Acute kidney injury in traumatic brain injury intensive care unit patients
2022-06-22ZhengYangHuangYongLiuHaoFanHuangShuHuaHuangJingXinWangJinFeiTianWenXianZengRongGuiLvSongJiangJunLingGaoYiGaoXiaXiaYu
lNTRODUCTlON
Traumatic brain injury(TBI)is a debilitating condition that can be exacerbated by the co-occurrence of acute kidney injury(AKI),which is a clinical syndrome characterized by the abrupt loss of the kidney's excretory function and is often combined with oliguria.The development of AKI usually occurs over the course of hours to days[1].AKI is observed in 9% of the patients with TBI,and 42% of those patients die in the hospital[2].Thus,early identification and subsequent clinical intervention of AKI in TBI patients are critical to survival[3].
Nevertheless,it is difficult to determine the true incidence and outcomes of AKI due to the use of different validation criteria[4-6].The reported incidence of AKI varies greatly,ranging from 15% to 74.2%[7-10].Moreover,serum creatinine(SCr)and urine output(UO)in patients with TBI are greatly impacted by muscle injury or breakdown secondary to decreased perfusion pressure and the use of osmotic diuretics like mannitol[4-6].Therefore,sensitive and reliable criteria for AKI are needed for diagnosis and staging,especially in TBI patients.
too long, the Vizier would threaten laughingly to tell the Chaliphess the subject of the discussion carried on one night outside the door of Princess Screech Owl
Since 2004,at least four different AKI definitions and criteria have been proposed.The “Risk,Injury,Failure,Loss of kidney function,and End-stage kidney disease”(RIFLE)classification was the first validated tool for AKI identification[11].It is based on SCr levels and UO and defines three severity classes of AKI(risk,injury,and failure)and two outcome classes(Loss of kidney function and End-stage kidney disease).Following that,the Acute Kidney Injury Network(AKIN)criteria were proposed in 2007 as a modification of the RIFLE criteria[12].The AKIN is based on evidence that suggests that even small increases in SCr are associated with a poor outcome.It is also based on SCr and UO and defines three stages(1,2,and 3).Following the evidence for small changes in SCr and outcomes,the creatinine kinetics(CK)model was proposed by Waikar and Bonventre[13],who defined AKI based on the absolute changes in baseline SCr levels over 24-48 h.In 2012,an updated consensus definition of AKI was further proposed by the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes(KDIGO)group to reconcile the subtle differences in the RIFLE and AKIN criteria and to establish a common definition known as the KDIGO criteria[14].Nevertheless,currently,there are no widely accepted criteria to determine the severity of AKI for patients with TBI in the intensive care unit(ICU)[2,7,15],and the power of the criteria above among TBI patients’ needs further exploration.
However, having been transported to her grotto upon my favourite couch, I spent several delicious days, soothed107 by the soft green light, which was like a beech108 wood in the spring, and by the murmuring of bees and the tinkle109 of falling water
MATERlALS AND METHODS
Subjects
The data for this study were extracted from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care(MIMICIII,https://mimic.physionet.org/about/mimic/).It is a large public single-center database[17]that contains information relating to patients admitted to the critical care units at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center during 2001-2012.The presence of TBI was defined by diagnostic code,ICD-9,in MIMIC-III[18].
This was a retrospective study of patients admitted to the ICU for neurotrauma from 2001 to 2012.The exclusion criteria were:(1)Discharged within 24 h;or(2)< 18 years of age;or(3)missing data;or(4)history of end-stage renal disease(ESRD).The patients were included in the AKI and non-AKI groups according to whether they were diagnosed with AKI based on the KDIGO criteria[16].
In conclusion,this study indicates that in patients with TBI,differences are seen in AKI diagnosis among the four AKI definitions or stages,and concordance varies,as well as the in-hospital mortality.Thus,more universal AKI criteria are needed in patients with TBI.Besides,the severity of AKI was not associated with in-hospital mortality rates when using any of the four definitions.
This she was all the more inclined to do as she loved children, and little Prince Featherhead, who never cried and grew prettier day by day, quite won her heart
The incidence of AKI and stages determined by each classification method were examined.The highest incidence of AKI was found by KDIGO(17.7%),followed by AKIN(17.1%),RIFLE(12.7%),and CK(11.5%).There were no differences in the incidence of AKI among the four definitions(= 0.967)(Table 4).
Data collection
Demographics and clinical data were retrieved for all patients,including sex,age,ethnicity,category diagnosis at ICU admission,Elixhauser score,simplified acute physiology score(SAPS II),SOFA score,Glasgow Coma Scale(GCS)score[19],serum creatinine concentration(SCr),including peak SCr and SCr at admission,previous treatment(craniotomy,transfusion and the use of antiplatelet drugs,anticoagulants,vancomycin,angiotensin receptor blocker/angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor(ARB/ACE-I)and aminoglycosides),length of stay(in days),UO,APACHE II classification,and inhospital,30-d,and 1-year mortality rates.Comorbidity was defined and calculated using the ICD-9-CM codes based on Elixhauser’s algorithm[20].Patients presenting with shock upon admission,organ failure,and multiple organ failure(MOF)were selected according to definitions previously published[21].
If the patient's weight value was missing,the patient's height was used to estimate the weight[22].Based on baseline SCr,the two groups in this study were assessed for the presence and stage of AKI using RIFLE[11],AKIN[12],CK[13],and KDIGO[16].Baseline SCr was calculated according to the theoretical baseline SCr value for a given patient,assuming normal GFR[11].
Statistical analysis
The matching factors for propensity score matching(PSM)were ethnicity,age,sex,Elixhaouser score,SAPS II,SOFA,GCS,craniotomy,max creatinine,creatinine at admission,use of antiplatelet drugs,use of anticoagulants,shock,use of vancomycin,use of ARB/ACE-I,use of aminoglycosides,transfusion,red blood cell,plasma,and UO.The matching ratio was 1:1.Statistical analyses were performed using STATA 12.0(StataCorp LP,College Station,TX,United States).The continuous data were tested for normal distribution using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test.Those with a normal distribution were presented as means ± SD and analyzed using Student’s-test;otherwise,they were presented as medians[interquartile ranges(IQR)]and analyzed using the Mann-Whitney-test.The categorical data were presented as numbers(percentages)and analyzed using the chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test.Univariable and multivariable(enter)logistic regression analyses were performed to explore the association between in-hospital mortality(dependent variable)and the AKI stages diagnosed by CK,RIFLE,AKIN,and KDIGO.In-hospital,30-d,and 1-year mortality rates were analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method and the log-rank test.The observed proportional agreement was used to examine the compatibility between the different scoring systems.The Marascuilo procedure was used for multiple comparisons.Two-sidedvalues < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Characteristics of the patients
From the 2862 patients retrieved from the MIMCS-III database,1214 were excluded(536 for being discharged within 24 h,39 for being < 18 years of age,529 with missing data,and 110 for being with ESRD),and 1648 were examined for the presence of AKI.Of those patients with TBI,291(17.7%)had AKI according to the KDIGO criteria(Figure 1).After PSM,the mean age of the patient cohort was 55.3 ± 23.9 years.Patients with AKI had higher SAPS II(36.6 ± 15.933.1 ± 13.4,= 0.004)and SOFA(4.8 ± 3.14.0 ± 2.7,= 0.001)scores,compared with patients without AKI.Moreover,patients with AKI had a higher frequency of shock(35.7%25.1%,= 0.007)and had more transfusions of red blood cells(RBC)(377.3 ± 1433.2174.1 ± 623.1 mL,= 0.027)(Table 1).Table 2 shows the characteristics of the study population before PSM.

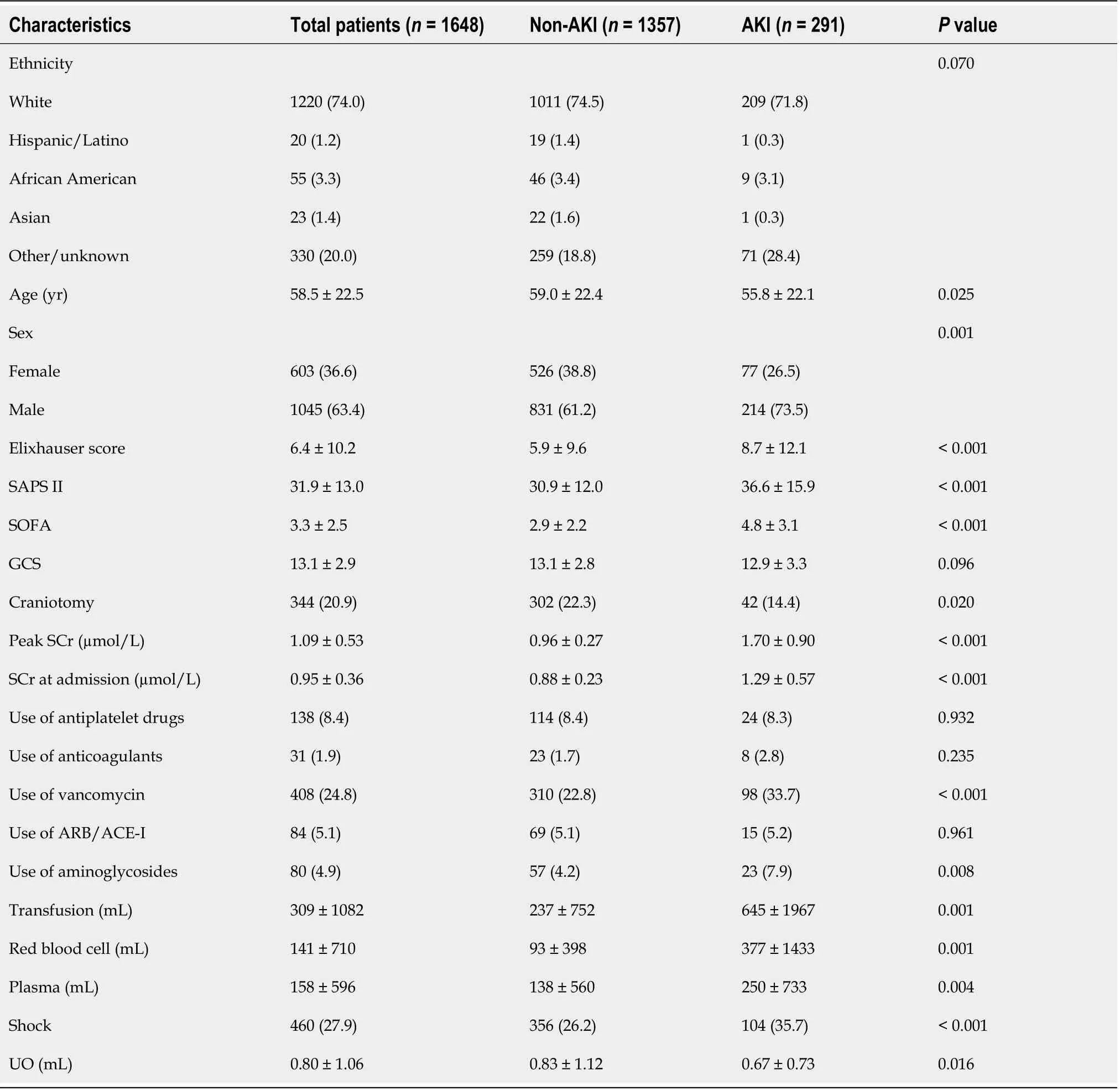





The patients with AKI were divided according to KDIGO stage 1(= 200),2(= 53),and 3(= 38)(Table 3).The patients with KDIGO stage 2 were older than in the two other groups(= 0.001)and had a higher proportion of females(< 0.001).The Elixhauser score,SAPS II,and SOFA scores were higher in the stage 3 group compared with the two other groups(all< 0.001).The proportion of shock was higher in stage 3(= 0.004),the use of vancomycin was higher in stage 1(< 0.001),the use of aminoglycosides was higher in stages 2 and 3(= 0.040),and transfusions were higher in stage 3 patients(all≤ 0.01).
12. Step-mother: The image of the evil stepmother occurs frequently in fairy tales. She is associated with jealousy69 and cruelty (Olderr 1986). In masculine psychology, the stepmother is a symbol of the unconscious in a destructive role (von Franz 1970). The stepmother figure is actually two sided, in that while she has destructive intentions, her actions often lead the protagonist70 into situations that identify and strengthen his or her best qualities.
Inter-definition agreement
This retrospective study was approved by the Ethics Committee for Human Research of Shenzhen Hospital,Southern Medical University(No.NYS2YYEC20180009),which waived the requirement for informed consent from subjects.

The identification of AKI overlaps across all the definitions(Figure 2).KDIGO identified the most AKI patients,and CK identified the least.Ten patients were identified as AKI only by KDIGO,while two and one were identified only by RIFLE and AKIN,respectively.KDIGO and AKIN failed to identify 14 and 22 AKI patients,respectively,while CK failed to identify 115 cases.For patients identified byAKIN and KDIGO only,the patients’ length of stay was the longest among all other combinations(12.9 d).

The concordance of AKI diagnosis and staging were further evaluated between KDIGO and the other classifications,using KDIGO as the diagnostic standard(Table 5).Compared with KDIGO,RIFLE correctly staged 1348/1357(99.3%)stage 0 patients,72/200(36.0%)stage 1 patients,19/53(35.9%)stage 2 patients,and 18/38(47.4%)stage 3 patients.Compared with KDIGO,AKIN correctly staged 1344/1357(99.1%)stage 0 patients,183/200(91.5%)stage 1 patients,48/53(90.6%)stage 2 patients,and 34/38(89.5%)stage 3 patients.Compared with KDIGO,CK correctly staged 1346/1357(99.3%)stage 0 patients,89/200(44.5%)stage 1 patients,6/53(11.3%)stage 2 patients,and 14/38(36.8%)stage 3 patients.Concordance was 88.4% between KDIGO and RIFLE,97.6% between KDIGO and AKIN,and 88.3% between KDIGO and CK.
Prognosis
Regardless of AKI determination criteria,the in-hospital mortality was higher for those with AKI than those without.Moreover,the in-hospital mortality increased with the AKI stage(all< 0.001)(Figures 3 and 4).
Little Red Riding Hood, hearing the big voice of the wolf, was at first afraid; but believing her grandmother had a cold and was hoarse6, answered, It is your grandchild Little Red Riding Hood, who has brought you a cake and a little pot of butter mother sends you.

When staged according to KDIGO,ventilation time increased with AKI stage(= 0.03),and ICU stay and hospitalization were longer for any-stage AKI compared to non-AKI(all< 0.05).In-hospital mortality(= 0.001),30-d mortality(< 0.001),and 1-year mortality(< 0.001)increased with the AKI stage(Table 6).
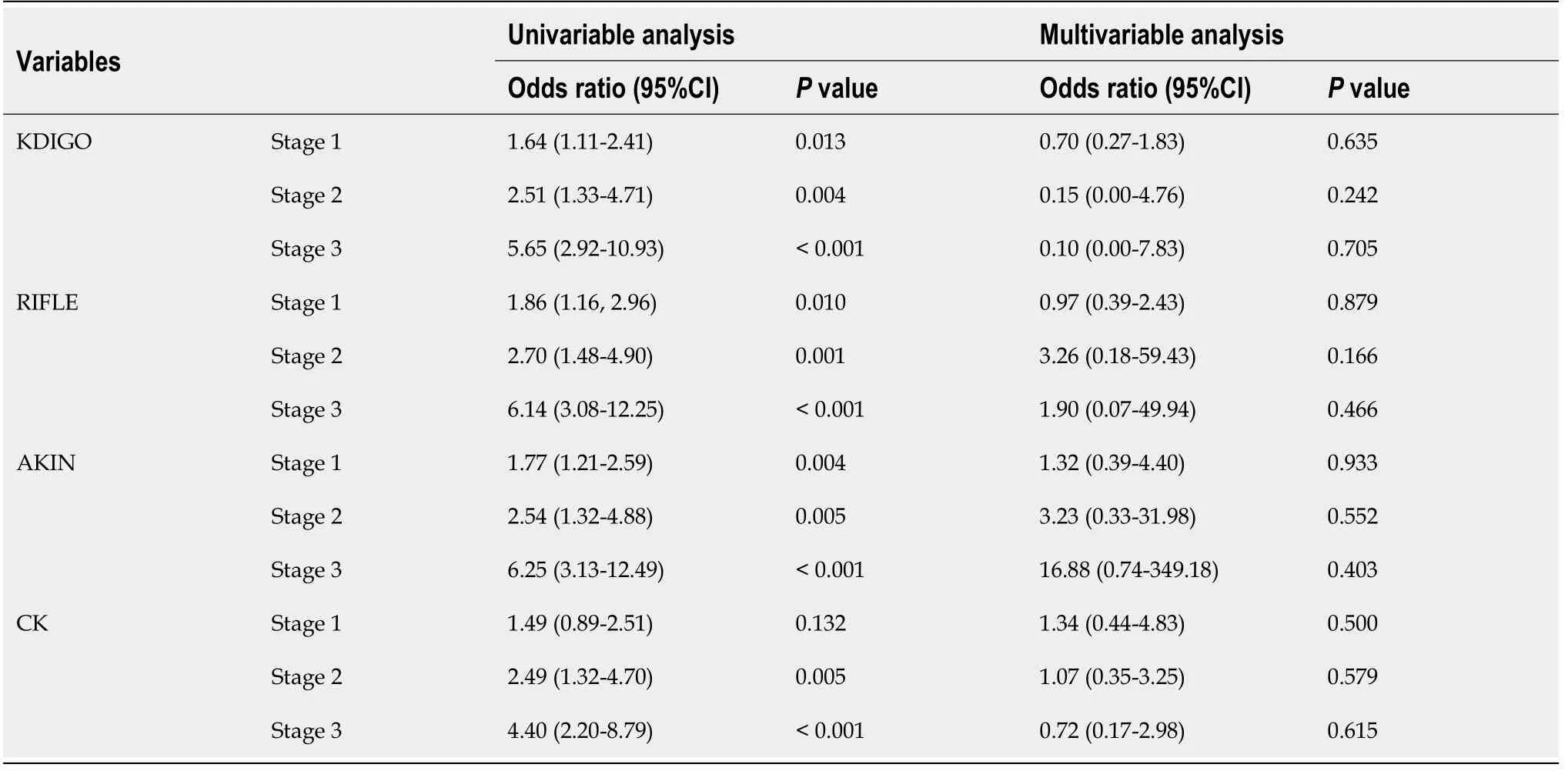
The association between severity of AKI by all definitions/stages and in-hospital mortality was tested.As shown in Table 7,the severity of AKI by all definitions and stages was associated with inhospital mortality in the univariable analyses(all< 0.05),except for stage 1 by CK(> 0.05),but the associations were no longer significant in the multivariable analyses(all> 0.05).
Therefore,the present study aimed to explore the compatibility among the RIFLE,AKIN,CK,and KDIGO definitions,and to compare the power of these criteria in determining the incidence and stage of AKI and explore the association between severity of AKI by all definitions/stages and in-hospital mortality of patients admitted to ICU for TBI.
DlSCUSSlON
For the diagnosis and staging of AKI,at least four different AKI criteria,RIFLE,AKIN,CK,and KDIGO,have been proposed.However,the power of these criteria among TBI patients needs further exploration.This study revealed that differences were seen in AKI diagnosis among the four AKI criteria.The highest incidence of AKI was found by KDIGO(17.7%),followed by AKIN(17.1%),RIFLE(12.7%),and CK(11.5%).Concordance to KDIGO was the lowest for CK,followed by RIFLE and AKIN.The in-hospital mortality rates increased with the AKI stage in all four definitions,but the severity of AKI by all definitions and stages was not associated with in-hospital mortality in the multivariable analyses.
The diagnosis of AKI in patients with TBI has significant clinical relevance,given the requirements for prompt medical intervention for AKI patients.Similar to the results of a previous study[23],this study suggested that the incidence of AKI varied depending on the criteria used,which may lead to confusion during criteria selection and may negatively affect the efficiency of clinical treatment.Some studies showed that KDIGO is more sensitive than AKIN and RIFLE in AKI diagnosis in patients with myocardial infarction and acute decompensated heart failure[9,10].In a study comparing KDIGO and CK in diagnosing AKI in trauma patients,KDIGO was shown to be more sensitive,and CK was found to be superior to KDIGO only in patients with pre-existing chronic kidney disease(CKD)[7].In the present study,the KDIGO classification identified the highest incidence of AKI and was more able to detect than RIFLE,CK,and AKIN.Although there were no significant differences in the proportions of patients with AKI according to the different criteria,misclassification was observed,particularly with the CK and RIFLE definitions.
More specifically,the present study showed the highest incidence of AKI was found by KDIGO(17.7%),followed by AKIN(17.1%),RIFLE(12.7%),and CK(11.5%)among patients with TBI patients.The reason for the difference may be the selection of the baseline SCr to be used for evaluating AKI.For example,the AKIN criteria consider the lowest SCr measurement during the ICU stay as the baseline SCr level,and it probably overestimates the AKI incidence,which can be as high as 74.2%-85.0%[24-27].However,when baseline SCr was estimated using the MDRD equation,AKI incidence was reported to be 11.6%-23% based on the RIFLE or AKIN criteria[7,10].The selection of baseline SCr could also affect the incidence of AKI in the general population when following the KDIGO criteria.A possible explanation for this finding is the temporary overhydration during hospitalization.The creatinine concentration extrapolated by the MDRD equation(with a GFR of 75 mL/min)might be more accurate,although it should be used with caution.Other influencing factors include,but are not limited to,UO and population heterogeneity,and further studies are needed in the future.
The KDIGO classification was rarely compared to other AKI definitions regarding its prognostic power in TBI patients.According to Tsai[24],the KDIGO classification has a relatively higher discriminatory power(0.840 ± 0.032)in predicting in-hospital mortality than the RIFLE(0.826 ± 0.033)and AKIN(0.836 ±0.032)classifications.Zeng[28]showed that the incidence of AKI changed with the definition but that all definitions were associated with in-hospital mortality.In the present study,KDIGO did not improve the predictive performance of in-hospital mortality,,the in-hospital mortality increased with the increasing stage in all four definitions.On the other hand,the associations disappeared for all four definitions in the multivariable regression analyses after adjusting for ethnicity,age,sex,Elixhauser score,SAPS II,SOFA,GCS,craniotomy,max creatinine,creatinine at admission,use of antiplatelet drugs,anticoagulant,vancomycin,ARB/ACE-I and aminoglycosides,transfusion,red blood cell,plasma,and shock.Therefore,the results mean that one or multiple factors included in the adjusted analyses are a stronger predictor of mortality than AKI in patients with TBI.A study by Ulger[25]showed that the in-hospital mortality for stage 2 and 3 AKI in AKIN,RIFLE,and KDIGO was nearly the same.These discrepancies might be attributable to the baseline creatine estimation based on the MDRD formula[15].Besides,clinically,death attributable to AKI is rare in TBI patients,which may explain the lack of association between the four definitions and in-hospital mortality.Osmotic therapy during ICU stay appears to affect the mortality due to AKI[29].A recent study suggested that the AKI stage was associated with mortality in patients with TBI,but not AKI duration or AKI burden;in addition,most deaths occurred during the first 3 d of ICU stay[30].The use of renoprotective measures affects the mortality due to AKI in patients with TBI[31].
There are some limitations to this research.First,as a retrospective,a single-center study from a single academic hospital,the generalizability of these findings is questionable.Incidence estimates,mortality rates,and procedures vary greatly among hospitals and countries.Second,baseline creatinine was calculated as a theoretical baseline SCr for a given patient assuming a normal GFR,which may overestimate or underestimate the incidence of AKI to some extent.Third,the patients were identified using the administrative codes entered in the database,which is subject to bias regarding the use of the incorrect code by the physicians and administrative personnel[17].
CONCLUSlON
In very ancient times there lived a King, whose power lay not only in the vast extent of his dominions1, but also in the magic secrets of which he was master
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee for Human Research of Shenzhen Hospital,Southern Medical University,No.YS2YYEC20180009.
ARTlCLE HlGHLlGHTS
Research background
Early identification and subsequent clinical intervention of acute kidney injury(AKI)in traumatic brain injury(TBI)patients are critical to survival.
Research motivation
The exact definition of AKI for patients with TBI is unknown.
Research objectives
We aimed to compare four AKI diagnostic criteria to determine AKI incidence/stage and their association with the in-hospital mortality rate of patients with TBI.
Research methods
The subjects in this study were assessed for the presence and stage of AKI using four different AKI diagnostic criteria.
Research results
The in-hospital mortality rates increased with the AKI stage in all four definitions.The severity of AKI by all definitions and stages was not associated with in-hospital mortality in the multivariable analyses(all> 0.05).
Research conclusions
This study revealed that Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes(KDIGO)is the best method to define AKI in patients with TBI.
Beautiful flowers, round which little bells were tied, stood in the corridors: what with the running to and fro and the draught, these bells tinkled so loudly that no one could speak to be heard
Research perspectives
In the future,it is necessary to increase the sample size for prospective studies to further explore.
FOOTNOTES
Yu XX and Liu Y conceived and coordinated the study,designed,performed and analyzed the experiments,wrote the paper;Wang JX,Tian JF,Zeng WX,Jiang S and Lv RG carried out the data collection and preprocess of the raw data;Huang ZY,Huang HF and Huang SH performed the data analysis;Liu Y and Gao JL revised the paper;all authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Saint Dympna, a seventh century princess and now the patron saint of the insane, was also wanted in marriage by her father, a king of Brittany, Britain or Ireland. When she refused and ran away, having already committed herself to her Christian63 faith, he found and beheaded her. She even has a godmother figure in her elderly confessor who dies with her (Warner 1994).Return to place in story.
As I was coming into Middle School, grade six, I was really excited because my friend Jennifer was going to be in the same Middle School as me! I was convinced2 that we would be the bestest buds(,). At first things were great, she introduced me to her friend Amy and we had lots of fun together. None of the girls from my elementary school were in my classes, but I wasn’t worried. I had Amy and Jennifer, and I could make some new friends. Then things started to change. Jennifer was very controlling: I couldn t make new friends, because if I hung out(,) with different people, she would decide that I was mad at her and Amy. So I didn t make new friends, and pretty soon being Jennifer s friend was a struggle.
Patients were not required to give informed consent to the study because the analysis used anonymous clinical data that were obtained after each patient agreed to treatment by written consent.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
No additional data are available.
This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers.It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial(CC BYNC 4.0)license,which permits others to distribute,remix,adapt,build upon this work non-commercially,and license their derivative works on different terms,provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial.See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
China
Zheng-Yang Huang 0000-0001-6387-570X;Yong Liu 0000-0002-4659-8576;Hao-Fan Huang 0000-0002-5639-6564;Shu-Hua Huang 0000-0003-2416-5849;Jing-Xin Wang 0000-0001-5410-5316;Jin-Fei Tian 0000-0002-9914-0091;Wen-Xian Zeng 0000-0002-4186-3668;Rong-Gui Lv 0000-0002-1628-4891;Song Jiang 0000-0002-1129-7431;Jun-Ling Gao 0000-0001-9174-1709;Yi Gao 0000-0003-0094-8316;Xia-Xia Yu 0000-0003-4811-5125.
But the clever servant had taken his master s place, and when the maid came he tore off the cloak she had wrapped herself in and hunted her off with a whip
Xing YX
Filipodia
How much time did that few more minutes take out of her day? Probably about five. Not so much time out of a busy day. So what if she got home a little later than she had planned?
Xing YX
杂志排行
World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Role of metabolites derived from gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease
- Roles of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway related microRNAs in esophageal cancer
- Associations between coagulation factor Xll,coagulation factor Xl,and stability of venous thromboembolism:A case-control study
- Nomogram to predict the risk of endoscopic removal failure with forceps/baskets for treating submandibular stones
- Animal models applied to acute-on-chronic liver failure:Are new models required to understand the human condition?
- Association between anesthesia technique and complications after hip surgery in the elderly population
