Corneal histomorphology and electron microscopic observation of R124L mutated corneal dystrophy in a relapsed pedigree
2022-09-14MengJunFuJingZhaoShanDuanHaoRunZhangJingJingZhaoLiZengRuiWangXingTaoZhou
INTRODUCTION
Corneal dystrophy (CD) with R124L mutation is a familial, primary, binocular autosomal dominant genetic disease
. According to the 2015 International Classification of Corneal Dystrophies (IC3D) and based on the affected anatomic site, CD is sub-classified: epithelial/sub-epithelial,epithelial-stromal, stromal, and endothelial dystrophy
. CD with R124L mutation belongs to epithelial-stromal CD
. The gene mutation sites of CD have been confirmed to be in the transforming growth factor B-induced (
or
)gene on chromosome 5q31
. The diagnostic basis of CD mainly includes clinical observation of lesion location and morphology, histopathological changes, and genetic testing and typing results
.
Current treatments for CD include phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK) and keratoplasty
. After surgery,the symptoms could be improved or relieved and vision could be improved. Some patients may inevitably suffer from aggravation or recurrence of corneal opacity
. The pathological changes of R124L mutant CD are reported to be mainly caused by accumulation of abnormal substances in the anterior stroma
. However, the corneal pathological changes of recurrent cases have not been reported. In this study, a Chinese CD family with R124L mutation who had a history of consanguineous marriage was enrolled. The pathological changes of cornea tissues with recurrence after keratoplasty were observed by electron microscopy and histopathological analysis. The sites of gene mutations were detected. Our findings may provide evidence for the pathological changes of recurrent CD caused by R124L.
本工程现已运行1年多的时间,运行过程中,尚未发现地表隆起、桩的变形,周边地基土变形等现象,目前使用正常,表明本方案的合理性。
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
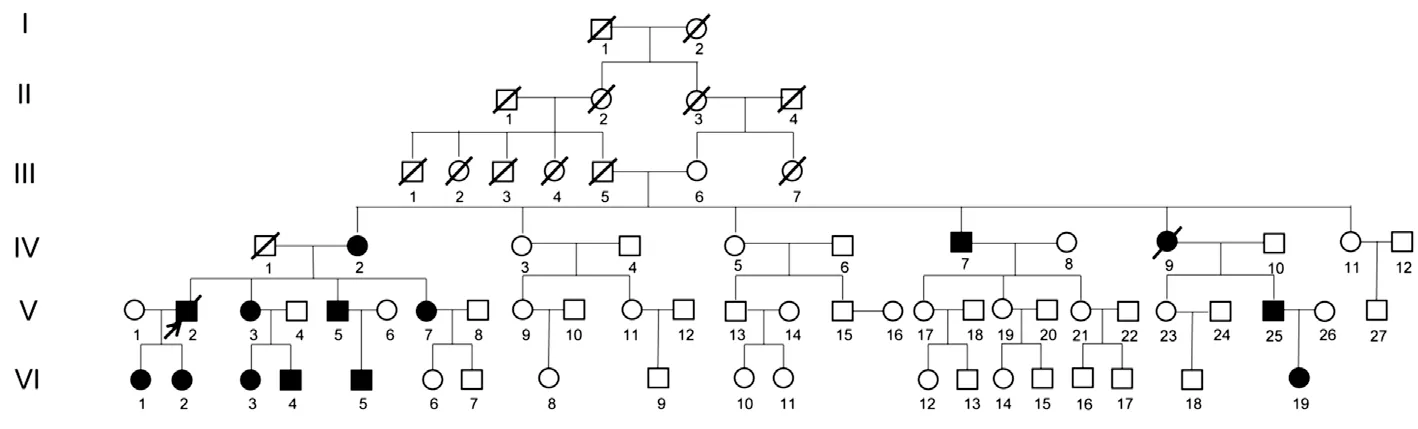
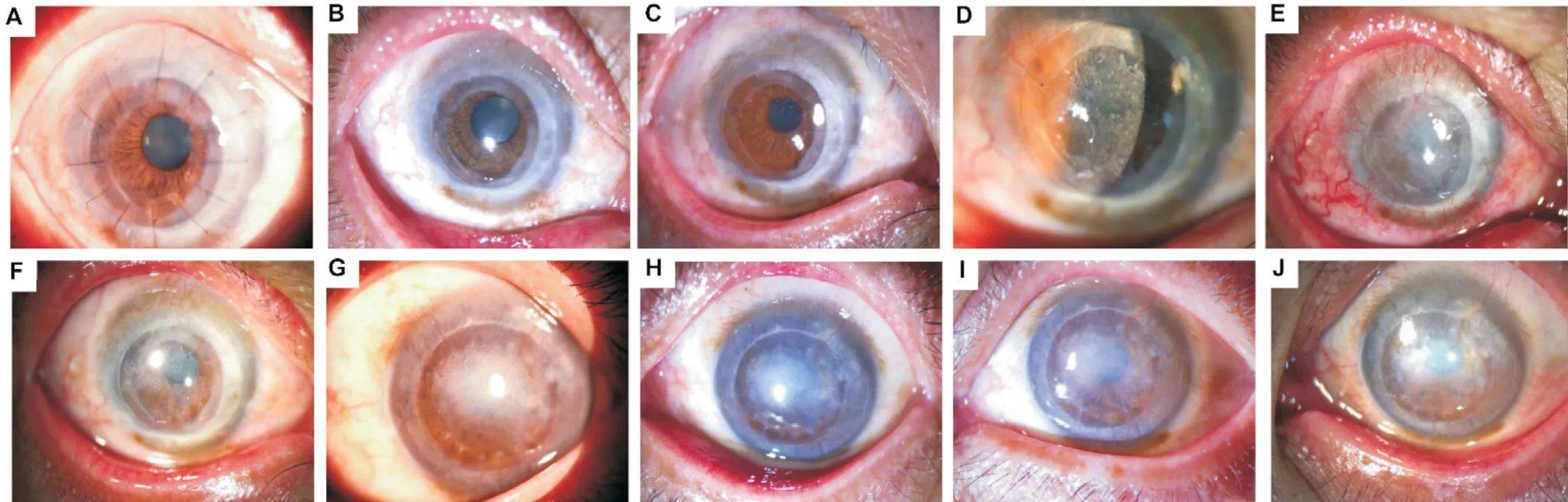
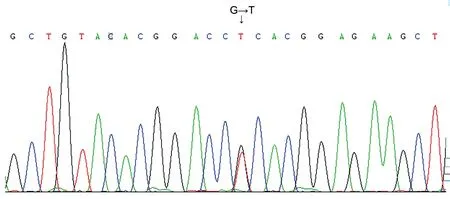
The 14 patients had recurrent eye pain, eye abrasion and tearing, accompanied by redness and progressive vision loss since childhood. After keratoplasty, the patients IV7, IV9, and V2 (Figure 1) had CD relapse at 33.5±3.0mo. For the corneal morphology of recurrent cases, it was observed that the corneal epithelium was rougher and the corneal roughness was more obvious. The corneal epithelium was eroded into clumps and the deposition was thicker and closer to the corneal surface(Figure 2). The clinical manifestations of the pedigree patients are shown in Table 1. All patients were found to have R124L mutation in the
gene (heterozygous mutation in exon 4 c.418 G>T; Figure 3).
Some studies have reported that the R124L mutation of CD has an early onset age and often has recurrent corneal epithelial erosion from childhood, with obvious symptoms and rapid progress
. Later, there may be corneal punctuated or map-like turbidity, which may gradually expand and merge,leading to vision loss and blindness
. Surgical treatments such as PTK or keratoplasty can be performed. Nevertheless,the disease often relapses within several years after the operation. When there is CD recurrence, PTK or keratoplasty can be performed again
. Therefore, the patients with CD recurrence in this study underwent PKP or LKP again.
Routine ophthalmological examinations, including visual acuity examination, slit lamp microscope examination, and,intraocular pressure and fundus examination were performed.
Peripheral blood (10 mL each) was collected from 14 patients with CD. The blood was anticoagulated with EDTA. DNA was extracted from peripheral blood with DNA extraction kit (Qiagen, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Gene sequencing was performed with BigDye terminator V3.1 cycle sequencing kit (Qiagen, Santa Clara, CA, USA) on an ABI 31300XL analyzer (ABI, Foster City, CA). Sequence Scanner V1.0 software was used for analyzing sequencing data, with reference to NCBI GeneBank(NM_000358 for
).
The corneal specimens were fixed with 2%paraformaldehyde glutaraldehyde, rinsed with phosphoric acid buffer, fixed with 4% osperium tetroxide, dehydrated with ethanol step by step, fixed with epoxy resin, made into ultrathin sections, stained with lead uranium acetate and lead citrate, and were observed under transmission electron microscope (TEM).
The corneal tissues were fixed with 0.4 g/L paraformaldehyde, dehydrated with graded ethanol, transparent with xylene, embedded with paraffin,and cut into 5 μm sections. Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining,Alcian blue staining, Periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining,Congo red staining, and Masson’s trichrome staining were carried out respectively according to routine procedures.The sections were observed and photographed under a light microscope.
一天,爱德华多很晚才从街上回家,看到克里斯蒂安的黑马拴在木桩上。老大穿着他那身最体面的衣服在院子里等他。女人捧着马黛茶罐进进出出。克里斯蒂安对爱德华多说:“我要到法里亚斯那儿去玩。胡利安娜就留给你啦;如果你喜欢她,你就派她用场吧。”
偿债能力分析,是指对企业偿还各种债务的能力和保障程度所作的分析,通过这种分析可以有效地揭示出企业存在的财务风险。分析和评价企业短期偿债能力的财务指标主要有流动比率、速动比率等。
RESULTS
The pedigree diagram of the family with a history of consanguineous marriage is shown in Figure 1. There were 59 members (14 patients with CD and 45 healthy people) of 4 generations in this family, all of whom were Han Chinese. Among the 14 patients with CD,1 patient (2 eyes) underwent penetrating keratoplasty (PKP)and CD recurred 36mo after the operation. The right eye of this patient underwent PKP again because of recurrence.One patient (1 eye) underwent PKP and CD recurred 30mo after the operation. One patient (2 eyes) underwent lamellar keratoplasty (LKP) and CD recurred 33mo after surgery. After recurrence, binocular LKP was performed again.
The study was carried out in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Weifang Eye Hospital Ethics Committee.Each patient provided the signed informed consent.
还有如《将帅》篇,论选将的重要性。秦观深感北宋兵权轮换制的流弊,提出“臣以为西北二边,宜各置统帅一人……进退赏罚,尽付其手,得以便宜从事。”刘勇刚先生谓“此文呼吁朝廷选用‘天下之将’,赋以重权,‘便宜从事,不烦庙堂之论’,可称剀切之论。”[4]而在这一点上,朱刚先生论述:“唯《将帅》篇谓西北二边之事,朝廷不必详其细节,宜全权委托统帅各一人,足以了事。似此有见于北宋兵权集中之流弊,但此策亦早见于苏轼的贤良进卷,秦观只承其说而已。”[2]54而且,在宋太祖时期就有“杯酒释兵权”一事,终宋一代都对统领兵权的武将有所忌惮,想要把兵权全权委托一名统帅,只能说是不切实际之言。
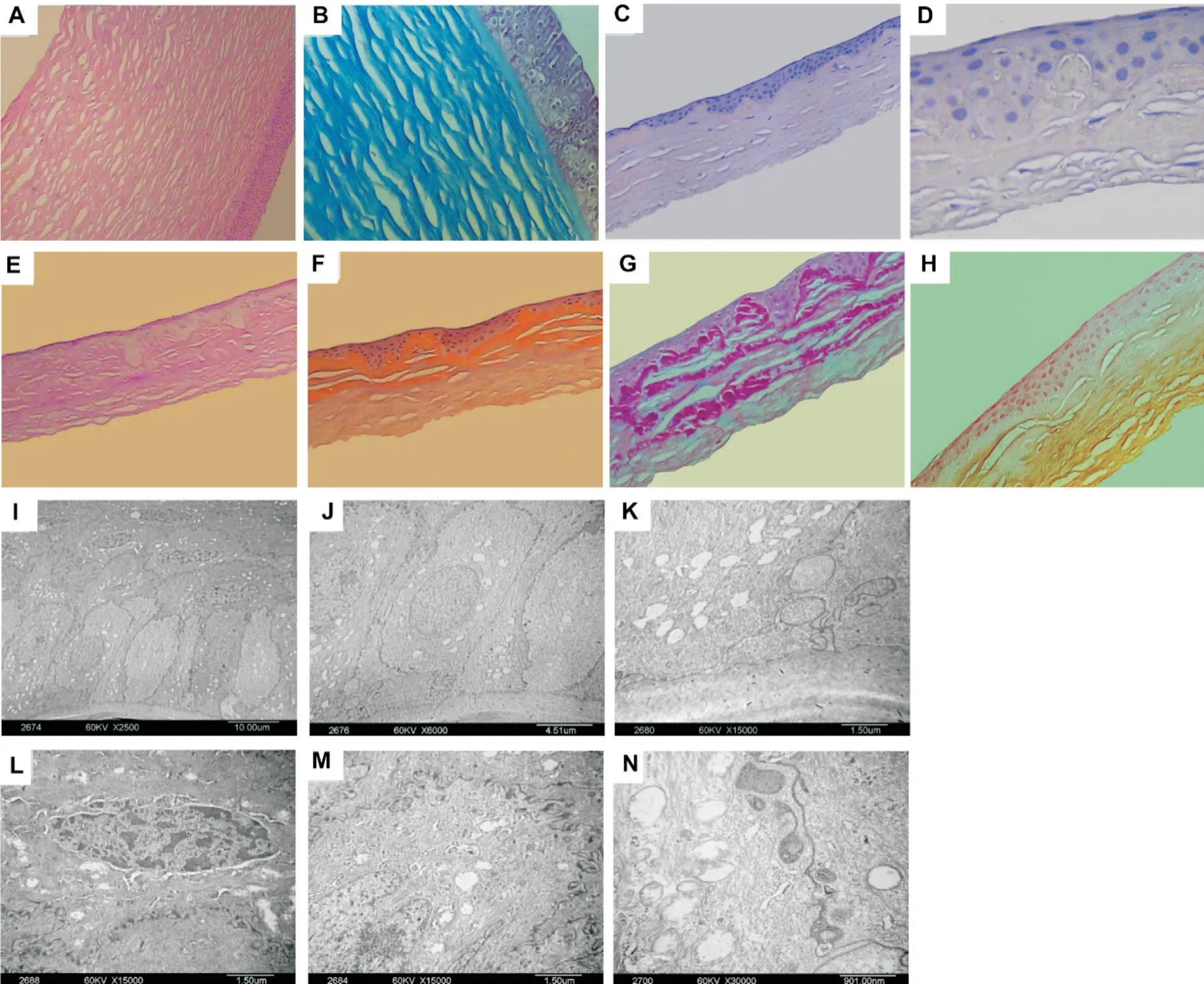
HE staining showed that there were 5 to 6 layers of epithelial cells in normal corneal tissue with regular arrangement and uniform thickness of the pre-elastic layer (Figure 4A).Masson’s trichrome staining showed regular arrangement of matrix collagen fiber bundles (Figure 4B). However, in the corneal tissue of recurrent cases, the thickness of corneal epithelium was uneven and the arrangement of epithelial cells was disordered (Figure 4C, 4D). The normal columnar structure of basal cells and the structure of the anterior elastic layer disappeared. Instead, a large amount of red staining substances were observed. Congo red staining was positive(Figure 4E). Orange red was observed in the sub-epithelial and anterior stroma. Masson’s trichrome staining was positive(Figure 4F). The sub-epithelial and anterior stroma was stained red and the stromal collagen fibers were stained blue.PAS staining was positive (Figure 4G). Red substance was seen in the sub-epithelial and anterior stroma of the cornea.Alcian blue staining was negative and no specific staining was observed.
商品住宅交付时多为毛坯房,绝大多数业主不具备装修专业知识或选择的装修公司不够专业,装修完全从自身的需求出发,随意改变房屋结构和功能。特别是在一些不好的户型中,容易出现大改动,易造成房屋结构的破坏,留下质量安全隐患。部分装修公司自身技术不过关,又缺乏有效的监管,装修完不久就出现吊顶开裂、墙砖脱落等问题,业主无处维权。
刘剑文解释道,在个人所得中,有劳动所得(积极所得),也有非劳动所得(消极所得)。前者比如工薪所得、劳务所得、稿酬所得和特许权使用费所得,而后者比如利息、股息、红利所得、偶然所得等,而按照目前的税制,只需缴纳20%的税。
Under TEM, it was observed that the epithelium microvilli of recurrent cornealspecimens reduced or disappeared. The shape of basal cells varied (Figure 4I). There was swelling of cell mitochondria(Figure 4J). There were vacuoles in the cytoplasm (Figure 4K). The nuclei were hyperchromatic, enriched, and crescentshaped, or became fragmented, distorted, contracted, or even disappeared. Typical apoptotic features were observed (Figure 4L). Desmosomal junctions between some cells were reduced or disappeared. The boundaries between the anterior elastic layer and basal cells were blurred or disappeared (Figure 4M).A large number of high-density abnormal substances were dispersed and accumulated, and no obvious fibrous structure was observed in the depositions (Figure 4N).
DISCUSSION
The characteristics of the CD family in this study were as follows. First, it has been reported that the earliest onset age was generally around 7 years old
. In this study, the youngest age of onset in this family was 1 year old. To our knowledge,this is the youngest reported age of onset. Second, this family was with a history of consanguineous marriage.
The gene mutation of CD and the pathological changes of cornea have been reported previously
. This paper is the first to report the pathological changes and TEM ultrastructure of the corneal graft with recurrent CD. In the CD classification in 2015, R124L mutation is classified as epithelial-basal CD. This paper was also one of the few families with R124L mutations reported with a history of consanguineous marriage.
In this study, gene sequencing found heterozygous gene mutation at the R124L locus in all patients, which was consistent with previous findings
. The R124L mutation is also a common mutation type. In other atypical cases,R125H, R555Q, R555W and a few mutations at the R124C,G623D, H572R and H626P sites have also been reported
.Our study also found that the CD of this pedigree had high incidence, early onset age, severe condition and high recurrence rate. A possible explanation is the genetic features of consanguineous marriage. The mutation from the polar hydrophilic arginine to the non-polar hydrophobic leucine may change the polarity and hydrophilicity of amino acids,thus changing the three-dimensional structure of protein and contributing to the severity of the disease.
Fourteen patients with CD from a family with a history of consanguineous marriage in China were enrolled.Among them, the ratio of male to female was 6:8. The youngest was 1 year old, and the oldest was 69 years old. The 14 patients underwent routine ophthalmological examination and peripheral blood collection. The diseased corneal tissues were collected from patients of IV7 and V2 (Figure 1) who had recurrence after keratoplasty and underwent keratoplasty again. For control, 3 pieces of normal corneal tissues donated by Weifang Eye Hospital were collected.
通过使用二元亮度差分方程(图5)获得了地面真实角点,检测结果得到了一定的改进。可能是因为采用二进制方法,非均匀平坦区域之间的角点可以得到更高的USAN,并且超过亮度差阈值。
In this study, HE staining clearly showed the scope and location of recurrent lesions, including uneven thickness of corneal epithelial cells, disordered cell arrangement, swelling of some corneal epithelial cells and disappearance of the normal cylindrical structure of basal cells. It is reported that PAS staining could be positive in CD with R124L mutations
.In this study, corneal tissue sections with recurrent lesions were stained with Congo red, showing lamellar orange color in the sub-epithelial and anterior stroma of the cornea, which confirmed that the extracellular substance was amyloidosis.Masson’s trichrome staining of the corneal epithelium and anterior stroma showed red staining, indicating that the extracellular depositions were acidic and microfibrous.Therefore, in this relapsed CD family with R124L mutation,the corneal depositions were extracellular amyloid fibrin. This was consistent with previous studies
.
Histopathological examination serves as the gold standard for diagnosis
. HE staining can clarify the scope, size and shape of the lesion. Specific staining can reveal specific components(intrinsic and extrinsic) of the lesion and can give a rough idea of the nature of its depositions. TEM can reveal the pathological changes at the cellular/ultrastructural level. In this study, TEM examination displayed that there were reduced or disappeared epithelium microvilli of recurrent corneal specimens. The basal cell morphology in the epithelium was different. Mitochondria in cells were swelling. Vacuoles were observed in the cytoplasm. Corneal histopathological and TEM ultrastructural changes of the recurrent cases further confirmed that the recurrent CD caused by R124L mutation had characteristic structural changes, which might be related to clinical symptoms and gene mutations
.
Limitations of this study: First, this study only observed the corneal tissues of recurrent cases and did not compare them with the corneal tissues after the first operation. Second, only one family with a history of consanguineous marriage was studied. The sample size should be expanded in future study.
In this Chinese recurrent CD family with R124L gene mutation, the corneal epithelium of the recurrent cases was rougher. The recurrent specimens suggested extracellular amyloid fibrin in the cornea. Early diagnosis of CD is based on slit lamp examination and clinical symptoms. The advanced cases of CD are classified and diagnosed according to corneal involvement, anatomical site, histopathological features, genetic pattern and genetic testing results. Although consanguineous marriage is now relatively rare in China, it still exists in relatively remote and economically underdeveloped parts of the country. Thus, earlier screening of patients and their families of consanguineous marriage should be performed.
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81770955); the Major Clinical Research Project of Shanghai Shenkang Hospital Development Center (No.SHDC2020CR1043B); the Project of Shanghai Xuhui District Science and Technology (No.2020-015);the Project of Weifang Science and Technology Bureau(No.2021RKX160).
None;
None;
None;
None;
None;
None;
None;
None.
1 Atia R, Jouve L, Georgon C, Laroche L, Borderie V, Bouheraoua N. Imaging of reis-Bückler corneal dystrophy.
2019;42(1):105-107.
2 Jun I, Ji YW, Choi SI, Lee BR, Min JS, Kim EK. Compound heterozygous mutations in TGFBI cause a severe phenotype of granular corneal dystrophy type 2.
2021;11:6986.
3 Moshirfar M, Bennett P, Ronquillo Y. Corneal Dystrophy. In:
Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
4 Cai JQ, Zhu LR, Zha Y, Kang QY. TGFBI gene mutation analysis in Chinese families with corneal dystrophies.
2016;20(7):388-392.
5 Zhang YL, Ying JL, Zhou WP, Zhu LR, Cai JQ. Analyses of TGFBI gene mutation spectrum in four Chinese families with corneal dystrophy.
2015;95(2):116-119.
6 Chao-Shern C, DeDionisio LA, Jang JH, Chan CC, Thompson V, Christie K, Nesbit MA, McMullen CBT. Evaluation of TGFBI corneal dystrophy and molecular diagnostic testing.
2019;33(6):874-881.
7 Nagano C, Nozu K, Yamamura T,
. TGFBI-associated corneal dystrophy and nephropathy: a novel syndrome?
2019;8(1):14-17.
8 Weiss JS, Møller HU, Lisch W,
. The IC3D classification of the corneal dystrophies.
2008;27(Suppl 2):S1-S83.
9 Lisch W, Weiss JS. Clinical and genetic update of corneal dystrophies.
2019;186:107715.
10 Matthaei M, Hribek A, Clahsen T, Bachmann B, Cursiefen C,Jun AS. Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy: clinical, genetic,pathophysiologic, and therapeutic aspects.
2019;5(4):151-175.
11 Lang SJ, Böhringer D, Reinhard T. Penetrating limbokeratoplasty for gelatinous corneal dystrophy.
2019;236(2):169-172.
12 Vinciguerra P, Vinciguerra R, Randleman JB, Torres I, Morenghi E,Camesasca FI. Sequential customized therapeutic keratectomy for reis-Bücklers’ corneal dystrophy: long-term follow-up.
2018;34(10):682-688.
13 Sridhar U, Tripathy K, Bansal Y. Repeated phototherapeutic keratectomy (PTK) followed by PTK with photorefractive keratectomy for anterior granular corneal dystrophy.
2020;68(12):3038.
14 Zeng L, Zhao J, Chen YJ, Shang JM, Aruma A, Zhou XT. Multiple phototherapeutic keratectomy treatments in a Chinese pedigree with corneal dystrophy and an R124L mutation: a 20-year observational study.
2019;19(1):191.
15 Chiou AG, Florakis GJ, Copeland RL, Williams VA, McCormick SA,Chiesa R. Recurrent meesmann’s corneal epithelial dystrophy after penetrating keratoplasty.
1998;17(5):566-570.
16 Zhao F, Liu Y, Guan T. Analysis of
gene mutations in three Chinese families with corneal dystrophy.
2019;2019:6769013.
17 Liang QF, Sun XG, Jin XY.
gene mutation in a Chinese pedigree with Reis-Bücklers corneal dystrophy.
2012;32(1):74-80.
18 Tanhehco TY, Eifrig DE Jr, Schwab IR, Rapuano CJ, Klintworth GK. Two cases of Reis-Bücklers corneal dystrophy (granular corneal dystrophy type III) caused by spontaneous mutations in the
gene.
2006;124(4):589-593.
19 Piao MZ, Zhou XT, Wu LC, Chu RY. Arg555Gln mutation of
gene in geographical-type Reis-Bücklers corneal dystrophy in a Chinese family.
2012;40(3):1149-1155.
20 Yang QN, Zhao YW, Guo LH, Yan NH, Liu XY, Cai SP. Arg124Cys mutation of the
gene in a Chinese pedigree of Reis-Bücklers corneal dystrophy.
2011;4(3):235-238.
21 Ma K, Liu G, Yang Y, Yu M, Sui RF, Yu WH, Chen XM, Deng YP, Yan NH, Cao GQ, Liu XY.
gene mutation analysis in a Chinese pedigree of Reis-Bücklers corneal dystrophy.
2010;16:556-561.
22 Li DD, Qi YH, Wang L, Lin H, Zhou N, Zhao LM. An atypical phenotype of Reis-Bücklers corneal dystrophy caused by the G623D mutation in TGFBI.
2008;14:1298-1302.
23 Wheeldon CE, de Karolyi BH, Patel DV, Sherwin T, McGhee CNJ,Vincent AL. A novel phenotype-genotype relationship with a TGFBI exon 14 mutation in a pedigree with a unique corneal dystrophy of Bowman’s layer.
2008;14:1503-1512.
24 Venkatraman A, Hochart G, Bonnel D, Stauber J, Shimmura S, Rajamani L, Pervushin K, Mehta JS. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry imaging of key proteins in corneal samples from lattice dystrophy patients with TGFBIH626R and TGFBI-R124C mutations.
2019;13(1):e1800053.
25 Trufanov SV, Tekeeva LY, Salovarova EP, Bag RZ, Sukhanova EV.Corneal dystrophies.
2018;134(5):118-125.
26 de Sousa Peixoto R, Mutch S, Eason J, Jaakson K, Haamer E,Maharajan VS. Association of unilateral lattice corneal dystrophy on slit lamp and bilateral confocal microscopy features with H572R mutation in the TGFBI gene.
2019;33(12):1973-1975.
27 Wang LY, Zhao CC, Zheng T, Zhang Y, Liu HR, Wang X, Tang XL,Zhao BW, Liu P. Torin 1 alleviates impairment of TFEB-mediated lysosomal biogenesis and autophagy in TGFBI (p.G623_H626del)-linked thiel-behnke corneal dystrophy.
2022;18(4):765-782.
28 Li DD, Qi YH, Han Q, Lin H, Zhao LM, Zhang CM. Analysis of TGFBI gene mutation in a Chinese family with atypical Reis-Buckler corneal dystrophy.
2009;26(3):245-248.
29 Qiu WY, Zheng LB, Pan F, Wang BB, Yao YF. New histopathologic and ultrastructural findings in Reis-Bücklers corneal dystrophy caused by the Arg124Leu mutation of TGFBI gene.
2016;16(1):158.
30 Nishino T, Kobayashi A, Mori N, Yokogawa H, Sugiyama K.
imaging of reis-Bücklers and thiel-behnke corneal dystrophies using anterior segment optical coherence tomography.
2020;14:2601-2607.
31 Liang QF, Pan ZQ, Sun XG, Baudouin C, Labbé A. Reis-Bücklers corneal dystrophy: a reappraisal using
and
imaging techniques.
2014;51(4):187-195.
32 Reda AM, Saad El-Din SA. Rare stromal corneal dystrophic diseases in Oman: a clinical and histopathological analysis for accurate diagnosis.
2020;13(2):70-75.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
International Journal of Ophthalmology的其它文章
- What can we learn from negative results in clinical trials for proliferative vitreoretinopathy?
- Suggestions on gut-eye cross-talk: about the chalazion
- A novel mutation of RPGR in a Chinese family with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa
- Novel technique of penetrating keratoplasty in high-risk grafts with significant corneal neovascularization
- COVlD-19 infection with keratitis as the first clinical manifestation
- Various configuration types of the foveal avascular zone with related factors in normal Chinese adults with or without myopia assessed by swept-source OCT angiography
