Results and Analysis on Proficiency Testing and Measurement Audit for Molds and Yeast in Cosmetics
2022-07-14MaQunmingZhouLeiChenRuiChenJingjingHuaXin
Ma Qunming,Zhou Lei,Chen Rui,Chen Jingjing,Hua Xin
Jiangsu Oppeal Daily Chemical Co.,Ltd.,China
Zhu Qingli,Yang Jia
Yangzhou Food and Drug Inspection and Detection Center,China
Abstract In order to improve and evaluate the proficiency testing of cosmetic microorganism detection laboratory,strengthen the control of cosmetic microbial detection quality.In 2019 and 2020,the laboratory of the author’s unit participated in the proficiency testing (NIFDC-PT-242) and measurement audit (NIFDCMA-2020-148) for molds and yeasts in cosmetics organized by the National Institutes for Food and Drug Control,respectively.According to the operation instruction for counting molds and yeasts in cosmetics and the Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmetics,the results of the sample for proficiency testing numbered NIFDC-PT-242 were unsatisfactory,and the results of the sample for measurement audit numbered NIFDCMA-2020-148 were satisfactory.In view of the unsatisfactory results,the laboratory analyzed and summarized from the aspects of “human,machine,material,method and environment”,providing reference for the laboratories participating in proficiency testing and measurement audit..
Key words proficiency testing;measurement audit;molds and yeasts;cosmetics
Due to the sustainable development of national economy,the disposable income of urban and rural residents in our country increases constantly,the demand and purchasing ability of consumers are continuously improved,the consumption habit of cosmetics is being cultivated gradually,and cosmetics have become daily indispensable necessities in people’s daily life.The count of molds and yeasts in cosmetics can objectively reflect the degree of fungal contamination in the production,processing,transportation and storage of cosmetics,which is one of the important indexes to judge the quality of cosmetics.In the process of counting molds and yeasts,errors caused by factors,such as sample dilution,cross contamination and medium selection,may lead to deviation of final results.
Proficiency testing:participants’ proficiency was evaluated against pre-established criteria with inter-laboratory comparisons.Measurement audit is a type of proficiency testing plan,which is sometimes referred to as “one-to-one” proficiency testing plan[1].As one of the internationally accepted scientific and effective laboratory quality control methods,proficiency testing and measurement audit are important means to evaluate laboratory detection ability.By participating in proficiency testing activities,the laboratory carries out quality control to improve the laboratory's detection ability[2].In 2019,the laboratory of the author's unit participated in the proficiency testing for the counting of molds and yeasts in cosmetics organized and implemented by the National Institutes for Food and Drug Control,and the results of samples with high and low concentrations were not satisfied.In 2020,we participated again in the measurement audit for the counting of mould and yeast in cosmetics organized and implemented by the National Institutes for Food and Drug Control,and the results of two samples with high concentration were satisfactory.Then,the implementation process and results of these two proficiency testing were analyzed by participating in the external quality control activities for the counting of molds and yeasts in cosmetics organized and implemented by the National Institutes for Food and Drug Control for two times,providing valuable experience for the laboratory to improve the detection technology level and effectively implement the internal quality control of molds and yeasts.
1 Experiments
1.1 Test samples
The samples for proficiency testing were 2 NIFDC-PT-242 counting samples of molds and yeasts in cosmetics,which were white bacteria balls and paste foundation in vials.The codes were CODE028 and CODE052 respectively,the samples were 1 g/vial provided by the National Institutes for Food and Drug Control,with the storage temperature of-20 ℃.
The samples for measurement audit were 2 NIFDC-MA-2020-148 counting samples for molds and yeasts in cosmetics,which were white bacteria balls and paste foundation in vials.The codes were CODE1 and CODE2 respectively,the samples were 1 g/vial provided by the National Institutes for Food and Drug Control,with the storage temperature of-20 ℃.
1.2 Reagents and instruments
OptiMairTMACB-4E1 vertical flow ultra-clean workbench (Esco (Shanghai) Trading Co.,Ltd.),SPX-150B-Z biochemical incubator (Shanghai Boxun Medical Biological Instrument Corp.),YXQ-70A vertical pressure steam sterilizer (Shanghai Boxun Medical Biological Instrument Corp.),Thermo ScientificTM digital scroll oscillator (Thermo Fisher Scientific (China) Co.,Ltd.),FA100A analytical balance (Shanghai Sunny Hengping Scientific Instrument Co.,Ltd.),sodium chloride (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co.,Ltd.),Rose Bengal culture medium (Beijing Land Bridge Technology Co.,Ltd.).
1.3 Experimental methods
1.3.1 Sample processing
Opening of vials:as the vials are in high vacuum state,they shall be opened in the biological safety cabinet.
1.3.2 Dilution of samples
5 mL of sterile normal saline was aseptically added into each vial of samples,which were completely dissolved and fully mixed it,shaken well with vortex shaker,and then transferred to sterilized test tube.Then,vials were washed twice with sterile normal saline,1mL each time,and 1:10 dilution test solution prepared with 10mL of sterile normal saline volume in final test tube.
1.3.3 Detection process
According to the methods to test molds and yeasts specified in Chapter V of the Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmetics (2015 Edition)[3],a 1 mL sterile pipette was used to suck 1mL of prepared 1:10(i.e.10-1) diluted test solution,which was then slowly injected into a sterile test tube containing 9mL diluent(sterile normal saline) along the tube wall,which was shaken well to mix it uniformly,for preparing 1:100(10-2) homogeneous sample solution to be detected.10-fold serial homogenate with diluted samples was prepared with the same method until reaching the homogenate with 10-6dilution to be detected.For each incremental dilution,the 1 mL sterile tip was replaced once.At the same time of 10 times incremental dilution,a set of blank plates were required to make,with 1mL of sample homogenate with all dilutions was absorbed into the sterile plates,and 2 plates for each dilution.15~20 mL of Rose Bengal culture medium was cooled to (45 ± 1) ℃ in time and poured into the plate,which was then shaken slowly to mix well.After the culture medium was solidified,the plate was inverted and cultured in a biochemical incubator at (28 ± 2) ℃ for 5 days.The results could be observed with naked eyes,and counted by magnifying glass or colony counter when necessary.According to the same procedures,the proficiency testing of NIFDC-PT-242 and measurement audit of NIFDC-MA-2020-148 was detected under the same operating conditions.
2 Results and Discussion
2.1 Test results
The average reading of the two plates was taken as the final result.The results of proficiency testing form olds and yeasts in NIFDC-PT-242 cosmetics and measurement audit form olds and yeasts in NIFDC-MA-2020-148 cosmetics are shown in Table 1 and Table 2,respectively.
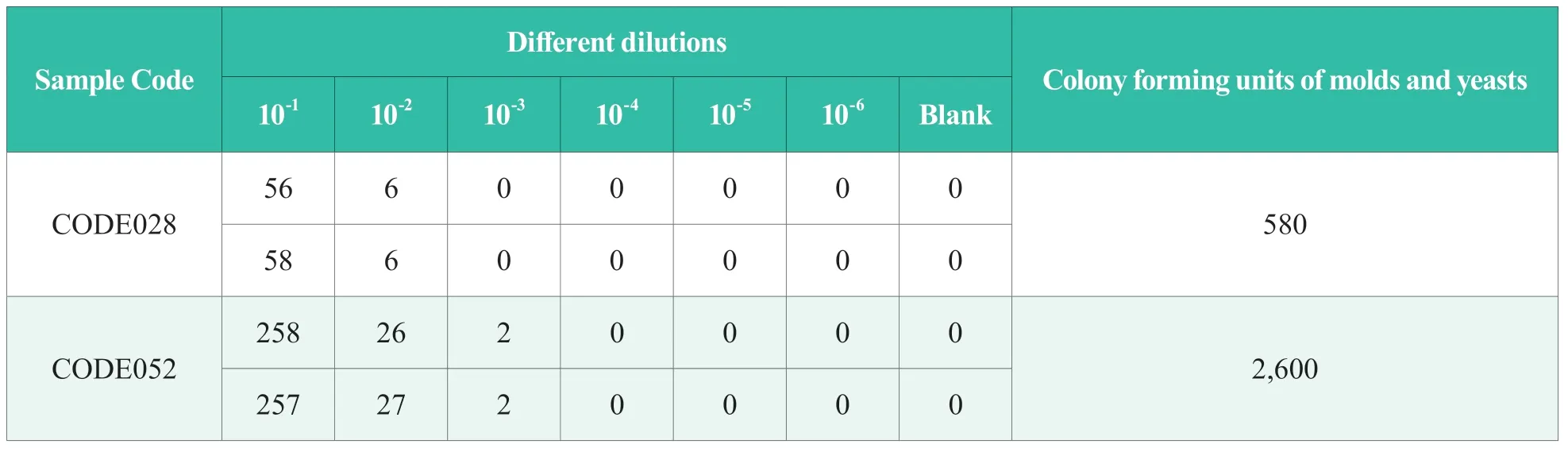
Table 1.Results of proficiency testing for molds and yeasts in NIFDC-PT-242 sample (CFU/g)
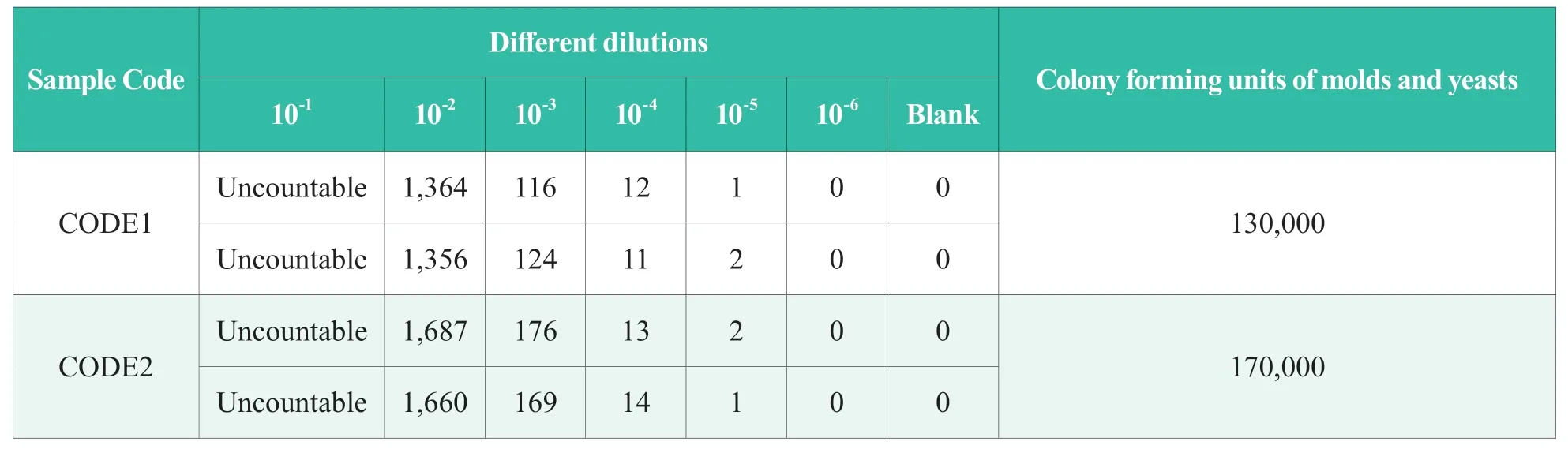
Table 2.Results of measurement audit for molds and yeasts in NIFDC-MA-2020-148 sample (CFU/g)
2.2 Analysis and discussion
The proficiency testing for molds and yeasts in NIFDC-PT-242 cosmetics was quantitative detection[4],which is a combination of high concentration sample and low concentration sample.The laboratory was required to report the content(CFU/g) of molds and yeasts in each sample of cosmetics.The results reported by the laboratory were unsatisfactory for both the samples with high and low concentrations,with 7.83 for the sample with low concentration and 7.46 for the sample with high concentration ,both of which were below the specified values (5.28 for the sample with high concentration,4.72 for the sample with low concentration,and 0.25 for the standard deviation of the proficiency testing).
The measurement audit for molds and yeasts in NIFDC-MA-2020-148 cosmetics was also quantitative detection,which was a sample group with double high concentration.The laboratory was required to report the content (CFU/g) of molds and yeasts in each sample of cosmetics.The results reported by the laboratory were satisfactory.CODE1 sample with high concentration was 0.66,CODE2 sample with high concentration was 0.20,both of which were close to the specified value.It shows that the author's laboratory has learned the lessons and experience from the proficiency testing in 2019,carefully understood the operation procedures and the Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmetics,paid attention to the accuracy of the dilution process,the counting principle of molds and yeasts,and the quality control of each link in the test.
2.2.1 Human
Each link of detection activity is connected by human,who play a very important role during the detection,with different influence on detection quality.The unsatisfactory results of post-hoc analysis (NIFDC-PT-242) on the detection ability for molds and yeasts in cosmetics mainly included the first participation in the proficiency testing of NIFDC,deviation in understanding the methods and lack of practical experience in proficiency testing.Specific manifestation is as follows:after reviewing the original test records,it was found that after the sample was added to 10 mL normal saline for treatment,the test solution which should be 1:10 dilution was mistaken by the test personnel as the test solution with 1:1 dilution,and the dilution degree was wrong.It can be preliminarily analyzed from the original records that the operation process was not completely interpreted in a timely and standardized manner,and the number of colonies was not selected according to the principle of selecting the plate counting with the number of colonies within the range of 5 to 50.
2.2.2 Machine
The instruments and equipment mentioned in the specification are standard configuration,and the instruments and equipment,such as ultraclean workbench,constant temperature incubator,sterilization scale pipette and autoclave pot affecting the test results have been verified,respectively,according to and referring to JG/T 292-2010Cleaning Workbench[5],JJF 1101-2019Calibration Specification for Environmental Testing Equipment for Temperature and Humidity Parameters[6],JJG196-2006National Metrological Verification Regulation of the People’s Republic of China-Working Glass Container[7]and JJF (Zhejiang) 1120-2019Calibration Specification for Temperature and Pressure Parameter of Steam Sterilizer[8],and the results complied with the corresponding metrological verification procedures.The instruments and equipment were not involved in the main testing process to measure,so the impact of instruments and equipment on unsatisfactory results of proficiency testing of NIFDC-PT-242 can be negligible.
2.2.3 Material
The first is the quality of samples.The samples prepared by the proficiency testing organization have been verified for storage stability,transportation stability and sample homogeneity according to CNAS-GL03:2006 Guidance on Evaluating the Homogeneity and Stability of Samples Used for Proficiency Testing[9]and CNAS-GL29:2010 Reference Materials-General and Statistical Principles for Certification[10],to ensure the objectivity and accuracy of evaluation results of proficiency testing.Therefore,the stability and homogeneity in the storage of proficiency testing samples can meet the requirements of proficiency testing.However,after receiving the samples,the laboratory shall keep the samples according to the requirements in the operation instruction and arrange the test as soon as possible within the specified time limit,so as to ensure the accuracy of the results.
The second is the quality of culture medium.The current specifications and national standards have no quality requirements for the culture medium and reagents for microbiological inspection of cosmetics.Each laboratory participating in the proficiency testing will generally select the culture medium produced by the manufacturer with good credibility,so as to minimize the uncertainty of the detection for molds and yeasts caused by the culture medium.
2.2.4 Method
In general,methods refer to the inspection methods for molds and yeasts in cosmetics in Chapter V of the Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmetics and the operation instructions formulated by the National Institutes for Food and Drug Control.Before the implementation of proficiency testing activities,quality control samples shall be purchased for more experiments to verify laboratory instruments and equipment and reagents,optimize experimental scheme,explore and establish SOP for proficiency testing of this project[1],and make detailed provisions and precautions for sample dilution,preparation of culture medium,testing process and various operation links of quality control,etc.The proficiency testing for molds and yeasts in NIFDC-PT-242 cosmetics was unsatisfactory,mainly due to the following errors of laboratory testing personnel:
1) Each dilution of the sample was not used up,and the detection data base formed was small,and the number of plates suitable for counting could be screened out was few.
2) The medium and sample dilution was not uniformly mixed,and the culture medium adsorbed colonies and grew into pellets and could not be counted.
3) The plates were not counted once after 48 h incubation,and the colonies were observed and counted every 12 h later,and the colonies could not be counted after spreading into pieces or spheres.
4) Without designer comparison and setup supervisor,the influence of personnel operation on test results cannot be ruled out.
2.2.5 Environment
Environment generally refers to the test environment,which is not specifically specified in the Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmetics and the operation instruction.In consideration of avoiding sample detection cross-contamination,the testing personnel will disinfect and verify the testing environment before the experiment.The key operations such as sample opening,dilution and plate pouring diluent are all operated in the ultra-clean workbench.In addition,it is also specified in the method that blank sample shall be made.Therefore,the test environment has no influence on the unsatisfactory results of NIFDCPT-242 sample for proficiency testing.

3 Conclusion
The test results show that the proficiency testing and measurement audit of samples are different from daily products,with certain difficulty.Based on the analysis and discussion on different results of proficiency testing and measurement audit of counting detection for molds and yeasts in cosmetics,it is concluded that before the laboratory participated in the proficiency testing activities of testing items,it is necessary to firstly use the tools of “human,machine,material,method and environment” to design the experiment scheme,and arrange the experimental personnel to carry out practical operation training in advance to avoid human error.Secondly,the abnormal data can be eliminated through the data of two-person crossover experiment.By participating in proficiency testing and measurement audit organized by national and provincial quality inspection institutions for many times,it is necessary to actively analyze unsatisfactory results,identify differences with counterparts,to provide effective methods for continuous improvement and management[11],and further improve the internal system management level of the laboratory.
