On the higher-order thermal vibrations of FG saturated porous cylindrical micro-shells integrated with nanocomposite skins in viscoelastic medium
2022-08-30ZeinbSoleimniJvidEhsnArshidSeedAmirMhdiBodghi
Zeinb Soleimni-Jvid ,Ehsn Arshid ,Seed Amir ,Mhdi Bodghi
a Department of Solid Mechanics,Faculty of Mechanical Engineering,University of Kashan,Kashan,Iran
b Department of Engineering,School of Science and Technology,Nottingham Trent University,Nottingham,NG11 8NS,UK
Keywords:Vibration analysis Cylindrical shells Saturate porous materials Nanocomposite materials Carbon nanotubes Sinusoidal shear deformation theory Viscoelastic medium
ABSTRACT Since the multi-layered structures are widely used nowadays,and due to interesting applications of cylindrical shells,this study is dedicated to analyzing free vibrational behaviors of functionally graded saturated porous micro cylindrical shells with two nanocomposite skins.Based on Biot's assumptions,constitutive relations for the core are presented and effective properties of the skins are determined via the rule of mixture.A sinusoidal theory is used to capture the shear deformation effects,and to account for the scale effects,the modified couple stress theory is employed which suggests a material lengthscale parameter for predicting the results in small-dimension.With the aid of extended form of Hamilton's principle for dynamic systems,differential equations of motion are extracted.Fourier series functions are used to obtain natural frequencies and after validating them,a set of parametric studies are carried out.The results show the significant effects of porosity and Skempton coefficient,pores placement patterns,CNTs addition and distribution patterns,temperature variations,material length-scale parameter and viscoelastic medium on the natural frequencies of the microstructure.The outcomes of this work could be used to design and manufacture more reliable micro cylindrical structures in thermodynamical environments.
1.Introduction
Due to the rapid development of cylindrical shells in different industries and their interesting capabilities in different fields of sciences,researchers have studied them and made them more efficient to employ in more cases.Cylindrical shells and panels such as pressure vessels have gained considerable attention because of their numerous applications in the aerospace and submarine industries[1].Single-layer structures have been analyzed by scholars to get a better understanding of their behaviors under different loading conditions.For instance,Lakis et al.[2] used classical thin shell theory and finite element (FE) method to analyze the nonlinear vibrational behavior of orthotropic cylindrical shells.Bert and Malik [3] used a numerical approach,namely the differential quadrature method (DQM) to investigate the vibrational response of thin cylindrical shells.They obtained the natural frequencies for different types of boundary conditions and compared them with previous studies to evaluate their results' accuracy.Bodaghi and Shakeri [4] considered the dynamic responses and free vibrations analysis of piezoelectric cylindrical shells,which are subjected to various impulsive loads.They employed the first-order shear deformation shell theory(FSDST)to assess the displacement fields,afterward;they applied three different types of electric conditions on its surfaces.The Fourier series utilized to derive the governing equations and also Laplace inversion and transform used to consider the time dependency.Also,in another work,a numerical scheme was employed by Gonçalves [5] to analyze cylindrical shells' vibrations.To overcome the shortcomings of simple singlelayer structures,using sandwich structures is one of the ways to get the best response.Sandwich structures are usually composed of three(or more)layers that are bonded to each other.The mid-layer of sandwich structures is called core and two other layers bonded to it are known as skins or face sheets.Naturally,according to the concept of sandwich structures,the core is much thicker than the skins while the skins are stiffer than the core.There are different choices for the core's material such as honeycomb,foams,or porous materials that can be integrated with stiffer skins.Previously,in sandwich structures(and especially their cylindrical types)the core was made of simpler materials.In this regard,static and dynamic behaviors of cylindrical shells which were covered by different types of coatings were considered by Sofiyev[6].He used the FSDST to take the shear deformation effect into account and also,presented closed-form solutions to obtain the results under uniform pressure.Liu et al.[7] used a three-dimensional (3D) elasticity theory to investigate displacement and stress in cylindrical shells with piezoelectric patches.Their achieved results indicated that both thickness ratio and stacking sequence had a significant impact on the bending of the shell.Natural frequencies of honeycomb sandwich cylindrical shell were investigated experimentally based on the theory simulations by Li et al.[8].They discussed the influence of structural parameters on flexural vibration.In another work,Li et al.[9]established a laminated shell model to study the dynamic response.The large amplitude vibration of a cylindrical shell with geometric nonlinearity was analyzed by Li et al.[10]and they proposed a new test method for testing the vibrations shell.A noted before,one of the best selection for the core of the sandwich structures is porous materials.In this regard,Solorza-Calder′on[11]based on Biot's assumptions investigated torsional waves of infinite fully saturated poroelastic cylinders.In another work,Babaei et al.[12]took a saturated porous cylinder into consideration to calculate its natural frequencies.Their work was based on three-dimensional elasticity theory and used Rayleigh-Ritz energy formulation and Newmark methods to solve differential equations.Nonlinear vibration analysis of nano cylinders was presented by Babaei and Eslami [13].The under evaluation model was composed of porous materials and their formulation also included the interaction between the model and nonlinear elastic foundation.Based on a sinusoidal shear deformation shells theory (SSDST),Wang and Wu[14] analyzed free vibration of functionally graded (FG) porous cylinders.The relationship between porosity and density coefficients was determined based on open-cell porous materials features.A unified dynamic model was established by Li et al.[15]for dealing with the thermal vibration behavior of FG porous stepped cylindrical shells with arbitrary shell thickness under complex operating conditions.Foroutan et al.[16] calculated the critical buckling load of imperfect FG porous cylindrical panels which were in a hygrothermal environment.They used the Galerkin method to solve the governing equations and found that increasing the porosity coefficients leads to a decrease in the static hygrothermal buckling response.Furthermore,other studies recently conducted on porous structures can be found in Refs.[17-23].Using composite materials helps to reach more efficient structures,but in many industries,stiffer and also lighter structures may be needed.Therefore,one of the ways that can reach this goal is to reinforce the composite structures with nano reinforcements.Reinforcements are available in different forms such as particles,clusters,or nanotubes.Carbon nanotubes (CNTs)reinforced functionally graded composites have full applications as structural members in advanced mechanical and aerospace industries.Owing to electrical,thermal and mechanical characteristics such as excellent stiffness,high strength and high value of aspect ratio but low density,CNTs have found considerable demand between designers and researchers in several industrial fields.Hence,understanding the static and dynamic behaviors of nanocomposite structures has become one of the emerging research topics in recent years[24-26].Due to the unique properties of CNTs such as their extremely high stiffness or their thermo-electric properties,they are mostly used nowadays.Accordingly,both high stiffness and lightweight properties are reached simultaneously.Several studies have been conducted [27-32] in this regard.Khayat et al.[33] presented their study on the nonlinear response of reinforced porous cylindrical shells integrated with two piezoelectric face sheets.They used higher-order shear deformation shells theory (HSDST) and also,Sander's nonlinear theory in their study.Shear deformable sandwich cylindrical shells were taken under evaluation by Balbin and Bisagni [34].They obtained the non-dimensional critical buckling load for cylindrical shells with composite skins.Wang et al.[35] used a trigonometric shear deformation theory to consider the dynamic stability of nanocomposite cylindrical micro panels.They used graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) as the reinforcement of the composite and evaluated the effect of different parameters on the structure's behavior.A semi-analytical scheme was conducted by Jiao et al.[36]to consider the dynamic buckling response of CNTs-reinforced composite shells.Galerkin and fourth-order Runge-Kutta methods were used to solve the governing equations.Arshid et al.[37] studied the vibrational behavior of a sandwich microplate which is contained FG porous materials core and piezoelectric nanocomposite face sheets.This structure is subjected to an electric field and Pasternak foundation.They assumed carbon nanotubes(CNTs)are added to make the faces stiffer via different distribution types.Due to the unique properties of porous material,two studies were conducted [38,39] that utilized this material in sandwich plates and investigated the effects of porosity factors on the behavior of functionally graded porous plates.Recently,Medani et al.[40] and Bendenia et al.[41] examined the effect of different FG-CNTs patterns on a sandwich plate.Also,shear deformation theory(FSDT)has been considered to obtain the motion equations and to study static and dynamic behaviors.Finally,it is explicitly shown that the(FG-CNT)face sheet has a high resistance compared to Epoxy faces and the symmetric type is more affected on the structure compared to other distributions of CNTs.In the field of micro-shells,based on the framework of modified couple stress theory(MCST),Mehralian et al.[42]analyzed the buckling response of an isotropic piezoelectric cylinder.They carried out a study to investigate the different parameters' influence on the critical buckling load.In another work,Ghorbani et al.[43]investigated the vibrational behavior of a cylindrical shell considering both surface and size dependencies.Gurtin-Morduch and nonlocal strain gradient theories were used to reach the aim.They found that surface's properties have significant effects on the vibrational behavior of the system.Stability analysis of FG cylindrical microshells was studied by Ning et al.[44].The under consideration model was subjected to swirling annular flow including the fluid viscosity.Sobhy and Zenkour [45] utilized the MCST to study the bending of a viscoelastic nanobeam.They simulated the structure laying on double layers of foundations with Kelvin-Voigt viscoelastic model and a shear layer.They showed the effects of viscoelastic damping,the stiffness and damping coefficients of the viscoelastic substrate on the deflections and stresses.Mohammadimehr and Mehrabi[46]studied small-scale effect on the stability and vibrations of sandwich cylindrical shells.They presented the formulation based on the MCST double-bonded Reddy shells theory and solved the equations via DQM.They solved the governing equations for simply-supported structure.Zenkour and El-Shahrany [47] considered vibration and deflection of a threelayered magnetostrictive plate,and discussed the influence of the magnitude of feedback control gain,viscoelastic foundations,and other properties on deflections and eigenfrequency values.Also,they concluded that viscoelastic foundation and the feedback control gain value affect the vibration behavior of the smart sandwich plates.In addition,Zenkour and El-Shahrany[48]studied the nonlinear hygrothermal effects on the vibration analysis of magnetostrictive viscoelastic laminated sandwich plates.These structures were rested on two parameters Pasternak's foundations.The material properties of the viscoelastic plate's layers were obtained based on the Kelvin-Voigt model.Bellal et al.[49] and Rouabhia et al.[50] studied Viscoelastic foundations that considered this foundation is embedded on a single-layered graphene sheet.The visco-Pasternak's medium is considered the damping effect to the classical foundation model that is modeled by the shear and linear foundation coefficient.In the results section,the impacts of the shear and linear foundation coefficients and damping parameters are examined.
Regarding the literature review,the lack of a study on sandwich micro cylindrical shells constituted of an FG saturated porous core and two CNTs-reinforced composite skins is obvious.So,the authors have been motivated to conduct this study.As stated,the mid-layer is made from FG porous material saturated by fluid that its constitutive relations are presented based on Biot's assumptions.CNTs are selected to reinforce the skins to enhance the whole structure's stiffness.The rule of mixture (RM) is used to evaluate the effective properties of the nanocomposite skins.Using SSDST,which accounts for the shear deformation effects via a sinusoidal shear function,leads to obtain more complex and also,more accurate results.Since this study is in small-scale,MCST which suggests a material length-scale parameter is employed.The extended form of Hamilton's principle for dynamic systems is applied to derive the governing motion equations and they are solved analytically based on Fourier series functions.A parametric study is carried out to investigate the effects of different parameters on the natural frequencies of the microstructure.Due to the absence of similar results in the specialized literature,this paper is likely to fill a gap in the state of the art of this problem,and provide pertinent results that are instrumental in the design of micro pressure vessels integrated with nanocomposite skins in thermal environments.
2.Constitutive relations
The model under evaluation is a three-layered cylindrical microshell in which the middle layer so-called the core,is composed of FG saturated porous materials coated with two nanocomposite skins.The configuration of the mentioned microstructure is shown in Fig.1.Thicknesses of the layers from the outer to the inner are respectively shown by h,h,and h,and hdenotes the total thickness of the microstructure.Moreover,the length of the shell is depicted by L and its curvature radius and central opening angle are shown by R and β,one after another.The thermal environment effect on the natural frequencies of the microstructure is examined and the viscoelastic medium is chosen as a seat for the whole structure.
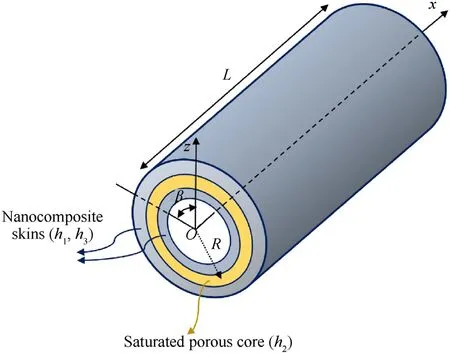
Fig.1.Schematic diagram of the under evaluation three-layered cylindrical micro shell.
The general form of constitutive law of the microstructure in a thermal environment for both face sheets and core can be written as follows [51]:

in which σand εdenote the stress and strain components,respectively and Cdemonstrates the elastic coefficients defined for the core and skins,separately.Also,αis the thermal expansion coefficient and ΔT shows temperature difference from the ambient one.
The elastic coefficients of Eq.(1)for the core can be expressed as[52]:
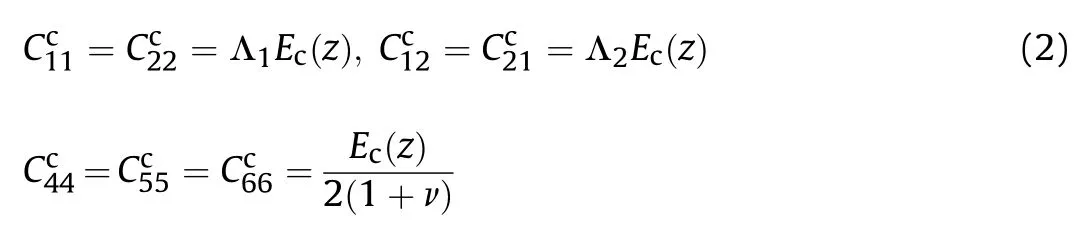
where E(z) is Young's elasticity modulus.Also,we have:
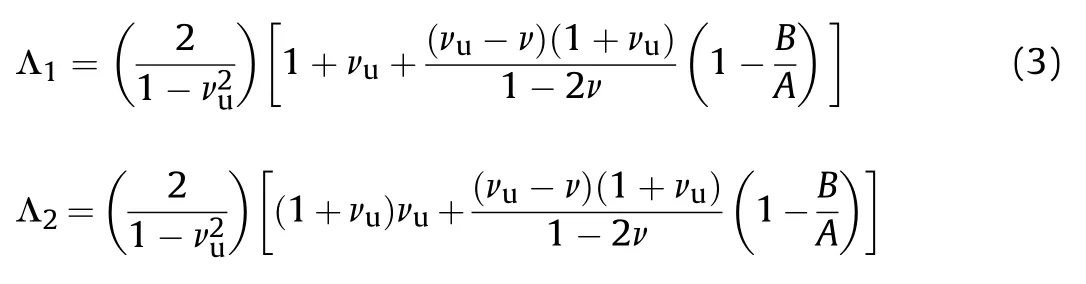
in which,ν and νare Poisson's ratios in drained and undrained states,respectively and:

G(z)denotes the shear modulus which is defined as G(z)=E(z)/(2 (1 +ν)) [53].It is noteworthy that in unsaturated porous materials,the drained and undrained are equal to each other,but considering the porous materials in a saturated condition leads to the above-mentioned relations that both drained and undrained Poisson's ratios appear in.In the saturated porous materials,the pressure of the fluid confined to the pores is shown by P which can be obtained with the aid of the below relation [54]:

where ξ denotes the fluid volume changes and η is the Biot's coefficient.Biot's modulus is shown by M defined as [55]:

In the undrained condition,Poisson's ratio obeys the below relation:

where B is the Skempton coefficient that is a dimensionless number and indicates the effect of the fluid within the pores.
Thermo-mechanical properties of the FG saturated porous core change through its thickness that indicates the pores placement.The Young's elasticity modulus,density,and thermal expansion coefficient vary across the core's thickness via the following general relations [56]:
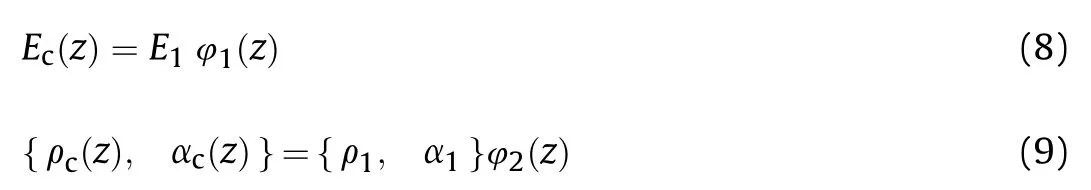
In the above relations,the maximum values of Young's modulus,density,and thermal expansion coefficient are respectively shown by E,ρ,and α.Also,φ(z)and φ(z)are porosity functions.For the first pattern of pores distribution that is called “Type Ain this paper,the pores are placed through the core's thickness asymmetrically.Therefore,the porosity functions are defined as [57]:
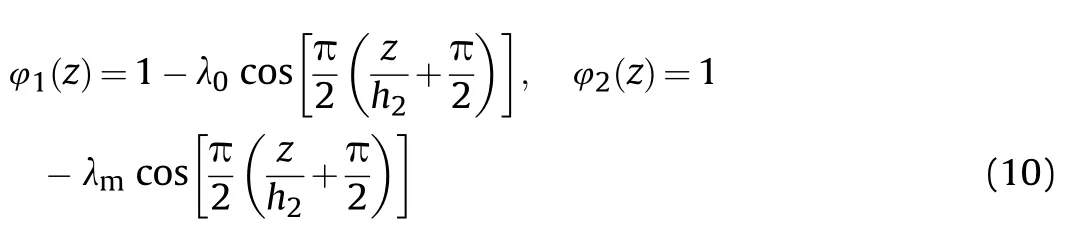
in which λis the porosity coefficient that shows the ratio of pores volume to the whole volume.Also,λis mass density coefficient that can be obtained via [58]:

As the second pattern of pores placement,symmetric one which is known as “Type Bis considered as:
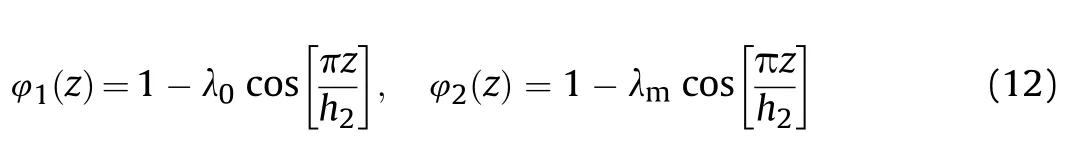
And as the third pattern or “Type C,if the pores are distributed monotonically through the thickness and the following porosity functions are ruled:
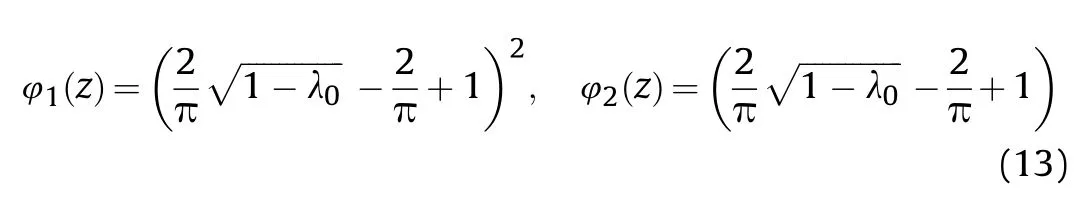
Next,it turns to consider the constitutive relations for the face sheets.The face sheets are made from FGCNTs-reinforced composites that Poly Methyl Methacrylate (PMMA) is selected as their matrix phase.The components of the elastic matrix introduced in Eq.(1) for the face sheets can be expressed as:

As can be understood from the above relations,the mechanical properties of the face sheets are graded functionally in the z-direction.To determine their effective values,different micromechanical models have been used by numerous researchers[59-62].Among these different models,RM is selected in this work to obtain the effective properties of the nanocomposite face sheets due to its accuracy and simplicity both together.Based on the RM scheme,the following relations are derived to determine the mechanical properties of the skins [25]:
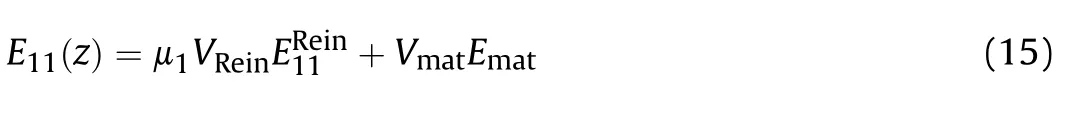
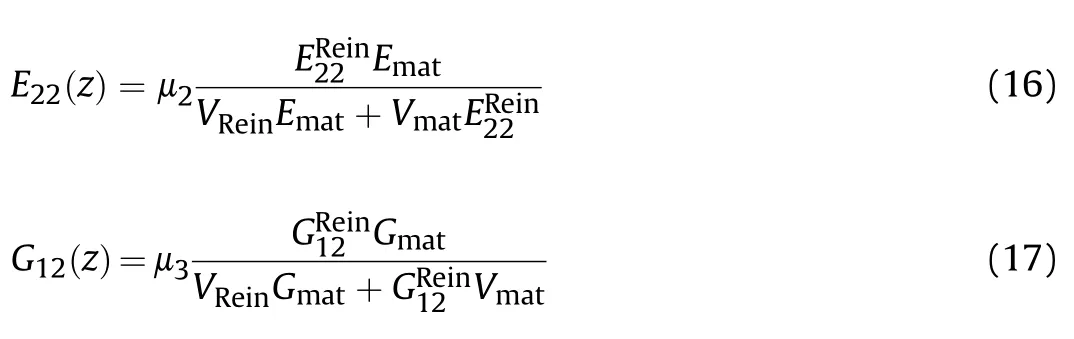
in which the longitudinal and transverse Young's and shear moduli of the skins are depicted by E(z),E(z),and G(z),one after another.It should be noted that superscript “Rein” and subscript“mat” denotes the mentioned properties in CNTs reinforcement and matrix.Also,to get the most accurate results,it is necessary to determine the CNTs' efficiency parameter μ(j=1,2,3).These efficiency parameters are obtained by comparing theoretical results achieved based on the RM and those of experiments or molecular dynamics simulations.In this study,they are estimated using molecular dynamic simulations,as reported in Ref.[63]and are listed in Table 1.Also,the RM can be developed for other thermomechanical properties such as density and thermal expansion coefficient of the skins as follows:

Table 1.Efficiency parameters of CNTs based on their volume fraction [63].
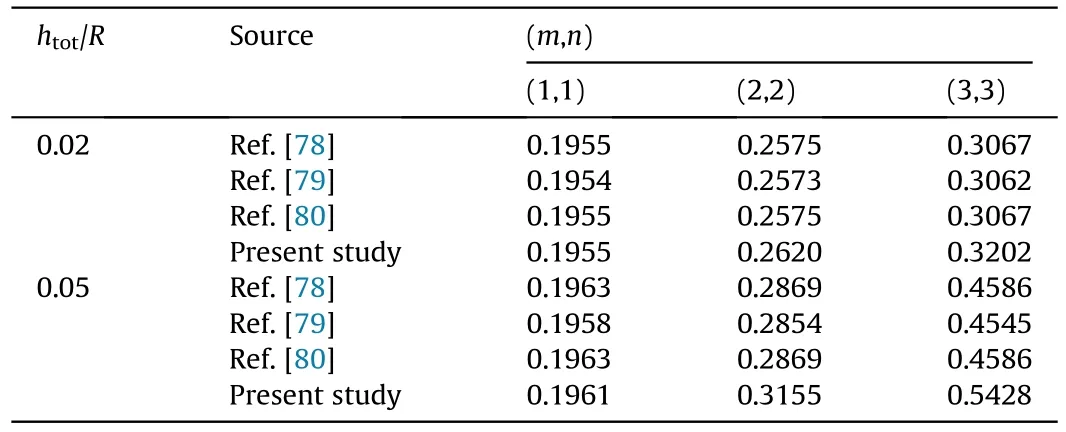
Table 2.Comparing the results in simpler state with those of previous studies.
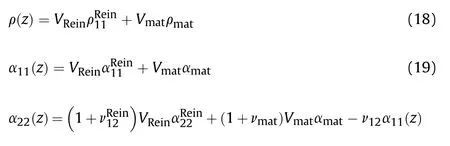
The CNTs are distributed in the skins based on uniform and FG types.Therefore,the following distribution patterns are considered here[64]:
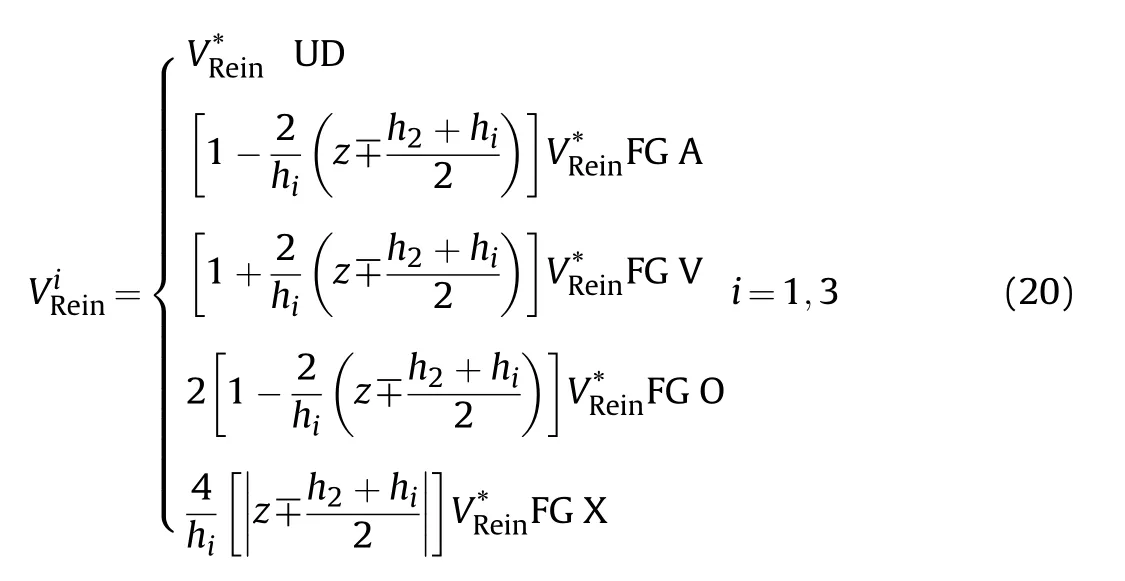
However,Poisson's ratio assumed to obey the following relation[65]:



3.Kinematic equations
Since the main purpose of the present study is to analyze global response of thin to moderately thick shells,equivalent single layer theory of the SSDST is used to describe the kinematics of deformation of the shell.The displacement components of each point(i.e.u,v,and w) based on the SSDST in the cylindrical coordinate system may be demonstrated as [14]:


The strain components of the under evaluation micro model can be determined via the following relations:

It should be noted that line elements lying perpendicular to the mid-surface do not change length during deformation,so that the transverse normal strain is zero throughout the shell.
In this work,the governing motion equations are derived using Hamilton's principle and variational approach.According to Hamilton's principle for dynamic systems,variation of the total energy of a system in a period equates to zero [66]:

where Udenotes strain energy of the micro cylindrical shell,K is its kinetic energy and the work done by external loads is shown by WTot.
Since the current structure is in micro-scale,MCST is used to capture the size effects,so the relation of total strain energy of all three layers can be written as follows [67]:

Higher-order stresses are shown by min the above equation expressed as:

In Eq.(27),l denotes the material length-scale parameter and setting it to zero,converts the microstructure to a macro one.Also,Lame's parameter is presented by μ(z),defined as [68]:

The symmetric rotation gradient tensor components can be obtained in cylindrical coordinate as [69]:



Now,for the kinetic energy of three layers,the following equation may be used [70]:
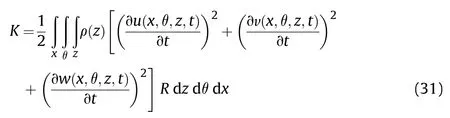
The applied external work to the microstructure arises from the viscoelastic medium and the thermal environment [71].So,the total work can be obtained by summing these two mentioned works(i.e.W=W+W)[72].The thermal load's work is determined as [73]:


The viscoelastic foundation consists of the springs,shear layer,and dashpots in which k,kD show parameters of spring,shear layer and dashpot[74].The following relation is used to obtain the work of the foundation [75].
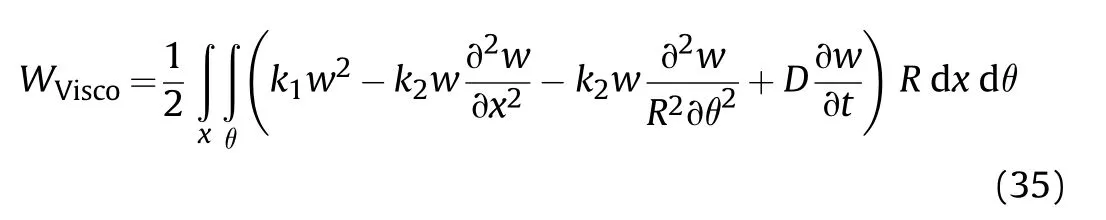
Consequently,its’ variations yields to

Inserting variations of total strain energy,kinetic energy,and also external work into Hamilton's principle relation leads the governing equations of motion as:



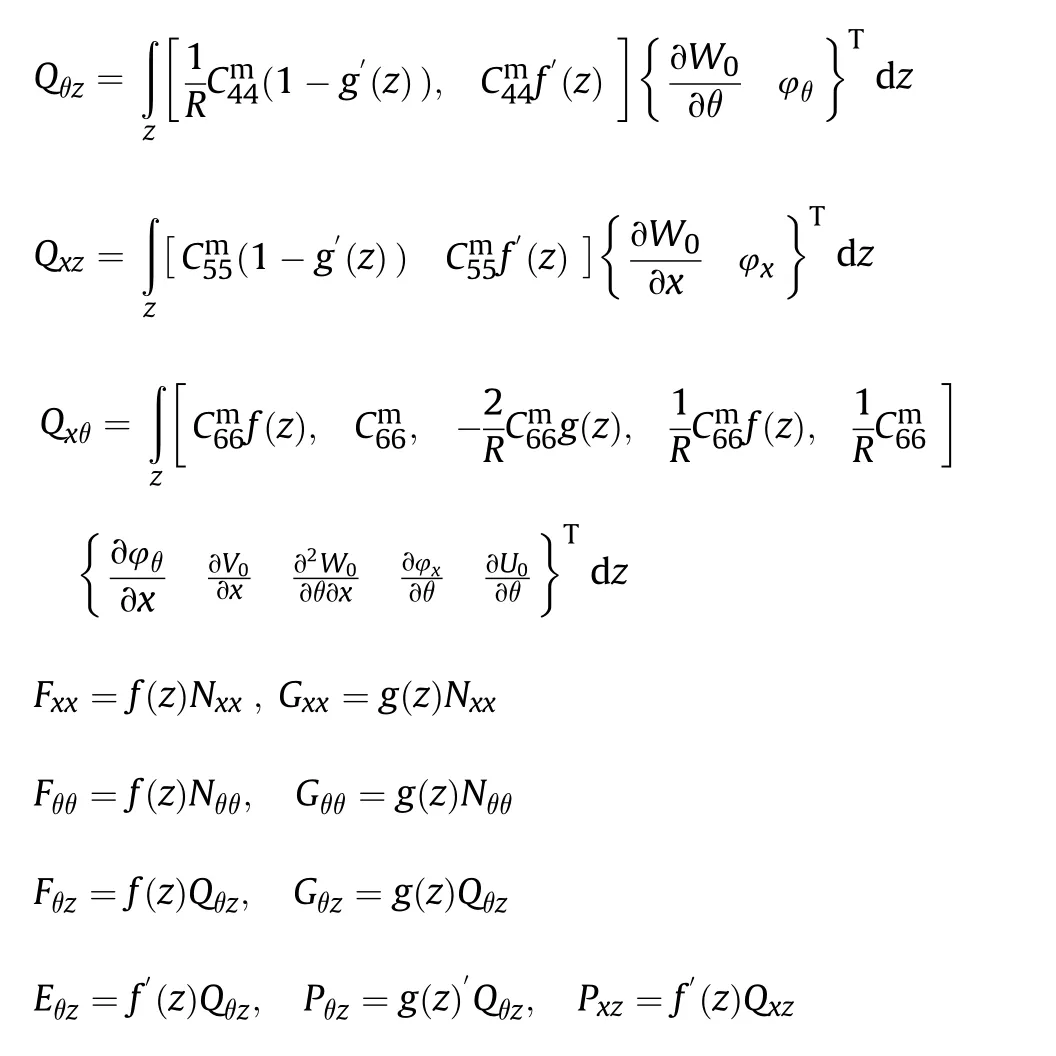
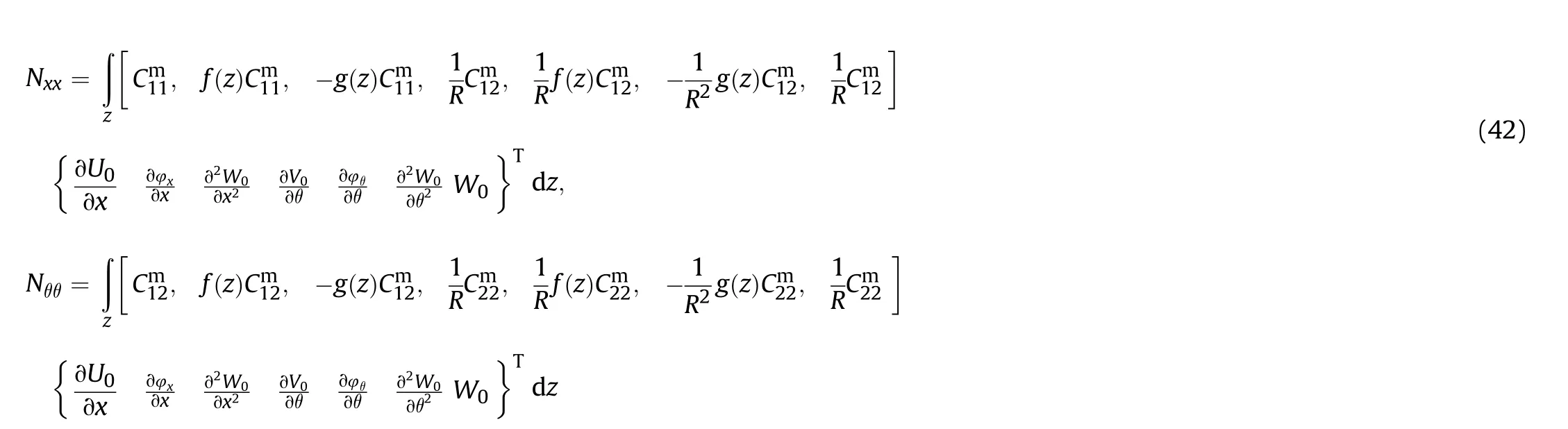
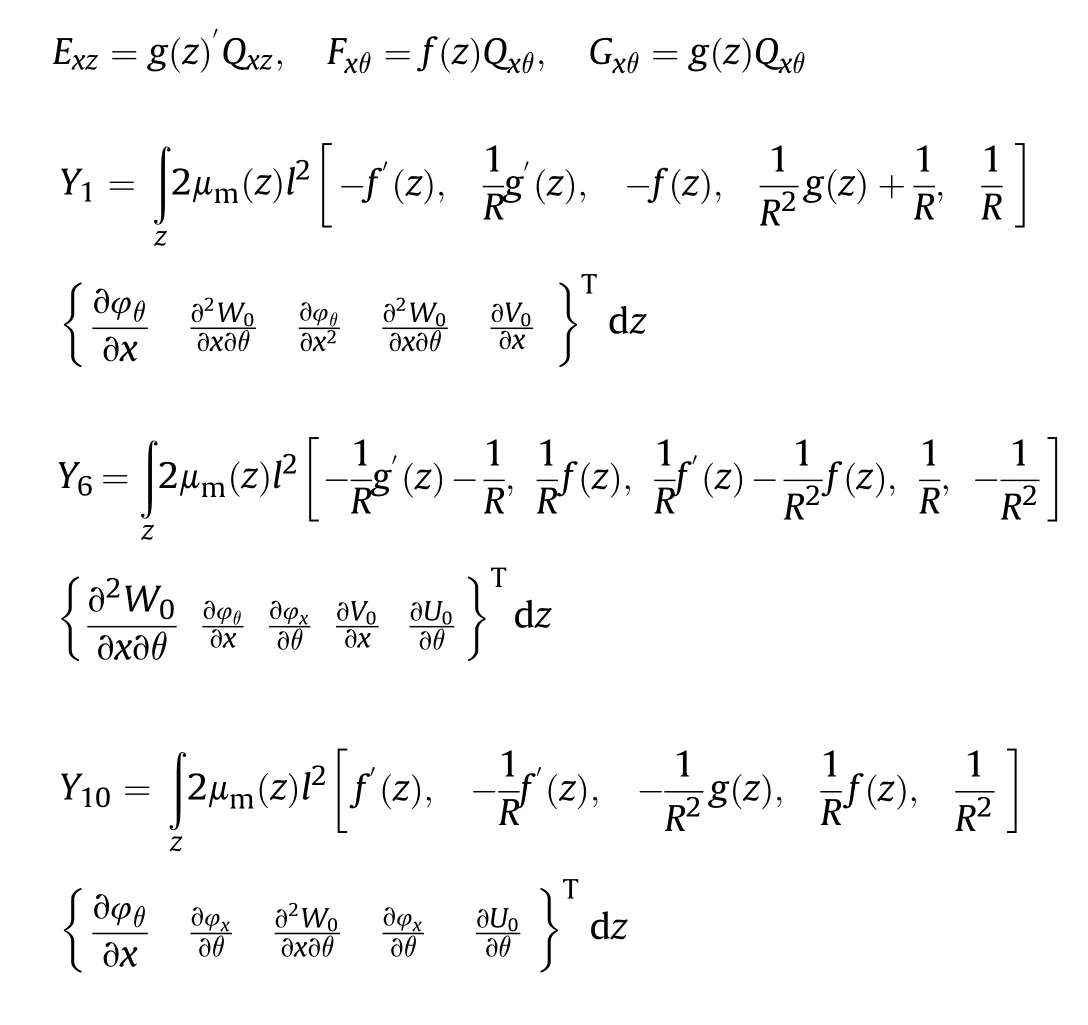


4.Solution technique
In this study,in order to solve the governing differential equations analytically,the Fourier series functions are employed which satisfy the geometrical simply-supported boundary conditions.Based on this scheme,the displacement components are assumed to be [76]:

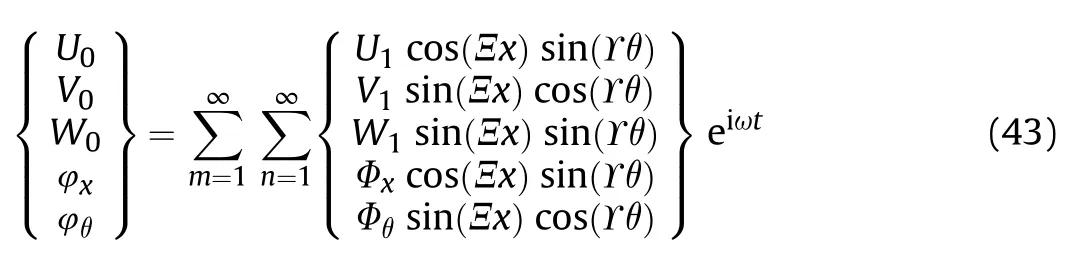
where U,V,W,Φ,and Φdenote the unknown coefficients.Also,Ξ=nπ/L and Υ=mπ/β,in which wavenumbers along x and θ directions are represented by n and m,respectively.By substituting the above-mentioned functions of Eq.(43) into the governing motion equations(37)-(41),they can be presented in the following matrix form [77]:
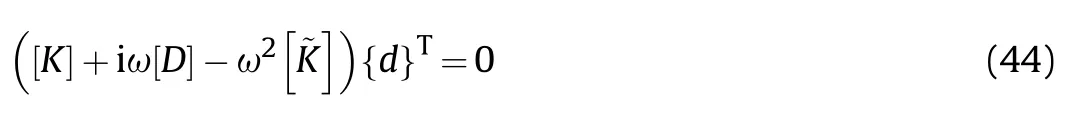
where [K],[D],and [~K] are the stiffness,damping,and mass matrices,respectively and displacement vector is presented by{d}.The non-zero components of these matrices are given in “Appendix”.The non-trivial solution of Eq.(44)leads to obtain the natural frequencies of the microstructure,i.e.ω.
5.Results and discussion
In the previous sections,the fundamental relations were presented to derive the motion equations related to a three-layered micro-shell.As stated before,the governing differential equations were solved via an analytical method.The results will be presented in this section.
5.1.Validation of the results
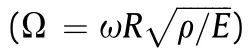
Table 3.Thermo-mechanical properties of the porous core and nanocomposite skins[20,81].

Fig.2.Effect of porosity and Skempton coefficients based on different patterns of pores distribution on the fundamental natural frequency.
5.2.Case study

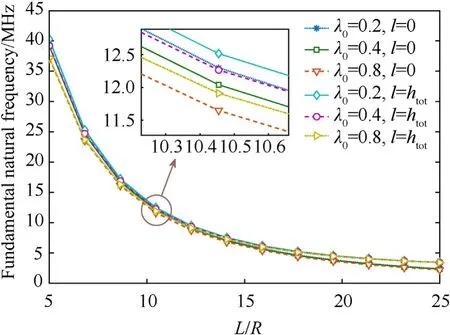
Fig.3.Effect of scale and porosity coefficient versus slenderness ratio on the fundamental natural frequency.
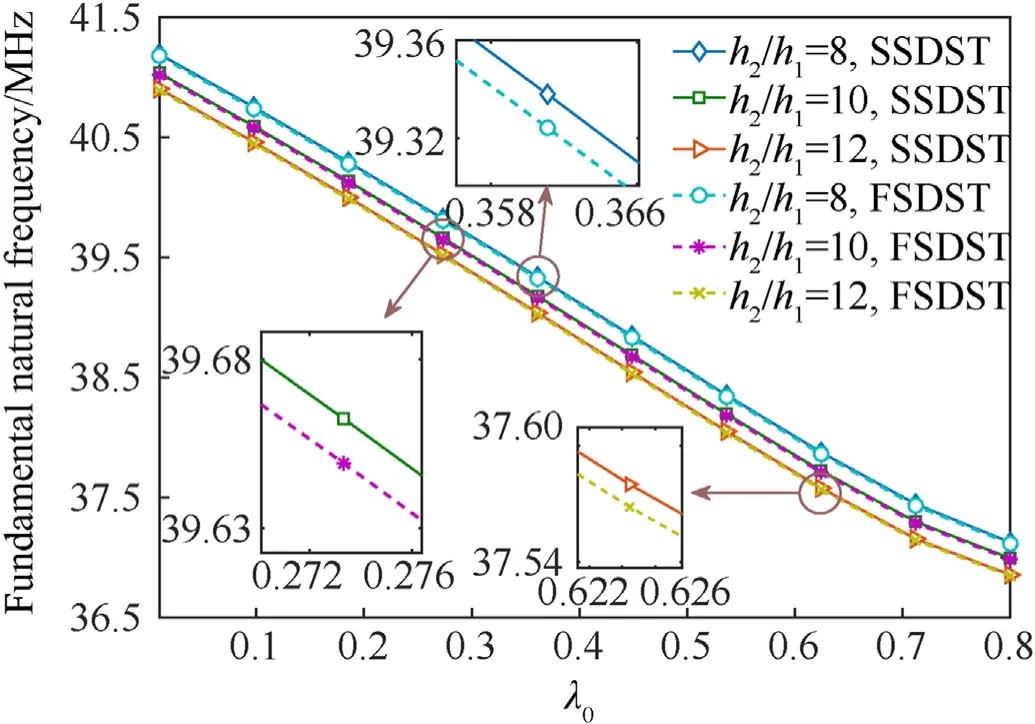
Fig.4.Thicknesses ratio effect on the natural frequency of the micro cylindrical shell based on both SSDST and FSDST.

Fig.5.Influence of central opening angle variations on the natural frequency of the microstructure.
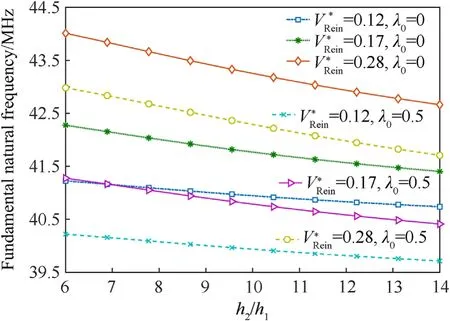
Fig.6.Considering the effect of CNT reinforcements volume fraction on the results.

Fig.7.Effect of different patterns of CNTs distribution across the skin's thickness versus L/htot.

Fig.8.Effect of mode number and central opening angle based on both SSDST and FSDST on the results.
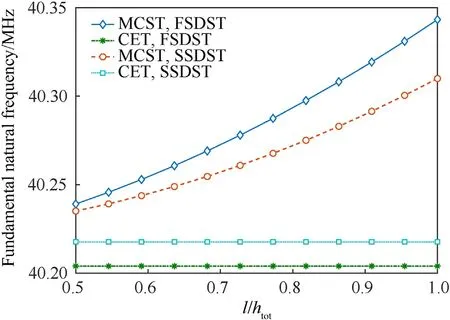
Fig.9.Influence of scale based on SSDST and FSDST on the 1st natural frequency.
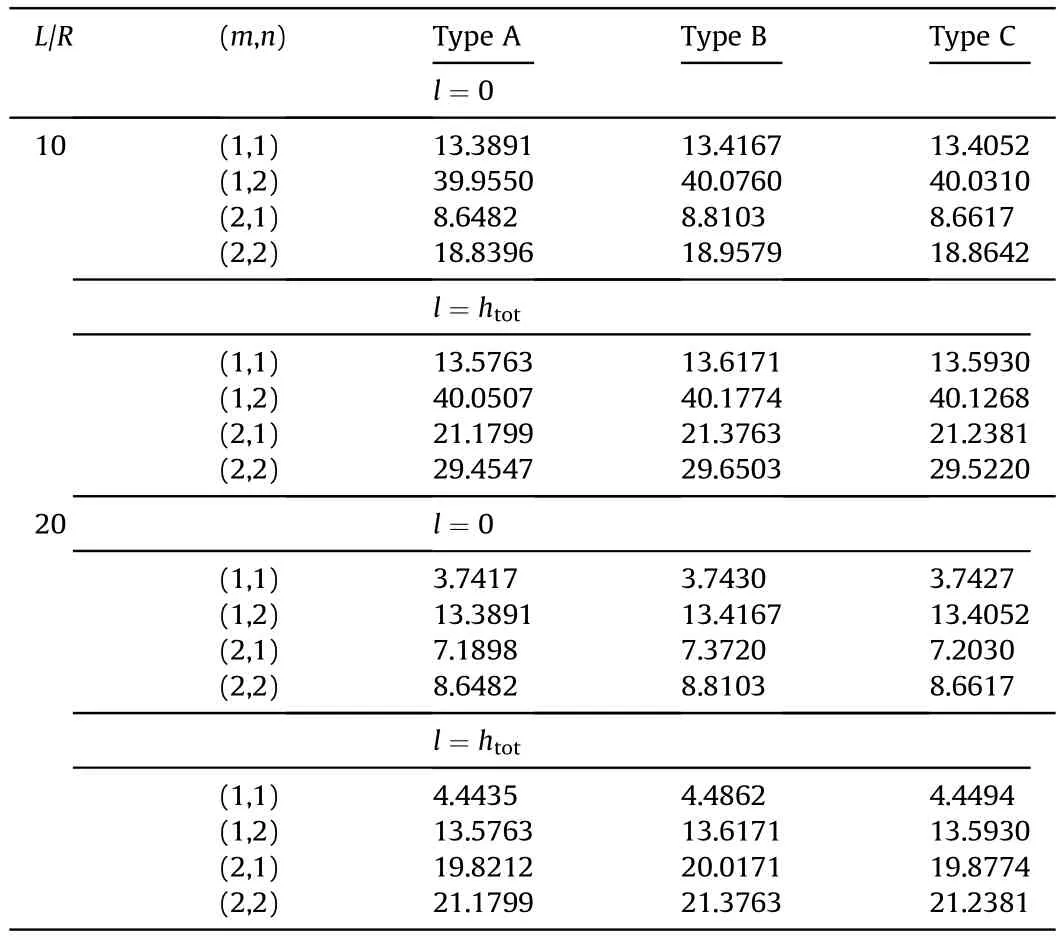
Table 4.Effect of different parameters on the first four natural frequencies based on SSDST.
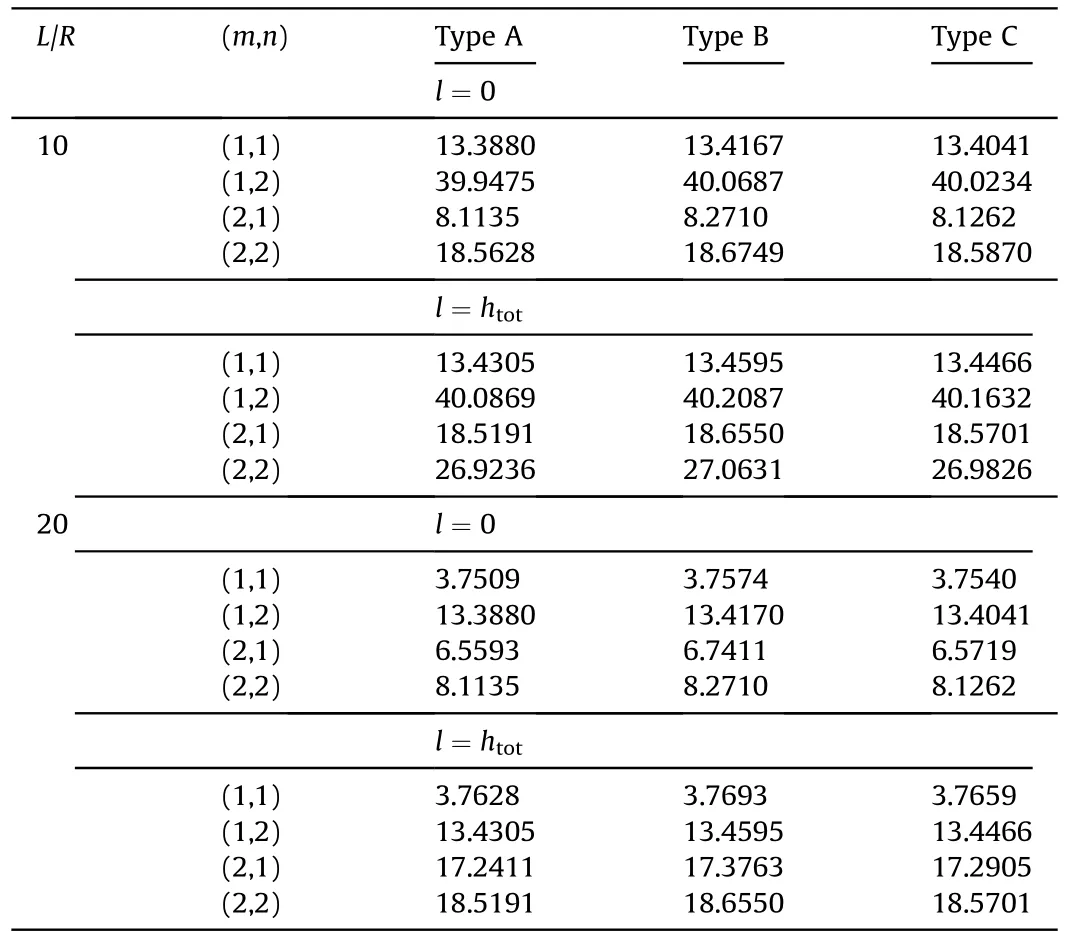
Table 5.Effect of different parameters on the first four natural frequencies based on FSDST.

Fig.10.Length-scale parameter effect on the fundamental natural frequency.
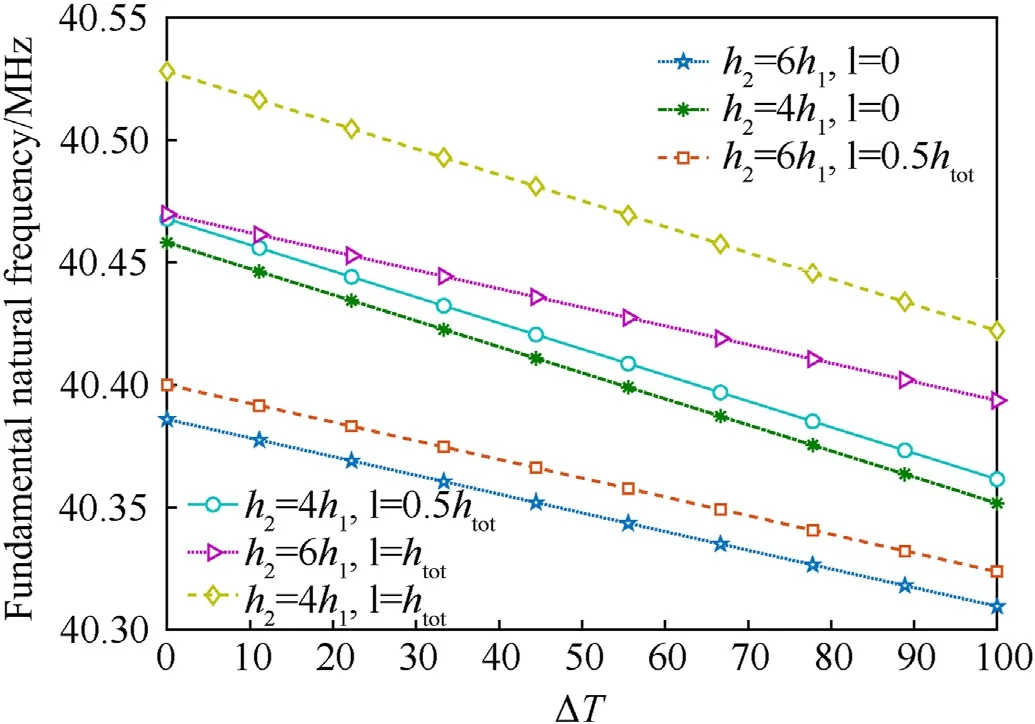
Fig.11.Temperature variations effect on the results for different thicknesses ratio.
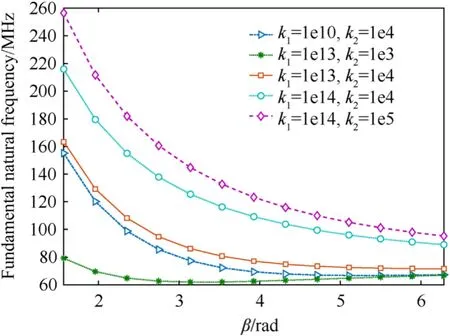
Fig.12.Effect of spring and shear layer parameters of elastic foundation on the first natural frequency of the micro cylindrical shell.
6.Conclusions
Natural frequencies of a three-layered cylindrical micro-shell composed of an FG saturated porous core and two nanocomposite skins were investigated in this work.The shear deformation and scale effects were captured with the aid of SSDST and MCST,respectively.The whole structure was put in a thermal environment and the viscoelastic medium effect was considered.Extended Hamilton's principle for dynamic systems was used to derive the differential motion equations that were solved analytically by Fourier series functions.The reliability of the results was ensured by validating them in a simpler state with the previous works and by considering the effect of the parameters on them.The following conclusions were made.It was observed that among different types of porosity distribution,the symmetric one leads to the highest natural frequencies.Also,increasing the porosity coefficient reduces the frequency due to a reduction in the structure's stiffness,but enhancement in the Skempton coefficient leads the natural frequency to increase.Regardless of CNTs distribution patterns,adding CNTs and also increasing their volume fraction,raises the frequency significantly.Among considered FG patterns for CNTs distribution,FG V-A and FG A-V ones lead to the highest and the lowest values of frequency,respectively.Increasing temperature makes the structure softer and accordingly,the frequency reduces.The results that are obtained based on CET(i.e.for macrostructure)are lower than those of MCST (i.e.microstructure) and increasing the material length-scale parameter of MCST,causes an enhancement in frequency.Among the three parameters of the viscoelastic medium,two of them,i.e.,springs'and shear layer's ones increase the natural frequency.But increasing the dashpots'parameter leads the results to reduce.The results supplied in the present work are expected to be instrumental toward a reliable design of micro pressure vessels integrated with nanocomposite skins in thermal environments.
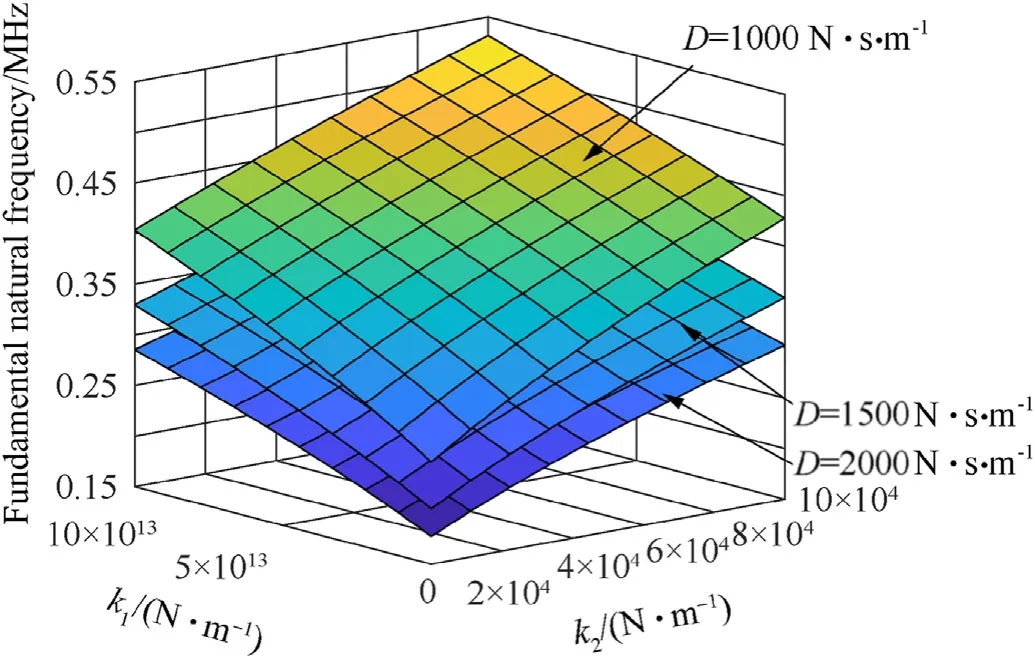
Fig.13.Simultaneous consideration on effect of three parameters of the viscoelastic medium on the natural frequency.
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
The components of stiffness,damping,and mass matrices noted in Eq.(44) are defined as:
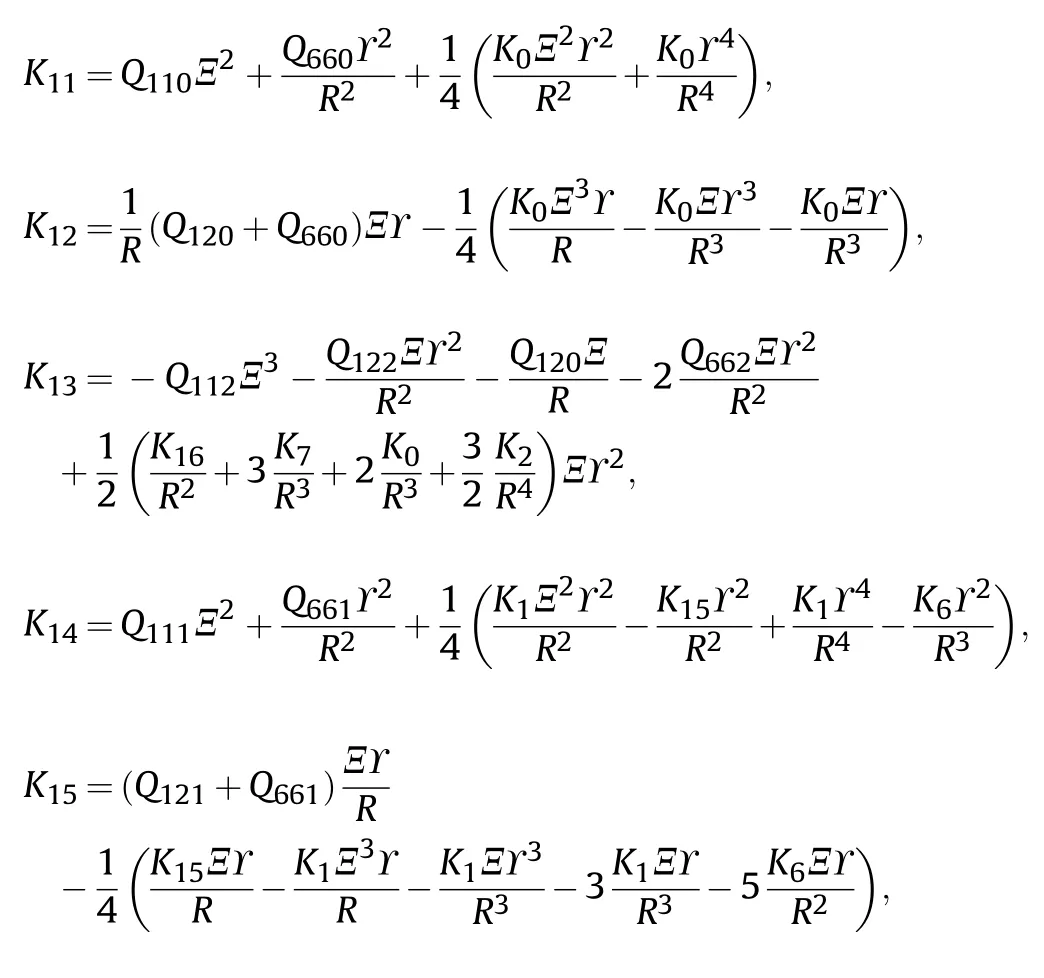






杂志排行
Defence Technology的其它文章
- Experimental study on propagation characteristics of rotating detonation wave with kerosene fuel-rich gas
- Adaptive robust control for triple avoidance -striking -arrival performance of uncertain tank mechanical systems
- Experimental study on WFeNiMo high-entropy alloy projectile penetrating semi-infinite steel target
- Numerical investigation of a muzzle multiphase flow field using two underwater launch methods
- Shock wave and bubble characteristics of underwater array explosion of charges
- A micro-chip exploding foil initiator based on printed circuit board technology
