A new handheld fundus camera combined with visual artificial intelligence facilitates diabetic retinopathy screening
2022-04-19ShangRuanYangLiuWeiTingHuHuiXunJiaShanShanWangMinLuSongMengXiShenDaWeiLuoTaoYeFengHuaWang
INTRO D UCTION
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is the most common retinal vascular complication of diabetes mellitus (DM)and the leading cause of vision impairment and blindness among working-age adults. In Chinese adults, the overall standardized prevalence of diabetes using the WHO criteria is 11.2%, of which prediabetes accounts for 35.2%. DR is largely asymptomatic in the early stages, but neural retinal damage and clinically invisible microvascular changes progress during these early stages. It has therefore been widely accepted that periodic eye examinations should be conducted on all patients with DM to detect significant retinopathy andprovide prompt interventions when necessary, which is thought to be the most effective method to reduce potential DR-related visual disabilities.
孔径分布和截留相对分子量采用一系列的PEG截留率结果并通过Matlab软件采用下述对数正态分布方程模拟计算得到[15]:
Traditional tabletop-based, mydriatic retinal imaging modality is effective but is less available in underdeveloped rural areas. Handheld cameras are now emerging as a new low cost tool for DR screening, which can be conveniently used for patients who may not have access to ophthalmological care,with the potential of improving DR screening.
In this study, we described a new portable Optomed Aurora fundus camera, and compared the image quality and DR detection with traditional tabletop fundus cameras. We also evaluated the feasibility of using a deep learning system(Phoebus, Shanghai, China) to detect different signs of DR to determine the possibility of combining the handheld fundus camera and AI technology during DR screening.
However, it is difficult for physicians to perform routine dilated examinations on screened patients to detect non-symptomatic conditions owing to a presumption of patient unwillingness,lack of time, and unwarranted fears of harming patients with known glaucoma. Therefore, the quality of photography under non-mydriatic conditions is a critical evaluation index in DR screening. Compared to conventional cameras, the Aurora has a smaller minimum pupil size requirement (Table 2).For images taken during a non-mydriasis state, the Aurora handheld fundus camera had significantly better quality in centration, clarity, and visible range (1.47±0.46, 1.48±0.40, and 1.40±0.47, respectively) than conventional tabletop cameras(1.30±0.58, 1.28±0.19, and 1.18±0.61, respectively;<0.001).During the mydriasis state, the Optomed Aurora color images had imaging and grading characteristics similar to those of conventional tabletop cameras. Importantly, the advantage of not requiring pupillary dilation could provide the impetus for DR screening in underdeveloped regions.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
The study was approved by the Shanghai General Hospital Institutional Review Board at Shanghai Jiao Tong University. Informed consent was obtained from all participants. The study was conducted in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki, in accordance with the ICH-GCP(International Conference on Harmonization-Good Clinical Practice) guidelines (clinicaltrials.gov Registration Number:NCT03903042).
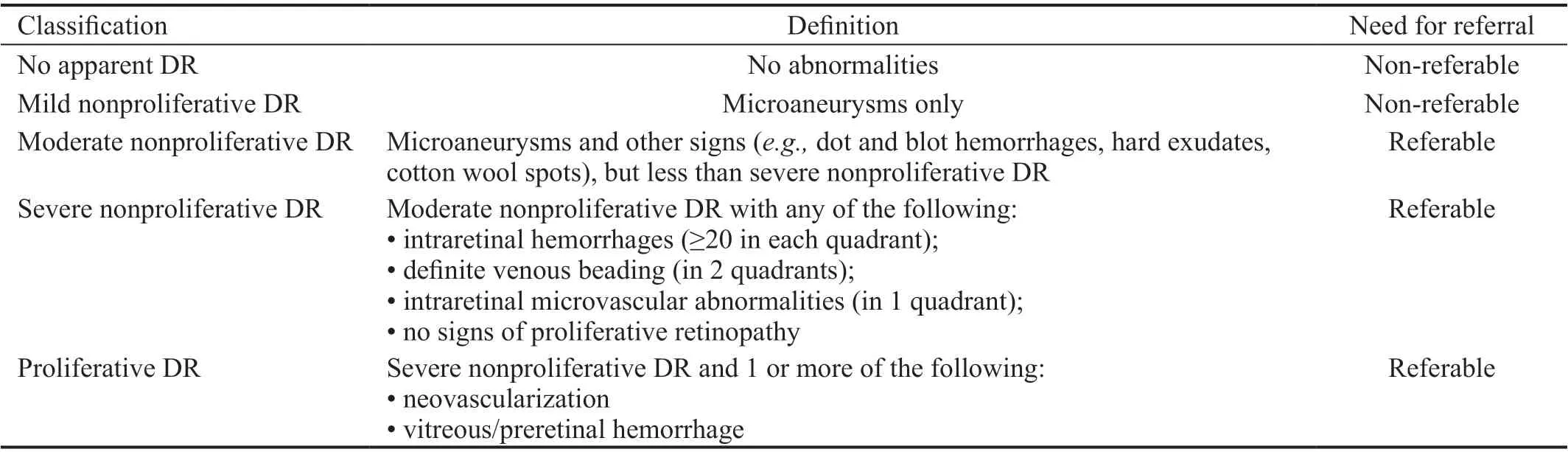
Three parameters were assessed by the graders to investigate various aspects of image quality (Figure 1). For each parameter the quality score ranged from 2 (excellent) to 0 (ungradable). Images were considered to be excellent quality if the macula or optic disc was well-centered, showing clarity of the fundus vessels,with any retinopathy and the whole image being visible. If the macula or optic disc was partially centered and the fundus vessels and any retinopathy were recognizable and more than 80% of the image was visible, the images were defined as acceptable. If images were not centered, blurred without recognition of the retinal vessels or retinopathy features, or less than 80% of the image was visible, they were defined as ungradable.
All photographs were randomized and presented to three masked and experienced ophthalmologists.The ophthalmologists separately evaluated their image quality and made diagnoses without information about the patients or the cameras used.
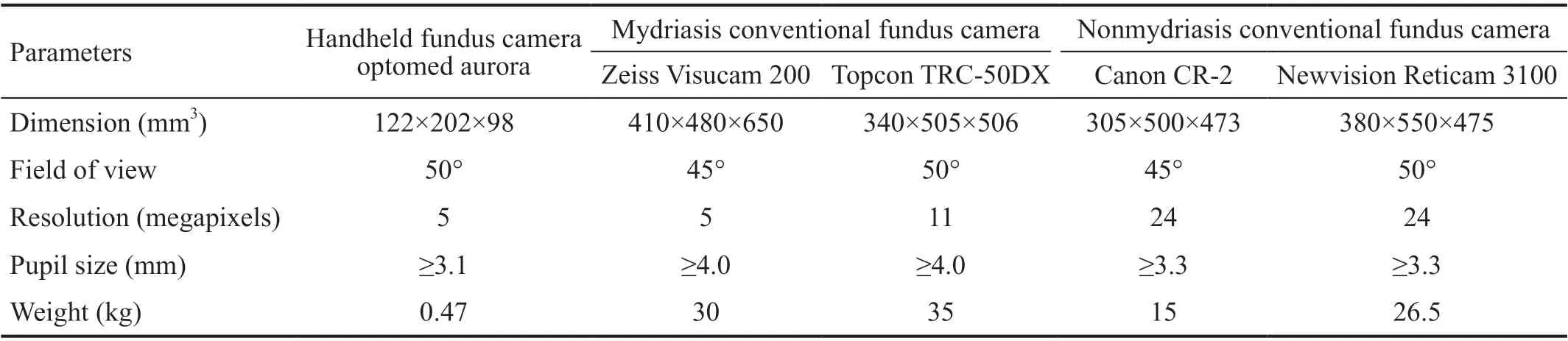
This was a multi-centered, double-blinded,observational clinical study enrolling patients from three hospitals (Shanghai General Hospital, Shanghai, China; West Nanjing Road Community Health Center, Shanghai, China;and Zhaoqing Gaoyao People's Hospital, Guangdong, China).Individuals of ages 18y and older who had been diagnosed with DM were enrolled. Patients were excluded if the retina specialist could not visualize the fundus on examination or if they had previously undergone vitreoretinal surgery and/or laser photocoagulation. Classification of the severity stage of DR was determined using the International Clinical Diabetic Retinopathy Disease Severity Scale grading system developed by the American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO)(Table 1).Four fundus photographs per eye were taken by a well-trained ophthalmic photographer: papilla- and maculacentered images using the tabletop and handheld Optomed Aurora fundus cameras (Optomed, Oulu, Finland), respectively,with or without pupil dilation with 1% tropicamide. The images obtained with the handheld fundus camera had a field of view of 50° and 5 mega-pixel resolution. Images from both kinds of cameras were acquired on the same day, which allowed for direct pathological identification and comparisons between these camera types. The characteristics of five types of fundus cameras are detailed in Table 2. The images were stored as JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) files after removing patient names. Fundus images were transferred to the grading center, Shanghai General Hospital through the INSIGHT real-world patient registry platform www.chinadr.org.cn (Phoebus Medical, Shanghai, China), for remote digital retinal imaging grading.In this study, the images were uploaded to the deep learning system, Phoebus (Phoebus), and the detection of DR features was assessed. Phoebus provides a DR grade per image as well as visual representations of detected microaneurysms, retinal hemorrhages, hard exudations, and macular edemas. The DR output from Phoebus was further used to generate a prediction for the referral requirement.

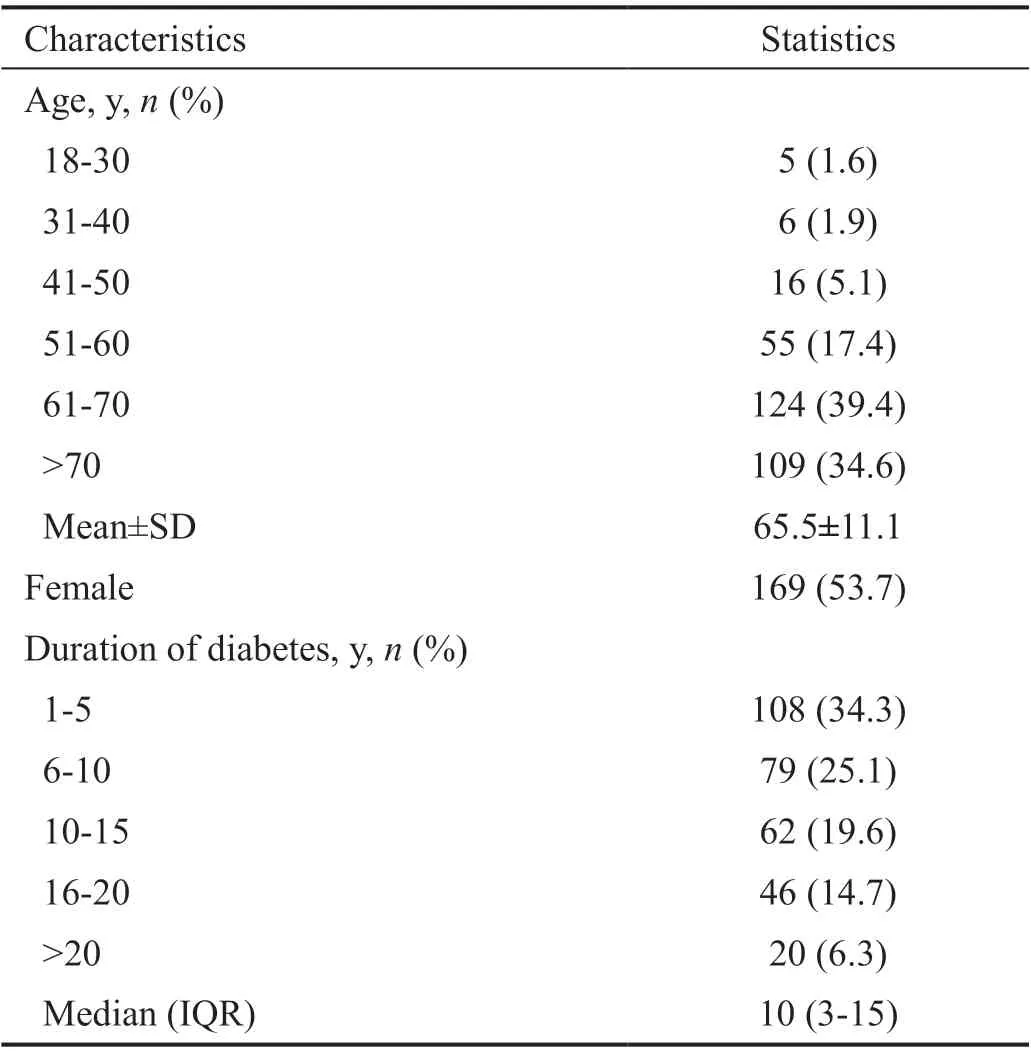
Overall, a total of 630 eyes of 315 DM patients were included in this study. The patients were on average 65.5±11.1y of age, and 53.7% were female (=169).The median duration of diabetes was 10y (3-15y), with more than one-third of the patients diagnosed with diabetes for less than 5y, and only 20 (6.3%) patients were diagnosed with diabetes for over 20y (Table 3).
RESULTS
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS statistical software for Windows, version 20.0 (SPSS,Chicago, IL, USA). The data are presented as the mean±SD or median (IQR) for continuous variables and frequency (%)for categorical variables. Participant age was categorized by intervals of 10y, and age at diagnosis of diabetes was categorized by intervals of 5y. Sensitivity, specificity, and area under the receiver operator curve (AUC) with a 95% confidence interval(95%CI) were calculated to evaluate diagnostic accuracy.We used a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve to evaluate the classification ability of our built model.
Of the 630 eyes examined, 242 eyes (38.4%)were photographed in the non-dilated state, while the remaining 388 eyes were dilated. The mean scores of the nonmydriasis image quality regarding image centration, sharpness,and visible range for the handheld fundus camera were 1.47,1.48, and 1.40, separately, resulting in a significant advantage over the conventional tabletop cameras (1.30, 1.28, 1.18,separately,<0.001). However, regarding the image sharpness score under mydriasis, photography with the conventional tabletop cameras performed better than the images acquired by the Aurora handheld fundus camera (<0.05). The assessment of mydriasis images regarding image centration (=0.146) and visible range (=0.945) did not reach a significant difference(Table 4).
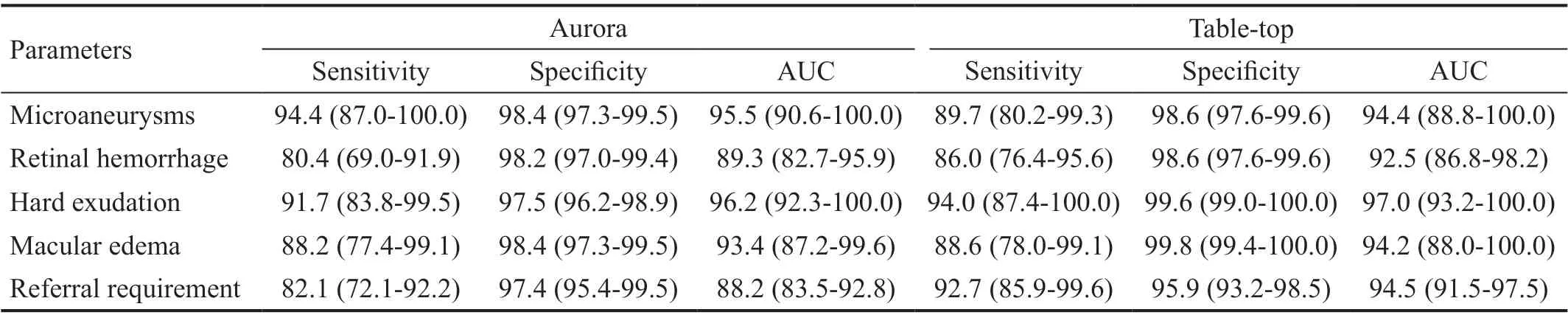
We compared the ability to reveal common manifestations of DR between the handheld and tabletop fundus cameras (Table 5). Thesensitivity and specificity to detect microaneurysms reached 94.4% (95%CI: 87.0%-100.0%) and 98.4% (95%CI: 97.3%-99.5%), respectively, using the Aurora camera, compared to 89.7% (95%CI: 80.2%-99.3%) and 98.6% (95%CI: 97.6%-99.6%) using the conventional tabletop camera (Table 6). Detection of retinal hemorrhage, hard exudation, and macular edema were comparable, with that of the AUC of the handheld fundus camera being slightly lower. When detecting referable DR, the Aurora camera obtained an AUC of 88.2%(95%CI: 83.5%-92.8%), corresponding to a sensitivity of 82.1% (95%CI: 72.1%-92.2%) and a specificity of 97.4%(95%CI: 95.4%-99.5%), when compared to 92.7% (95%CI:85.9%-99.6%) and 95.9% (95%CI: 93.2%-98.5%) using the conventional tabletop camera. The corresponding ROC curves are shown in Figure 2.
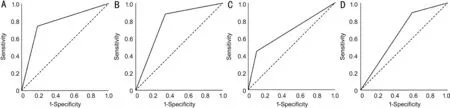

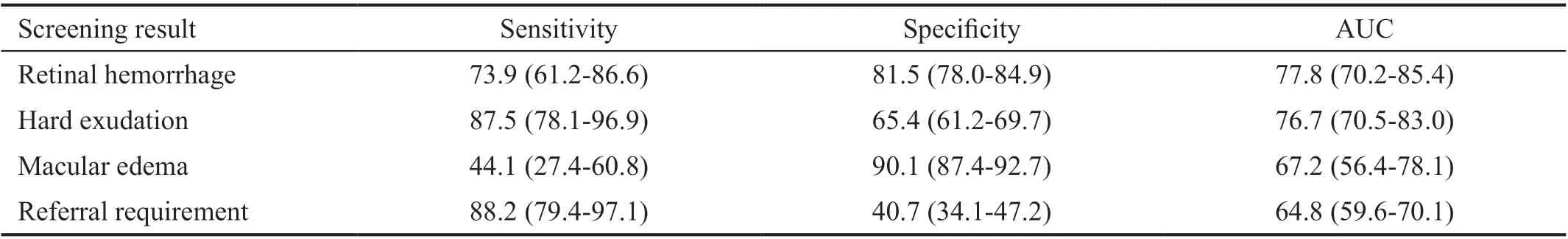
The performance of AI detection of DR using the Phoebus Algorithm is shown in Table 6. On images taken from the handheld camera, the Phoebus Algorithm achieved an AUC of 77.8% (95%CI 70.2%-85.4%) when detecting retinal hemorrhage, corresponding to a sensitivity of 73.9% (95%CI 61.2%-86.6%) and a specificity of 81.5% (95%CI 78.0%-84.9%). When detecting hard exudation, the Phoebus Algorithm obtained an AUC of 76.7% (95%CI 70.5%-83.0%),corresponding to a sensitivity of 87.5% (95%CI 78.1%-96.9%) and a specificity of 65.4% (95%CI 61.2%-69.7%). For the referral requirements, the Phoebus Algorithm achieved an AUC of 64.8 (95%CI 59.6%-70.1%), corresponding to a sensitivity of 88.2% (95%CI 79.4%-97.1%) and a specificity of 40.7% (95%CI 34.1%-47.2%). The corresponding ROC curves are shown in Figure 3.
这自然也包括占星术,“在俘囚期时代,即使是在巴比伦当地,第二以赛亚便不止嘲讽一般的巴比伦巫师,而且特别也嘲讽了巴比伦的天文学与占星术。到了俘囚期之后与拉比时代,星宿在以色列毫无用武之地的原则依然存在。”[注][德]韦伯:《古犹太教》,康乐、简美惠译,桂林:广西师范大学出版社,2007年,第268页。 而占星术在中国是表明王朝合理性的永恒证据,儒家或儒教根本不会去触动这一自新石器晚期巫酋时代就业已形成的根深蒂固的观念,并且作为历代王朝的主要辅助者或捍卫者,儒家只会去不断改善和强化这一传统;故占星术同样也是儒家或儒教的深厚传统。
DISCUSSION
In this study, we introduced a new handheld Optomed Aurora fundus camera, and found it significantly better than traditional tabletop fundus cameras regarding image quality during the non-mydriasis state. The detections of different signs of DR were comparable with the tabletop cameras. The Aurora fundus camera combined with an autonomous AI system had high sensitivity and specificity for DR detection. Furthermore,it was safe and effective in the detection of referable DR in real practice.
During the last two decades, automated image diagnosis based on AI has been used for detection and classification of DR with the advantages of increased efficiency, reproducibility, and coverage of screening programs. However, application in real world situations remains a challenge due to inconsistent image quality and other aspects such as comorbidity. The accuracy of screening by fundus photography is highly dependent on the performance in detecting different manifestations of DR, using either manual grading or AI-assisted grading. The performances in DR screening between the Aurora and tabletop cameras were comparable in principle. It is worth noting that the Aurora was better than the tabletop cameras in screening sensitivity for detecting microaneurysms (94.4%89.7%),possibly because of the better image quality of the Aurora during the non-mydriasis state. The sensitivity and specificity of the Aurora in the detection of referral-warranted DR were 82.1% and 97.4%, respectively, which met the criteria of The British Diabetic Association, when considering 80% sensitivity and 95% specificity for a viable DR screening program.Overall, these results indicated a satisfactory quality of Aurora for AI-assisted grading.
二是参考标杆管理,对标对表明确专科发展方向。结合建设西南一流、国内有较大影响力的现代化大型三甲综合医院发展目标,医院要求各专科全面对标《国家区域医疗中心设置标准(综合医院)》,深入分析存在的差距与不足,通过“走出去、请进来”的方式,不断加大外出进修学习、外请专家来院指导力度,以实现在日常工作中持续整改、不断提升专科技术水平的最终目的。
基于此,提出了基于生成对抗文本的人脸图像翻译方法,相比其他翻译方法,本文的翻译结果更好,在人脸图像上具有很好的适应性。
Fundus photography has served as a useful tool in detecting and documenting the presence and the progression of retinopathy in diabetic patients in communities. On this basis, the development of digital fundus cameras further facilitates rapid acquisition and interpretation of fundus images and the rapid deployment of retinal imaging for DR screening worldwide. These cameras produce high quality images that can be assessed for the presence of DR by eye care providers (optometrists or ophthalmologists)or trained readers in a deferred manner on site or remotely.Moreover, many computer-aided algorithms for automated image analysis have been developed, which are expected to be a promising alternative for retinal fundus image analysis for future applications in eye care. Artificial intelligence(AI) systems have been widely demonstrated to lower cost,improve diagnostic accuracy, and increase patient access to DR screening. In April 2018, the United States Food and Drug Administration approved the world's first AI medical device for detecting DR, the IDx-DR.
Early detection and prompt treatment of DR is the key to reducing preventable vision loss worldwide, which requires regular fundus screening. However, because of the paucity of ophthalmologists in China, there are only about 20 practitioners per million people, which reduces the accessibility of DR screenings. Even in the United States and the United Kingdom, the absolute number of ophthalmologists (49 and 59 ophthalmologists per million people, respectively) still cannot meet the need of a growing number of DR patients,especially in rural areas. Fundus photography has been widely proven to be an effective method to monitor the extent of DR and to identify patients who could benefit from early treatment. However, the large size, weight, and high cost of the conventional tabletop fundus cameras limit its use for large-scale screening in communities lacking a sufficient screening process. In rural and remote communities with few ophthalmologists or table-top fundus cameras, teleophthalmology based on portable fundus cameras used by well-trained physicians is a viable solution to increase DR screening. Therefore, non-mydriatic portable ocular fundus photography is a promising solution when combined with telemedicine. The dimension of our new handheld Aurora fundus camera is approximately 122×202×98 mm, which is much smaller than all tabletop cameras (Table 2), making it possible to be carried and used for training for those without experience.
We used our self-designed Phoebus algorithm system to examine the performance in detecting DR. The system had independent, validated detectors for lesions characteristic of DR, including retinal hemorrhages, hard exudates, and macular edemas, the outputs of which were then fused into a DR referral requirement output, using a separately trained and validated machine learning algorithm. Several studies have reported the diagnostic performance of AI-based software in the detection of referable DR. The published results appeared promising, showing a sensitivity ranging from 74% to 92.5%,and a specificity between 73.3% and 98.5%. In the present study, the sensitivity and specificity of the Phoebus Algorithm system in identifying referable DR was 88.2% and 40.7%,respectively, which met the FDA superiority sensitivity cut-offs of 85%, but did not reach a specificity of 82.5%. However,in contrast, its sensitivity and specificity of macular edema were 44.1% and 90.1%, respectively. One of the possible reasons was that macular edema is not easily captured using 2-dimensional fundus photographs. In contrast, optical coherence tomography, as a standard diagnostic tool for the assessment of intra- and subretinal fluids, is more sensitive in detecting macular edemas. Sensitivity is a patient safety criterion, because the AI system's primary goal is to identify as many potential patients with DR that require further evaluation by eye care providers. Tanreported an algorithm that achieved a sensitivity and specificity of 62.57% and 98.93%,respectively, for retinal hemorrhages. Our detection sensitivity and specificity of retinal hemorrhages were 73.9% and 81.5%,respectively, with the corresponding AUC of 77.8%. The AIassisted grading system of both mydriatic and non-mydriatic images could therefore be valuable in DR screening.
This study had some limitations. First, the inclusion of multiples images was from multiple devices with different fields of view and resolutions. However, it could also be a strength for the resulting algorithms, which could be more reliable in the real world with different camera brands or types.Second, the AI-based specificity of referable DR was relatively low, which could affect the number of people who received a referral but did not actually need one because they had only no DR or mild DR. This could have been due to the small sample size of the study. Real-world data of more DR patients will be needed to improve the analysis.
In conclusion, our study showed that the handheld Aurora fundus camera was well-suited for DR screening with or without mydriasis. This camera had high sensitivity of DR detection as well as satisfactory image quality, but its specificity needs to be improved with better modeling of the data. Our Phoebus AI system helped to improve DR screening. Use of a handheld fundus camera with an AI system was safe and effective in the detection of referable DR in the real world practice.
叶晓晓不慌不忙,眨着单眼皮的小眼睛微微一笑,说:“从我的眼神。我的眼睛告诉你的是纯真,不是隐晦和暗示什么。”
制造任务特征主要描述了该任务中区别于其他任务的典型特征信息,包括加工特征、设备特征和工艺特征等。例如某轴承加工任务,其制造任务特征为车削加工、车床、材料、尺寸等。该特征的确定一般根据制造任务所加工的产品对象的工艺过程特点来确定该制造任务执行过程中的制造任务特征。
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81970845); European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement (No.778089).
None;None;is an employee of Shanghai Phoebus Medical Co. Ltd.None;None;None;None;None;None;None.
猜你喜欢
杂志排行
International Journal of Ophthalmology的其它文章
- Comment on: Real-world outcomes of two-year Conbercept therapy for diabetic macular edema
- Efficacy of intravitreal conbercept combined with panretinal photocoagulation for severe nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy without macular edema
- Efficacy of conbercept after switching from bevacizumab/ranibizumab in eyes of macular edema secondary to central retinal vein occlusion
- lntraoperative complication rates in cataract surgery performed by resident trainees and staff surgeons in a tertiary eyecare center in Hungary
- Comparing surgical efficiencies between phacoemulsification systems: a single surgeon retrospective study of 2000 eyes
- Factors associated with corneal astigmatism change after ptosis surgery
