GSK-3β; Piperine may reverse GSK-3β activation induced by D-Gal by modulating PKC and PI3K-Akt pathways in the hippocampus of aging mice. In this study, the mRNA expression and protein expression of GSK-3β and PKC were determined by RT-time PCR, Western Blot and immunohistochemistry. It was found from the experimental results that when GSK-3β was highly expressed in the model group, PKC was in a state of low activity and low expression, and the relative expression level of P-Tau protein showed an increasing trend with heavy phosphorylation. After TSG administration, the expression level of GSK-3β decreased, the expression level of PKC was upregulated, and p-Tau expression decreased, which saved p-Tau hyperphosphorylation to a certain extent.
Because protein kinase substrates are usually highly selective for primary sequences around receptor serine and threonine residues,a single kinase cannot completely phosphorylate Tau at all sites[26].Protein kinase A is one of the most important protein kinases catalyzing Tau phosphorylation, recent studies have shown that[27-29], PKA interacts with GSK-3β, and increased PKA activity leads to overactivation of GSK-3β; The pre-phosphorylation of Tau by PKA enhances the further phosphorylation of Tau by GSK-3β. The pre-phosphorylation of PKA can significantly promote the phosphorylation of Tau regulated by GSK-3β at multiple sites, leading to Tau hyperphosphorylation. In this study, the mRNA expression and protein expression of GSK-3β and PKA were determined by RT-time PCR, Western Blot and immunohistochemistry. The experimental results showed that while GSK-3β was highly expressed in the model group,PKA was also highly expressed in the model group, and Tau protein phosphorylation in the model group also showed excessive phosphorylation; After TSG administration, the expression level of GSK-3β, PKA and P-Tau decreased. Thus, the mechanism of TSG's intervention on Tau phosphorylation through GSK-3β pathway is speculated as follows: First, by activating the PI3K-PKB pathway, GSK-3β level is decreased and protein kinase activity is reduced; The other was to decrease GSK-3β protein kinase activity by increasing PKC expression; Third, by inhibiting PKA activity,Tau protein without PKA pre-phosphorylation is not easy to be in a state of hyperphosphorylation, thus regulating the process of Tau phosphorylation. It was found that TSG has a regulatory effect on GSK-3β, PI3K, PKC, PKB and PKA in the hippocampus of Aβ25-35induced dementia rat model. By regulating the expression of these factors, Tau hyperphosphorylation can be inhibited and Tau hyperphosphorylation can be improved, thus it is possible to treat AD. However, the specific mechanism and target involved are still unclear, and more basic research is needed.
Author conflict of interest statement All authors declare no conflict of interest Author contribution
Corresponding author Zhongshi Huang designed the experiment and reviewed the article. Zhu Xiaoying, Liao Yanhua provided technical guidance for pathological index detection and immunohistochemical experiment; Li Zhenzhong provided technical guidance for Western blot and Q-PCR. Meng Wanying, Liu Chaoyu,Xia Xiaoyan and Li Yanbing were responsible for animal model establishment, drug intervention, sampling, index detection and data analysis; Meng Wanying wrote the paper.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Application of adipose-derived stem cells in treatment of neurodegenerative diseases: A review
- Physiological and pharmacological functions of G protein coupled receptor 124: A review
- Clinical efficacy of Chinese herbal compound in the treatment of infertility with kidney deficiency: A meta-analysis
- Analysis of hyperuricemia in physical examination population of a hospital in Haikou
- Berberine protects diabetic nephropathy rats by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress
- Effect of Simiao Yongan Decoction on atherosclerotic carotid plaque in ApoE-/- mice via antagonizing Ox-LDL lipid metabolism pathway
