18F-FDG PET/CT代谢参数及临床指标在弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤中期评估及预后预测中的意义
2022-03-28张帆张国旭刘秀婷王吉刚刘彦琴佟丹江刘景华周凡
张帆?张国旭?刘秀婷?王吉刚?刘彦琴?佟丹江?刘景华?周凡
【摘要】 目的 探討18F-氟代脱氧葡萄糖(18F-FDG)PET/CT的代谢参数及临床指标在弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤(DLBCL)中期评估及预后预测中的意义。方法 收集194例DLBCL患者临床资料,记录患者的中期评估结果,比较不同临床指标[β2 -微球蛋白(β2-MG)、双表达、三表达、Ann Arbor分期、淋巴瘤国际预后评分 (IPI)、多维尔5分法(D5PS)评分]和18F-FDG PET/CT代谢参数[最大标准化摄取值(SUVmax)、病灶累及部位SUVmax的总和(SUVmaxsum)、平均标准化摄取值(SUVmean)和SUVmax下降幅度(△SUVmax)]中达完全缓解(CR)者所占比例的差异,应用Cox回归和Kaplan-Meier生存分析法分析18F-FDG PET/CT代谢参数及临床指标对DCBCL患者2年无进展生存期(PFS)的影响,并对SUVmax与β2-MG、Ann Arbor分期和IPI评分进行相关性分析。结果 β2-MG > 2.3 mg/L、Ann Arbor分期Ⅲ/Ⅳ期、IPI > 2分、SUVmax > 17.00和SUVmaxsum > 38.60者达CR的比例较低;疗效达CR者△SUVmax大于未达CR者(P均 < 0.05)。Cox单因素分析显示,β2-MG、Ann Arbor分期、IPI评分、双表达、三表达、SUVmaxsum及D5PS评分均与DLBCL患者2年PFS有关(P均 < 0.05);多因素分析显示,Ann Arbor分期Ⅲ/Ⅳ期(HR = 4.486,P = 0.001)为DLBCL患者2年PFS的独立危险因素,D5PS 评分1~3分(HR = 0.256,P < 0.001)为DLBCL患者2年PFS的独立保护因素。Spearman秩相关分析显示,SUVmax与β2-MG(rs = 0.348,P = 0.001)、Ann Arbor分期(rs = 0.236,P = 0.022)和IPI评分(rs = 0.305,P = 0.003)均有关。结论 18F-FDG PET/CT的代谢参数与临床指标相关,Ann Arbor分期和D5PS可作为DLBCL患者预后的参考指标。
【关键词】 氟代脱氧葡萄糖正电子发射断层显像/计算机断层显像;弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤;最大标准化摄取值;
病灶累及部位最大标准化摄取值的总和;多维尔5分法
Significance of metabolic parameters and biochemical indexes of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the mid-term evaluation and prognosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma Zhang Fan△, Zhang Guoxu, Liu Xiuting, Wang Jigang, Liu Yanqin, Tong Danjiang, Liu Jinghua, Zhou Fan. △The Graduate Training Base of the Northern Theater General Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University, Shenyang 110016, China
Corresponding author, Zhou Fan, E-mail: 1079249735@qq.com; Liu Jinghua, E-mail: mtljh7646@163.com
【Abstract】 Objective To investigate the significance of metabolic parameters and biochemical indexes of 18F-FDG-PET/CT in the mid-term evaluation and prognosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Methods Clinical data of 194 patients with DLBCL were analyzed retrospectively. The mid-term evaluation results were recorded. The proportion of patients who achieved complete remission (CR) was statistically compared among different clinical indexes(β2-microglobulin (β2-MG), dual expression, triple expression, Ann Arbor stage, international prognostic index (IPI) and Deauville 5-point scale (D5PS) score) and metabolic parameters of 18F-FDG-PET/CT (the maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax), the sum of the maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmaxsum), the mean standardized uptake value (SUVmean) and the maximum decrease range of SUV (△SUVmax)). The influence
of metabolic parameters and biochemical indexes of 18F-FDG-PET/CT on the 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) was evaluated by Cox regression models and Kaplan-Meier survival analysis. The correlation between SUVmax and β2-MG, Ann Arbor stage and IPI score was analyzed. Results The proportion of patients with β2-MG > 2.3 mg/L, Ann Arbor stage Ⅲ/Ⅳ, IPI score > 2, SUVmax > 17.00 and SUVmaxsum > 38.60 who achieved CR was significantly decreased, the △SUVmax of patients achieving CR was significantly higher than that of those without CR(all P < 0.05). Univariate Cox regression analysis showed that β2-MG, Ann Arbor stage, IPI score, dual expression, triple expression, SUVmaxsum and D5PS socre were significantly correlated with the 2-year PFS of DLBCL patients (all P < 0.05). Multivariate analysis showed that Ann Arbor stage Ⅲ/Ⅳ (HR = 4.486, P = 0.001) was an independent risk factor for the 2-year PFS, and D5PS score of 1-3 (HR = 0.256, P < 0.001) was an independent protective factor for the 2-year PFS of patients with DLBCL. Spearmans rank correlation analysis demonstrated that SUVmax was significantly associated with β2-MG (rs = 0.348, P = 0.001), Ann Arbor stage (rs = 0.236, P = 0.022) and IPI score (rs = 0.305, P = 0.003). Conclusions The metabolic parameters of
18F-FDG-PET/CT are associated with clinical indexes. Ann Arbor stage and D5PS can be utilized as reference indexes for clinical prognosis of DLBCL patients.
【Key words】 FDG PET/CT; DLBCL; SUVmax; SUVmaxsum; D5PS
18F-氟代脱氧葡萄糖(18F-FDG)PET/CT是淋巴瘤患者分期及反应评估的重要手段,其评估肿瘤细胞的活性比CT更精准。18F-FDG PET/CT检查不仅可以用于判断治疗后的病情缓解程度,而且可用于淋巴瘤的中期评估,以区分对化学治疗反应欠佳而需要调整治疗方案的患者[1]。本研究收集了近年我院收治的194例弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤(DLBCL)患者的临床特点,分析DLBCL中期评估时18F-FDG PET/CT 检查中最大标准化摄取值(SUVmax)、平均标准化摄取值(SUVmean)、病灶累及部位SUVmax的总和(SUVmaxsum)和SUVmax下降幅度(△SUVmax)等代谢指标及临床指标与中期评估及2年无进展生存期(PFS)的相关性,以更好地指导临床治疗。
对象与方法
一、研究對象
收集2010年6月至2019年6月在中国人民解放军北部战区总医院收治的194例DLBCL患者临床资料,患者的年龄为58(19,85)岁。病例纳入标准:①经病理活组织检查(活检)确诊为DLBCL;②完成至少3~5个疗程的化学治疗;③治疗后2年内可随访。排除标准:①合并其他肿瘤;②临床资料缺失。本研究经医院伦理委员会批准[批件号:论审Y(2021)126号],所有入组患者均已签署知情同意书。
二、方 法
收集194例DLBCL患者的临床资料,包括年龄、乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)是否升高(> 250 U/L)、
β2 -微球蛋白(β2-MG) 是否升高(> 2.3 mg/L)、双表达(C- MYC≥40%和Bcl-2≥50%)、三表达(C- MYC≥40%和Bcl-2≥50%且Bcl-6≥50%)、Ann Arbor分期、淋巴瘤国际预后评分 (IPI);同时收集患者超声、CT、MRI及18F-FDG PET/CT等辅助检查结果,其中92例患者行18F-FDG PET/CT检查。收集患者初诊时18F-FDG PET/CT 的SUVmax、病灶累及部位的SUVmean、病灶累及部位(淋巴结及结外各脏器)的SUVmaxsum,按各指标的中位数分类。于患者至少完成3~5个疗程规律化学治疗后再行CT及MRI或者18F-FDG PET/CT,计算2次18F-FDG PET/CT的△SUVmax,并按照2014版Lugano评价标准进行中期评估,评价患者是否达完全缓解(CR)。所有患者通过门诊或电话随访,末次随访时间截至2021年6月,中位随访时间12.33个月。PFS定义为患者病理确诊至首次发现肿瘤复发、进展、死亡或随访结束的时间。应用多维尔5分法(D5PS)评估患者预后,根据D5PS分值分为1~3分组及4~5分组。
三、统计学处理
采用SPSS 25.0处理数据。计数资料以例(%)表示,组间比较采用χ2检验和Bonferroni法校正。不符合正态分布的计量资料以M(P25,P75)表示,组间比较采用Wilcoxon秩和检验。应用Kaplan-Meier生存分析及Cox回归分析相关指标与2年PFS的关系,单因素分析中P < 0.20者进行多因素回归分析(输入法)。采用Spearman秩相关分析SUVmax与患者β2-MG、Ann Arbor分期、IPI评分关系。α = 0.05。
结 果
一、DLBCL患者临床相关指标与CR的关系
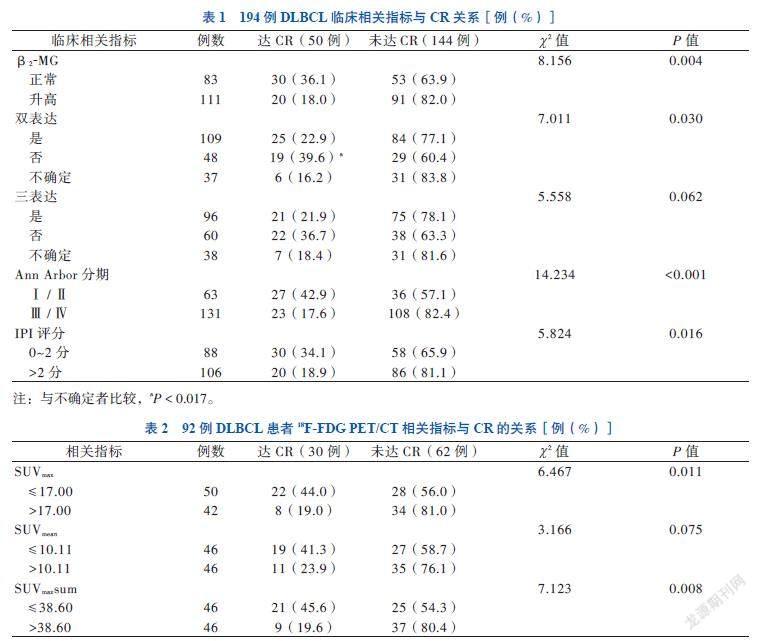
194例DLBCL患者中,β2-MG升高、Ann Arbor分期Ⅲ/Ⅳ期、IPI评分 > 2分者达CR比例分别低于β2-MG和(或)LDH正常、Ann Arbor分期Ⅰ/Ⅱ期、IPI评分 ≤ 2分者(P均 < 0.05)。双表达不确定者达CR比例低于无双表达者(P < 0.017),见表1。
二、DLBCL患者18F-FDG PET/CT相关指标与CR的关系
92例行18F-FDG PET/CT的DLBCL患者中,SUVmax > 17.00和SUVmaxsum > 38.60者中达CR比例低于SUVmax≤ 17.00和SUVmaxsum≤38.60者,见表2。达CR者的△SUVmax为79.66(66.43,87.43),大于未达CR者的63.63(40.35,77.55),组间比较差异有统计学意义(Z = 3.390,P = 0.001)。
三、DLBCL患者2年PFS的影响因素分析
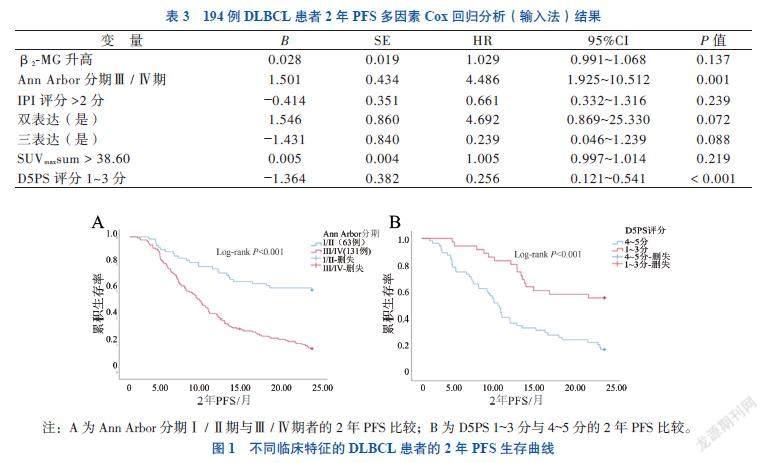
应用单因素Cox回归分析显示,β2-MG升高、Ann Arbor分期Ⅲ/Ⅳ期、IPI评分 > 2分、双表达(是)、三表达(是)、SUVmaxsum升高及D5PS评分 1~3分的HR分别为1.044、3.259、1.533、0.804、0.802、1.008及0.626,上述指标均与DLBCL患者2年PFS相关(P均 < 0.05);多因素分析(输入法)显示,Ann Arbor分期Ⅲ/Ⅳ期(HR = 4.486,P = 0.001)为DLBCL患者2年PFS的独立危险因素,D5PS 评分1~3分(HR = 0.256,P < 0.001)为DLBCL患者2年PFS的独立保护因素,见表3。Ann Arbor分期Ⅰ/Ⅱ期患者2年PFS优于Ⅲ/Ⅳ期者,D5PS评分1~3分患者2年PFS优于4~5分者(P均 < 0.05),见图1。
四、SUVmax与其他临床指标的相关性分析
Spearman秩相关分析显示,SUVmax与β2-MG(rs = 0.348,P = 0.001)、Ann Arbor分期(rs = 0.236,P = 0.022)和IPI评分(rs = 0.305,P = 0.003)均有关。
讨 论
DLBCL是非霍奇金淋巴瘤中最常见的类型,其治疗手段以化学治疗为主。多数DLBCL患者在经过蒽环类药物为基础的化学治疗后病情缓解,但有部分患者对化学治疗反应欠佳,病情发展,预后较差。PET/CT可以显示淋巴瘤的病灶及部位,并可根据代谢指标对肿瘤进行定性定位,目前已经成为评价淋巴瘤疗效的重要手段。18F-FDG PET/CT有助于DLBCL分期、评估疾病情况并指导治疗。本研究中,中期评估达CR者初诊时β2-MG、双表达、三表达、Ann Arbor分期Ⅲ/Ⅳ期及IPI评分与未达CR者比较差异有统计学意义,与Liang等[2]、Zhu等[3]、胡利娟等[4]和Han等[5]研究结果一致,提示上述临床指标与患者的中期评估有关。本研究双表达高的原因可能是未纳入临床资料不完整和未能完成3~5个疗程化学治疗患者。
本研究中初诊18F-FDG-PET/CT中SUVmax > 17.00者在3~5个疗程化学治疗后达CR者比例較低,提示该类患者预后较差。Li等[6]和Xia等[7]研究分别以9.5、9.65为SUVmax截断值,认为SUVmax≥9.5、SUVmax≥9.65为NK/T细胞淋巴瘤预后的危险因素。这可能与DBLCL本身代谢活性偏高有关。Chihara等[8]通过多变量分析揭示了DLBCL高 SUVmax 和低 CR 率之间的独立关联。本研究在此基础上统计患者3~5个疗程化学治疗前后的SUVmax,计算2次下降幅度与CR关系,结果表明达CR者△SUVmax大于未达CR者。Li 等[9]研究表明,△SUVmax可用于PET/CT对DLBCL患者的中期疗效评价和预后预测。Okuyucu等[10]研究显示,SUVmean可更准确反映原发性结外淋巴瘤的肿瘤活动,其灵敏度为88%,特异度为64%,临界值为5.15。Pak等[11]研究显示,18F-FDG PET/CT测量的SUVmax和SUVmean可能是结外鼻型NK/T细胞淋巴瘤患者预后的重要预测因素。本研究中,SUVmean并未显示对DLBCL患者预后有价值,可能与本研究并未单独研究原发结外DLBCL有关。Baratto等[12]研究表明,基线SUVmaxsum与患者总生存期相关。本研究在前人研究的基础上观察基线SUVmaxsum与DLBCL患者中期PFS的关系,结果显示初诊时SUVmaxsum > 38.60者达CR比例较低,预后较差。
Uluk?ylü Mengü?等[13]和Albano等[14]研究表明,中期18F-FDG-PET/CT D5PS 4~5分者PFS和总生存期均比1~3分患者短。Chen等 [15]和Qian等[16]研究表明D5PS是PFS的独立危险因素。Xu等[17]研究表明治疗中期、结束的D5PS以及中期 SUVmax是PFS的重要预测因子。AlShehry等[18]研究表明中期FDG-PET/CT 的 SUVmax在预测 PFS 方面表现最佳。Sun等[19]等应用Cox回归显示,18F-FDG-PET/CT D5PS 4~5分者的预后不良风险高于D5PS 1~3分者。Qin等[20]和Jiang[21]等多因素分析提示D5PS评分系统是PFS和总生存期的独立预测因子。本研究主要针对患者进展风险,未分析相关危险因素对2年总生存期的影响。多因素分析显示,D5PS 1~3分为2年PFS的独立保护因素,D5PS 1~3分患者进展的风险比是4~5分患者的25.6%。
本研究多因素Cox分析显示,Ann Arbor分期是DLBCL患者的影响因素,与Xu等[17]研究一致。本研究相关性分析中,SUVmax与β2-MG、Ann Arbor分期和IPI评分均有关。
总之,在DBLCL中初诊、中期18F-FDG-PET/CT的代谢参数以及临床指标有助预测患者2年内进展风险,另外18F-FDG-PET/CT中SUVmax与患者β2-MG、Ann Arbor分期和IPI评分均有关,对评估淋巴瘤侵袭与增殖具有重要意义。
参 考 文 献
[1] Al Tabaa Y, Bailly C, Kanoun S. FDG-PET/CT in lymphoma: where do we go now? Cancers, 2021, 13(20): 5222.
[2] Liang X, Guo L, Hu X, et al. Analysis of clinical characteristics and prognosis of patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Medicine, 2021, 100(13): e25194.
[3] Zhu L, Meng Y, Guo L, et al. Predictive value of baseline
18 F-FDG PET/CT and interim treatment response for the prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma receiving R-CHOP chemotherapy. Oncol Lett, 2021, 21(2): 132.
[4] 胡利娟, 刘相富, 胡小山, 等. HBV与LDH对弥漫性大B细胞淋巴瘤患者化学治疗效果的影响——附144例报告. 新医学, 2015, 46(12): 808-811.
[5] Han B, Kim S, Koh J, et al. Immunophenotypic landscape and prognosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with MYC/BCL2 double expression: an analysis of a prospectively immunoprofiled cohort. Cancers, 2020, 12(11): 3305.
[6] Li H, Shao G, Zhang Y, et al. Nomograms based on SUVmax of 18F-FDG PET/CT and clinical parameters for predicting progression-free and overall survival in patients with newly diagnosed extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Cancer Imaging, 2021, 21: 9.
[7] Xia X, Wang Y, Yuan J, et al. Baseline SUVmax of 18F-FDG PET-CT indicates prognosis of extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Medicine, 2020, 99(37): e22143.
[8] Chihara D, Oki Y, Onoda H, et al. High maximum standard uptake value (SUVmax) on PET scan is associated with shorter survival in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Int J Hematol, 2011, 93(4): 502-508.
[9] Li X, Xie X, Zhang L, et al. Research on the midterm efficacy and prognosis of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by different evaluation methods in interim PET/CT. Eur J Radiol, 2020, 133: 109301.
[10] Okuyucu K, Ozayd?n S, Alagoz E, et al. Prognosis estimation under the light of metabolic tumor parameters on initial FDG-PET/CT in patients with primary extranodal lymphoma. Radiol Oncol, 2016, 50(4):360-369.
[11] Pak K, Kim B S, Kim K, et al. Prognostic significance of standardized uptake value on F18-FDG PET/CT in patients with extranodal nasal type NK/T cell lymphoma: a multicenter, retrospective analysis. Am J Otolaryngol, 2018, 39(1): 1-5.
[12] Baratto L, Wu F, Minamimoto R, et al. Correlation of 18-fluorodeoxyglucose PET/computed tomography parameters and clinical features to predict outcome for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nucl Med Commun, 2021, 42(7): 792-799.
[13] Uluk?ylü Mengü? M, Mehtap ?, et al. The role of interim PET/CT on survival in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk, 2021, 21(11): e922-e927.
[14] Albano D, Mazzoletti A, Zilioli V R, et al. Clinical and prognostic role of interim 18F-FDG PET/CT in elderly Hodgkin lymphoma: a dual-center experience. Leuk Lymphoma, 2020, 61(13): 3209-3216.
[15] Chen X, Zhao S, Wang H, et al. Assessment of the prognostic value of interim fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in nasal-type extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Quant Imaging Med Surg, 2021, 11(4): 1220-1233.
[16] Qian L, Yan M, Zhang W, et al. Prognostic value of interim 18F-FDG PET/CT in T-cell lymphomas. Leuk Lymphoma, 2020, 61(4): 927-933.
[17] Xu P, Guo R, You J, et al. Dynamic evaluation of the prognostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Ann Hematol, 2021, 100(4): 1039-1047.
[18] AlShehry N F, Shanker R, Zaidi S Z A, et al. Role of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography imaging in the prediction of prognosis in patients with indolent lymphoma: prospective study. JMIR Form Res, 2021, 5(11):e24936.
[19] Sun N, Qiao W, Xing Y, et al. Prognostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT in T-Lymphoblastic lymphoma before and after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Clin Transl Oncol, 2021, 23(8): 1571-1576.
[20] Qin C, Yang S, Sun X, et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT for prognostic stratification of patients with extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Clin Nucl Med, 2019, 44(3): 201-208.
[21] Jiang C, Liu J, Li L, et al. Predictive approaches for post-therapy PET/CT in patients with extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma: a retrospective study. Nucl Med Commun, 2017, 38(11): 937-947.
(收稿日期:2021-11-15)
(本文編辑:林燕薇)
