ls it necessary to fuse to the pelvis when correcting scoliosis in cerebral palsy?
2022-05-30ShaneStromMatthewHessAchrafJardalyMichaelConklinShawnGilbert
lNTRODUCTlON
Patients with neuromuscular scoliosis may benefit from surgery with improved standing balance, sitting positioning, and overall better caregiver satisfaction[1]. However, these surgeries are challenging due to severe deformity and presence of comorbidities. Complications are high (20% to 40%) compared to adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (5% to 23%)[2-5]. Posterior spinal instrumentation and fusion is the most common procedure performed. Proximally, fusion is begun T1 or T2 to prevent the development of proximal junctional kyphosis (PJK) which can lead to pain and neurologic deficits[6,7]. The distal extent of the fusion, however, remains controversial. Neuromuscular scoliosis is commonly characterized by pelvic obliquity which affects sitting balance and the development of iliac ulcers[8]. There is debate as to whether pelvic fixation is necessary to correct pelvic obliquity with some authors advocating that those with pelvic obliquity less than 10°-15° do not require fixation to the pelvis[6-8]. The majority of authors, however, advocate for fusion to the pelvis to not only correct the pelvic obliquity but also decrease the risk of distal curve progression and revision surgery[9-11].
The studies that discuss pelvic fusion either focus on children with flaccid forms of paralysis or include a pooled patient cohort including both spastic and flaccid disorders[9-13]. Since these neuromuscular disorders have varying levels of pelvic obliquity and do not necessarily act the same way, we sought to analyze our patients with cerebral palsy (CP) with regards to radiographic outcomes and complications as a function of fusion to the pelvis compared with higher levels of fusion.
King Kojata at once tried to seize the vessel5, but though he endeavoured to grasp it with his right hand, and then with his left, the wretched thing always eluded6 his efforts and refused to let itself be caught
MATERlALS AND METHODS
But the King replied: I have seen the whole castle, and shall find out what is in there ; and with these words he approached the door and wanted to force it open
Statistical analysis was performed using the IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 25 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).-tests andtests were used when appropriate. The relative risk (RR) and 95%CI were calculated to assess whether the fusion level affected the risk of developing postoperative complications.values ≤ 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
In the churchyard where the walls were surrounded with sandClara lay buried. Jurgen did not seem to know this; it did not enterhis mind, which could only retain fragments of the past. EverySunday he went to church with the old people, and sat theresilently, staring vacantly before him. One day, when the Psalms werebeing sung, he sighed deeply, and his eyes became bright; they werefixed upon a place near the altar where he had knelt with his friendwho was dead. He murmured her name, and became deadly pale, andtears rolled down his cheeks. They led him out of church; he toldthose standing round him that he was well, and had never been ill; he,who had been so grievously afflicted, the outcast, thrown upon theworld, could not remember his sufferings. The Lord our Creator is wise and full of loving kindness- who can doubt it?
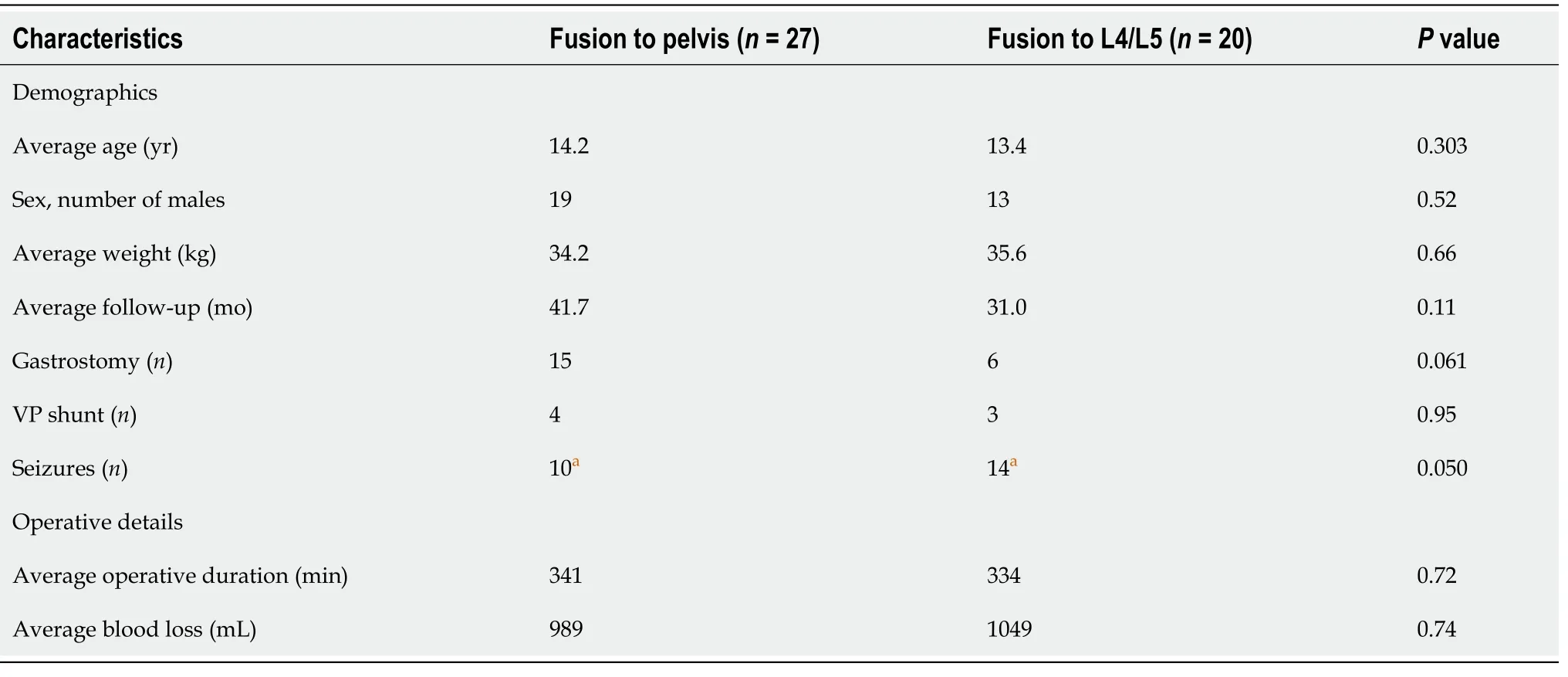
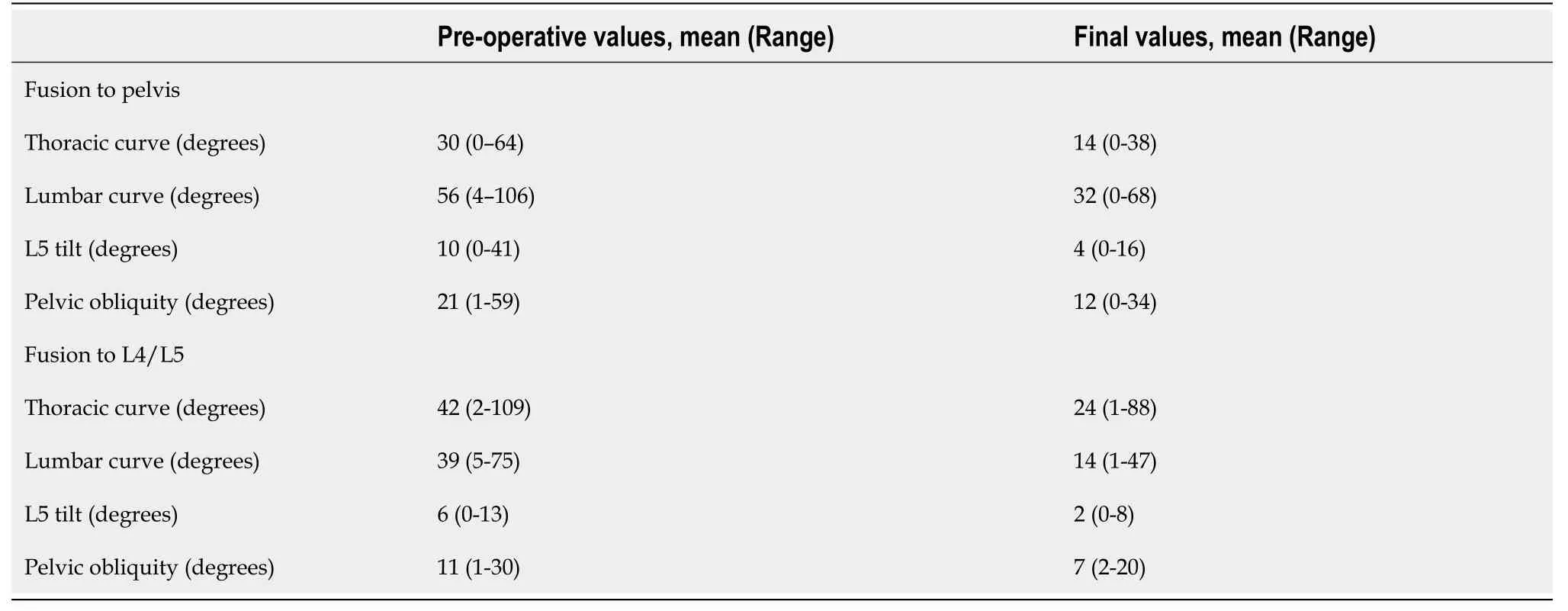
Patients fused to the pelvis and those fused to L4/L5 were similar with regards to their age, sex distribution, weight, follow-up, and comorbidities. The one exception was that fewer patients fused to the pelvis had seizures. Patient details are included in Table 1. The operative duration and blood loss were not different between both groups. Length of stay was also similar in both groups and was six days on average. With respect to pre-operative radiographic parameters, patients fused to the pelvis had a larger lumbar curve by 17° (= 0.017), greater L5 tilt by 4° (= 0.04), and greater pelvic obliquity by 10° (= 0.0033). The thoracic curve magnitude was similar in both groups (= 0.17). Table 2 includes the radiographic parameters immediately before surgery and at final follow-up. At the final follow-up, patients who were fused to the pelvis had their thoracic curve corrected by 53%, and their lumbar curve corrected by 38%. Corrections of their L5 tilt and pelvic obliquity were 60% and 43%, respectively. Patients who were fused to L4/L5 had 43% correction of their thoracic curve, 64% of their lumbar curve, 67% of their L5 tilt, and 36% of the pelvic obliquity. The degree of correction of the L5 tilt and pelvic obliquity was similar regardless of fusing to the pelvis (= 0.22 and 0.12, respectively).
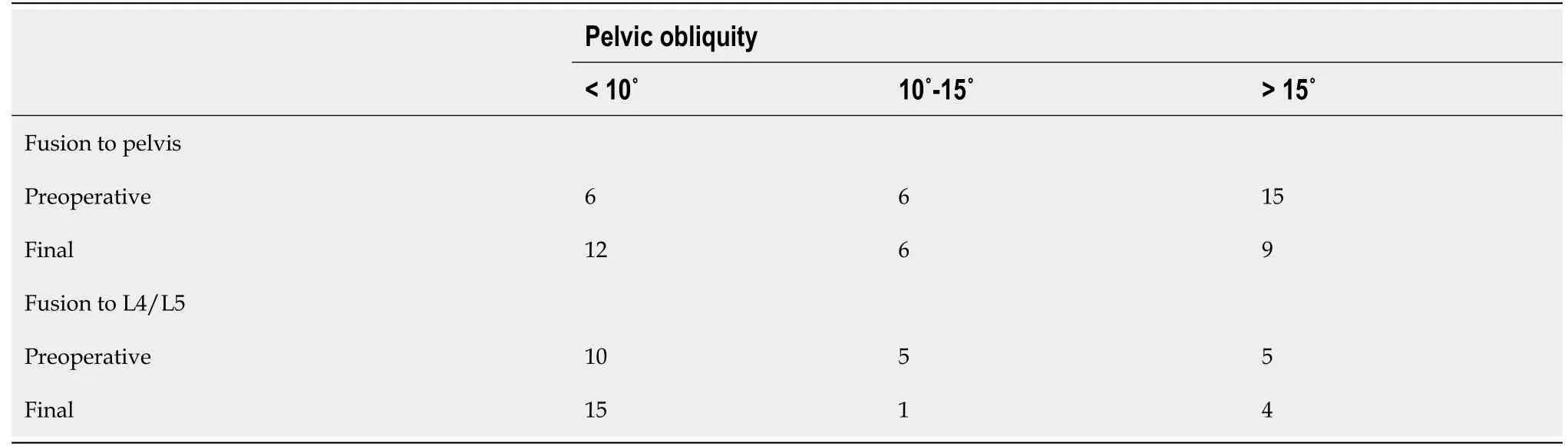
Pelvic obliquity of 10° is considered by some to be the threshold for pelvic fusion[6]. Twenty-one of 27 patients fused to the pelvis exceeded this threshold, with a mean of 25° (range: 11°-59°). This was corrected by 40% to 15° (range: 2°-34°). In the L4/L5 group, 10 of 20 also had a pelvic obliquity greater than 10°, with an average of 18° (range: 11°-30°). Their pelvic obliquity was corrected by 44%, from a mean of 18° (range: 11°-30°) to 10° (range: 4°-20°). The magnitude of pelvic obliquity correction was clinically and statistically similar in both groups (= 0.12). Table 3 stratifies patients according to their preoperative and final pelvic obliquity, and Figure 1 is sample cases of patients who were fused short of the pelvis or whose fusion included the pelvis, respectively.

The complications encountered are detailed in Table 4. The most frequent complications were pulmonary complications (14.9%), pressure ulcers (12.8%), and instrumentation (8.5%). No postoperative neurological deficits or deaths occurred. Two patients underwent reoperation for deep SSI and PJK. Both had been fused to the pelvis. Also two patients had hardware break and one had instrumentation prominence, but all were asymptomatic and were simply observed. Patients with fusion to the pelvis had more total complications (63.0%30%,= 0.025; RR = 2.099; 95%CI: 1.012-4.35,= 0.046). Their RR for minor complications was 2.41 (95%CI: 0.92-6.29,0.073) and for major complications was 1.48 (95%CI: 0.30-7.31,= 0.63). Even after adjusting for the differences in radiographic parameters (lumbar curve, L5 tilt, and pelvic obliquity), the risk for complications remained increased (RR = 1.79; 95%CI: 1.011-3.41).

DlSCUSSlON
Children with CP scoliosis frequently have pelvic obliquity that affects their sitting balance and interferes with transfers. To correct pelvic obliquity and reduce risk of distal adding on, fusion to the pelvis is often recommended[1,10]. Pelvic fusion, however, can lead to surgical morbidity and complications[11,18]. In this study, we compare outcomes in children with CP scoliosis with regards to the distal extent of spine fusion. Pelvic fusion did not increase the operative time or blood loss compared to higher levels of fusion. Published studies have differed, with some demonstrating longer surgeries and more blood loss with pelvic fixation, while other studies did not find a difference[13,19-21]. The long duration of surgery and magnitude of blood loss along with case to case variation may make it difficult to detect differences with statistical significance.
There was now joy in all the palace and over the whole country on account of the beautiful prince; but no one knew that the queen s first-born was a lindorm, and lay in the wild forest
We did find differences in complication rates. In our cohort, children fused to the pelvis had an increased risk to develop post-operative complications, with a RR of 2.099, mainly attributable to higher occurrences of minor complications, most notably pressure ulcers and hardware complications. Pelvic fusion leads to a more rigid seating position[1]. In patients with limited mobility, this could increase their risk for decubitus ulcers. We only had few occurrences of SSIs and wound complications, but they are also an important consideration. Deep SSIs are a common cause for reoperation which puts patients at repeated risks of anesthetic complications, bleeding, and injury due to reinstrumentation. This is particularly important in patients with GMFCS levels IV and V, who have significant co-morbidities, are frequently malnourished, and are at increased risk for abnormal wound healing and infections. Again, published reports have conflicting results. Toll[14] in their evaluation of risk factors following scoliosis surgery in neuromuscular patients did not find that fusion to the pelvis was a risk factor for complications. On the other hand, other studies found an increased risk[22,23]. One possible explanation of this discrepancy is the heterogeneity of the reports which include different neuromuscular conditions in the same analysis.
The two most commonly used determinants for including the pelvis in the fusion are L5 stability and pelvic obliquity. The L5-sacrum articulation is considered stable when the L5 tilt is less than 15°, and it is considered unstable when it is greater than 15°. Fusion to the pelvis is also recommended for pelvic obliquity greater than 10°. In our cohort, even though decision making was not standardized, all patients with a large L5 tilt were fused to the pelvis. However, not all patients with pelvic tilt were fused to the pelvis. The pelvic fusion did have greater L5 tilt and pelvic obliquity than patients fused to L4/L5. Interestingly, the degree of correction of both parameters was similar in both groups. The L5 tilt was corrected by 60% with pelvic fusion and by 67% with fusion to L4/L5 (= 0.22). Similarly, the pelvic obliquity was corrected by 43% and 36% in each group, respectively (= 0.12), so fusing to the pelvis did not offer a significantly greater correction of pelvic obliquity. This was also true for the subset of patients with a pelvic obliquity greater than 10°. In this population, correction of pelvic obliquity was 40% for patients fused to the pelvis and 44% for those fused to L4/L5, indicating that even with patients who have a large pelvic tilt, fusion to the pelvis does not necessarily achieve better pelvic obliquity correction. Therefore, a large pelvic obliquity by itself might not be an indication to include the pelvis in the distal extent of the spinal fusion, particularly since these patients experience more complications. Furthermore, fusion to the pelvis may not be necessary in all children with CP scoliosis. This could still lead to satisfactory surgical outcomes including pelvic tilt while decreasing the risk of postoperative complications. Future studies can better delineate selection criteria regarding whether to fuse to the pelvis or not in these children.
Fusing to the pelvis in cerebral palsy scoliosis did not achieve better correction of patients' pelvic obliquity and L5 tilt. However, it did increase the risk of postoperative complications. Therefore, spinal fusion can be stopped at the distal lumbar levels in a select patient population, without necessarily compromising the surgical outcomes.
CONCLUSlON
In conclusion, this study demonstrated that in children with CP scoliosis, fusion short of the pelvis can lead to acceptable final pelvic tilt in some cases and may decrease the risk of developing post-operative complications.
ARTlCLE HlGHLlGHTS
Research background
The study was a retrospective, cohort study that utilized chart and radiographic review to determine the outcomes and complications associated with cerebral palsy scoliosis correction in children who were fused to L4/L5 as compared to those fused to the pelvis.
Research motivation
This study was carried out to fill the gap in the literature on whether it is necessary to fuse to the pelvis when correcting cerebral palsy scoliosis. The need for a homogeneous cohort (i.e. children with cerebral palsy and not other forms of neuromuscular scoliosis) was an additional reason for carrying out the study.
Research objectives
No additional data are available.
Research methods
The distal extent of the fusion in children with cerebral palsy scoliosis is a controversial topic. There is not enough evidence on whether it is necessary to include the pelvis in the distal fusion to correct for pelvic obliquity in these patients.
Research results
In the analysis of 47 patients, the L5 tilt was corrected by 60% in patients fused to the pelvis, comparable to the 67% achieved in patients fused to L4/L5 (0.22). The pelvic obliquity was also corrected by a similar degree; 43% in patients fused to the pelvis and 36% in patients fused to L4/L5 (= 0.12). As for complications, patients fused to the pelvis had a higher number of total complications (63.0%30%, respectively,= 0.025).
Just then the laughing and shouting of drunken soldiers could be heard coming down the road. Carl Meier fled. With no time to summon her father, Albertha scrabbled in the dirt with her bare hands, scooped19 up the bulbs from their hiding place, and reburied them in the rubble next door.
Research conclusions
Our study has several limitations. As a retrospective study, information was gathered from the medical records, which might lead to some inaccuracies. We aimed to have a homogenous cohort, so we only included children with CP, making our sample size moderate. This made the study underpowered to detect differences at the level of individual complications, but did allow identification of higher total complication rate. Sagittal plane deformities were not assessed. There were no predetermined selection criteria for choosing distal fusion level to the pelvis. Although traditional criteria for fusion to the pelvis were not strictly followed, patients who were fused to the pelvis had more pelvic and L5 tilt, indicating selection bias. This might limit the generalizability of the present study, but the conclusion that in a select patient population, posterior fusion does not necessarily have to include the pelvis remains valid. In addition, our outcomes focused on complications. Other factors that can affect surgical planning, like patient and caregiver satisfaction, were not assessed. Additional studies that focus on patient reported outcomes in this patient population will provide valuable insights.
Over the study period, 65 children with CP had surgery for scoliosis at our hospital. We excluded 18 cases: 3 had predominant kyphosis rather than scoliosis, 8 had unavailable radiographs, and 7 were lost to follow-up. Our analysis therefore included 47 patients. These were 29 males and 18 females, with an average age of 13.9 years (range: 9.6-19.9 years). All procedures were posterior spinal fusion and instrumentation. The median number of fused vertebrae was 16 (range: 14-17), and 27 patients (57.4%) were fused to the pelvis. Median follow-up duration was 31 mo (range: 7-101 mo).
Research perspectives
Future studies can investigate delineating specifically which patients might benefit from including the pelvis in their distal fusion. This might aid the surgeons in their preoperative planning and in guiding their choice of surgical technique.
Jardaly AH, Conklin MJ, and Gilbert SR designed the research study; Strom SF, Hess MC, Jardaly AH, Conklin MJ, and Gilbert SR performed the data collection; Jardaly AH analyzed the data; Strom SS, Hess MC, and Jardaly AH wrote the manuscript; all authors thoroughly edited the manuscript; all authors have read and approve the final manuscript.
What power seemed to lie in the depths of those dark eyes! Theyoung man felt the truth of the proverb, Still waters run deep: and his heart had sunk into their depths. He often talked of hisadventures, and the mamma was as simple and eager in her questionsas on the first evening they met. It was a pleasure to hear Alfreddescribe anything. He showed them colored plates of Naples, andspoke of excursions to Mount Vesuvius, and the eruptions17 of firefrom it. The naval officer s widow had never heard of them before. Good heavens! she exclaimed. So that is a burning mountain; butis it not very dangerous to the people who live near it?
The University of Alabama’s Institutional Review Board approved this study. The approval ID is IRB-300005435.
Informed consent was waived as per the University of Alabama at Birmingham’s IRB guidelines.
Following institutional review board approval, we retrospectively reviewed our electronic medical records. Surgically treated CP scoliosis patients who had gross motor function classification system levels IV or V and were less than 21 years of age were included. Exclusion criteria were surgery for predominant kyphosis, follow-up less than six months, or incomplete charts. The analysis spanned records from 2007 to 2018 at a single institution. We excluded patients with other indications for surgery, patients with unavailable radiographs, and those with follow-up less than six months. Demographic information, operative details, and the development of complications were recorded. We stratified complications into major and minor as previously described.Major complications were those that prolonged the duration of hospitalization or required additional surgical procedures. These included severe pulmonary complications (pneumonia, respiratory failure), deep surgical site infections (SSI), hemodynamic instability, pseudarthrosis, and PJK. Minor complications were those that were asymptomatic, self-resolving, or effectively treated non-surgically. Examples include intraoperative durotomy, fever occurring more than 24 h after surgery, decubitus ulcers, superficial SSIs, and superficial wound dehiscence. Pre-operative and final follow up radiographs were measured and Cobb angles, L5-S1 tilt and pelvic obliquity using the Maloney method were recorded[14-17].
All authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
The primary objective was to compare the radiographic outcome (Cobb angles and pelvic obliquity) of cerebral palsy scoliosis treatment in children who were fused to the pelvis vs those who were fused to L4/L5. The secondary objective was to determine the complications associated with each of the two procedures.
The authors have read the STROBE Statement-checklist of items, and the manuscript was prepared and revised according to the STROBE Statement-checklist of items.
This article is an open-access article that was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial (CC BYNC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is noncommercial. See: https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by-nc/4.0/
United States
From this time on no one asked the Cat to stand godmother; but when the winter came and there was nothing to be got outside, the Mouse remembered their provision and said, Come, Cat, we will go to our pot of fat which we have stored away; it will taste very good
Shane F Strom 0000-0001-6926-4109; Matthew C Hess 0000-0003-0435-5215; Achraf H Jardaly 0000-0003-2779-9994; Michael J Conklin 0000-0001-7966-3816; Shawn R Gilbert 0000-0002-0683-3172.
The men on the ship saw a strange object lying on the beach. It was moving toward them—perhaps twenty feet an hour. The men went over to look and could hardly believe it was a man.
Wang JL
A
Wang JL
杂志排行
World Journal of Orthopedics的其它文章
- Existing fixation modalities for Jones type fifth metatarsal fracture fixation pose high rates of complications and nonunion
- lntegrity of the hip capsule measured with magnetic resonance imaging after capsular repair or unrepaired capsulotomy in hip arthroscopy
- Direct anterior approach hip arthroplasty: How to reduce complications - A 10-years single center experience and literature review
- Minimally invasive outpatient management of iliopsoas muscle abscess in complicated spondylodiscitis
- Comparing complications of outpatient management of slipped capital femoral epiphysis and Blount’s disease: A database study
- Lateral epicondylitis: New trends and challenges in treatment
